Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
This article provides the detailed resource limits for Azure SQL Database elastic pools and pooled databases using the vCore purchasing model.
- For single database vCore resource limits, see vCore resource limits - Azure SQL Database and vCore resource limits - elastic pools.
- For more information regarding the different purchasing models, see Compare vCore and DTU-based purchasing models of Azure SQL Database.
Database properties for pooled databases
For each elastic pool, you can optionally specify per database minimum and maximum vCores to modify resource consumption patterns within the pool. You can also set maximum storage per database, for example to prevent a single database from consuming all pool storage.
- Specified min and max vCore values apply to all databases in the pool. Customizing min and max vCores for individual databases in the pool isn't supported.
- Maximum storage per database can be configured independently for each database.
The following table describes per database properties for pooled databases.
| Property | Configuration level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Max vCores per database | Configured for all databases in the pool | The maximum number of vCores that any database in the pool can use, if available based on utilization by other databases in the pool. Max vCores per database isn't a resource guarantee for a database. If the workload in each database doesn't need all available pool resources to perform adequately, consider setting max vCores per database to prevent a single database from monopolizing pool resources. Some degree of over-committing is expected since the pool generally assumes hot and cold usage patterns for databases, where all databases aren't simultaneously peaking. |
| Min vCores per database | Configured for all databases in the pool | The minimum number of vCores reserved for any database in the pool. Consider setting a min vCores per database when you want to guarantee resource availability for each database regardless of resource consumption by other databases in the pool. The min vCores per database can be set to 0, and is also the default value. This property is set to anywhere between 0 and the average vCores utilization per database. |
| Max storage per database | Configured per database | The maximum database size set by the user for a database in a pool. Pooled databases share allocated pool storage, so the size a database can reach is limited to the smaller of remaining pool storage and maximum database size. Maximum database size refers to the maximum size of the data files and doesn't include the space used by the log file. |
Important
Because resources in an elastic pool are finite, setting min vCores per database to a value greater than 0 implicitly limits resource utilization by each database. If, at a point in time, most databases in a pool are idle, resources reserved to satisfy the min vCores guarantee are not available to databases active at that point in time.
Additionally, setting min vCores per database to a value greater than 0 implicitly limits the number of databases that can be added to the pool. For example, if you set the min vCores to 2 in a 20 vCore pool, it means that you will not be able to add more than 10 databases to the pool, because 2 vCores are reserved for each database.
Even though the per database properties are expressed in vCores, they also govern consumption of other resource types, such as data IO, log IO, buffer pool memory, and worker threads. As you adjust min and max per database vCore values, reservations and limits for all resource types are adjusted proportionally.
Min and max per database vCore values apply to resource consumption by user workloads, but not to resource consumption by internal processes. For example, for a database with a per database max vCores set to half of the pool vCores, user workload can't consume more than one half of the buffer pool memory. However, this database can still take advantage of pages in the buffer pool that were loaded by internal processes. For more information, see Resource consumption by user workloads and internal processes.
The resource limits of individual databases in elastic pools are generally the same as for single databases outside of pools that have the same compute size (service objective). For example, the max concurrent workers for a GP_S_Gen5_10 database is 750 workers. So, the max concurrent workers for a database in a GP_Gen5_10 pool is also 750 workers. Note, the total number of concurrent workers in GP_Gen5_10 pool is 1050. For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Single database resource limits.
Each read-only replica of an elastic pool has its own resources, such as vCores, memory, data IOPS, tempdb, workers, and sessions. Each read-only replica is subject to elastic pool resource limits detailed later in this article.
You can set the service tier, compute size (service objective), and storage amount using:
Important
For scaling guidance and considerations, see Scale elastic pool resources in Azure SQL Database.
If all vCores of an elastic pool are busy, then each database in the pool receives an equal amount of compute resources to process queries. Azure SQL Database provides resource sharing fairness between databases by ensuring equal slices of compute time. Elastic pool resource sharing fairness is in addition to any amount of resource otherwise guaranteed to each database when the vCore min per database is set to a non-zero value.
