Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
As mentioned in the Microsoft Digital Defense Report from October 2023,
...threats to digital peace have reduced trust in technology and highlighted the urgent need for improved cyber defenses at all levels...
...at Microsoft, our more than 10,000 security experts analyze over 65 trillion signals each day... driving some of the most influential insights in cybersecurity. Together, we can build cyber resilience through innovative action and collective defense.
As part of this work, we're making Microsoft-managed policies available in Microsoft Entra tenants around the world. These simplified Conditional Access policies require multifactor authentication, which a recent study finds reduces the risk of compromise by more than 99%.
How Microsoft-managed policies work
Administrators with at least the Conditional Access Administrator role assigned find these policies in the Azure Portal under Microsoft Entra ID > Security > Conditional Access > Policies.
You can edit the state of a policy and what identities the policy should exclude. Exclude your break-glass or emergency access accounts from managed policies just like other Conditional Access policies. Consider duplicating these policies if you need to make more changes than what's allowed in the Microsoft-managed policies.
Microsoft enables these policies no less than 45 days after they're introduced in your tenant if they're left in the Report-only state. You can turn on these policies sooner, or opt out by setting the policy state to Off. Customers are notified through emails and Message center posts 28 days before the policies are enabled.
Note
In some cases, policies might be enabled faster than 45 days. If this change applies to your tenant:
- It's mentioned in emails and Microsoft 365 message center posts you receive about Microsoft-managed policies.
- It's mentioned in the policy details in the Microsoft Entra admin center.
Policies
These Microsoft-managed policies allow administrators to make simple modifications like excluding users or turning them from report-only mode to on or off. Organizations can't rename or delete any Microsoft-managed policies. As administrators get more comfortable with Conditional Access policy, they might choose to duplicate the policy to create custom versions.
As threats evolve, Microsoft might update these policies to use new features, functionality, or improve their effectiveness. Microsoft‑managed Conditional Access policies automatically adapt to changes within a tenant to maintain consistent security posture without requiring administrator action. As Microsoft identifies new users, groups, or workloads that meet the eligibility criteria for an existing MMP policy, they are automatically included in the policy’s scope. These updates do not modify the policy’s settings, conditions, or grant controls, and any admin‑configured exclusions are always preserved to prevent accidental lockouts. This ensures that coverage stays current as the tenant evolves, while maintaining predictable behavior for administrators. Microsoft communicates these updates through standard notification channels to keep tenants informed.
- Block legacy authentication
- Block device code flow
- Multifactor authentication for admins accessing Microsoft Admin portals
- Multifactor authentication for all users
- Multifactor authentication for per-user multifactor authentication users
Block legacy authentication
This policy blocks sign-in attempts using legacy authentication and legacy authentication protocols. These authentications might come from older clients like Office 2010, or clients that use protocols like IMAP, SMTP, or POP3.
Based on Microsoft's analysis, more than 99 percent of password spray attacks use these legacy authentication protocols. These attacks would stop with basic authentication disabled or blocked.
Block device code flow
This policy blocks device code flow, where a user initiates authentication on one device, completes on another, and their token is sent back to the original device. This type of authentication is common where users can't enter their credentials, like smart TVs, Microsoft Teams Room devices, IoT devices, or printers.
Device code flow is rarely used by customers, but is frequently used by attackers. Enabling this Microsoft-managed policy for your organization helps remove this attack vector.
