Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you create a logical server in Azure and a Hyperscale database in Azure SQL Database using the Azure portal, a PowerShell script, or an Azure CLI script, with the option to create one or more High Availability (HA) replicas. If you would like to use an existing logical server in Azure, you can also create a Hyperscale database using Transact-SQL.
Tip
Simplified pricing for SQL Database Hyperscale arrived in December 2023. Review the Hyperscale pricing blog for details.
Prerequisites
- An active Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a trial account.
- The latest version of either Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI, if you would like to follow the quickstart programmatically. Alternately, you can complete the quickstart in the Azure portal.
- An existing logical server in Azure is required if you would like to create a Hyperscale database with Transact-SQL. For this approach, you will need to run Transact-SQL via the Azure portal query editor, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), sqlcmd, or the client of your choice.
Permissions
To create databases via Transact-SQL: CREATE DATABASE permissions are necessary. To create a database a login must be either the server admin login (created when the Azure SQL Database logical server was provisioned), the Microsoft Entra admin of the server, a member of the dbmanager database role in master. For more information, see CREATE DATABASE.
To create databases via the Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST API: Azure RBAC permissions are needed, specifically the Contributor, SQL DB Contributor, or SQL Server Contributor Azure RBAC role. For more information, see Azure RBAC built-in roles.
Create a Hyperscale database
This quickstart creates a single database in the Hyperscale service tier.
To create a single database in the Azure portal:
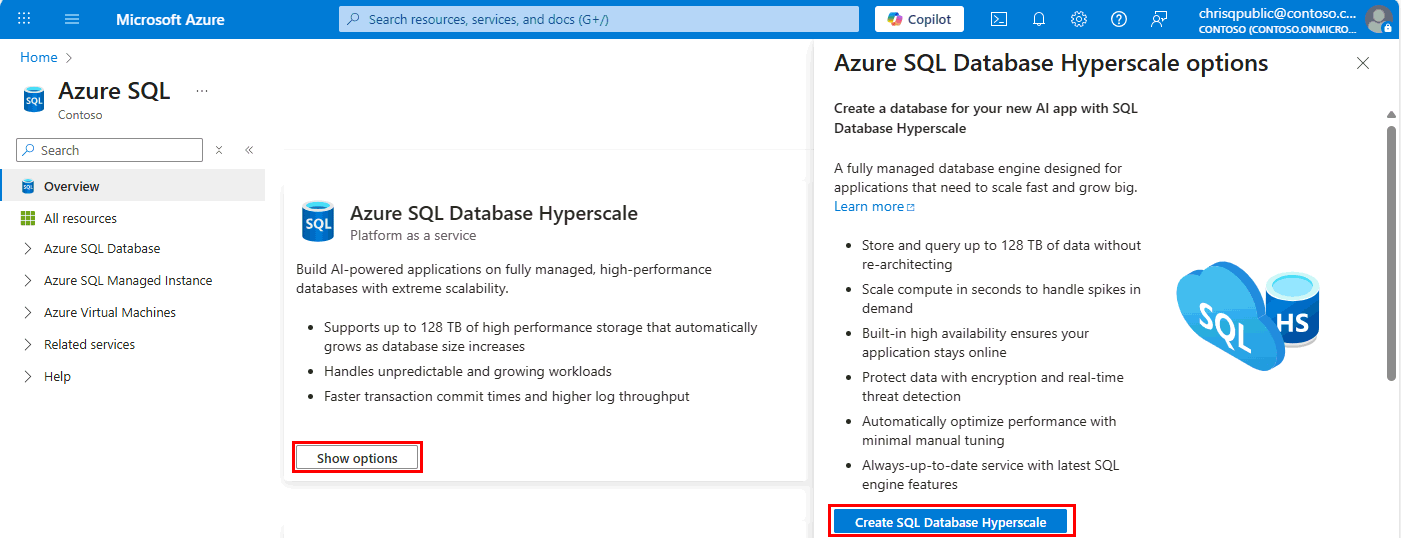
Go to Azure SQL hub. In the pane for Azure SQL Database Hyperscale, select Show options.
In the Azure SQL Database Hyperscale options window, select Create SQL Database Hyperscale.
On the Basics tab of the Create SQL Database form, under Project details, select the desired Azure Subscription.
For Resource group, select Create new, enter myResourceGroup, and select OK.
For Database name, enter mySampleDatabase.
For Server, select Create new, and fill out the New server form with the following values:
- Server name: Enter mysqlserver, and add some characters for uniqueness. We can't provide an exact server name to use because server names must be globally unique for all servers in Azure, not just unique within a subscription. Enter a name such as mysqlserver12345, and the portal will let you know if it's available.
- Server admin login: Enter azureuser.
- Password: Enter a password that meets requirements, and enter it again in the Confirm password field.
- Location: Select a location from the dropdown list.
Select OK.
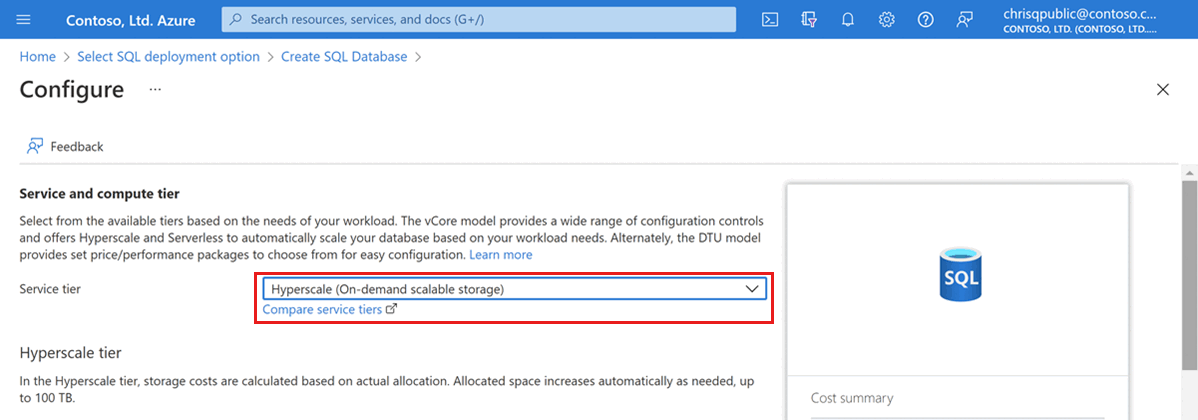
Under Compute + storage, select Configure database.
This quickstart creates a Hyperscale database. For Service tier, select Hyperscale.
Under Compute Hardware, select Change configuration. Review the available hardware configurations and select the most appropriate configuration for your database. For this example, we will select the Standard-series (Gen5) configuration.
Select OK to confirm the hardware generation.
