Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Azure SQL Edge will be retired on September 30, 2025. For more information and migration options, see the Retirement notice.
Note
Azure SQL Edge no longer supports the ARM64 platform.
Create and manage your Azure SQL Edge instances natively in Kubernetes. Deploy Azure SQL Edge to containers managed by Kubernetes. In Kubernetes, a container with an Azure SQL Edge instance can automatically recover in case a cluster node fails. You can configure the SQL Edge container image with a Kubernetes persistent volume claim (PVC). Kubernetes monitors the Azure SQL Edge process in the container. If the process, pod, container, or node fail, Kubernetes automatically bootstraps another instance and reconnects to the storage.
Kubernetes 1.6 and later versions has support for storage classes, persistent volume claims.
In this configuration, Kubernetes plays the role of the container orchestrator.
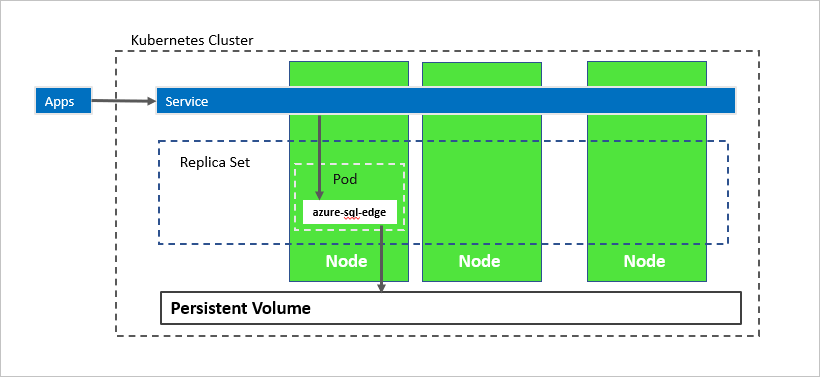
In the preceding diagram, azure-sql-edge is a container in a pod. Kubernetes orchestrates the resources in the cluster. A replica set ensures that the pod is automatically recovered after a node failure. Applications connect to the service. In this case, the service represents a load balancer that hosts an IP address that stays the same after failure of the azure-sql-edge.
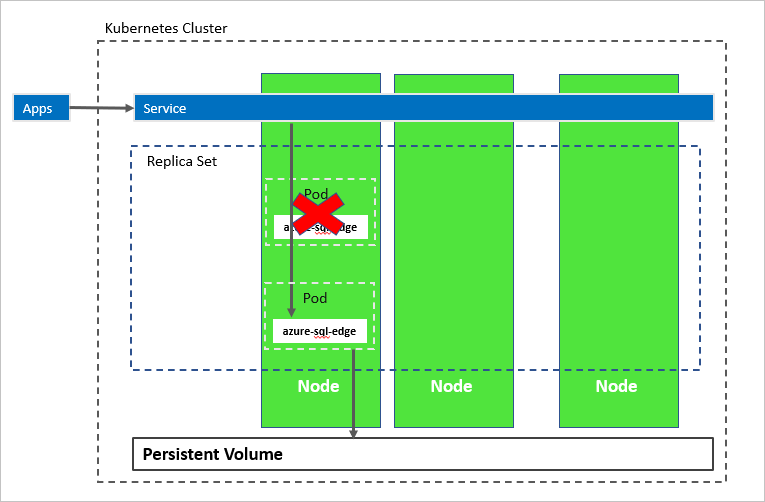
In the following diagram, the azure-sql-edge container has failed. As the orchestrator, Kubernetes guarantees the correct count of healthy instances in the replica set, and starts a new container according to the configuration. The orchestrator starts a new pod on the same node, and azure-sql-edge reconnects to the same persistent storage. The service connects to the re-created azure-sql-edge.
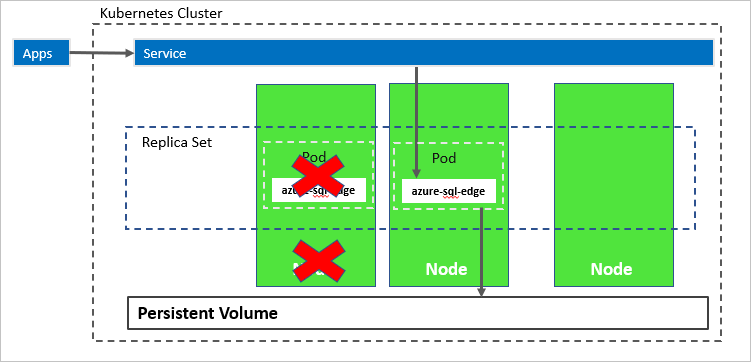
In the following diagram, the node hosting the azure-sql-edge container has failed. The orchestrator starts the new pod on a different node, and azure-sql-edge reconnects to the same persistent storage. The service connects to the re-created azure-sql-edge.
To create a container in Kubernetes, see Deploy an Azure SQL Edge container in Kubernetes
To deploy Azure SQL Edge containers in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), see the following articles: