Public access in Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL
APPLIES TO:
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL (powered by the Citus database
extension to PostgreSQL)
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL supports three networking options:
- No access
- This is the default for a newly created cluster if public or private access is not enabled. No computers, whether inside or outside of Azure, can connect to the database nodes.
- Public access
- A public IP address is assigned to the coordinator node.
- Access to the coordinator node is protected by firewall.
- Optionally, access to all worker nodes can be enabled. In this case, public IP addresses are assigned to the worker nodes and are secured by the same firewall.
- Private access
- Only private IP addresses are assigned to the cluster’s nodes.
- Each node requires a private endpoint to allow hosts in the selected virtual network to access the nodes.
- Security features of Azure virtual networks such as network security groups can be used for access control.
When you create a cluster, you may enable public or private access, or opt for the default of no access. Once the cluster is created, you can choose to switch between public or private access, or activate them both at once.
This page describes the public access option. For private access, see Private access in Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL.
Firewall overview
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL server firewall prevents all access to your coordinator node until you specify which computers have permission. The firewall grants access to the server based on the originating IP address of each request. To configure your firewall, you create firewall rules that specify ranges of acceptable IP addresses. You can create firewall rules at the server level.
Firewall rules: These rules enable clients to access your coordinator node, that is, all the databases within the same logical server. Server-level firewall rules can be configured by using the Azure portal. To create server-level firewall rules, you must be the subscription owner or a subscription contributor.
All database access to your coordinator node is blocked by the firewall by default. To begin using your server from another computer, you need to specify one or more server-level firewall rules to enable access to your server. Use the firewall rules to specify which IP address ranges from the Internet to allow. Access to the Azure portal website itself isn't affected by the firewall rules. Connection attempts from the internet and Azure must first pass through the firewall before they can reach your PostgreSQL database, as shown in the following diagram:
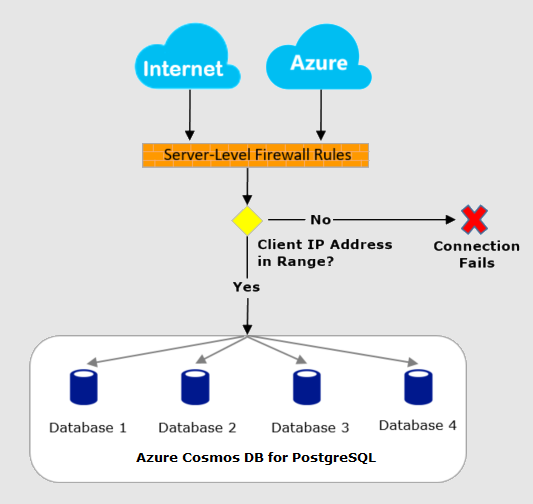
Connect from the internet and from Azure
A cluster firewall controls who can connect to the group's coordinator node. The firewall determines access by consulting a configurable list of rules. Each rule is an IP address, or range of addresses, that are allowed in.
When the firewall blocks connections, it can cause application errors. Using the PostgreSQL JDBC driver, for instance, raises an error like this:
java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: FATAL: no pg\_hba.conf entry for host "123.45.67.890", user "citus", database "citus", SSL
See Create and manage firewall rules to learn how the rules are defined.
Troubleshoot the database server firewall
When access to the Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL service doesn't behave as you expect, consider these points:
Changes to the allow list haven't taken effect yet: There may be as much as a five-minute delay for changes to the Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL firewall configuration to take effect.
The user isn't authorized or an incorrect password was used: If a user doesn't have permissions on the server or the password used is incorrect, the connection to the server is denied. Creating a firewall setting only provides clients with an opportunity to attempt connecting to your server. Each client must still provide the necessary security credentials.
For example, using a JDBC client, the following error may appear.
java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "yourusername"Dynamic IP address: If you have an Internet connection with dynamic IP addressing and you're having trouble getting through the firewall, you could try one of the following solutions:
Ask your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for the IP address range assigned to your client computers that access the coordinator node, and then add the IP address range as a firewall rule.
Get static IP addressing instead for your client computers, and then add the static IP address as a firewall rule.
Next steps
For articles on creating server-level and database-level firewall rules, see: