Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Synapse Analytics
Transparent data encryption (TDE) helps protect Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics against the threat of malicious offline activity by encrypting data at rest. It performs real-time encryption and decryption of the database, associated backups, and transaction log files at rest without requiring changes to the application. By default, TDE is enabled for all newly deployed Azure SQL Databases and must be manually enabled for older databases of Azure SQL Database. For Azure SQL Managed Instance, TDE is enabled at the instance level and newly created databases. TDE must be manually enabled for Azure Synapse Analytics.
Note
This article applies to Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics (dedicated SQL pools (formerly SQL DW)). For documentation on Transparent Data Encryption for dedicated SQL pools inside Synapse workspaces, see Azure Synapse Analytics encryption.
Some items considered customer content, such as table names, object names, and index names, might be transmitted in log files for support and troubleshooting by Azure.
TDE performs real-time I/O encryption and decryption of the data at the page level. Each page is decrypted when it's read into memory and then encrypted before being written to disk. TDE encrypts the storage of an entire database by using a symmetric key called the Database Encryption Key (DEK). On database startup, the encrypted DEK is decrypted and then used for decryption and re-encryption of the database files in the SQL Server database engine process. DEK is protected by the TDE protector. TDE protector is either a service-managed certificate (service-managed transparent data encryption) or an asymmetric key stored in Azure Key Vault (customer-managed transparent data encryption).
For Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse, the TDE protector is set at the server level and is inherited by all databases associated with that server. For Azure SQL Managed Instance, the TDE protector is set at the instance level and inherited by all encrypted databases on that instance. The term server refers both to server and instance throughout this document, unless stated differently.
Important
All newly created SQL databases are encrypted by default by using service-managed transparent data encryption. When the database source is encrypted, the target databases created through restore, geo-replication, and database copy are encrypted by default. However, when the database source isn't encrypted, the target databases created through restore, geo-replication, and database copy aren't encrypted by default. Existing SQL databases created before May 2017 and existing SQL Managed Instance databases created before February 2019 aren't encrypted by default. SQL Managed Instance databases created through restore inherit encryption status from the source. To restore an existing TDE-encrypted database, the required TDE certificate must first be imported into the SQL Managed Instance. To find out the encryption status for a database, execute a select query from the sys.dm_database_encryption_keys DMV and check the status of the encryption_state_desc column.
Note
TDE can't be used to encrypt system databases, such as the master database, in SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance. The master database contains objects that are needed to perform TDE operations on user databases. It's recommended not to store any sensitive data in system databases. The exception is tempdb, which is always encrypted by a special asymmetric key owned by Microsoft. This is by design and ensures that temporary objects are protected.
Service-managed transparent data encryption
In Azure, the default setting for TDE is that the DEK is protected by a built-in server certificate. The built-in server certificate is unique for each server and the encryption algorithm used is AES 256 in Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) mode. If a database is in a geo-replication relationship, both the primary and geo-secondary databases are protected by the primary database's parent server key. If two databases are connected to the same server, they also share the same built-in certificate. Azure automatically rotates these certificates once a year, in compliance with the internal security policy and the root key is protected by a Azure internal secret store. Customers can verify SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance compliance with internal security policies in independent third-party audit reports available on the Azure Trust Center.
Azure also seamlessly moves and manages the keys as needed for geo-replication and restores.
Customer-managed transparent data encryption - Bring Your Own Key
Customer-managed TDE is also referred to as Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) support for TDE. In this scenario, the TDE Protector that encrypts the DEK is a customer-managed asymmetric key, which is stored in a customer-owned and managed Azure Key Vault (Azure's cloud-based external key management system) and never leaves the key vault. The TDE Protector can be generated by the key vault. SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse need to be granted permissions to the customer-owned key vault to decrypt and encrypt the DEK. If permissions of the server to the key vault are revoked, a database will be inaccessible, and all data is encrypted.
With TDE with Azure Key Vault integration, users can control key management tasks including key rotations, key vault permissions, key backups, and enable auditing/reporting on all TDE protectors using Azure Key Vault functionality. Azure Key Vault provides central key management, and enables separation of duties between management of keys and data to help meet compliance with security policies. To learn more about BYOK for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse, see Azure SQL transparent data encryption with customer-managed key.
To start using TDE with Azure Key Vault integration, see the how-to guide PowerShell and Azure CLI: Enable Transparent Data Encryption with customer-managed key from Azure Key Vault.
Move a transparent data encryption-protected database
You don't need to decrypt databases for operations within Azure. The TDE settings on the source database or primary database are transparently inherited on the target. Operations that are included involve:
- Geo-restore
- Self-service point-in-time restore
- Restoration of a deleted database
- Active geo-replication
- Creation of a database copy
- Restore of backup file to Azure SQL Managed Instance
Important
Taking manual COPY-ONLY backup of a database encrypted by service-managed TDE isn't supported in Azure SQL Managed Instance, since the certificate used for encryption isn't accessible. Use point-in-time-restore feature to move this type of database to another SQL Managed Instance, or switch to customer-managed key.