Optionally, adjust the vCores slider if you would like to increase the number of vCores for your database. For this example, we will select 2 vCores.
Adjust the High-Availability Secondary Replicas slider to create one High Availability (HA) replica.
Select Apply.
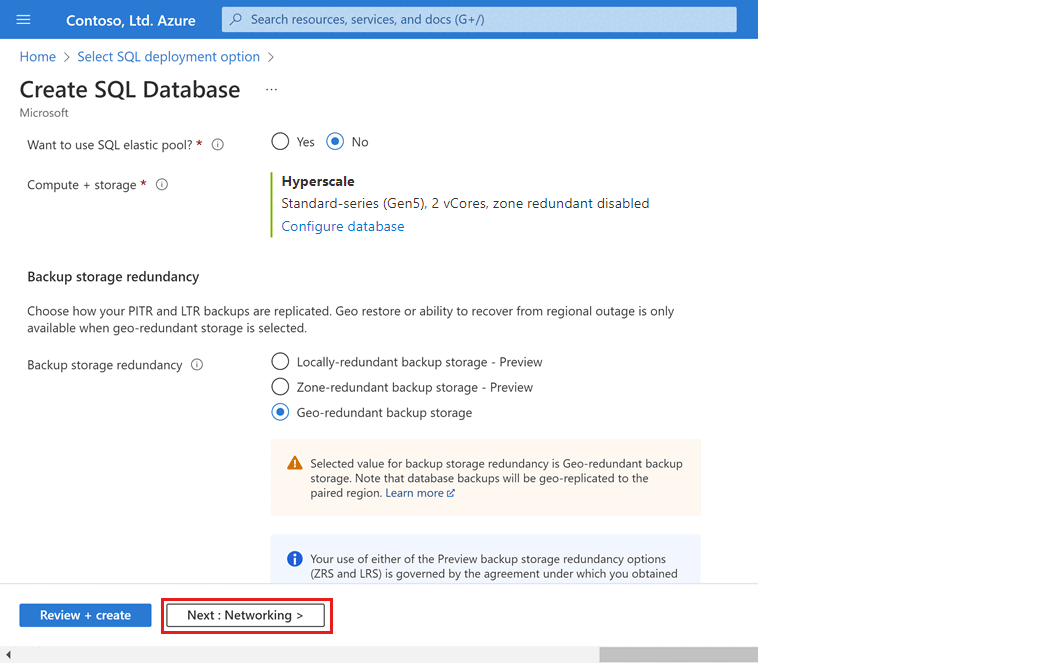
Carefully consider the configuration option for Backup storage redundancy when creating a Hyperscale database. Storage redundancy can only be specified during the database creation process for Hyperscale databases. You can choose locally redundant, zone-redundant, or geo-redundant storage. The selected storage redundancy option will be used for the lifetime of the database for both data storage redundancy and backup storage redundancy. Existing databases can migrate to different storage redundancy using database copy or point in time restore.
Select Next: Networking at the bottom of the page.
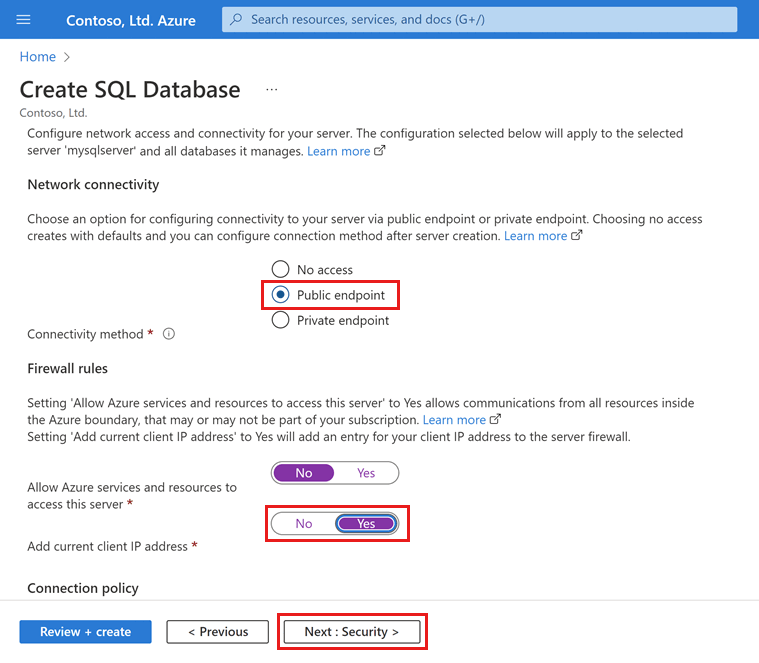
On the Networking tab, for Connectivity method, select Public endpoint.
For Firewall rules, set Add current client IP address to Yes. Leave Allow Azure services and resources to access this server set to No.
Select Next: Security at the bottom of the page.
Optionally, enable Microsoft Defender for SQL.
Select Next: Additional settings at the bottom of the page.
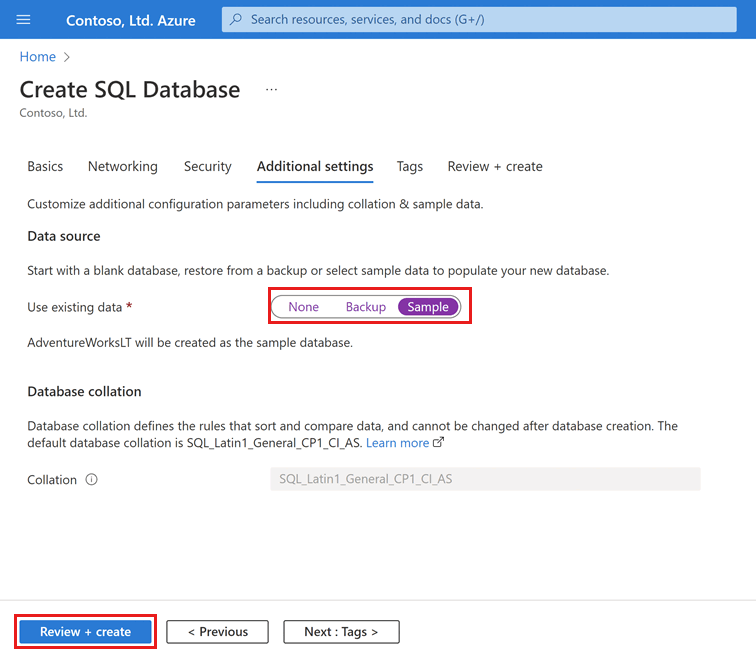
On the Additional settings tab, in the Data source section, for Use existing data, select Sample. This creates an AdventureWorksLT sample database so there's some tables and data to query and experiment with, as opposed to an empty blank database.
Select Review + create at the bottom of the page:
On the Review + create page, after reviewing, select Create.
Query the database
Once your database is created, you can use the Query editor (preview) in the Azure portal to connect to the database and query data. If you prefer, you can alternately query the database by connecting with SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), or the client of your choice to run Transact-SQL commands (sqlcmd, etc.).
In the portal, search for and select SQL databases, and then select your database from the list.
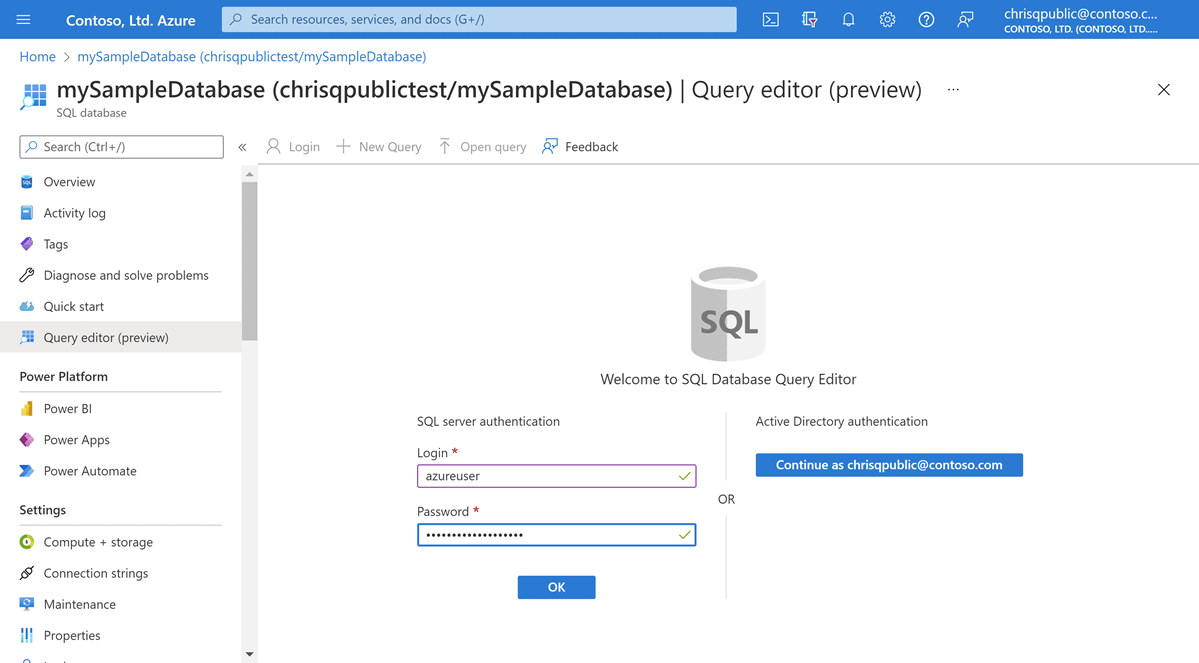
On the page for your database, select Query editor (preview) in the left menu.
Enter your server admin login information, and select OK.
