Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Known issues and limitations that are associated with online migrations from SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance are described as follows.
Important
With online migrations of SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance, migration of sql_variant data types isn't supported.
Backup requirements
Backup media
Make sure to take every backup on a separate backup media (backup files). Azure Database Migration Service doesn't support backups that are appended to a single backup file. Take full, differential, and log backups to separate backup files.
Data and log file layout
Number of log files
Azure Database Migration Service doesn't support databases with multiple log files. If you have multiple log files, shrink and reorganize them into a single transaction log file. Because you can't remote to log files that aren't empty, you need to back up the log file first.
SQL Server features
FileStream/FileTables
SQL Managed Instance currently doesn't support FileStream and FileTables. For workloads dependent on these features, we recommend that you opt for SQL Server running on Azure Virtual Machines as your Azure target.
In-memory tables
In-memory OLTP is available in the Premium and Business Critical tiers for SQL Managed Instance; the General Purpose tier doesn't support In-memory OLTP.
Migration resets
Deployments
SQL Managed Instance is a PaaS service with automatic patching and version updates. During migration of your SQL Managed Instance, non-critical updates are held for up to 36 hours. Afterwards (and for critical updates), if the migration is disrupted, the process resets to a full restore state.
Migration cutover can only be called after the full backup is restored and catches up with all log backups. If your production migration cutovers are affected by unexpected issues, open a support ticket to get assistance.
SMB file share connectivity
Issues connecting to the SMB file share are likely the result of a permissions issue.
To test SMB file share connectivity, follow these steps:
Save a backup to the SMB file share.
Verify network connectivity between the subnet of Azure Database Migration Service and the source SQL Server. The easiest way to do this is to deploy a SQL Server virtual machine to the DMS subnet and connect to the source SQL Server using SQL Server Management Studio.
Restore the header on the source SQL Server from the backup on the fileshare:
RESTORE HEADERONLY FROM DISK = N'\\<SMB file share path>\full.bak';
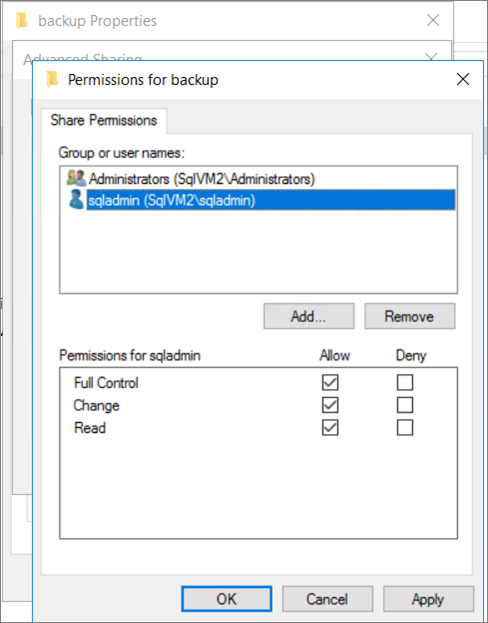
If you're unable to connect to the file share, configure permissions with these steps:
Navigate to your file share using File Explorer.
Right-click the file share and select properties.
Choose the Sharing tab and select Advanced Sharing.
Add the Windows account used for migration, and assign it full control access.
Add the SQL Server service account, and assign it full control access. Check the SQL Server Configuration Manager for the SQL Server service account if you're not sure which account is being used.