Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
Kafka Connect for Azure Cosmos DB is a connector to read from and write data to Azure Cosmos DB. The Azure Cosmos DB sink connector allows you to export data from Apache Kafka topics to an Azure Cosmos DB database. The connector polls data from Kafka to write to containers in the database based on the topics subscription.
Prerequisites
- Start with the Confluent platform setup because it gives you a complete environment to work with. If you don't wish to use Confluent Platform, then you need to install and configure Zookeeper, Apache Kafka, Kafka Connect, yourself. You also need to install and configure the Azure Cosmos DB connectors manually.
- Create an Azure Cosmos DB account, container setup guide
- Bash shell
- Download Java 11+
- Download Maven
Install sink connector
If you're using the recommended Confluent platform setup, the Azure Cosmos DB Sink Connector is included in the installation, and you can skip this step.
Otherwise, you can download the JAR file from the latest Release or package this repo to create a new JAR file. To install the connector manually using the JAR file, refer to these instructions. You can also package a new JAR file from the source code.
# clone the azure-sdk-for-java repo if you haven't done so already
git clone https://github.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-java.git
cd sdk/cosmos
mvn -e -DskipTests -Dgpg.skip -Dmaven.javadoc.skip=true -Dcodesnippet.skip=true -Dspotbugs.skip=true -Dcheckstyle.skip=true -Drevapi.skip=true -pl ,azure-cosmos,azure-cosmos-tests -am clean install
mvn -e -DskipTests -Dgpg.skip -Dmaven.javadoc.skip=true -Dcodesnippet.skip=true -Dspotbugs.skip=true -Dcheckstyle.skip=true -Drevapi.skip=true -pl ,azure-cosmos-kafka-connect clean install
# include the following JAR file in Kafka Connect installation
ls target/azure-cosmos-kafka-connect-*.jar
Create a Kafka topic and write data
If you're using the Confluent Platform, the easiest way to create a Kafka topic is by using the supplied Control Center UX. Otherwise, you can create a Kafka topic manually using the following syntax:
./kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper <ZOOKEEPER_URL:PORT> --replication-factor <NO_OF_REPLICATIONS> --partitions <NO_OF_PARTITIONS> --topic <TOPIC_NAME>
For this scenario, we create a Kafka topic named "hotels" and write nonschema embedded JSON data to the topic. To create a topic inside Control Center, see the Confluent guide.
Next, start the Kafka console producer to write a few records to the "hotels" topic.
# Option 1: If using Codespaces, use the built-in CLI utility
kafka-console-producer --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic hotels
# Option 2: Using this repo's Confluent Platform setup, first exec into the broker container
docker exec -it broker /bin/bash
kafka-console-producer --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic hotels
# Option 3: Using your Confluent Platform setup and CLI install
<path-to-confluent>/bin/kafka-console-producer --broker-list <kafka broker hostname> --topic hotels
In the console producer, enter:
{"id": "h1", "HotelName": "Marriott", "Description": "Marriott description"}
{"id": "h2", "HotelName": "HolidayInn", "Description": "HolidayInn description"}
{"id": "h3", "HotelName": "Motel8", "Description": "Motel8 description"}
The three records entered are published to the "hotels" Kafka topic in JSON format.
Create the sink connector
Create an Azure Cosmos DB sink connector in Kafka Connect. The following JSON body defines config for the sink connector. Make sure to replace the values for azure.cosmos.account.endpoint and azure.cosmos.account.key, properties that you saved from the Azure Cosmos DB setup guide in the prerequisites.
For more information on each of these configuration properties, see sink properties.
{
"name": "cosmosdb-sink-connector-v2",
"config": {
"connector.class": "com.azure.cosmos.kafka.connect.CosmosSinkConnector",
"tasks.max": "5",
"topics": "{topic}",
"value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"value.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"key.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"key.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"azure.cosmos.account.endpoint":"{endpoint}",
"azure.cosmos.account.key":"{masterKey}",
"azure.cosmos.applicationName": "{applicationName}",
"azure.cosmos.sink.database.name":"{databaseName}",
"azure.cosmos.sink.containers.topicMap":"{topic}#{container}"
}
}
Once you have all the values filled out, save the JSON file somewhere locally. You can use this file to create the connector using the REST API.
Create connector using Control Center
An easy option to create the connector is by going through the Control Center webpage. Follow this installation guide to create a connector from Control Center. Instead of using the DatagenConnector option, use the CosmosSinkConnector tile instead. When configuring the sink connector, fill out the values as filled in the JSON file.
Alternatively, in the connectors page, you can upload the JSON file created earlier by using the Upload connector config file option.
Create connector using REST API
Create the sink connector using the Kafka Connect REST API:
# Curl to Kafka connect service
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d @<path-to-JSON-config-file> http://localhost:8083/connectors
Confirm data written to Azure Cosmos DB
Sign into the Azure portal and navigate to your Azure Cosmos DB account. Check that the three records from the "hotels" topic are created in your account.
Cleanup
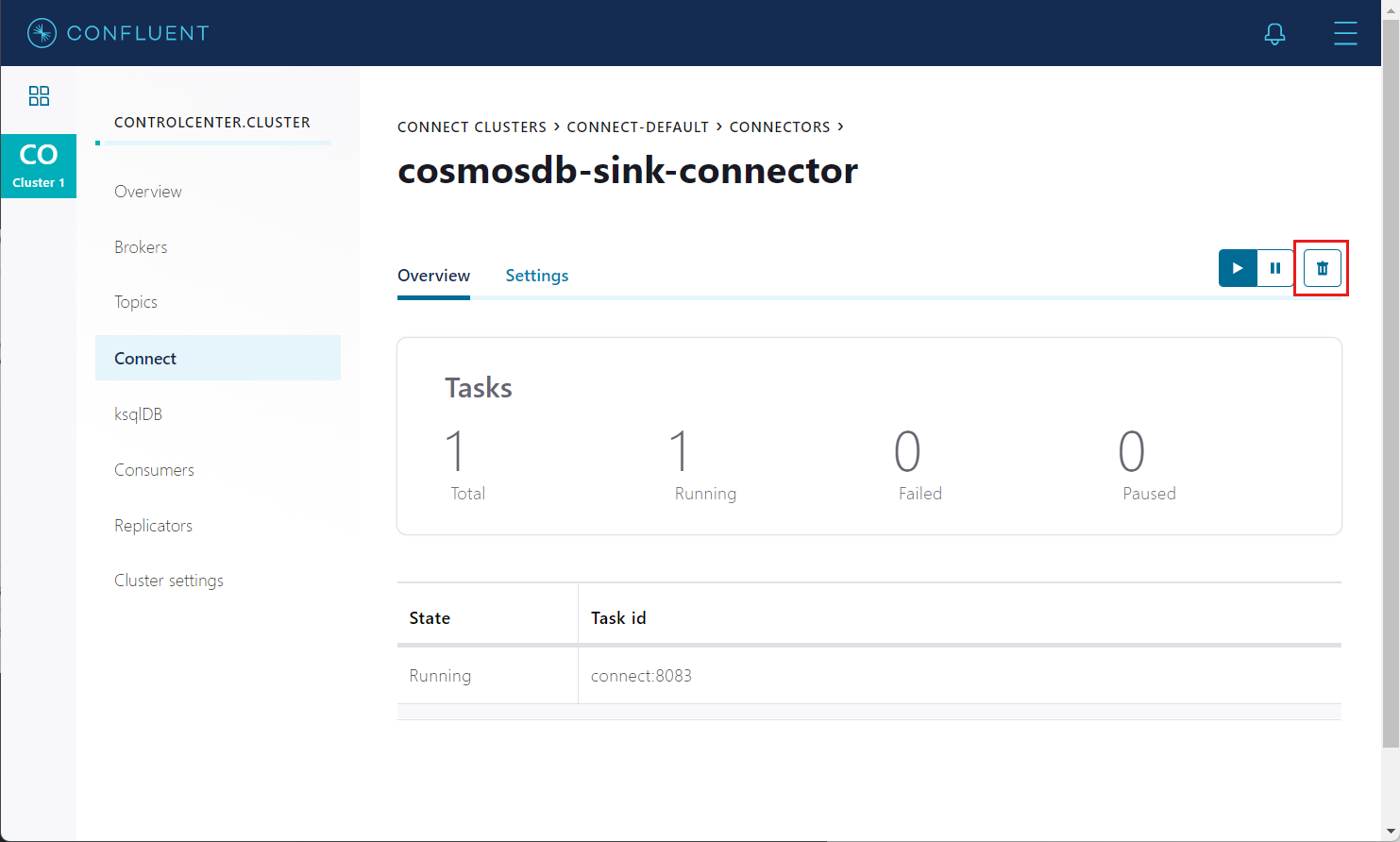
To delete the connector from the Control Center, navigate to the sink connector you created and select the Deletion icon.
Alternatively, use the Kafka Connect REST API to delete:
# Curl to Kafka connect service
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8083/connectors/cosmosdb-sink-connector
To delete the created Azure Cosmos DB service and its resource group using Azure CLI, refer to these steps.
Sink configuration properties
The following settings are used to configure an Azure Cosmos DB Kafka sink connector. These configuration values determine the Kafka topics to be consumed, which Azure Cosmos DB container is written into, and the formats to serialize the data. For an example configuration file with the default values, refer to this config.
| Config Property Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
connector.class |
None | Class name of the Azure Cosmos DB source. It should be set to com.azure.cosmos.kafka.connect.CosmosSinkConnector |
azure.cosmos.account.endpoint |
None | Cosmos DB Account Endpoint Uri |
azure.cosmos.account.environment |
Azure |
The Azure environment of the Cosmos DB account: AzureChina. |
azure.cosmos.account.tenantId |
"" |
The tenantId of the Cosmos DB account. Required for ServicePrincipal authentication. |
azure.cosmos.auth.type |
MasterKey |
There are two auth types are supported currently: MasterKey(PrimaryReadWriteKeys, SecondReadWriteKeys, PrimaryReadOnlyKeys, SecondReadWriteKeys), ServicePrincipal |
azure.cosmos.account.key |
"" |
Cosmos DB Account Key (only required if auth.type is MasterKey) |
azure.cosmos.auth.aad.clientId |
"" |
The clientId/ApplicationId of the service principal. Required for ServicePrincipal authentication. |
azure.cosmos.auth.aad.clientSecret |
"" |
The client secret/password of the service principal. |
azure.cosmos.mode.gateway |
false |
Flag to indicate whether to use gateway mode. By default it's false, means SDK uses direct mode. |
azure.cosmos.preferredRegionList |
[] |
Preferred regions list to be used for a multi region Cosmos DB account. This is a comma separated value provided preferred regions to be used as hint. You should use a collocated kafka cluster with your Cosmos DB account and pass the kafka cluster region as preferred region. |
azure.cosmos.application.name |
"" |
Application name. It is added as the userAgent suffix. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.enabled |
false |
A flag to indicate whether throughput control is enabled. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.account.endpoint |
"" |
Cosmos DB Throughput Control Account Endpoint Uri. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.account.environment |
Azure |
The Azure environment of the Cosmos DB account: AzureChina. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.account.tenantId |
"" |
The tenantId of the Cosmos DB account. Required for ServicePrincipal authentication. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.auth.type |
MasterKey |
There are two auth types are supported currently: MasterKey(PrimaryReadWriteKeys, SecondReadWriteKeys, PrimaryReadOnlyKeys, SecondReadWriteKeys), ServicePrincipal |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.account.key |
"" |
Cosmos DB Throughput Control Account Key (only required if throughputControl.auth.type is MasterKey). |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.auth.aad.clientId |
"" |
The clientId/ApplicationId of the service principal. Required for ServicePrincipal authentication. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.auth.aad.clientSecret |
"" |
The client secret/password of the service principal. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.preferredRegionList |
[] |
Preferred regions list to be used for a multi region Cosmos DB account. This is a comma separated value which provides preferred regions to be used as hint. You should use a collocated kafka cluster with your Cosmos DB account and pass the kafka cluster region as preferred region. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.mode.gateway |
false |
Flag to indicate whether to use gateway mode. By default it's false, means SDK uses direct mode. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.group.name |
"" |
Throughput control group name. Since customer is allowed to create many groups for a container, the name should be unique. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.targetThroughput |
-1 |
Throughput control group target throughput. The value should be larger than 0. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.targetThroughputThreshold |
-1 |
Throughput control group target throughput threshold. The value should be between (0,1]. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.priorityLevel |
None |
Throughput control group priority level. The value can be None, High, or Low. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.globalControl.database.name |
"" |
Database to be used for throughput global control. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.globalControl.container.name |
"" |
Container to be used for throughput global control. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.globalControl.renewIntervalInMS |
-1 |