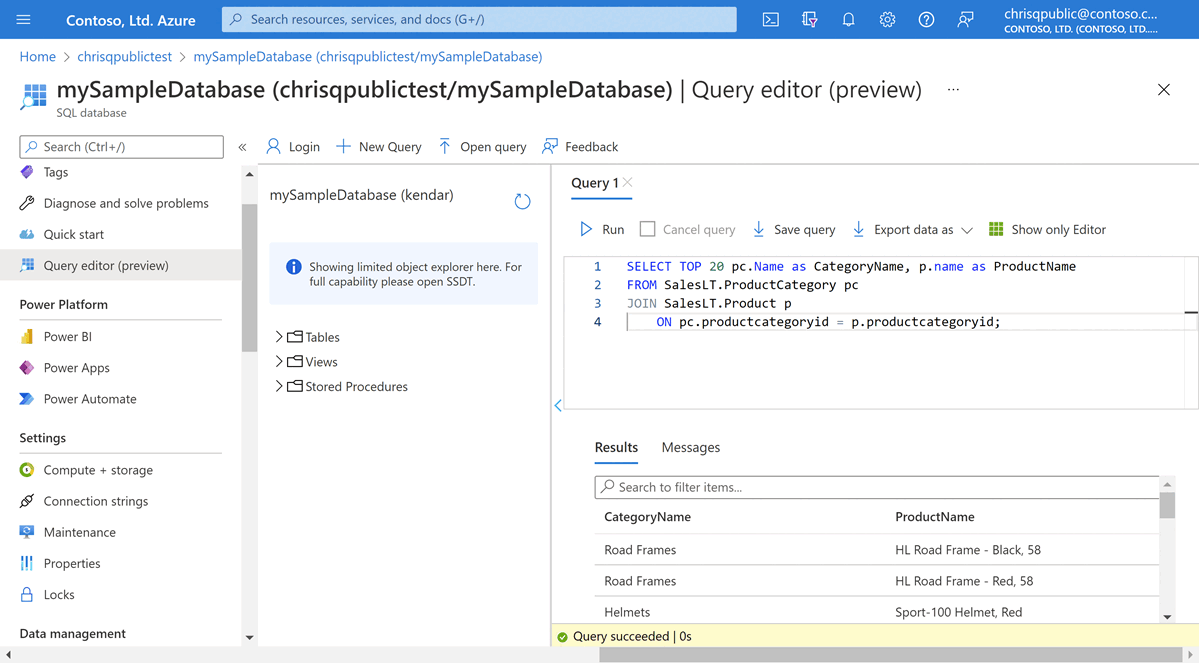
If you created your Hyperscale database from the AdventureWorksLT sample database, enter the following query in the Query editor pane.
SELECT TOP 20 pc.Name as CategoryName, p.name as ProductName FROM SalesLT.ProductCategory pc JOIN SalesLT.Product p ON pc.productcategoryid = p.productcategoryid;If you created an empty database using the Transact-SQL sample code, enter another example query in the Query editor pane, such as the following:
CREATE TABLE dbo.TestTable( TestTableID int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, TestTime datetime NOT NULL, TestMessage nvarchar(4000) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT PK_TestTable_TestTableID PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED (TestTableID ASC) ) GO ALTER TABLE dbo.TestTable ADD CONSTRAINT DF_TestTable_TestTime DEFAULT (getdate()) FOR TestTime GO INSERT dbo.TestTable (TestMessage) VALUES (N'This is a test'); GO SELECT TestTableID, TestTime, TestMessage FROM dbo.TestTable; GOSelect Run, and then review the query results in the Results pane.
Close the Query editor page, and select OK when prompted to discard your unsaved edits.
Clean up resources
Keep the resource group, server, and single database to go on to the next steps, and learn how to connect and query your database with different methods.
When you're finished using these resources, you can delete the resource group you created, which will also delete the server and single database within it.
To delete myResourceGroup and all its resources using the Azure portal:
- In the portal, search for and select Resource groups, and then select myResourceGroup from the list.
- On the resource group page, select Delete resource group.
- Under Type the resource group name, enter myResourceGroup, and then select Delete.
Related content
Connect and query your database using different tools and languages:
- Connect and query using SQL Server Management Studio
- sqlcmd
- Azure portal query editor for Azure SQL Database
Learn more about Hyperscale databases in the following articles: