Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
The following terms are defined for the Scale out with Azure SQL Database. The tools are used to manage shard maps, and include the client library, the split-merge tool, elastic pools, and queries.
These terms are used in Adding a shard using Elastic Database tools and Using the RecoveryManager class to fix shard map problems.
Database: A database in Azure SQL Database.
Data dependent routing: The functionality that enables an application to connect to a shard given a specific sharding key. See Use data-dependent routing to route a query to an appropriate database. Compare to Multi-shard querying using elastic database tools.
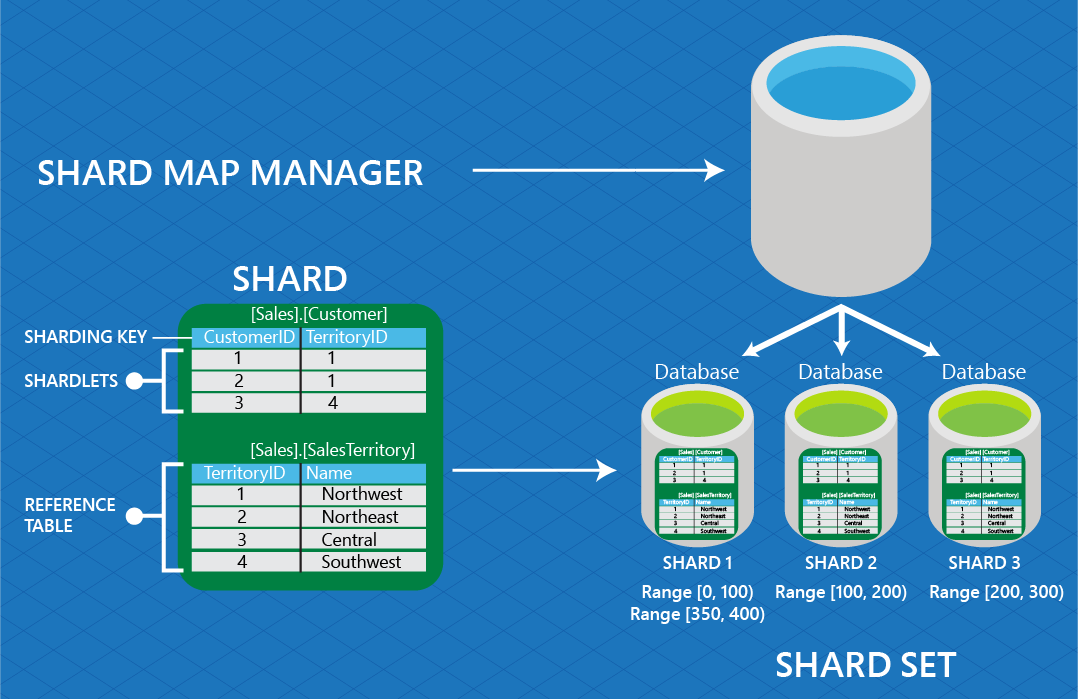
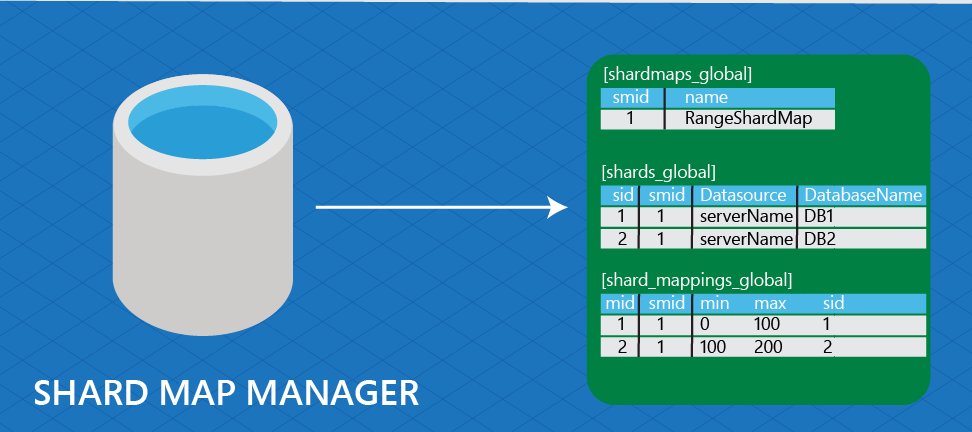
Global shard map: The map between sharding keys and their respective shards within a shard set. The global shard map is stored in the shard map manager. Compare to local shard map.
List shard map: A shard map in which sharding keys are mapped individually. Compare to Range Shard Map.
Local shard map: Stored on a shard, the local shard map contains mappings for the shardlets that reside on the shard.
Multi-shard query: The ability to issue a query against multiple shards; results sets are returned using UNION ALL semantics (also known as "fan-out query"). Compare to data dependent routing.
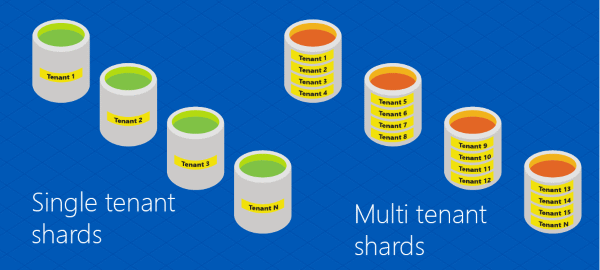
Multi-tenant and Single-tenant: This shows a single-tenant database and a multi-tenant database:
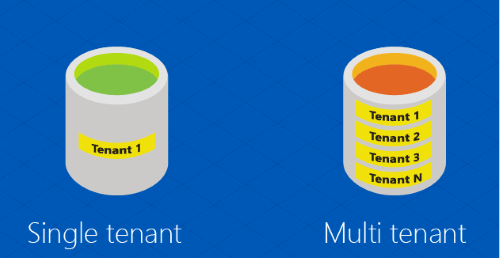
Here is a representation of sharded single and multi-tenant databases.
Range shard map: A shard map in which the shard distribution strategy is based on multiple ranges of contiguous values.
Reference tables: Tables that are not sharded but are replicated across shards. For example, zip codes can be stored in a reference table.
Shard: A database in Azure SQL Database that stores data from a sharded data set.
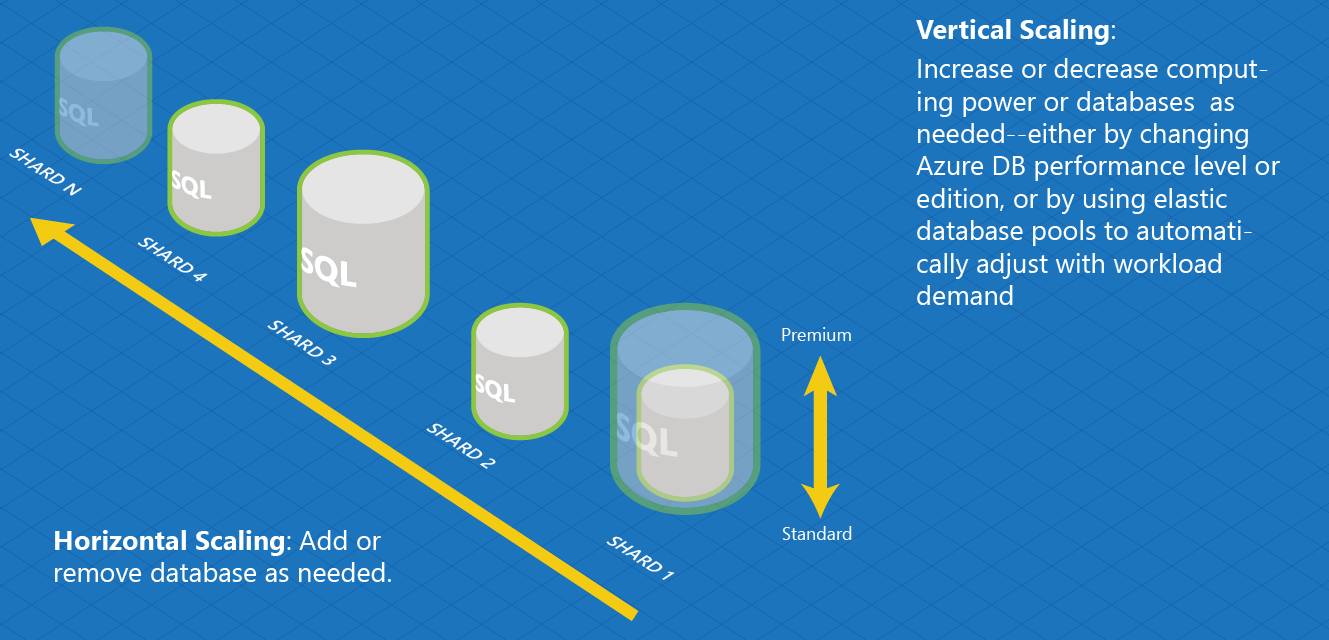
Shard elasticity: The ability to perform both horizontal scaling and vertical scaling.
Sharded tables: Tables that are sharded, i.e., whose data is distributed across shards based on their sharding key values.
Sharding key: A column value that determines how data is distributed across shards. The value type can be one of the following: int, bigint, varbinary, or uniqueidentifier.
Shard set: The collection of shards that are attributed to the same shard map in the shard map manager.
Shardlet: All of the data associated with a single value of a sharding key on a shard. A shardlet is the smallest unit of data movement possible when redistributing sharded tables.
Shard map: The set of mappings between sharding keys and their respective shards.
Shard map manager: A management object and data store that contains the shard map(s), shard locations, and mappings for one or more shard sets.
Verbs
Horizontal scaling: The act of scaling out (or in) a collection of shards by adding or removing shards to a shard map, as shown below.
Merge: The act of moving shardlets from two shards to one shard and updating the shard map accordingly.
Shardlet move: The act of moving a single shardlet to a different shard.
Shard: The act of horizontally partitioning identically structured data across multiple databases based on a sharding key.
Split: The act of moving several shardlets from one shard to another (typically new) shard. A sharding key is provided by the user as the split point.
Vertical Scaling: The act of scaling up (or down) the compute size of an individual shard. For example, changing a shard from Standard to Premium (which results in more computing resources).
Related content
Not using elastic database tools yet? Check out our Getting Started Guide.