Applies to:  Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This article provides examples to modify automated backup settings for Azure SQL Managed Instance, such as the short-term retention policy and the backup storage redundancy option that's used for backups. For Azure SQL Database, see Change automated backup settings for Azure SQL Database.
Change short-term retention policy
You can change the default point-in-time recovery (PITR) backup retention period by using the Azure portal, PowerShell, or the REST API. The following examples illustrate how to change the PITR retention to 28 days.
Warning
If you reduce the current retention period, you lose the ability to restore to points in time older than the new retention period. Backups that are no longer needed to provide PITR within the new retention period are deleted.
If you increase the current retention period, you don't immediately gain the ability to restore to older points in time within the new retention period. You gain that ability over time, as the system starts to retain backups for longer periods.
Note
These APIs will affect only the PITR retention period. If you configured long-term retention (LTR) for your database, it won't be affected. For information about how to change long-term retention periods, see Long-term retention.
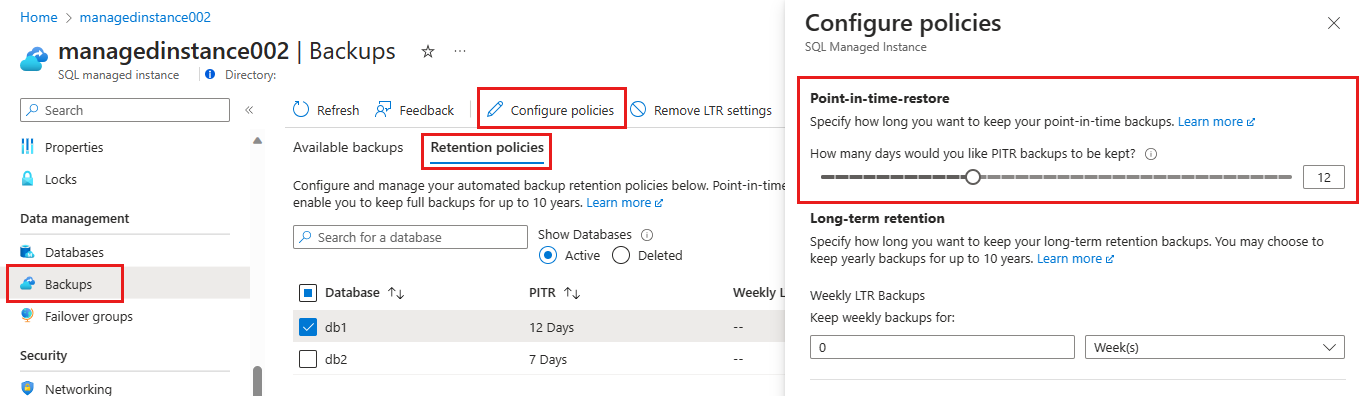
To change the PITR backup retention period for active databases by using the Azure portal:
- Go to the managed instance with the databases whose retention period you want to change.
- Select Backups on the left pane, and then select the Retention policies tab.
- Select the databases for which you want to change the PITR backup retention.
- Select Configure policies from the action bar.
Prepare your environment for the Azure CLI:
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
Use the following example to change the PITR backup retention of a single active database in a managed instance:
# Set a new PITR backup retention period on an active individual database
# Valid backup retention must be 1 to 35 days
az sql midb short-term-retention-policy set \
--resource-group myresourcegroup \
--managed-instance myinstance \
--name mymanageddb \
--retention-days 1 \
Use the following example to change the PITR backup retention for all active databases in a managed instance:
# Set a new PITR backup retention period for all active databases
# Valid backup retention must be 1 to 35 days
az sql midb short-term-retention-policy set \
--resource-group myresourcegroup \
--managed-instance myinstance \
--retention-days 1 \
For more information, see the Backup retention Azure CLI command.
To change the PITR backup retention for a single active database in a managed instance, use the following PowerShell example:
# Set a new PITR backup retention period on an active individual database
# Valid backup retention must be 1 to 35 days
Set-AzSqlInstanceDatabaseBackupShortTermRetentionPolicy -ResourceGroupName resourceGroup -InstanceName testserver -DatabaseName testDatabase -RetentionDays 1
To change the PITR backup retention for all active databases in a managed instance, use the following PowerShell example:
# Set a new PITR backup retention period for all active databases
# Valid backup retention must be 1 to 35 days
Get-AzSqlInstanceDatabase -ResourceGroupName resourceGroup -InstanceName testserver | Set-AzSqlInstanceDatabaseBackupShortTermRetentionPolicy -RetentionDays 1
To change the PITR backup retention for a single deleted database in a managed instance, use the following PowerShell example:
# Set a new PITR backup retention on an individual deleted database
# Valid backup retention must be 0 (no retention) to 35 days. Valid retention rate can only be lower than the retention period when database was active, or the remaining backup days of a deleted database.
Get-AzSqlDeletedInstanceDatabaseBackup -ResourceGroupName resourceGroup -InstanceName testserver -DatabaseName testDatabase | Set-AzSqlInstanceDatabaseBackupShortTermRetentionPolicy -RetentionDays 0
To change the PITR backup retention for all deleted databases in a managed instance, use the following PowerShell example:
# Set a new PITR backup retention for all deleted databases
# Valid backup retention must be 0 (no retention) to 35 days. Valid retention rate can only be lower than the retention period when database was active, or the remaining backup days of a deleted database
Get-AzSqlDeletedInstanceDatabaseBackup -ResourceGroupName resourceGroup -InstanceName testserver | Set-AzSqlInstanceDatabaseBackupShortTermRetentionPolicy -RetentionDays 0
Zero days of retention would denote that a backup is immediately deleted and no longer kept for a deleted database. After you reduce PITR backup retention for a deleted database, you can no longer increase it.
