Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Attention: All Microsoft Defender for Cloud features will be officially retired in Azure in China region on August 18, 2026 per the announcement posted by 21Vianet.
Microsoft Defender for Containers is the cloud-native solution for securing your containers. It helps protect your clusters whether they're running in:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Microsoft's managed service for developing, deploying, and managing containerized applications.
Other Kubernetes distributions (using Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes): Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) certified Kubernetes clusters hosted on-premises or on infrastructure as a service (IaaS). For more information, see Containers support matrix in Defender for Cloud.
You can first learn how to connect and help protect your containers in these articles:
- Protect your Azure containers with Defender for Containers
- Protect your on-premises Kubernetes clusters with Defender for Containers
Note
Defender for Containers support for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters is a preview feature. The preview feature is available on a self-service, opt-in basis.
Previews are provided as is and as available. They're excluded from the service-level agreements and the limited warranty.
To learn more about the supported operating systems, feature availability, outbound proxy, and more, see Containers support matrix in Defender for Cloud.
Network requirements
Validate that the following endpoints are configured for outbound access so that the Defender sensor can connect to Microsoft Defender for Cloud to send security data and events.
The Defender sensor must connect to the configured Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace. By default, AKS clusters have unrestricted outbound (egress) internet access. If event egress from the cluster requires the use of an Azure Monitor Private Link Scope (AMPLS), you must:
- Define the cluster with Container insights and a Log Analytics workspace.
- Define the cluster's Log Analytics workspace as a resource in the AMPLS.
- Create in the AMPLS a virtual network private endpoint between the virtual network of the cluster and the Log Analytics resource. The virtual network private endpoint integrates with a private DNS zone.
For instructions, refer to Create an Azure Monitor Private Link Scope.
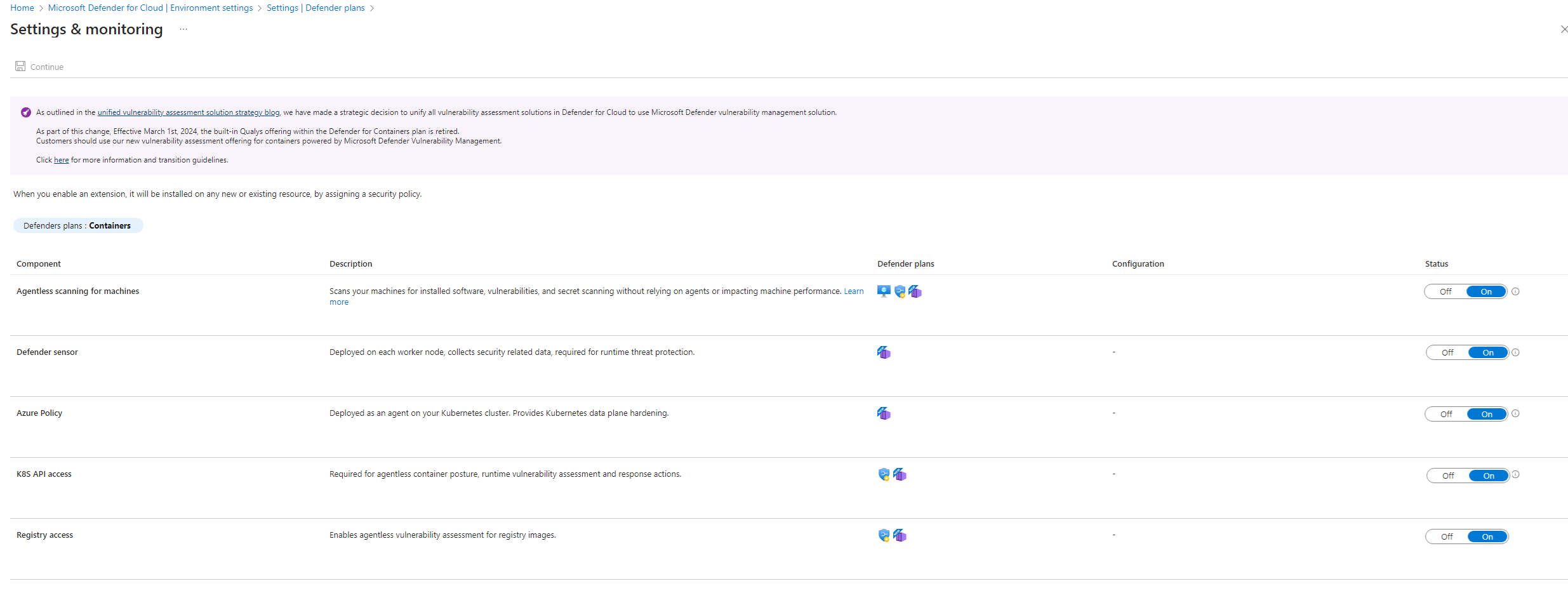
Enable the plan
In Defender for Cloud, select Environment Settings, and then select the relevant subscription.
On the Defender plans page, toggle the Containers plan to On and then select its Settings link.
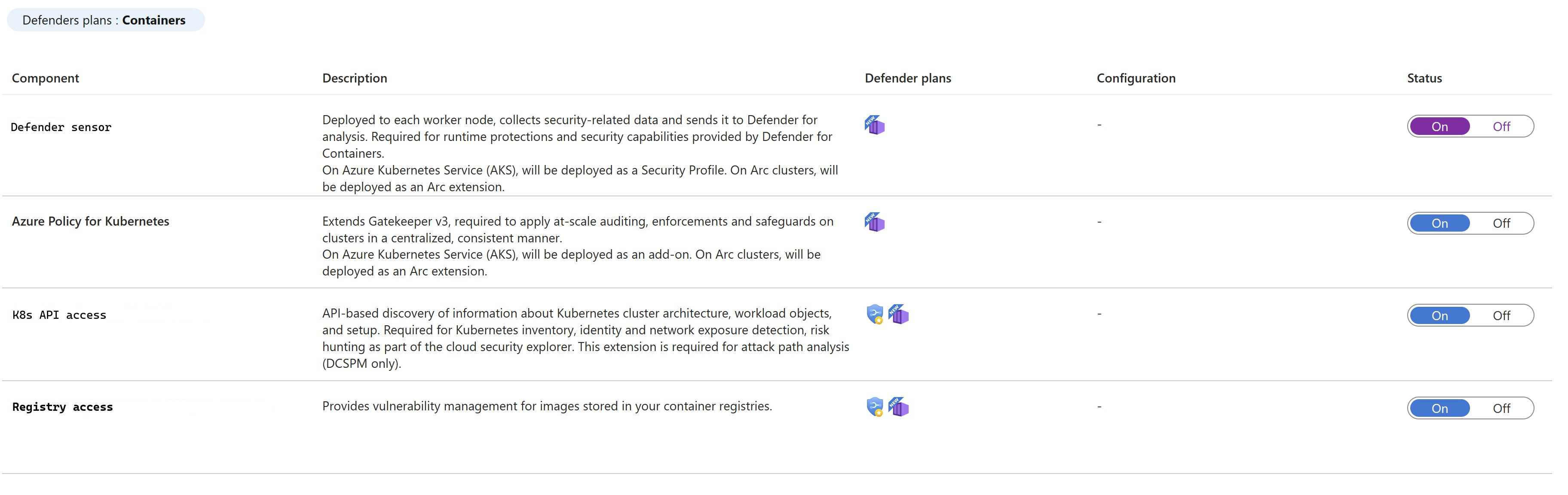
Turn on the relevant component.
Note
- Defender for Containers customers who joined before August 2023 and don't have K8S API access turned on as part of Defender cloud security posture management (CSPM) when they enabled the plan must manually enable the K8S API access toggle within the Defender for Containers plan.
- When you turn off Defender for Containers, the components are set to Off. They're not deployed to any more containers, but they're not removed from containers where they're already installed.
Enablement method per capability
By default, when you enable the plan through the Azure portal, Microsoft Defender for Containers is configured to automatically enable all capabilities and install all required components to provide the protections that the plan offers. This configuration includes the assignment of a default workspace.
If you don't want to enable all capabilities of the plans, you can manually select which specific capabilities to enable by selecting the Settings link for the Containers plan. Then, on the Settings & monitoring page, select the capabilities that you want to enable.
You can also modify this configuration from the Defender plans page after initial configuration of the plan.
For detailed information on the enablement method for each capability, see the support matrix.
Roles and permissions
Learn more about the roles for provisioning Defender for Containers extensions.
Assign a custom workspace for the Defender sensor
You can assign a custom workspace through Azure Policy.
Manual deployment of the Defender sensor or Azure policy agent without automatic provisioning by using recommendations
Capabilities that require sensor installation can also be deployed on one or more Kubernetes clusters. Use the appropriate recommendation:
| Sensor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Defender sensor for Kubernetes | Azure Kubernetes Service clusters should have Defender profile enabled |
| Defender sensor for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes | Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have the Defender extension installed |
| Azure Policy agent for Kubernetes | Azure Kubernetes Service clusters should have the Azure Policy Add-on for Kubernetes installed |
| Azure Policy agent for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes | Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have the Azure Policy extension installed |
To deploy the Defender sensor on specific clusters:
On the Microsoft Defender for Cloud Recommendations page, open the Enable enhanced security security control or search for one of the preceding recommendations. (You can also use the preceding links to open the recommendation directly.)
View all clusters without a sensor by opening the Unhealthy tab.
Select the clusters where you want to deploy the sensor, and then select Fix.
Select Fix X resources.
Deploy the Defender sensor: All options
You can enable the Defender for Containers plan and deploy all of the relevant components by using the Azure portal, the REST API, or an Azure Resource Manager template. For detailed steps, select the relevant tab.
After the Defender sensor is deployed, a default workspace is automatically assigned. You can assign a custom workspace in place of the default workspace through Azure Policy.
Note
The Defender sensor is deployed to each node to provide the runtime protections and collect signals from those nodes by using eBPF technology.
Use the Fix button from the Defender for Cloud recommendation
You can use Azure portal pages to enable the Defender for Cloud plan and set up automatic provisioning of all the necessary components for defending your Kubernetes clusters at scale. The process is streamlined.
A dedicated Defender for Cloud recommendation provides:
- Visibility into which of your clusters has the Defender sensor deployed.
- A Fix button to deploy the sensor to clusters that don't have it.
To deploy the sensor:
On the Microsoft Defender for Cloud Recommendations page, open the Enable enhanced security security control.
Use the filter to find the recommendation named Azure Kubernetes Service clusters should have Defender profile enabled.
Tip
Notice the Fix icon in the Actions column.
Select the clusters to see the details of the healthy and unhealthy resources (clusters with and without the sensor).
In the list of unhealthy resources, select a cluster. Then select Remediate to open the pane with the remediation confirmation.
Select Fix X resources.
Enable the plan
In Defender for Cloud, select Settings, and then select the relevant subscription.
On the Defender plans page, select Containers > Settings.
Turn on the relevant component.
Note
When you turn off Defender for Containers, the components are set to Off. They're not deployed to any more containers, but they're not removed from containers where they're already installed.
By default, when you enable the plan through the Azure portal, Microsoft Defender for Containers is configured to automatically install required components to provide the protections that the plan offers. This configuration includes the assignment of a default workspace.
If you want to disable automatic installation of components during the onboarding process, select Edit configuration for the Containers plan. The advanced options appear, and you can disable automatic installation for each component.
You can also modify this configuration from the Defender plans page.
Note
If you choose to disable the plan at any time after you enable it through the portal, you'll need to manually remove Defender for Containers components deployed on your clusters.
You can assign a custom workspace through Azure Policy.
If you disable the automatic installation of any component, you can easily deploy the component to one or more clusters by using the appropriate recommendation:
- Azure Policy add-on for Kubernetes: Azure Kubernetes Service clusters should have the Azure Policy add-on for Kubernetes installed
- Azure Kubernetes Service profile: Azure Kubernetes Service clusters should have Defender profile enabled
- Defender extension for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes: Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have the Defender extension installed
- Azure Policy extension for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes: Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have the Azure Policy extension installed
Learn more about the roles for provisioning Defender for Containers extensions.
