Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Mapping data flows in Azure Data Factory and Synapse pipelines support the use of parameters. Define parameters inside of your data flow definition and use them throughout your expressions. The parameter values are set by the calling pipeline via the Execute Data Flow activity. You have three options for setting the values in the data flow activity expressions:
- Use the pipeline control flow expression language to set a dynamic value
- Use the data flow expression language to set a dynamic value
- Use either expression language to set a static literal value
Use this capability to make your data flows general-purpose, flexible, and reusable. You can parameterize data flow settings and expressions with these parameters.
Create parameters in a mapping data flow
To add parameters to your data flow, click on the blank portion of the data flow canvas to see the general properties. In the settings pane, you'll see a tab called Parameter. Select New to generate a new parameter. For each parameter, you must assign a name, select a type, and optionally set a default value.
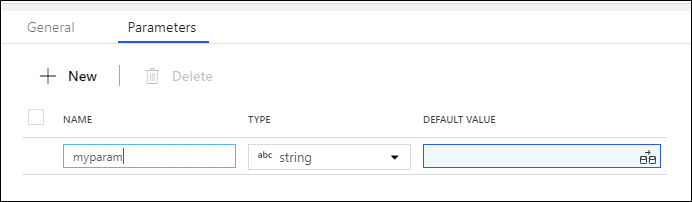
Use parameters in a mapping data flow
Parameters can be referenced in any data flow expression. Parameters begin with $ and are immutable. you'll find the list of available parameters inside of the Expression Builder under the Parameters tab.
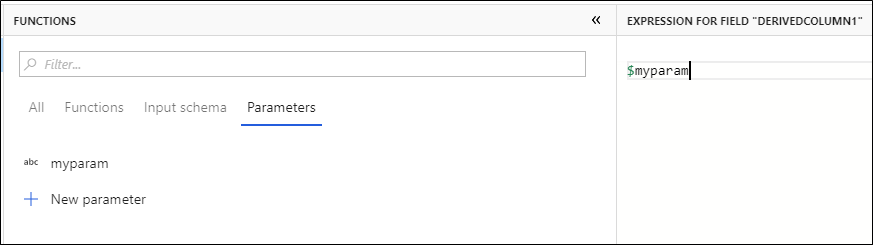
You can quickly add additional parameters by selecting New parameter and specifying the name and type.
Using parameterized linked services in a mapping data flow
Parameterized linked services can be used in a mapping data flow (for either dataset or inline source types).
For the inline source type, the linked service parameters are exposed in the data flow activity settings within the pipeline as shown below.
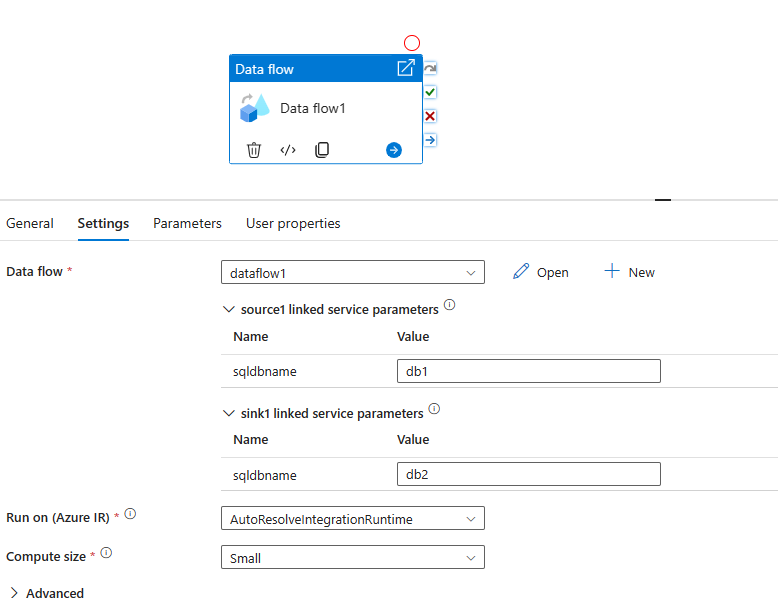
For the dataset source type, the linked service parameters are exposed directly in the dataset configuration.
Assign parameter values from a pipeline
Once you've created a data flow with parameters, you can execute it from a pipeline with the Execute Data Flow Activity. After you add the activity to your pipeline canvas, you'll be presented with the available data flow parameters in the activity's Parameters tab.
When assigning parameter values, you can use either the pipeline expression language or the data flow expression language based on spark types. Each mapping data flow can have any combination of pipeline and data flow expression parameters.
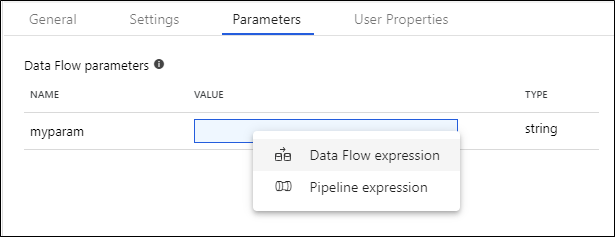
Pipeline expression parameters
Pipeline expression parameters allow you to reference system variables, functions, pipeline parameters, and variables similar to other pipeline activities. When you click Pipeline expression, a side-nav will open allowing you to enter an expression using the expression builder.
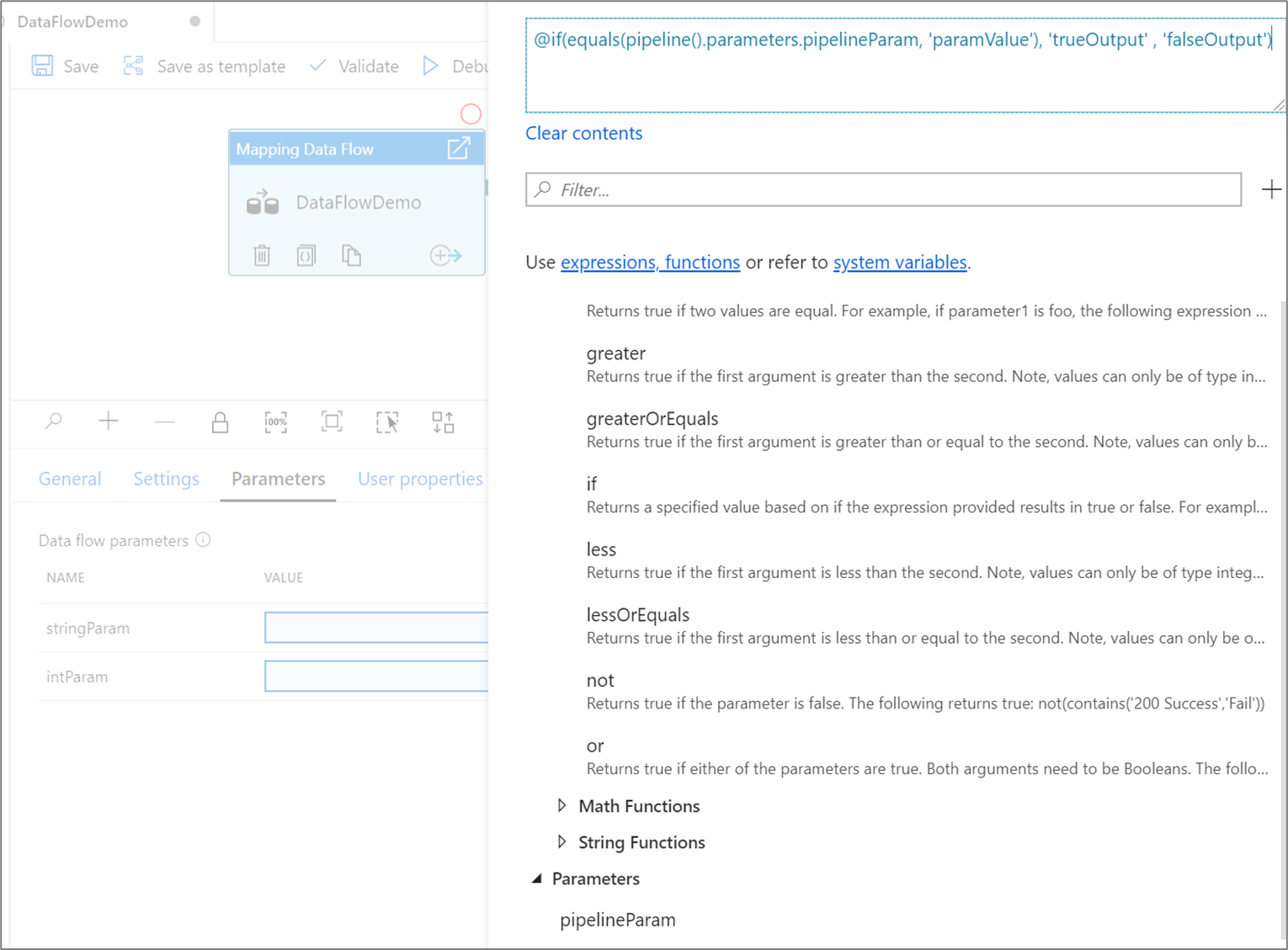
When referenced, pipeline parameters are evaluated and then their value is used in the data flow expression language. The pipeline expression type doesn't need to match the data flow parameter type.