For the same number of vCores, resources provided to an elastic pool can exceed the resources provided to a single database outside of an elastic pool. This means it's possible for the CPU, Data IO, and Log write utilization of an elastic pool to be less than the summation of CPU, Data IO, and Log write utilization across databases within the pool, depending on workload patterns. For example, in an extreme case with only one database in an elastic pool where database Data IO utilization is 100%, it's possible for pool Data IO utilization to be 50% for certain workload patterns. This can happen even if max vCores per database remains at the maximum supported value for the given pool size.
Note
The Gen5 hardware in the vCore purchasing model has been renamed to standard-series (Gen5).
General Purpose - provisioned compute - standard-series (Gen5)
General Purpose - standard-series (Gen5) (part 1 of 3)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) for General Purpose standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention GP_Gen5_ followed by the number of max vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: GP_Gen5_2, GP_Gen5_4, GP_Gen5_6, GP_Gen5_8, and GP_Gen5_10:
| vCores | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 10.4 | 20.8 | 31.1 | 41.5 | 51.9 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 100 | 200 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Max data size (GB) | 512 | 756 | 1536 | 2048 | 2048 |
| Max log size (GB) 2 | 154 | 227 | 461 | 461 | 461 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
64 | 128 | 192 | 256 | 320 |
| Storage type | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage |
| Read IO latency 6 | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms |
| Write IO latency 6 | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms |
| Max data IOPS per pool 3 | 1,400 | 2,800 | 4,200 | 5,600 | 7,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 4 | 210 | 420 | 630 | 840 | 1050 |
| Max concurrent logins per pool | 210 | 420 | 630 | 840 | 1050 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 5 | 21 | 42 | 63 | 84 | 105 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 |
| Number of replicas | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Included backup storage | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 For documented max data size values. Reducing max data size reduces max log size proportionally.
3 The maximum value for IO sizes ranging between 8 KB and 64 KB. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance.
4 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using Gen5 and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on Gen5 there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
5 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
6 Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
General Purpose - standard-series (Gen5) (part 2 of 3)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) for General Purpose standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention GP_Gen5_ followed by the number of max vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: GP_Gen5_12, GP_Gen5_14, GP_Gen5_16, GP_Gen5_18, and GP_Gen5_20:
| vCores | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 62.3 | 72.7 | 83 | 93.4 | 103.8 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Max data size (GB) | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 3072 | 3072 |
| Max log size (GB) 2 | 614 | 614 | 614 | 922 | 922 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
384 | 448 | 512 | 576 | 640 |
| Storage type | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage |
| Read IO latency 6 | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms |
| Write IO latency 6 | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms |
| Max data IOPS per pool 3 | 8,400 | 9,800 | 11,200 | 12,600 | 14,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 4 | 1260 | 1470 | 1680 | 1890 | 2100 |
| Max concurrent logins per pool | 1260 | 1470 | 1680 | 1890 | 2100 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 5 | 126 | 147 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 |
| Number of replicas | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Included backup storage | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 For documented max data size values. Reducing max data size reduces max log size proportionally.
3 The maximum value for IO sizes ranging between 8 KB and 64 KB. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance.
4 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
5 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
6 Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
General Purpose - standard-series (Gen5) (part 3 of 3)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) for General Purpose standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention GP_Gen5_ followed by the number of max vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: GP_Gen5_24, GP_Gen5_32, GP_Gen5_40, GP_Gen5_80, and GP_Gen5_128:
| vCores | 24 | 32 | 40 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 124.6 | 166.1 | 207.6 | 415.2 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Max data size (GB) | 3072 | 4096 | 4096 | 4096 |
| Max log size (GB) 2 | 922 | 1229 | 1229 | 1229 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
768 | 1024 | 1280 | 2560 |
| Storage type | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage | Premium (Remote) Storage |
| Read IO latency 6 | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms | 5-10 ms |
| Write IO latency 6 | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms | 5-7 ms |
| Max data IOPS per pool 3 | 16,800 | 22,400 | 28,000 | 32,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 4 | 2520 | 3360 | 4200 | 8400 |
| Max concurrent logins per pool | 2520 | 3360 | 4200 | 8400 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 5 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 40 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48, 80 |
| Number of replicas | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Included backup storage | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 For documented max data size values. Reducing max data size reduces max log size proportionally.
