Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Are you looking for a database solution for high-scale scenarios with a 99.999% availability service level agreement (SLA), instant autoscale, and automatic failover across multiple regions? Consider Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL.
Azure Cosmos DB Graph database is multiple-regionally distributed so applications can use multiple read endpoints.
Reasons to choose more than one region:
- Horizontal read scalability - as application load increases it may be prudent to route read traffic to different Azure regions.
- Lower latency - you can reduce network latency overhead of each traversal by routing read and write traffic to the nearest Azure region.
Data residency requirement is achieved by setting Azure Resource Manager policy on Azure Cosmos DB account. Customer can limit regions into which Azure Cosmos DB replicates data.
Traffic routing
Azure Cosmos DB Graph database engine is running in multiple regions, each of which contains multiple clusters. Each cluster has hundreds of machines. Azure Cosmos DB Graph account DNS CNAME accountname.gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn resolves to DNS A record of a cluster. A single IP address of a load-balancer hides internal cluster topology.
A regional DNS CNAME record is created for every region of Azure Cosmos DB Graph account. Format of regional endpoint is accountname-region.gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn. Region segment of regional endpoint is obtained by removing all spaces from Azure region name. For example, "China East 2" region for "contoso" multiple-region database account would have a DNS CNAME contoso-chinaeast2.gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn
TinkerPop Gremlin client is designed to work with a single server. Application can use multiple-regional writable DNS CNAME for read and write traffic. Region-aware applications should use regional endpoint for read traffic. Use regional endpoint for write traffic only if specific region is configured to accept writes.
Note
Azure Cosmos DB Graph engine can accept write operation in read region by proxying traffic to write region. It is not recommended to send writes into read-only region as it increases traversal latency and is subject to restrictions in the future.
Multiple-region database account CNAME always points to a valid write region. During server-side failover of write region, Azure Cosmos DB updates multiple-region database account CNAME to point to new region. If application can't handle traffic rerouting after failover, it should use multiple-region database account DNS CNAME.
Note
Azure Cosmos DB does not route traffic based on geographic proximity of the caller. It is up to each application to select the right region according to unique application needs.
Portal endpoint discovery
The easiest way to get the list of regions for Azure Cosmos DB Graph account is overview blade in Azure portal. It will work for applications that do not change regions often, or have a way to update the list via application configuration.
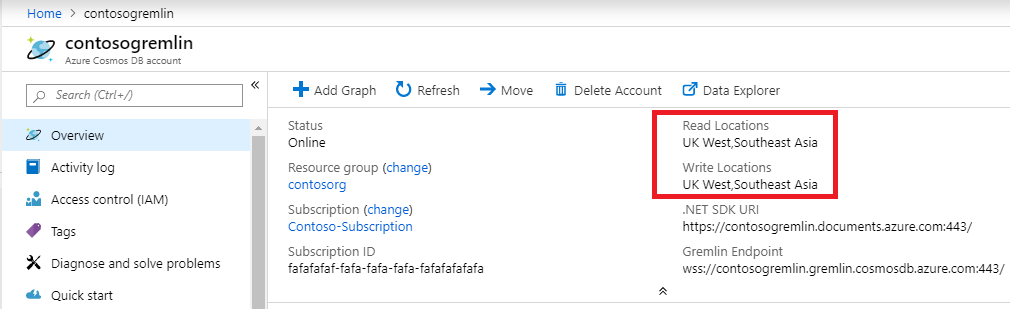
Example below demonstrates general principles of accessing regional Gremlin endpoint. Application should consider number of regions to send the traffic to and number of corresponding Gremlin clients to instantiate.
// Example value: China East, China North and China East 2 . This can be found in the overview blade of you Azure Cosmos DB Gremlin Account.
// Look for Write Locations in the overview blade. You can click to copy and paste.
string[] gremlinAccountRegions = new string[] {"China East", "China North" ,"China East 2"};
string gremlinAccountName = "PUT-COSMOSDB-ACCOUNT-NAME-HERE";
string gremlinAccountKey = "PUT-ACCOUNT-KEY-HERE";
string databaseName = "PUT-DATABASE-NAME-HERE";
string graphName = "PUT-GRAPH-NAME-HERE";
foreach (string gremlinAccountRegion in gremlinAccountRegions)
{
// Convert preferred read location to the form "[acountname]-[region].gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn".
string regionalGremlinEndPoint = $"{gremlinAccountName}-{gremlinAccountRegion.ToLowerInvariant().Replace(" ", string.Empty)}.gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn";
GremlinServer regionalGremlinServer = new GremlinServer(
hostname: regionalGremlinEndPoint,
port: 443,
enableSsl: true,
username: "/dbs/" + databaseName + "/colls/" + graphName,
password: gremlinAccountKey);
GremlinClient regionalGremlinClient = new GremlinClient(
gremlinServer: regionalGremlinServer,
graphSONReader: new GraphSON2Reader(),
graphSONWriter: new GraphSON2Writer(),
mimeType: GremlinClient.GraphSON2MimeType);
}
SDK endpoint discovery
Application can use Azure Cosmos DB SDK to discover read and write locations for Graph account. These locations can change at any time through manual reconfiguration on the server side or service-managed failover.
TinkerPop Gremlin SDK doesn't have an API to discover Azure Cosmos DB Graph database account regions. Applications that need runtime endpoint discovery need to host 2 separate SDKs in the process space.
// Depending on the version and the language of the SDK (.NET vs Java vs Python)
// the API to get readLocations and writeLocations may vary.
IDocumentClient documentClient = new DocumentClient(
new Uri(cosmosUrl),
cosmosPrimaryKey,
connectionPolicy,
consistencyLevel);
DatabaseAccount databaseAccount = await cosmosClient.GetDatabaseAccountAsync();
IEnumerable<DatabaseAccountLocation> writeLocations = databaseAccount.WritableLocations;
IEnumerable<DatabaseAccountLocation> readLocations = databaseAccount.ReadableLocations;
// Pick write or read locations to construct regional endpoints for.
foreach (string location in readLocations)
{
// Convert preferred read location to the form "[acountname]-[region].gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn".
string regionalGremlinEndPoint = location
.Replace("http:\/\/", string.Empty)
.Replace("documents.azure.cn:443/", "gremlin.cosmos.azure.cn");
// Use code from the previous sample to instantiate Gremlin client.
}