String literals vs expressions
When assigning a pipeline expression parameter of type string, by default quotes will be added and the value will be evaluated as a literal. To read the parameter value as a data flow expression, check the expression box next to the parameter.
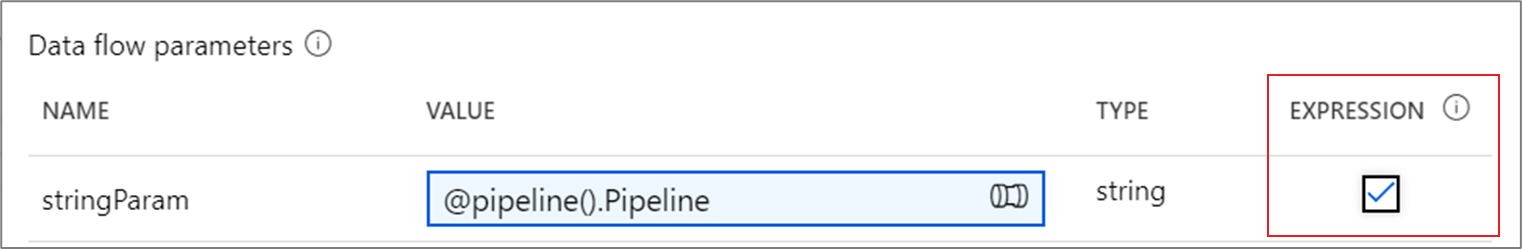
If data flow parameter stringParam references a pipeline parameter with value upper(column1).
- If expression is checked,
$stringParamevaluates to the value of column1 all uppercase. - If expression isn't checked (default behavior),
$stringParamevaluates to'upper(column1)'
Passing in timestamps
In the pipeline expression language, System variables such as pipeline().TriggerTime and functions like utcNow() return timestamps as strings in format 'yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSSSSZ'. To convert these into data flow parameters of type timestamp, use string interpolation to include the desired timestamp in a toTimestamp() function. For example, to convert the pipeline trigger time into a data flow parameter, you can use toTimestamp(left('@{pipeline().TriggerTime}', 23), 'yyyy-MM-dd\'T\'HH:mm:ss.SSS').
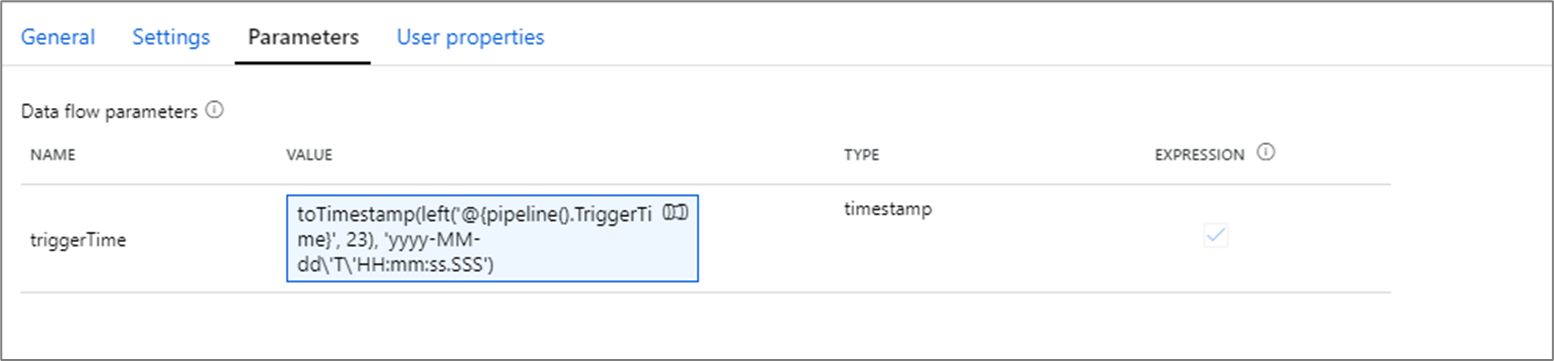
Note
Data Flows can only support up to 3 millisecond digits. The left() function is used trim off additional digits.