Prerequisites
Before you deploy the sensor, ensure that you:
- Connect the Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc.
- Complete the prerequisites listed in the documentation for generic cluster extensions.
Deploy the Defender sensor
You can deploy the Defender sensor by using a range of methods. For detailed steps, select the relevant tab.
Use the Fix button from the Defender for Cloud recommendation
A dedicated Defender for Cloud recommendation provides:
- Visibility into which of your clusters has the Defender sensor deployed.
- A Fix button to deploy the sensor to clusters that don't have it.
To deploy the sensor:
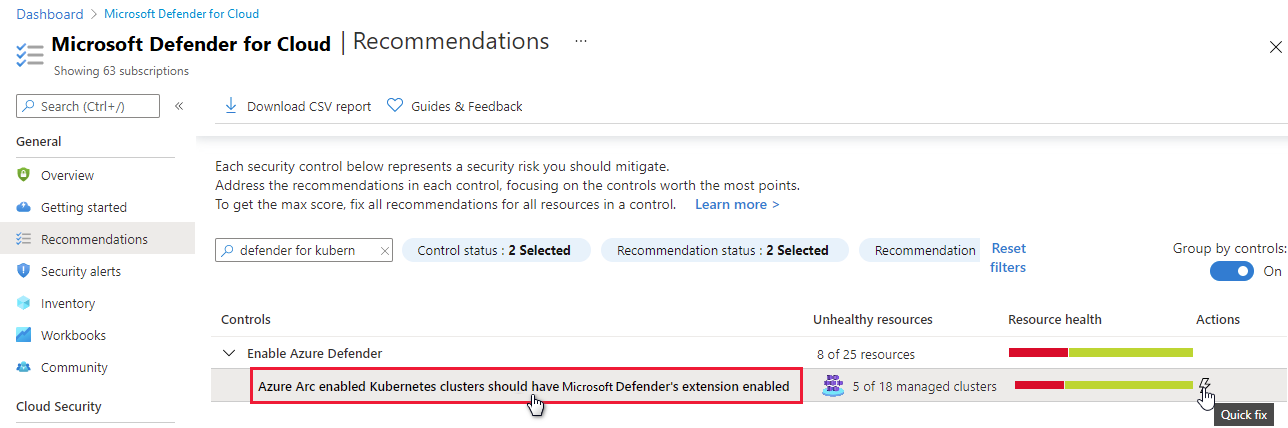
On the Microsoft Defender for Cloud Recommendations page, open the Enable enhanced security security control.
Use the filter to find the recommendation named Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have Microsoft Defender's extension enabled.
Tip
Notice the Fix icon in the Actions column.
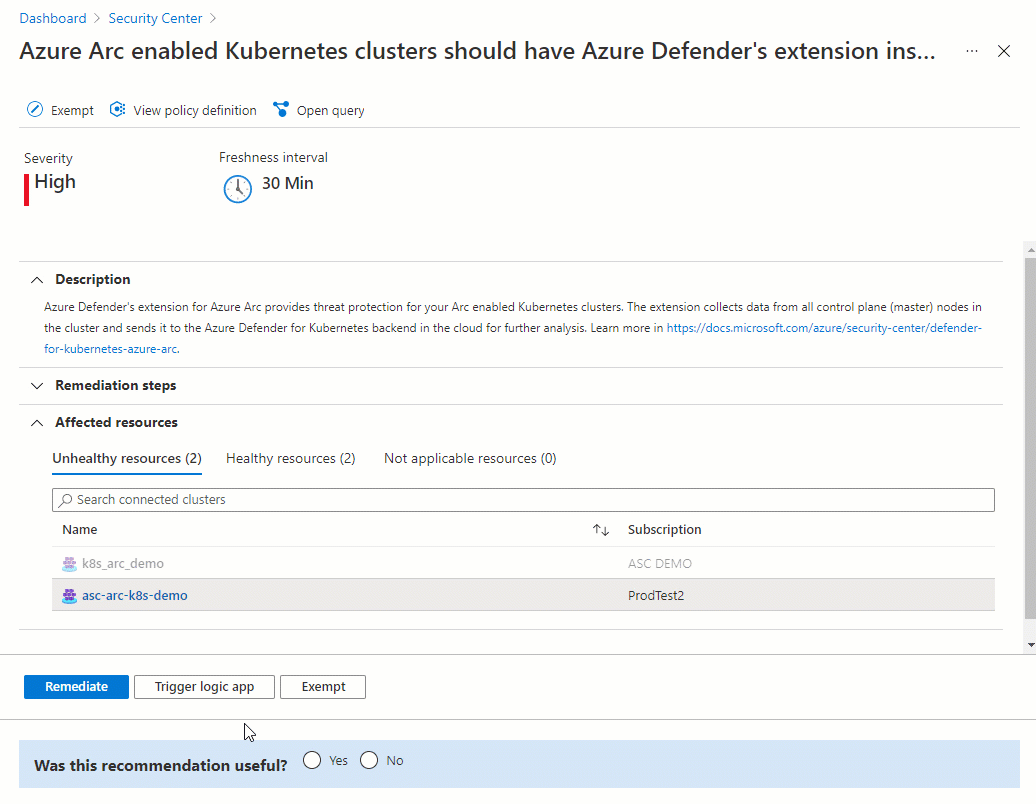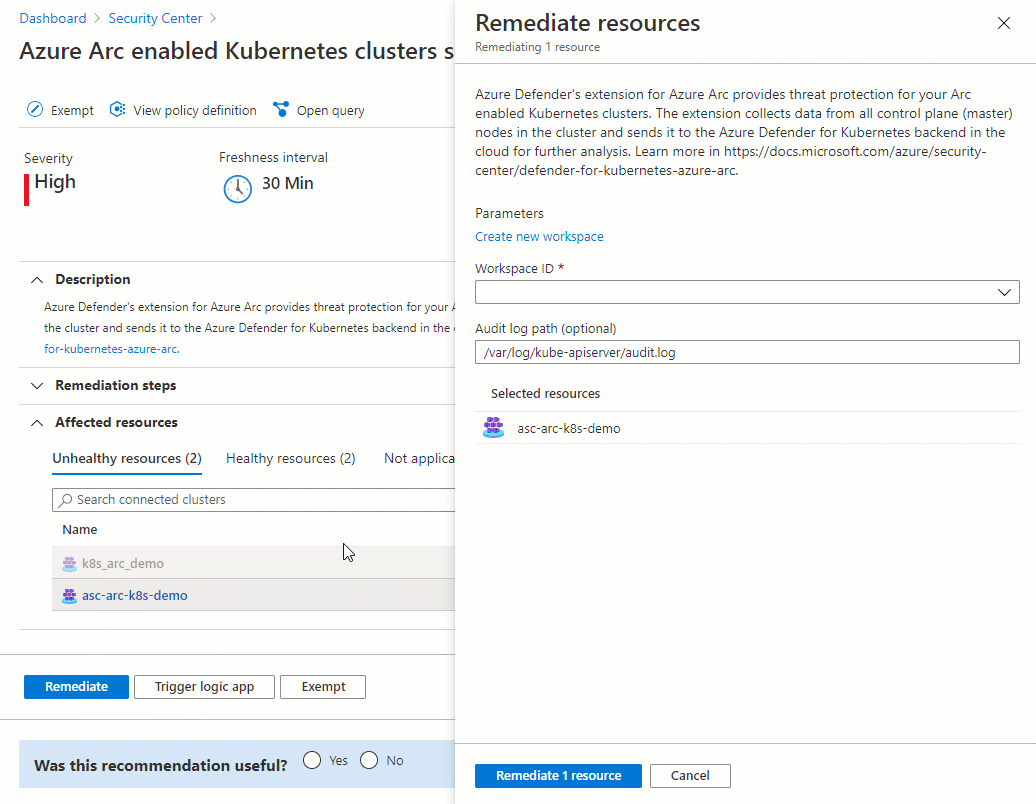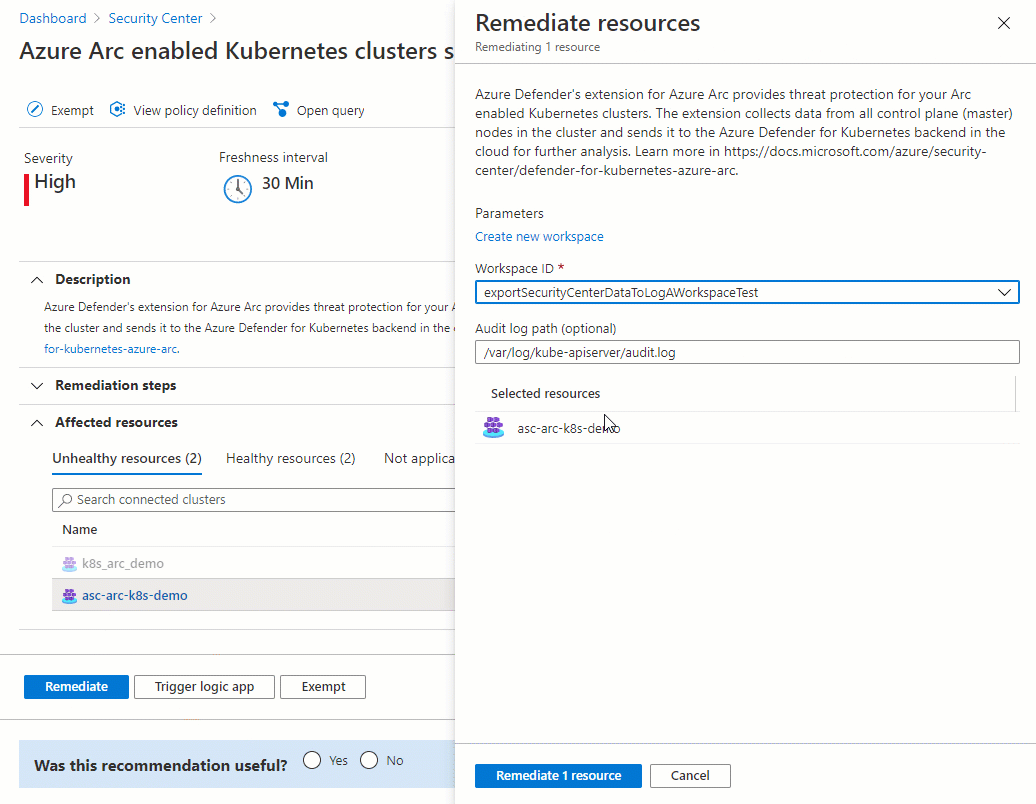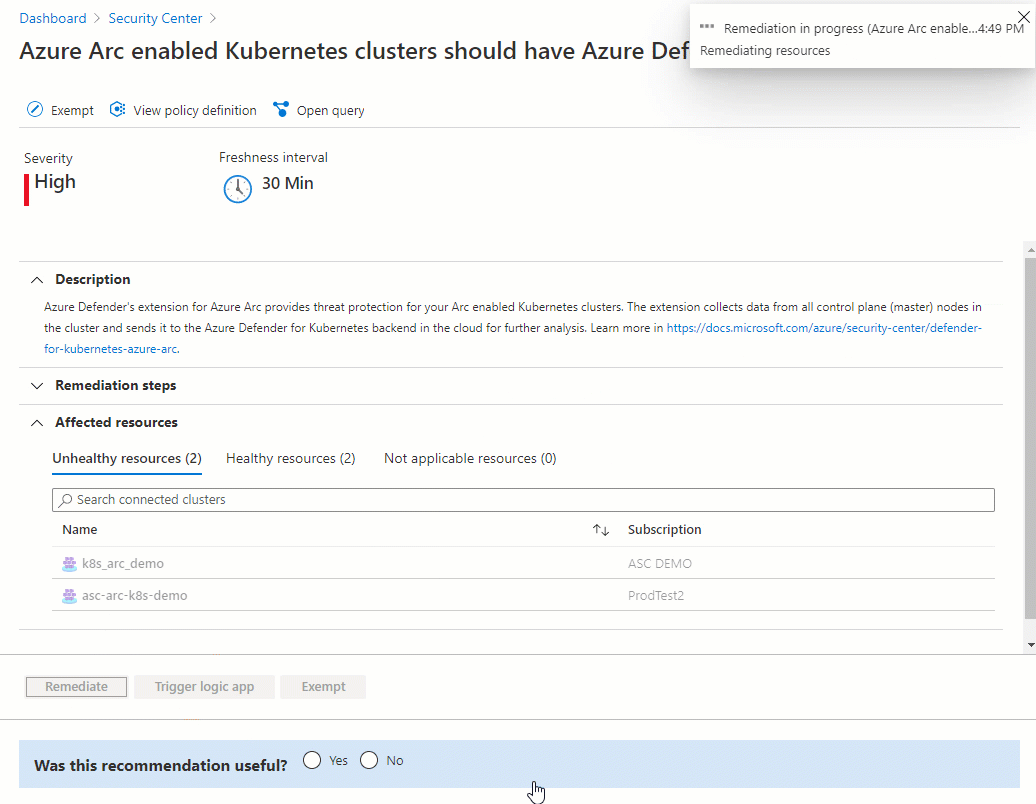
Select the sensor to see the details of the healthy and unhealthy resources (clusters with and without the sensor).
