Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
- If the CDN acceleration domain name is not accessible, what information should I provide to help investigate the issue?
- Why can't I cache my URL?
- Why are domain names resolved to the source station?
- What does the "CNAME cannot be used for system prompts" message mean?
- Why is return-to-source traffic greater than Content Delivery Network traffic?
- Since I started using the CDN, the website doesn't open.
- Since I started using the CDN, website logins aren't working properly.
- Cache refresh failed.
- Why is there CDN traffic when I haven't set the CNAME to Azure CDN?
If the Content Delivery Network acceleration domain name is not accessible, what information should I provide to help troubleshoot the issue?
If the Content Delivery Network acceleration domain name is not accessible, help identify the problem as quickly as possible by providing the following information:
* The Content Delivery Network node IP you were accessing when the problem occurred. To find the IP, do the following:
- Select Win+R, enter cmd, and then select OK so that the cmd.exe window is displayed.
- Enter the nslookup domain name, and obtain the IP address that corresponding to Address. For example, if the acceleration domain name is www.cdntest.com, enter nslookup www.cdntest.com in the command window and then select Enter.
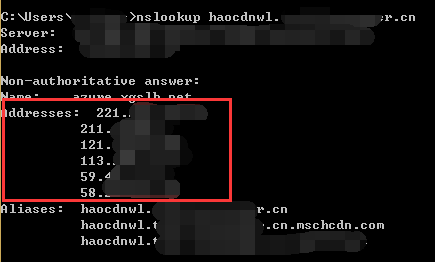
* The problematic URL as copyable text, because troubleshooters might need to copy long URLs to save time. Similar:http://www.eaxmple.com/aaabbbb.jpg
* The terminal egress IP.
* Screenshots of problems such as pages that will not open, loops, and 5x, and other information that screenshots can help visualize.
* The approximate time when the problem occurred.
Why can't I cache my URL?
The inability to cache a URL usually results from one of the following reasons:
* The corresponding header for the URL on the source station includes the following information:
- Set-Cookie (and the ignore Set-Cookie option has not been checked in the cache rules).
Note
When Set-Cookie is used for user sign-in and identification, the ignore Set-Cookie option cannot be checked. Otherwise, it could cause problems with functions.
Cache-Control: No-store/no-cache/private (and the ignore Cache-Control) option has not been checked in the cache rules.
- The Expires time is a time in the past. Expires sets the point in time when the cache expires. If this time is in the past, it makes the URL impossible to cache.
- The value of Max-age is very small. Max-age sets the length of the caching time in seconds. If the value is too small, for example, less than two digits, it expires very quickly and makes the URL impossible to cache.
Cache rules have not been configured or there is a configuration error, and the URL cannot hit any of the buffer rules. For example, if a user accidentally enter the following rules: "[any character ](.gif|.jpg|.bmp) (.gif|.jpg|.bmp)", even the image type can't hit the rule because the extension is duplicated.
* No users have so far accessed the URL, because some nodes cache the content only after it has been accessed.
Why are domain names resolved to the source station?
If the acceleration region of a domain name Content Delivery Network is China, overseas internet users or Chinese internet users who use non-Chinese Domain Name System (DNS) resolutions may be resolved to the source station. The Azure Content Delivery Network platform's default configuration for such situations is to use Content Delivery Network nodes in China to serve overseas visits.
What does the "CNAME cannot be used for system prompts" message mean?
Although we have not placed restrictions on accelerated domain names, it is possible that some domain-name management companies do not allow the use of CNAME for domain names that include the host name. You can resolve this issue by changing either the accelerated domain name or your domain name management company.
Why is return-to-source traffic greater than Content Delivery Network traffic?
In general, return-to-source traffic is less than or equal to Content Delivery Network traffic. But in certain circumstances, return-to-source traffic can also be greater than Content Delivery Network traffic (for example, if the visitor sends a request for a relatively large file). For example, if a 100-MB file has not been cached by the nodes, the network nodes retrieve it from the source station, which for a file of this size naturally takes some time. However, the visitor might not keep waiting at this time, with the result that the connection is disconnected. In such a situation, the network nodes still bring over the entire 100-MB file. By the time that the network nodes recognize that the visitor no longer wants the file, it no longer has any way to go back, so the return-to-source traffic reaches 100 MB, while the network traffic does not.
What causes a relatively high return-to-source rate?
* Cache rule configuration has issues.
* The amount of resources that can be cached is small.
* The cache time is short.
Since I started using the CDN, the website doesn't open.
There are several possible reasons:
* The source station malfunctions.
* The source station has a firewall that is shielding the Content Delivery Network nodes.
* The nodes are shielding the client IP.
* If you have added a new domain name or the domain name status has changed and there is problem with the node configuration, you might need to wait for a while until the problem is resolved, usually about 60 minutes.
* Equipment fails.
Since I started using the CDN, website logins aren't working properly.
It's likely that a resource that should not be cached is set in the cache rules. The user's backend login folder (for example: /user or /admin, etc.) must not be cached; if it is a non-login or user callback site, the cache rule is configured, please disable cookies in cache rules.
Cache refresh failed.
After a manual refresh is submitted, the system identifies the equipment that is working normally to allocate tasks. But if an anomaly occurs in a particular device during the allocation process, the system automatically detects and disables it. (Clients are not parsed to the relevant node after the service status has been closed, and it does not affect the acceleration service.) Other normal devices continue to be allocated tasks until they are complete, at which time the interface displays "Refresh failed." At the same time, customer service and operations and maintenance receive an email notification to deal with the issue as soon as possible, even if the refresh failure does not affect the Content Delivery Network service.
Why is there CDN traffic when I haven't set the CNAME to Azure CDN?
If the accelerated domain name service status is enabled, it is possible that our detection equipment will still detect the source station and acceleration details even if you haven't "CNAME-ed" to the Azure Content Delivery Network. This is also why we recommend that you choose smaller files whenever possible when you select URL monitoring. If you do not want accelerated domain names with no CNAME to consume data traffic, you can switch the service to the disabled status.