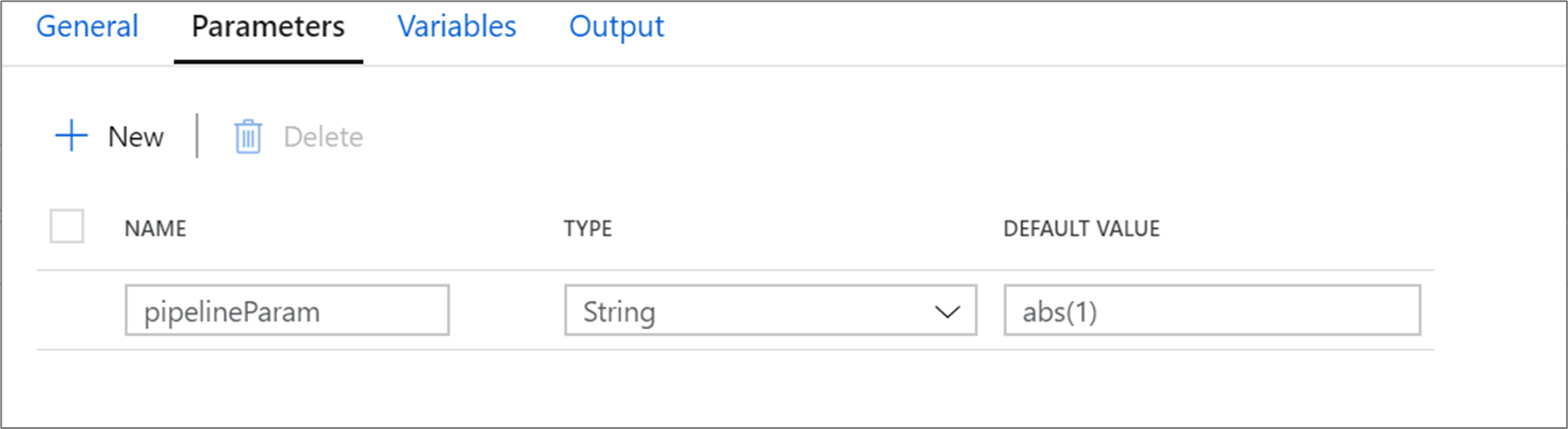
Pipeline parameter example
Say you have an integer parameter intParam that is referencing a pipeline parameter of type String, @pipeline.parameters.pipelineParam.