In the list of unhealthy resources, select a cluster. Then select Remediate to open the pane with the remediation options.
Select the relevant Log Analytics workspace, and then select Remediate x resource.
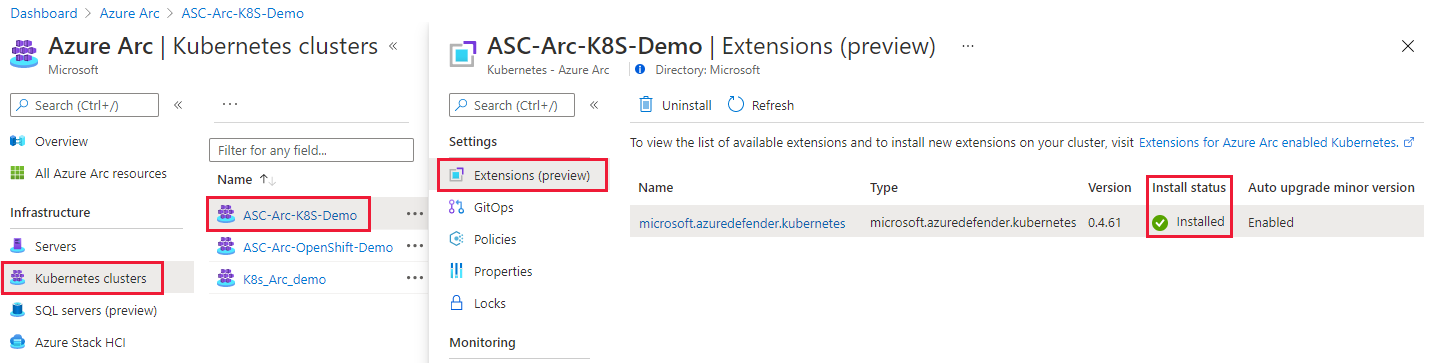
Verify the deployment
To verify that your cluster has the Defender sensor installed on it, follow the steps on one of the following tabs.
Use Defender for Cloud recommendations to verify the status of your sensor
On the Microsoft Defender for Cloud Recommendations page, open the Enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud security control.
Select the recommendation named Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have Microsoft Defender's extension enabled.
Check that the cluster on which you deployed the sensor is listed as Healthy.
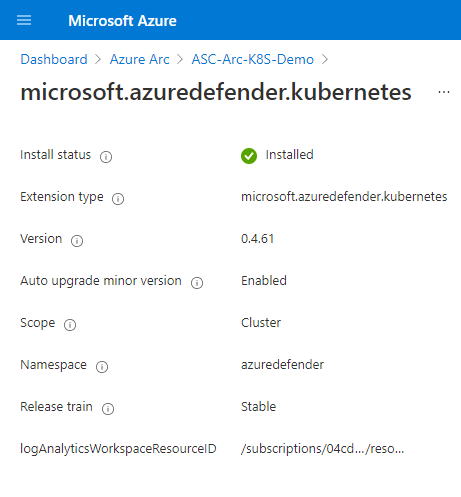
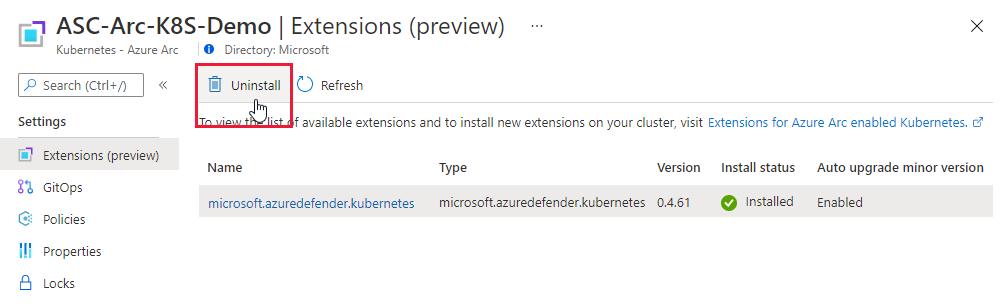
Remove the Defender sensor
To remove this (or any) Defender for Cloud extension, it's not enough to turn off automatic provisioning:
- Enabling automatic provisioning potentially affects existing and future machines.
- Disabling automatic provisioning for an extension affects only the future machines. Nothing is uninstalled when you disable automatic provisioning.
Note
To disable the Defender for Containers plan entirely, go to Environment settings and turn off Microsoft Defender for Containers.
Nevertheless, to ensure that the Defender for Containers components aren't automatically provisioned to your resources from now on, disable automatic provisioning of the extensions.
You can remove the extension from currently running machines by using the Azure portal, the Azure CLI, or the REST API, as explained on the following tabs.