When you export a TDE-protected database to a BACPAC file, the exported content of the database isn't encrypted. If you import into an existing empty database, the encryption depends on whether TDE is enabled on that database or not. If a new database is created during the import, it uses the default TDE settings of the logical server for Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Manage transparent data encryption
Manage TDE in the Azure portal.
To configure TDE through the Azure portal, you must be connected as the Azure Owner, Contributor, or SQL Security Manager.
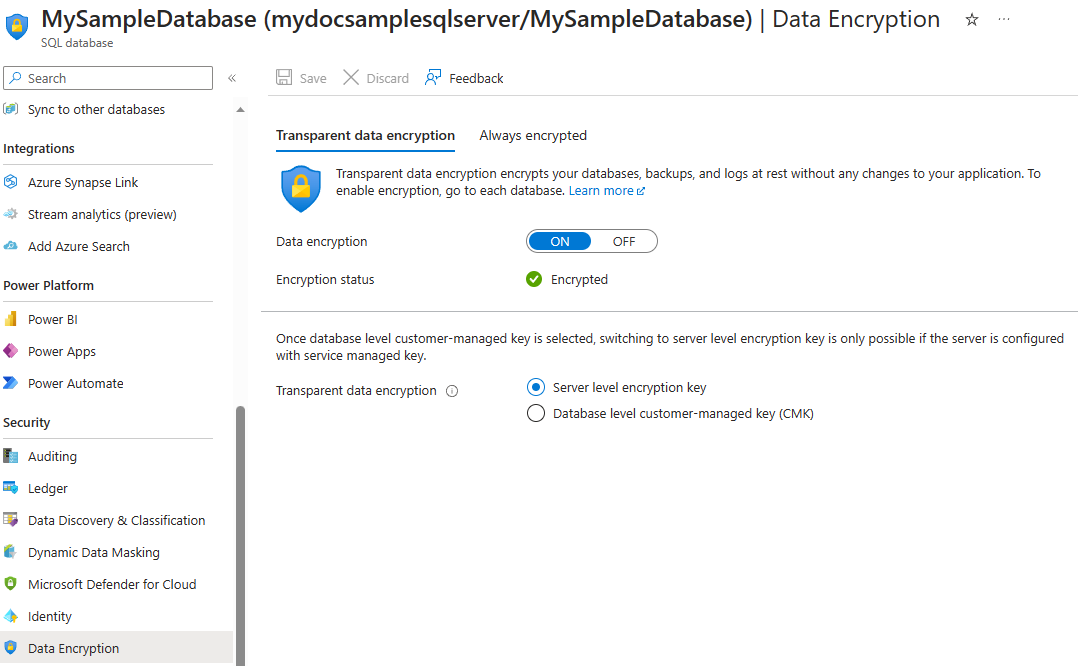
Enable and disable TDE on the database level. For Azure SQL Managed Instance use Transact-SQL (T-SQL) to turn TDE on and off on a database. For Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse, you can manage TDE for the database in the Azure portal after you've signed in with the Azure Administrator or Contributor account. Find the TDE settings under your user database. By default, server level encryption key is used. A TDE certificate is automatically generated for the server that contains the database.
You set the TDE master key, known as the TDE protector, at the server or instance level. To use TDE with BYOK support and protect your databases with a key from Azure Key Vault, open the TDE settings under your server or managed instance.
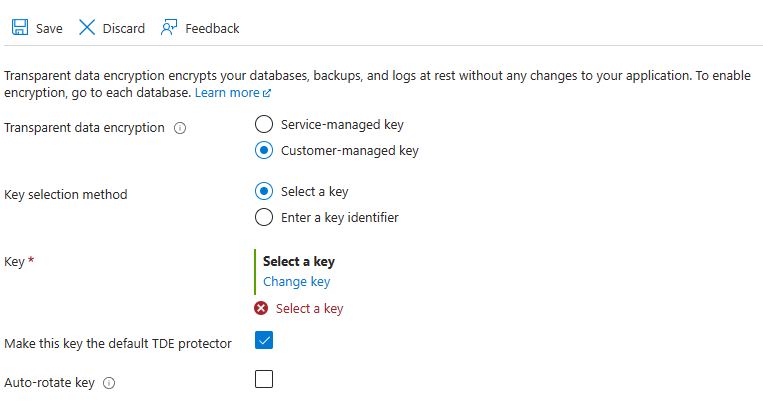
You can also use a customer-managed key for TDE on a database level for Azure SQL Database. For more information, see Transparent data encryption (TDE) with customer-managed keys at the database level.
Related content
- Extensible Key Management using Azure Key Vault (SQL Server)
- Transparent data encryption (TDE)
- Azure SQL transparent data encryption with customer-managed key
- PowerShell and Azure CLI: Enable Transparent Data Encryption with customer-managed key from Azure Key Vault
- Secure access to an Azure Key Vault