This controls how often the client is going to update the throughput usage of itself and adjust its own throughput share based on the throughput usage of other clients. Default is 5 s, the allowed min value is 5 s. |
azure.cosmos.throughputControl.globalControl.expireIntervalInMS |
-1 |
This controls how quickly we detect the client has been offline and hence allow its throughput share to be taken by other clients. Default is 11 s, the allowed min value is 2 * renewIntervalInMS + 1. |
azure.cosmos.sink.database.name |
"" |
Cosmos DB database name. |
azure.cosmos.sink.containers.topicMap |
"" |
A comma delimited list of Kafka topics mapped to Cosmos containers. For example: topic1#con1, topic2#con2. |
azure.cosmos.sink.errors.tolerance.level |
None |
Error tolerance level after exhausting all retries. None for fail on error. All for log and continue |
azure.cosmos.sink.bulk.enabled |
true |
Flag to indicate whether Cosmos DB bulk mode is enabled for Sink connector. By default it's true. |
azure.cosmos.sink.bulk.maxConcurrentCosmosPartitions |
-1 |
Cosmos DB Max Concurrent Cosmos Partitions. If not specified it is determined based on the number of the container's physical partitions which would indicate every batch is expected to have data from all Cosmos physical partitions. If specified it indicates the number of Cosmos DB Physical Partitions for each batch data. So this config can be used to make bulk processing more efficient when input data in each batch is repartitioned to balance to how many Cosmos partitions each batch needs to write. This is useful for large containers (with hundreds of physical partitions. |
azure.cosmos.sink.bulk.initialBatchSize |
1 |
Cosmos DB initial bulk micro batch size - a micro batch to be flushed to the backend when the number of documents enqueued exceeds this size - or the target payload size is met. The micro batch size is getting automatically tuned based on the throttling rate. By default the initial micro batch size is 1. Reduce this when you want to avoid that the first few requests consume too many RUs. |
azure.cosmos.sink.write.strategy |
ItemOverwrite |
Cosmos DB writes Strategy: ItemOverwrite (using upsert), ItemAppend (using create, ignore preexisting items that are, Conflicts), ItemDelete (deletes based on id/pk of data frame), ItemDeleteIfNotModified (deletes based on id/pk of data frame if etag hasn't changed since collecting id/pk), ItemOverwriteIfNotModified (using create if etag is empty, update/replace with etag precondition otherwise, if document was updated the pre-condition failure is ignored), ItemPatch (Partial update all documents based on the patch config) |
azure.cosmos.sink.maxRetryCount |
10 |
Cosmos DB max retry attempts on write failures for Sink connector. By default, the connector retries on transient write errors for up to 10 times. |
azure.cosmos.sink.id.strategy |
ProvidedInValueStrategy |
A strategy used to populate the document with an id. Valid strategies are: TemplateStrategy, FullKeyStrategy, KafkaMetadataStrategy, ProvidedInKeyStrategy, ProvidedInValueStrategy. Configuration properties prefixed withid.strategy are passed through to the strategy. For example, when using id.strategy=TemplateStrategy , the property id.strategy.template is passed through to the template strategy and used to specify the template string to be used in constructing the id. |
azure.cosmos.sink.write.patch.operationType.default |
Set |
Default Cosmos DB patch operation type. Supported ones include none, add, set, replace, remove, increment. Choose none for no-op. |
azure.cosmos.sink.write.patch.property.configs |
"" |
Cosmos DB patch json property configs. It can contain multiple definitions matching the following patterns separated by comma. property(jsonProperty).op(operationType) or property(jsonProperty).path(patchInCosmosdb).op(operationType) - The difference of the second pattern is that it also allows you to define a different Cosmos DB path. Note: It doesn't support nested json property config. |
azure.cosmos.sink.write.patch.filter |
"" |
Used for Conditional patch |
Data is written to the Azure Cosmos DB as JSON without any schema.
Supported data types
The Azure Cosmos DB Kafka Sink Connector converts sink record into JSON document supporting the following schema types:
| Schema type | JSON data type |
|---|---|
| Array | Array |
| Boolean | Boolean |
| Float32 | Number |
| Float64 | Number |
| Int8 | Number |
| Int16 | Number |
| Int32 | Number |
| Int64 | Number |
| Map | Object (JSON) |
| String | String Null |
| Struct | Object (JSON) |
The sink Connector also supports the following AVRO logical types:
| Schema Type | JSON Data Type |
|---|---|
| Date | Number |
| Time | Number |
| Timestamp | Number |
Note
Byte deserialization is currently not supported by the Azure Cosmos DB Sink Connector.
Single Message Transforms(SMT)
Along with the sink connector settings, you can specify the use of Single Message Transformations (SMTs) to modify messages flowing through the Kafka Connect platform. For more information, see Confluent SMT Documentation.
Using the InsertUUID SMT
You can use InsertUUID SMT to automatically add item IDs. With the custom InsertUUID SMT, you can insert the id field with a random UUID value for each message, before it's written to Azure Cosmos DB.