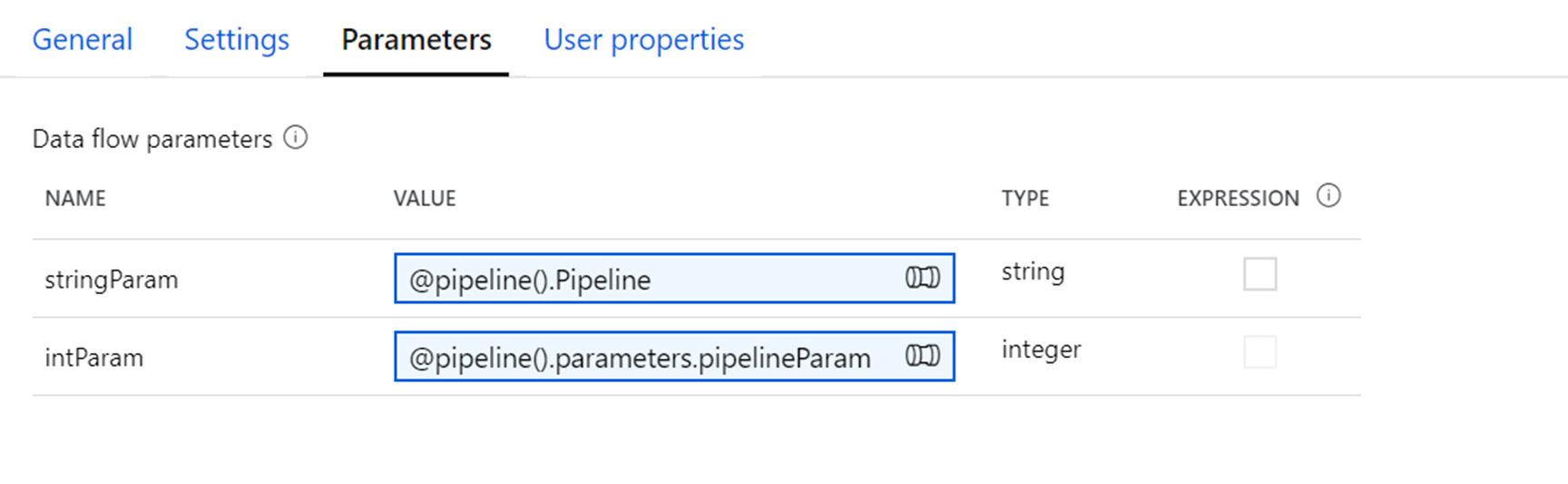
@pipeline.parameters.pipelineParam is assigned a value of abs(1) at runtime.
When $intParam is referenced in an expression such as a derived column, it will evaluate abs(1) return 1.

Data flow expression parameters
Select Data flow expression will open up the data flow expression builder. You'll be able to reference functions, other parameters and any defined schema column throughout your data flow. This expression will be evaluated as is when referenced.
Note
If you pass in an invalid expression or reference a schema column that doesn't exist in that transformation, the parameter will evaluate to null.
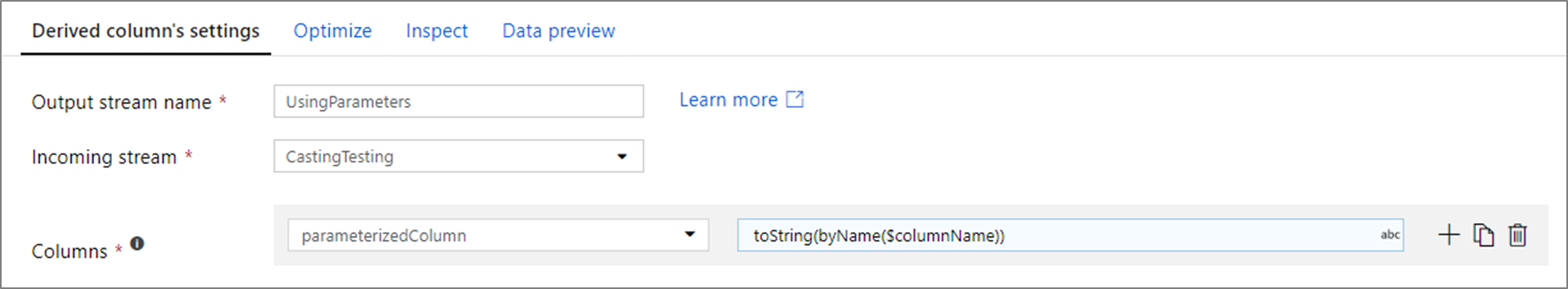
Passing in a column name as a parameter
A common pattern is to pass in a column name as a parameter value. If the column is defined in the data flow schema, you can reference it directly as a string expression. If the column isn't defined in the schema, use the byName() function. Remember to cast the column to its appropriate type with a casting function such as toString().
For example, if you wanted to map a string column based upon a parameter columnName, you can add a derived column transformation equal to toString(byName($columnName)).
Note
In data flow expressions, string interpolation (substituting variables inside of the string) isn't supported. Instead, concatenate the expression into string values. For example, 'string part 1' + $variable + 'string part 2'