3 The maximum value for IO sizes ranging between 8 KB and 64 KB. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance.
4 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
5 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
6 Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
Business Critical - provisioned compute - standard-series (Gen5)
Business Critical - standard-series (Gen5) (part 1 of 3)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) in the Business Critical standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention BC_Gen5_ followed by the number of vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: BC_Gen5_4, BC_Gen5_6, BC_Gen5_8, BC_Gen5_10, and BC_Gen5_12:
| vCores | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 20.8 | 31.1 | 41.5 | 51.9 | 62.3 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | 3.14 | 4.71 | 6.28 | 8.65 | 11.02 |
| Max data size (GB) | 1024 | 1536 | 2048 | 2048 | 3072 |
| Max log size (GB) 2 | 307 | 307 | 461 | 461 | 922 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
128 | 192 | 256 | 320 | 384 |
| Max local storage size (GB) | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 |
| Storage type | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD |
| Read IO latency 6 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Write IO latency 6 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Max data IOPS per pool 3 | 18,000 | 27,000 | 36,000 | 45,000 | 54,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 60 | 90 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 4 | 420 | 630 | 840 | 1050 | 1260 |
| Max concurrent logins per pool | 420 | 630 | 840 | 1050 | 1260 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 5 | 42 | 63 | 84 | 105 | 126 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 |
| Number of replicas | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Included backup storage | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 For documented max data size values. Reducing max data size reduces max log size proportionally.
3 The maximum value for IO sizes ranging between 8 KB and 64 KB. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance.
4 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
5 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
6 Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
Business Critical - standard-series (Gen5) (part 2 of 3)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) in the Business Critical standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention BC_Gen5_ followed by the number of vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: BC_Gen5_14, BC_Gen5_16, BC_Gen5_18, BC_Gen5_20, and BC_Gen5_24:
| vCores | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 72.7 | 83 | 93.4 | 103.8 | 124.6 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | 13.39 | 15.77 | 18.14 | 20.51 | 25.25 |
| Max data size (GB) | 3072 | 3072 | 3072 | 3072 | 4096 |
| Max log size (GB) 2 | 922 | 922 | 922 | 922 | 1229 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
448 | 512 | 576 | 640 | 768 |
| Max local storage size (GB) | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 |
| Storage type | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD |
| Read IO latency 5 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Write IO latency 5 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Max data IOPS per pool 3 | 63,000 | 72,000 | 81,000 | 90,000 | 108,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 4 | 1470 | 1680 | 1890 | 2100 | 2520 |
| Max concurrent logins per pool | 1470 | 1680 | 1890 | 2100 | 2520 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 5 | 147 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24 |
| Number of replicas | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Included backup storage | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 For documented max data size values. Reducing max data size reduces max log size proportionally.
3 The maximum value for IO sizes ranging between 8 KB and 64 KB. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance.
4 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
5 Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
Business Critical - standard-series (Gen5) (part 3 of 3)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) in the Business Critical standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention BC_Gen5_ followed by the number of vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: BC_Gen5_32, BC_Gen5_40, and BC_Gen5_80:
| vCores | 32 | 40 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 166.1 | 207.6 | 415.2 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | 37.94 | 52.23 | 131.68 |
| Max data size (GB) | 4096 | 4096 | 4096 |
| Max log size (GB) 2 | 1229 | 1229 | 1229 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
1024 | 1280 | 2560 |
| Max local storage size (GB) | 4829 | 4829 | 4829 |
| Storage type | Local SSD | Local SSD | Local SSD |
| Read IO latency 6 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Write IO latency 6 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Max data IOPS per pool 3 | 144,000 | 180,000 | 256,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 4 | 3360 | 4200 | 8400 |
| Max concurrent logins per pool | 3360 | 4200 | 8400 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 5 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 40 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 40, 48, 80 |
| Number of replicas | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Included backup storage | 1X DB size | 1X DB size | 1X DB size |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 For documented max data size values. Reducing max data size reduces max log size proportionally.
3 The maximum value for IO sizes ranging between 8 KB and 64 KB. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance.
4 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
5 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
6 Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
Hyperscale - provisioned compute - standard-series (Gen5)
Hyperscale - standard-series (Gen5) (part 1 of 2)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) in the Hyperscale standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention HS_Gen5_ followed by the number of vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: HS_Gen5_4, HS_Gen5_6, HS_Gen5_8, HS_Gen5_10, HS_Gen5_12, and HS_Gen5_14:
| vCores | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Memory (GB) | 20.8 | 31.1 | 41.5 | 51.9 | 62.3 | 72.7 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Max data size per pool (TB) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
128 | 192 | 256 | 320 | 384 | 448 |
| Max local SSD IOPS per pool 2 | 18,000 | 27,000 | 36,000 | 45,000 | 54,000 | 63,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| Local read IO latency 3 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Remote read IO latency 3 | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms |
| Write IO latency 3 | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms |
| Storage type | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 5 | 420 | 630 | 840 | 1050 | 1260 | 1470 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 6 | 42 | 63 | 84 | 105 | 126 | 147 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 |
| Secondary pool replicas | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 Hyperscale is a multi-tiered architecture with separate compute and storage components. Review Hyperscale service tier and Hyperscale service tier for more information.
3 Besides local SSD IO, workloads use remote page server IO. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance, and Data IO in resource utilization statistics. Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
4 Latency is 1-2 ms for data on local compute replica SSD, which caches most used data pages. Higher latency for data retrieved from page servers.
5 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
6 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
Hyperscale - standard-series (Gen5) (part 2 of 2)
Compute sizes (service level objectives, or SLOs) in the Hyperscale standard-series elastic pools follow the naming convention HS_Gen5_ followed by the number of vCores.
The following table covers these SLOs: HS_Gen5_16, HS_Gen5_18, HS_Gen5_20, HS_Gen5_24, HS_Gen5_32, HS_Gen5_40, and HS_Gen5_80:
| vCores | 16 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 32 | 40 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 | Gen5 |
| Max number DBs per pool 1 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Memory (GB) | 83 | 93.4 | 103.8 | 124.6 | 166.1 | 207.6 | 415.2 |
| Columnstore support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| In-memory OLTP storage (GB) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Max data size per pool (TB) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
tempdb max data size (GB) |
512 | 576 | 640 | 768 | 1024 | 1280 | 2560 |
| Max local SSD IOPS per pool 2 | 72,000 | 81,000 | 90,000 | 108,000 | 144,000 | 180,000 | 256,000 |
| Max log rate per pool (MiB/s) | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| Local read IO latency 3 | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms | 1-2 ms |
| Remote read IO latency 3 | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms | 1-5 ms |
| Write IO latency 3 | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms | 3-5 ms |
| Storage type | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 | Multi-tiered 4 |
| Max concurrent workers per pool 5 | 1680 | 1890 | 2100 | 2520 | 3360 | 4200 | 8400 |
| Max concurrent external connections per pool 6 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Max concurrent sessions | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Min/max elastic pool vCore choices per database | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 40 | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 40, 80 |
| Secondary replicas | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 | 0-4 |
| Multi-AZ | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read Scale-out | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1 See Resource management in dense elastic pools for additional considerations.
2 Hyperscale is a multi-tiered architecture with separate compute and storage components. Review Hyperscale service tier and Hyperscale service tier for more information.
3 Besides local SSD IO, workloads use remote page server IO. Actual IOPS are workload-dependent. For details, see Data IO Governance, and Data IO in resource utilization statistics. Latency numbers are approximate and representative for typical workloads at steady state, but aren't guaranteed.
4 Latency is 1-2 ms for data on local compute replica SSD, which caches most used data pages. Higher latency for data retrieved from page servers.