Use the Azure portal to remove the extension
Set a default Log Analytics workspace for AKS
The Defender sensor uses the Log Analytics workspace as a data pipeline to send data from the cluster to Defender for Cloud. The workspace doesn't retain any of the data. As a result, users aren't billed in this use case.
The Defender sensor uses a default Log Analytics workspace. If you don't have a default Log Analytics workspace, Defender for Cloud creates a new resource group and default workspace when you install the Defender sensor. The default workspace is based on your region.
The naming convention for the default Log Analytics workspace and resource group is:
- Workspace: DefaultWorkspace-[subscription-ID]-[geo]
- Resource group: DefaultResourceGroup-[geo]
Assign a custom workspace
When you enable automatic provisioning, a default workspace is automatically assigned. You can assign a custom workspace through Azure Policy.
To check if you have a workspace assigned:
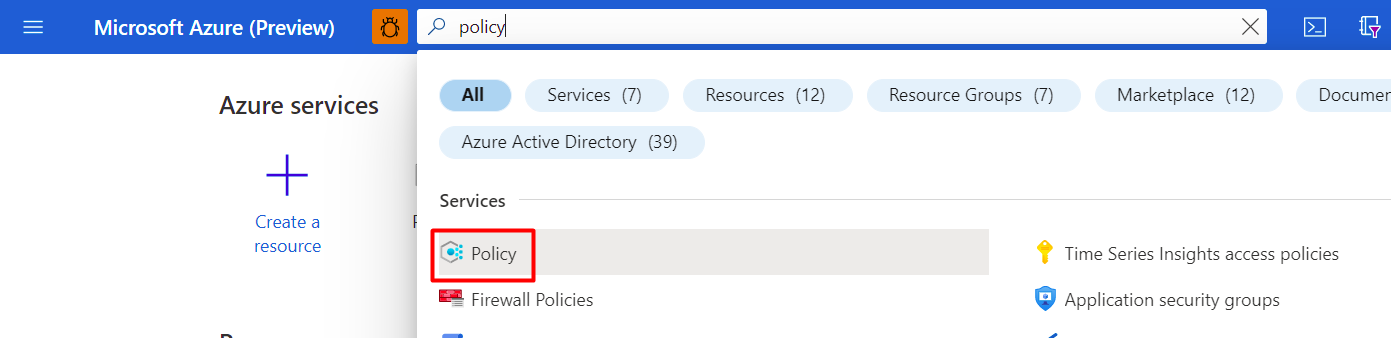
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Search for and select Policy.
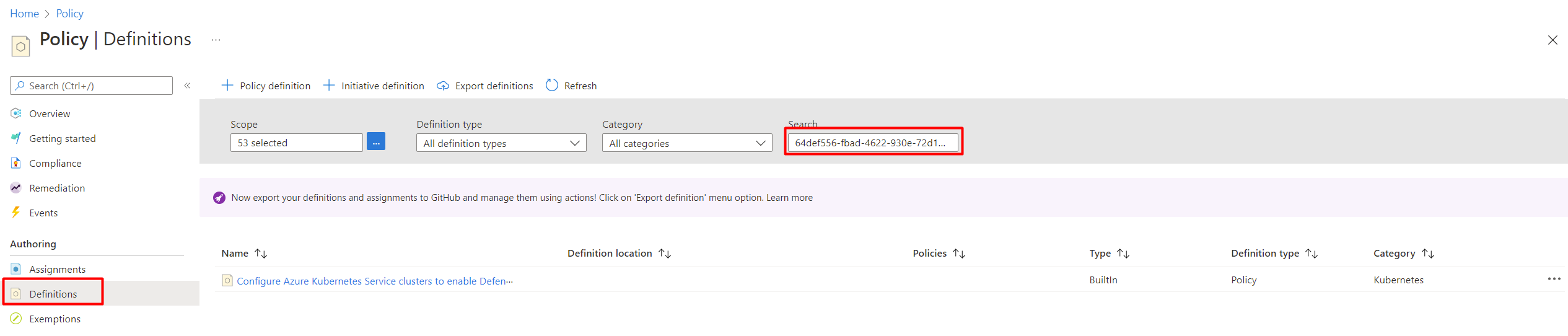
Select Definitions.
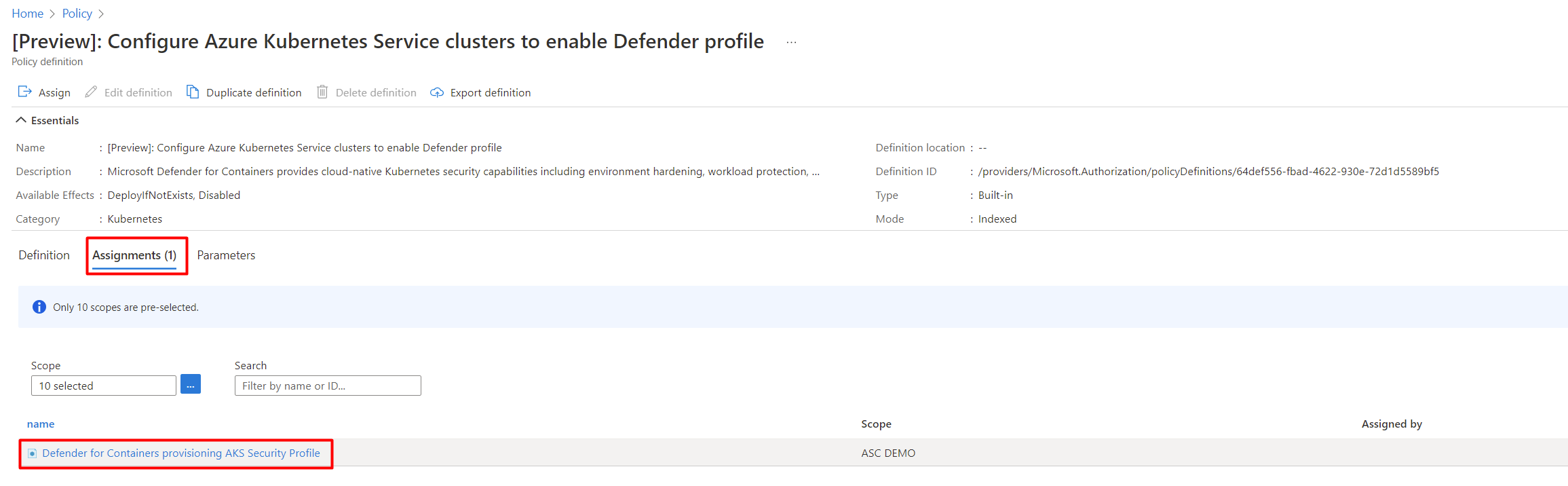
Search for policy ID
64def556-fbad-4622-930e-72d1d5589bf5.Select Configure Azure Kubernetes Service clusters to enable Defender profile.