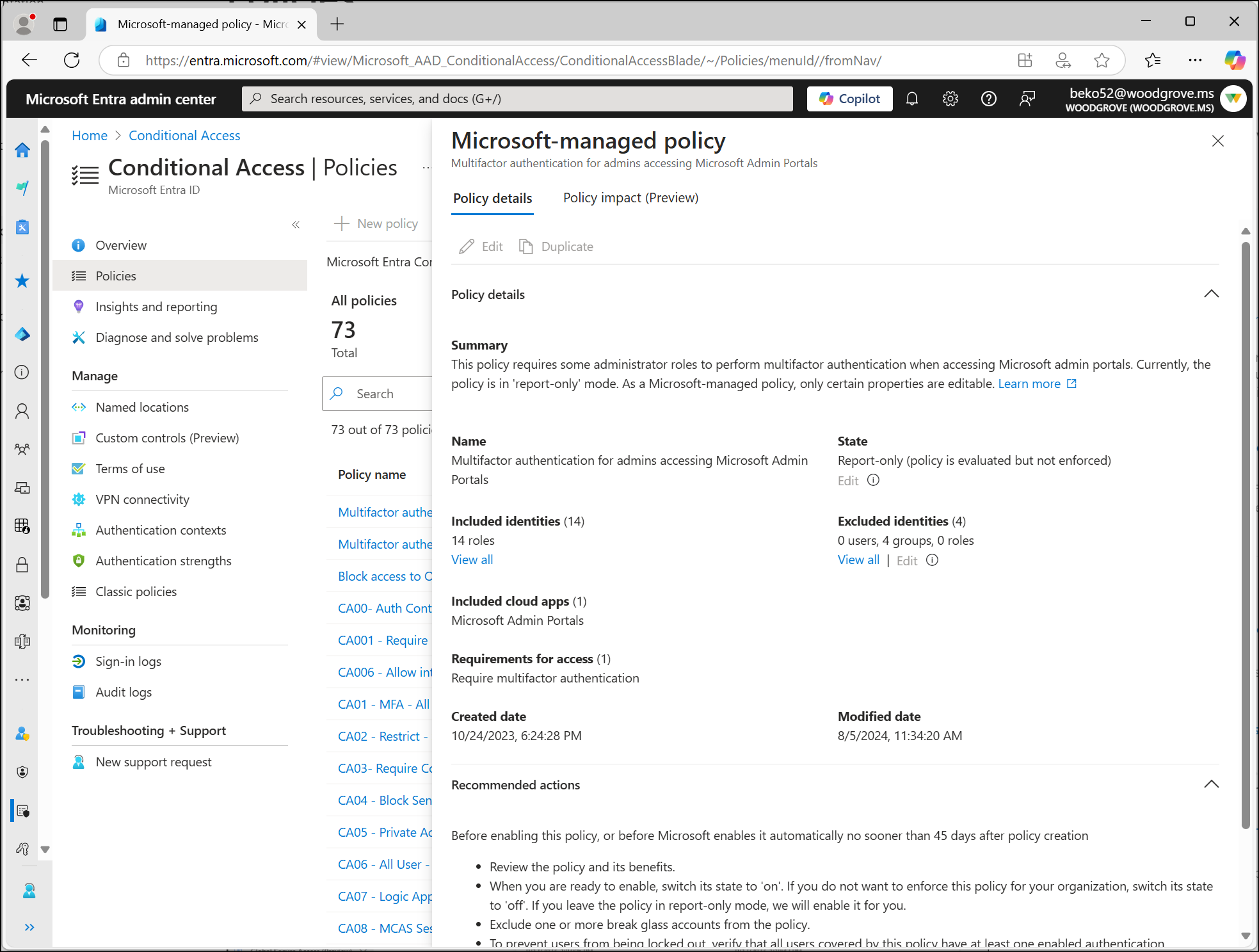
Multifactor authentication for admins accessing Microsoft Admin portals
This policy covers 14 admin roles that are highly privileged, who access the Microsoft Admin Portals, and requires them to perform multifactor authentication.
This policy applies to Microsoft Entra ID P1 and P2 tenants where security defaults aren't enabled.
Tip
Microsoft-managed policies requiring multifactor authentication differ from the announcement of mandatory multifactor authentication for Azure sign-ins made in 2024, which started gradual rollout in October of 2024.
Multifactor authentication for all users
This policy covers all users in your organization and requires them to use multifactor authentication whenever they sign in. In most cases, the session persists on the device, and users don't need to complete multifactor authentication when they interact with another application.
Multifactor authentication for per-user multifactor authentication users
This policy covers users per-user MFA, a configuration that Microsoft no longer recommends. Conditional Access offers a better admin experience with many extra features. Consolidating all multifactor authentication policies to Conditional Access can help you be more targeted in requiring multifactor authentication, lowering end user friction while maintaining security posture.
This policy targets:
- Organizations with Microsoft Entra ID P1 and P2 licensed users
- Organizations where security defaults aren't enabled
- Organizations with less than 500 per-user MFA enabled or enforced users
To apply this policy to more users, duplicate it and change the assignments.
Tip
Using the Edit pencil at the top to modify the Microsoft-managed per-user multifactor authentication policy might result in a failed to update error. To work around this issue, select Edit under the Excluded identities section of the policy.
Security defaults policies
The following policies are available for when you upgrade from using security defaults.
- Block legacy authentication
- Require multifactor authentication for Azure management
- Require multifactor authentication for admins
- Require multifactor authentication for all users
Block legacy authentication
This policy blocks legacy authentication protocols from accessing applications. Legacy authentication refers to an authentication request made by:
- Clients that don't use modern authentication (for example, an Office 2010 client)
- Any client that uses older mail protocols such as IMAP, SMTP, or POP3
- Any sign-in attempts to use legacy authentication.
Most observed compromising sign-in attempts come from legacy authentication. Because legacy authentication doesn't support multifactor authentication, attackers can bypass multifactor authentication requirements by using older protocols.
Require multifactor authentication for Azure management
This policy covers all users when they're trying to access various Azure services managed through the Windows Azure Service Management API including:
- Azure portal
- Microsoft Entra admin center
- Azure PowerShell
- Azure CLI
Users must complete multifactor authentication to access these resources.
Require multifactor authentication for admins
This policy applies to users with highly privileged admin roles:
- Global Administrator
- Application Administrator
- Authentication Administrator
- Billing Administrator
- Cloud Application Administrator
- Conditional Access Administrator
- Exchange Administrator
- Helpdesk Administrator
- Password Administrator
- Privileged Authentication Administrator
- Privileged Role Administrator
- Security Administrator
- SharePoint Administrator
- User Administrator
These accounts must use multifactor authentication to sign in to any application.
Require multifactor authentication for all users
This policy applies to all users in your organization and requires multifactor authentication for every sign-in. In most cases, sessions persist on devices, so users don't need to complete multifactor authentication when interacting with other applications.
Monitor and review
The managed policy and the sign-in logs are the two places where you can see the effect of these policies on your organization.
Review the Policy impact tab of the managed policy to see a summary of how the policy affects your environment.
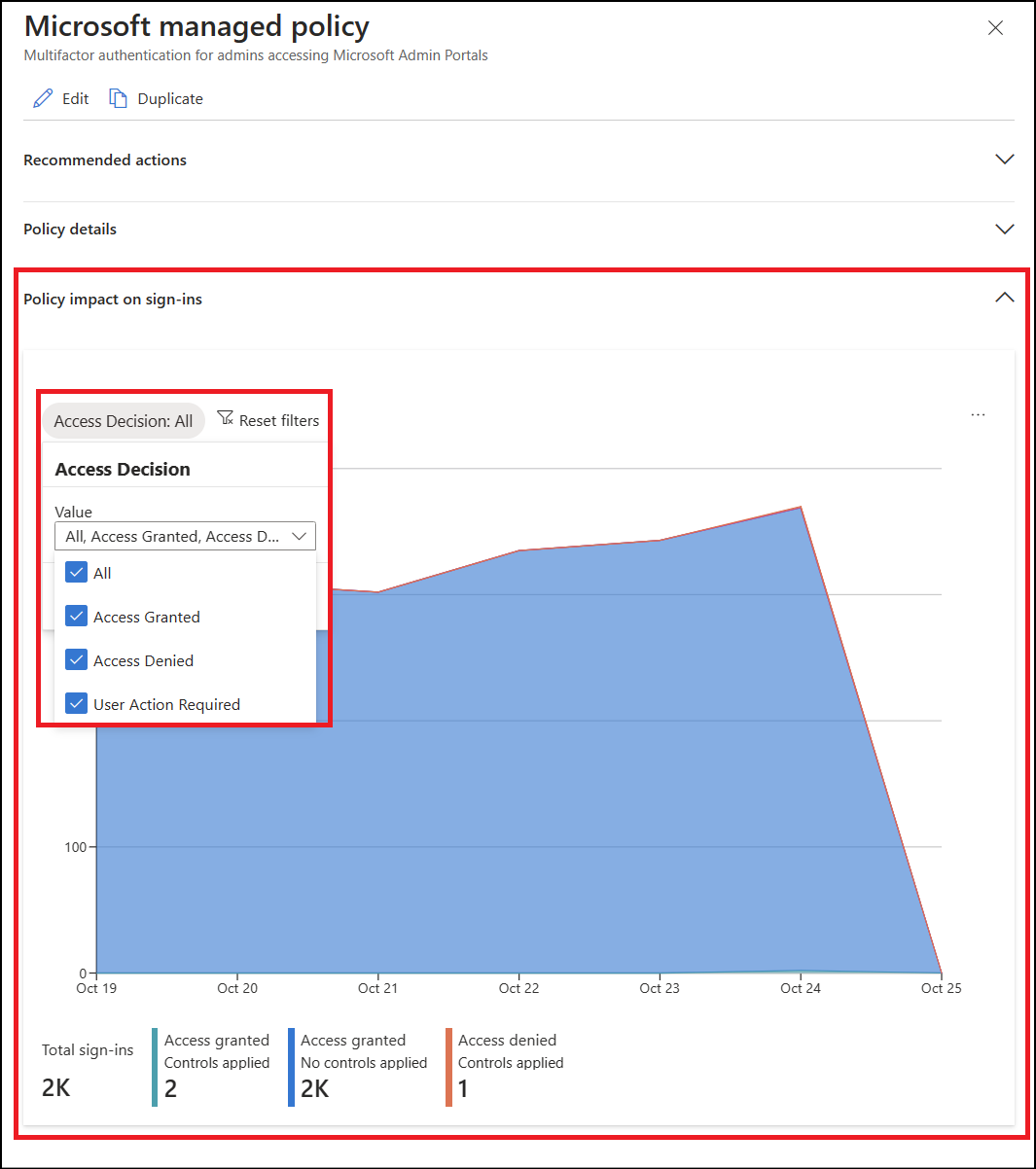
Analyze the Microsoft Entra sign-in logs to see details about how the policies affect sign-in activity.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Reports Reader.
- Browse to Entra ID > Monitoring & health > Sign-in logs.
- Use some or all of the following filters:
- Correlation ID when you have a specific event to investigate.