5 For the max concurrent workers for any individual database, see Resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model. For example, if the elastic pool is using standard-series (Gen5) and the max vCore per database is set at 2, then the max concurrent workers value is 200. If max vCore per database is set to 0.5, then the max concurrent workers value is 50 since on standard-series (Gen5) there are a max of 100 concurrent workers per vCore. For other max vCore settings per database that are less 1 vCore or less, the number of max concurrent workers is similarly rescaled.
6 For more information on what counts as an external connection, see External Connections.
Previously available hardware
This section includes details on previously available hardware.
- Gen4 hardware has been retired and isn't available for provisioning, upscaling, or downscaling. Migrate your database to a supported hardware generation for a wider range of vCore and storage scalability, accelerated networking, best IO performance, and minimal latency. For more information, see Support has ended for Gen 4 hardware on Azure SQL Database.
You can use Azure Resource Graph Explorer to identify all Azure SQL Database resources that currently use Gen4 hardware, or you can check the hardware used by resources for a specific logical server in the Azure portal.
You must have at least read permissions to the Azure object or object group to see results in Azure Resource Graph Explorer.
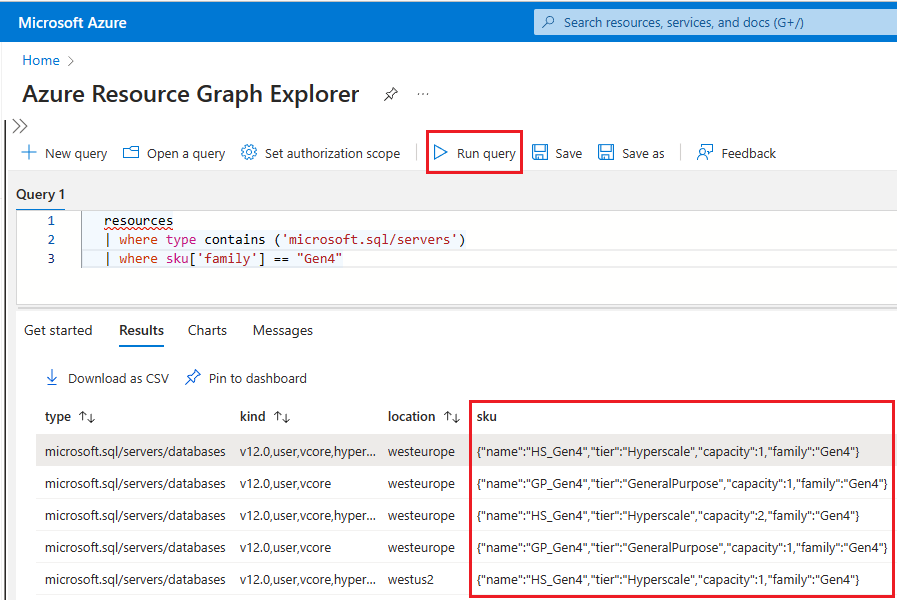
To use Resource Graph Explorer to identify Azure SQL resources that are still using Gen4 hardware, follow these steps:
Go to the Azure portal.
Search for
Resource graphin the search box, and choose the Resource Graph Explorer service from the search results.In the query window, type the following query and then select Run query:
resources | where type contains ('microsoft.sql/servers') | where sku['family'] == "Gen4"The Results pane displays all the currently deployed resources in Azure that are using Gen4 hardware.
To check the hardware used by resources for a specific logical server in Azure, follow these steps:
- Go to the Azure portal.
- Search for
SQL serversin the search box and choose SQL servers from the search results to open the SQL servers page and view all servers for the chosen subscription(s). - Select the server of interest to open the Overview page for the server.
- Scroll down to available resources and check the Pricing tier column for resources that are using gen4 hardware.

To migrate resources to standard-series hardware, review Change hardware.
Related content
- For vCore resource limits for a single database, see resource limits for single databases using the vCore purchasing model
- For information about general Azure limits, see Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
- For information about resource limits on a logical SQL server, see overview of resource limits on a logical SQL server for information about limits at the server and subscription levels.