Select Assignments.
Use one of the next sections in this article as follows:
- If the policy isn't yet assigned to the relevant scope, follow the Create a new assignment with a custom workspace steps.
- If the policy is already assigned and you want to change it to use a custom workspace, follow the Update an assignment with a custom workspace steps.
Create a new assignment with a custom workspace
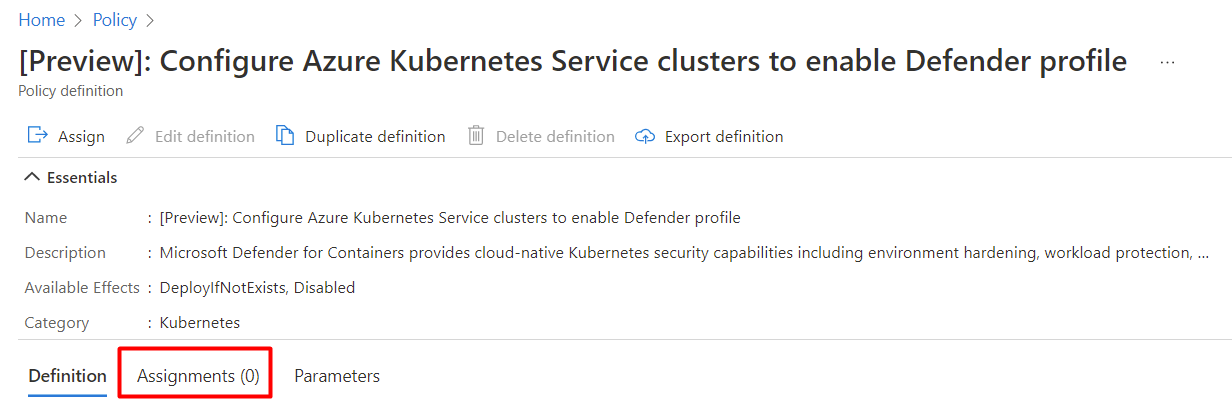
If the policy isn't yet assigned, the Assignments tab shows the number 0.
To assign a custom workspace:
Select Assign.
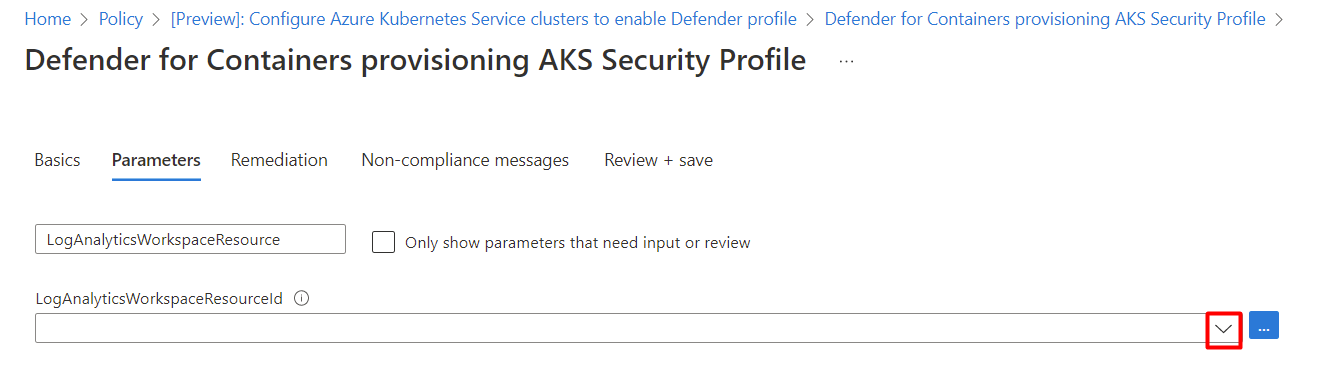
On the Parameters tab, clear the Only show parameters that need input or review option.
Select a LogAnalyticsWorkspaceResourceId value from the dropdown menu.
Select Review + create.
Select Create.