Warning
Use this SMT only if the messages don’t contain the id field. Otherwise, the id values will be overwritten and you may end up with duplicate items in your database. Using UUIDs as the message ID can be quick and easy but are not an ideal partition key to use in Azure Cosmos DB.
Install the SMT
Before you can use the InsertUUID SMT, you need to install this transform in your Confluent Platform setup. If you're using the Confluent Platform setup from this repo, the transform is already included in the installation, and you can skip this step.
Alternatively, you can package the InsertUUID source to create a new JAR file. To install the connector manually using the JAR file, refer to these instructions.
# clone the kafka-connect-insert-uuid repo
https://github.com/confluentinc/kafka-connect-insert-uuid.git
cd kafka-connect-insert-uuid
# package the source code into a JAR file
mvn clean package
# include the following JAR file in Confluent Platform installation
ls target/*.jar
Configure the SMT
Inside your sink connector config, add the following properties to set the id.
"transforms": "insertID",
"transforms.insertID.type": "com.github.cjmatta.kafka.connect.smt.InsertUuid$Value",
"transforms.insertID.uuid.field.name": "id"
For more information on using this SMT, see the InsertUUID repository.
Using SMTs to configure Time to live (TTL)
Using both the InsertField and Cast SMTs, you can configure TTL on each item created in Azure Cosmos DB. Enable TTL on the container before enabling TTL at an item level. For more information, see the time-to-live doc.
Inside your Sink connector config, add the following properties to set the TTL in seconds. In this following example, the TTL is set to 100 seconds. If the message already contains the TTL field, these SMTs will overwrite the TTL value.
"transforms": "insertTTL,castTTLInt",
"transforms.insertTTL.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.InsertField$Value",
"transforms.insertTTL.static.field": "ttl",
"transforms.insertTTL.static.value": "100",
"transforms.castTTLInt.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.Cast$Value",
"transforms.castTTLInt.spec": "ttl:int32"
For more information on using these SMTs, see the InsertField and Cast documentation.
Troubleshooting common issues
Here are solutions to some common problems that you may encounter when working with the Kafka sink connector.
Read non-JSON data with JsonConverter
If you have non-JSON data on your source topic in Kafka and attempt to read it using the JsonConverter, you see the following exception:
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.DataException: Converting byte[] to Kafka Connect data failed due to serialization error:
…
org.apache.kafka.common.errors.SerializationException: java.io.CharConversionException: Invalid UTF-32 character 0x1cfa7e2 (above 0x0010ffff) at char #1, byte #7)
The source topic being serialized in either Avro or another format such as CSV string can cause this error.
Solution: If the topic data is in AVRO format, then change your Kafka Connect Sink Connector to use the AvroConverter as shown below.
"value.converter": "io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"value.converter.schema.registry.url": "http://schema-registry:8081",
Read non avro data with AvroConverter
This scenario is applicable when you try to use the Avro converter to read data from a topic that isn't in Avro format. Which, includes data written by an Avro serializer other than the Confluent Schema Registry’s Avro serializer, which has its own wire format.
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.DataException: my-topic-name
at io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter.toConnectData(AvroConverter.java:97)
…
org.apache.kafka.common.errors.SerializationException: Error deserializing Avro message for id -1
org.apache.kafka.common.errors.SerializationException: Unknown magic byte!
Solution: Check the source topic’s serialization format. Then, either switch the connector to use the right converter or switch the upstream format to Avro.
Read a JSON message without the expected schema/payload structure
Kafka Connect supports a special structure of JSON messages containing both payload and schema as follows.
{
"schema": {
"type": "struct",
"fields": [
{
"type": "int32",
"optional": false,
"field": "userid"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "name"
}
]
},
"payload": {
"userid": 123,
"name": "Sam"
}
}
If you try to read JSON data that doesn't contain the data in this structure, you get the following error:
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.DataException: JsonConverter with schemas.enable requires "schema" and "payload" fields and may not contain additional fields. If you are trying to deserialize plain JSON data, set schemas.enable=false in your converter configuration.
To be clear, the only JSON structure that is valid for schemas.enable=true has schema and payload fields as the top-level elements as shown above. As the error message states, if you just have plain JSON data, you should change your connector’s configuration to:
"value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"value.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
Limitations
- Autocreation of databases and containers in Azure Cosmos DB aren't supported. The database and containers must already exist, and they must be configured correctly.
Next steps
You can learn more about bulk operations in V4 Java SDK with the following docs:
- Perform bulk operations on Azure Cosmos DB data
- Kafka Connect for Azure Cosmos DB source connector