- Conditional Access to see policy failure and success.
- Username to see information related to specific users.
- Date scoped to the time frame in question.
- Select a specific sign-in event, then select Conditional Access.
- To investigate further, select the Policy Name to drill down into the configuration of the policies.
- Explore the other tabs to see the client user and device details that were used for the Conditional Access policy assessment.
Common questions
What is Conditional Access?
Conditional Access is a Microsoft Entra feature that allows organizations to enforce security requirements when accessing resources. Conditional Access is commonly used to enforce multifactor authentication, device configuration, or network location requirements.
These policies can be thought of as logical if then statements.
If the assignments (users, resources, and conditions) are true, then apply the access controls (grant and/or session) in the policy. If you're an administrator, who wants to access one of the Microsoft admin portals, then you must perform multifactor authentication to prove it's really you.
What if I want to make more changes?
Administrators might choose to make further changes to these policies by duplicating them using the Duplicate button in the policy list view. This new policy can be configured in the same way as any other Conditional Access policy with starting from a Microsoft recommended position. Be careful not to lower your security posture with those changes.
What administrator roles are covered by these policies?
- Global Administrator
- Application Administrator
- Authentication Administrator
- Billing Administrator
- Cloud Application Administrator
- Conditional Access Administrator
- Exchange Administrator
- Helpdesk Administrator
- Password Administrator
- Privileged Authentication Administrator
- Privileged Role Administrator
- Security Administrator
- SharePoint Administrator
- User Administrator
What if I use a different solution for multifactor authentication?
Multifactor authentication using external authentication methods satisfies the MFA requirements of Microsoft-managed policies.
When multifactor authentication is completed via a federated identity provider (IdP), it might satisfy Microsoft Entra ID MFA requirements depending on your configuration. For more information, see Satisfy Microsoft Entra ID multifactor authentication (MFA) controls with MFA claims from a federated IdP.
What if I use custom controls?
Custom controls don't satisfy multifactor authentication claim requirements. If your organization uses custom controls you should migrate to external authentication methods, the replacement of custom controls. Your external authentication provider must support external authentication methods and provide the necessary configuration guidance for integration.
How do I monitor when Microsoft makes a change to these policies or adds a new one?
Administrators with AuditLog.Read.All and Directory.Read permissions can query the audit log for entries initiated by Microsoft Managed Policy Manager in the Policy category.