For more information, see the Backup retention PowerShell command.
Sample request
PUT https://management.chinacloudapi.cn/subscriptions/00000000-1111-2222-3333-444444444444/resourceGroups/resourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances/testManagedInstance/databases/testDatabase/backupShortTermRetentionPolicies/default?api-version=2017-10-01-preview
Request body
{
"properties":{
"retentionDays":28
}
}
Sample response
Status code: 200
{
"id": "/subscriptions/00000000-1111-2222-3333-444444444444/providers/Microsoft.Sql/resourceGroups/resourceGroup/managedInstances/testserver/databases/testDatabase/backupShortTermRetentionPolicies/default",
"name": "default",
"type": "Microsoft.Sql/resourceGroups/managedInstances/databases/backupShortTermRetentionPolicies",
"properties": {
"retentionDays": 28
}
}
For more information, see the Backup retention REST API.
Configure backup storage redundancy for SQL Managed Instance by using the Azure portal, the Azure CLI, and Azure PowerShell.
In the Azure portal, during instance creation, the default option for the backup storage redundancy is geo-redundancy. To change it:
Go to the Basics tab and select Configure Managed Instance.
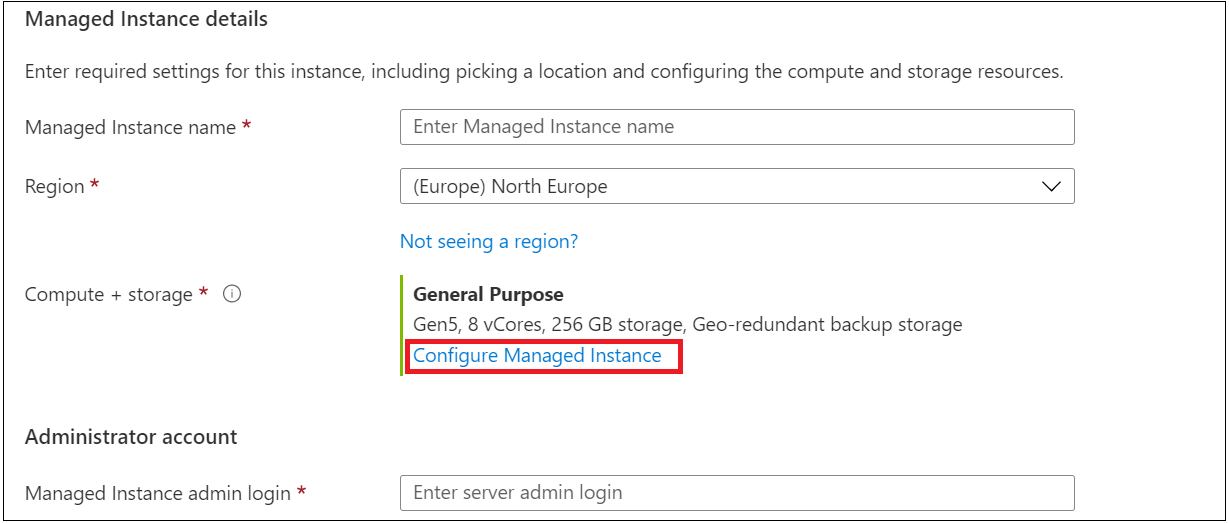
On the Compute + storage pane, select the option for the type of backup storage redundancy that you want.

Select Apply. For now, this change will be applied only for PITR backups. Long-term retention backups will retain the old storage redundancy type.
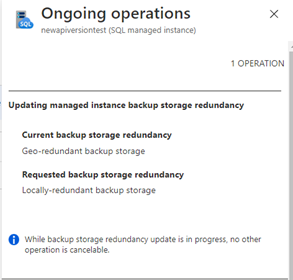
The time it takes to perform the backup redundancy change depends on the size of the all the databases within a single managed instance. Changing the backup redundancy will take more time for instances that have large databases. It's possible to combine the backup storage redundancy change with the operation to update the service-level objective (SLO).
Use the Notification pane of the Azure portal to view the status of the change operation.
To change the backup storage redundancy after you create a managed instance by using the Azure CLI, specify the -BackupStorageRedundancy parameter with the az sql mi update cmdlet. View the update mi backup storage redundancy example.
Possible values for -BackupStorageRedundancy are Geo for geo-redundant, Zone for zone-redundant, Local for locally redundant, and GeoZone for geo-zone redundant backup storage.
To configure backup storage redundancy when you create a managed instance, specify the -BackupStorageRedundancy parameter with the New-AzSqlInstance cmdlet. To change the backup storage redundancy for an existing managed instance, specify the -BackupStorageRedundancy parameter with the Set-AzSqlInstance cmdlet. To learn more, review the Update an existing instance to be zone redundant example.
Possible values for -BackupStorageRedundancy are Geo for geo-redundant, Zone for zone-redundant, Local for locally redundant, and GeoZone for geo-zone redundant backup storage.
It's not currently possible to change the backup storage redundancy option by using the REST API.
Next steps
Azure SQL Managed Instance