Update an assignment with a custom workspace
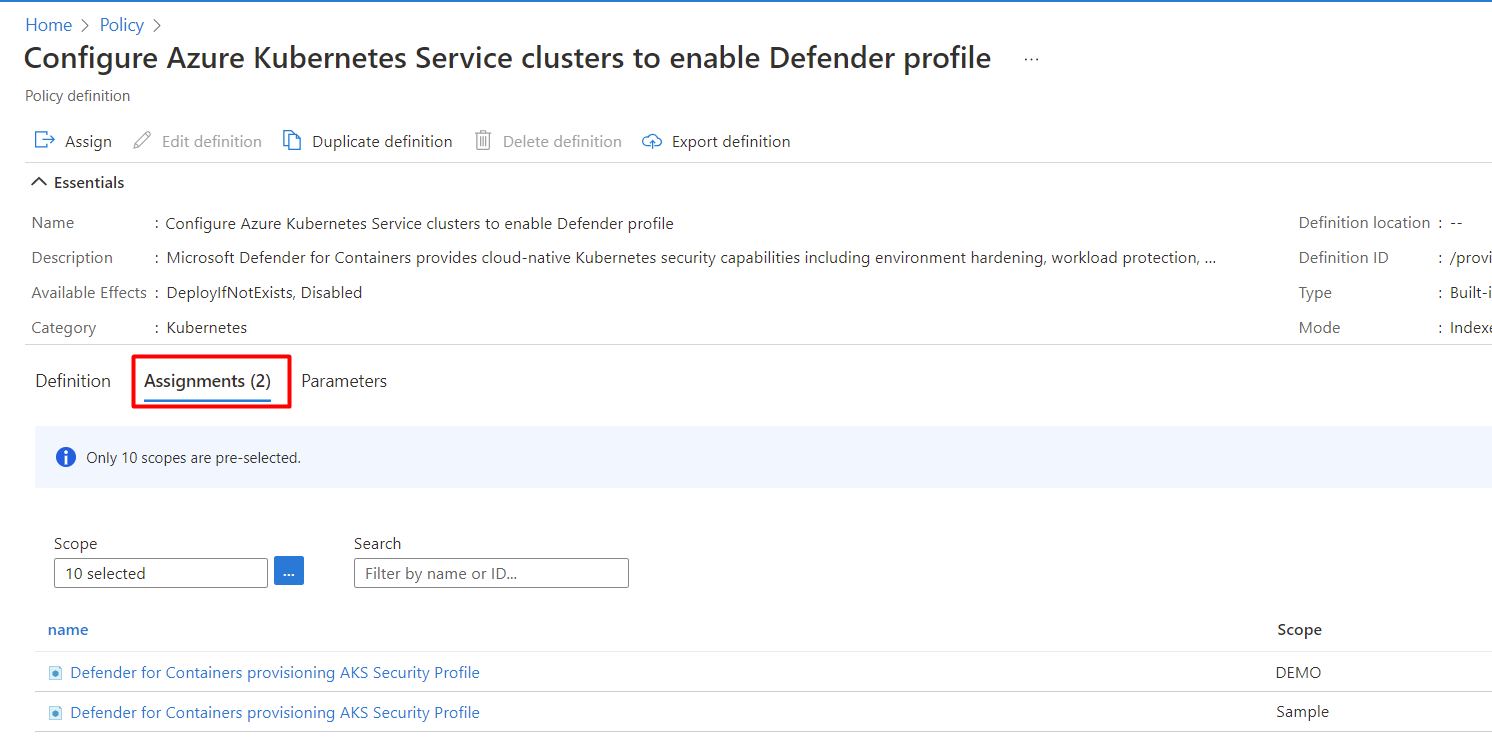
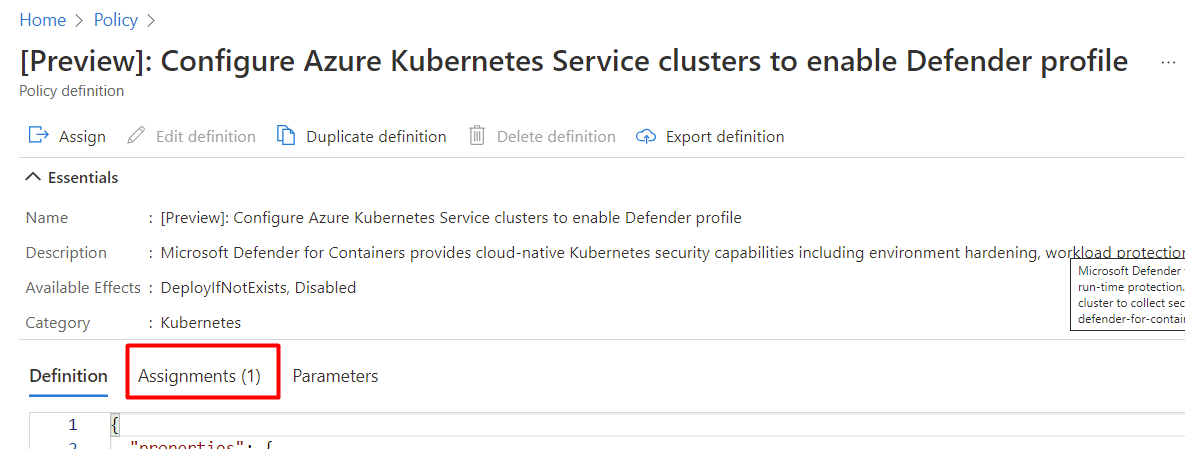
If the policy is assigned to a workspace, the Assignments tab shows the number 1.
Note
If you have more than one subscription, the number might be higher.
To assign a custom workspace:
Remove the Defender sensor
To remove this (or any) Defender for Cloud extension, it's not enough to turn off automatic provisioning:
- Enabling automatic provisioning potentially affects existing and future machines.
- Disabling automatic provisioning for an extension affects only the future machines. Nothing is uninstalled when you disable automatic provisioning.
Note
To disable the Defender for Containers plan entirely, go to Environment settings and turn off Microsoft Defender for Containers.
Nevertheless, to ensure that the Defender for Containers components aren't automatically provisioned to your resources from now on, disable automatic provisioning of the extensions.
You can remove the extension from currently running machines by using the REST API, the Azure CLI, or a Resource Manager template, as explained on the following tabs.
Use the REST API to remove the Defender sensor from AKS
To remove the extension by using the REST API, run the following PUT command:
https://management.chinacloudapi.cn/subscriptions/{{SubscriptionId}}/resourcegroups/{{ResourceGroup}}/providers/Microsoft.ContainerService/managedClusters/{{ClusterName}}?api-version={{ApiVersion}}
The command includes these parameters:
| Name | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
SubscriptionId |
Cluster's subscription ID | Yes |
ResourceGroup |
Cluster's resource group | Yes |
ClusterName |
Cluster's name | Yes |
ApiVersion |
API version; must be 2022-06-01 or later | Yes |
This is the request body:
{
"location": "{{Location}}",
"properties": {
"securityProfile": {
"defender": {
"securityMonitoring": {
"enabled": false
}
}
}
}
}
The request body has these parameters:
| Name | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
location |
Cluster's location | Yes |
properties.securityProfile.defender.securityMonitoring.enabled |
Determines whether to enable or disable Microsoft Defender for Containers on the cluster | Yes |
Next steps
Now that you enabled Defender for Containers, you can:
- Scan your supported environment images for vulnerabilities with Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management
- Check out common questions about Defender for Containers.