Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Firewall supports built-in autoscaling to dynamically adjust capacity based on CPU utilization, throughput, and connection volume. For mission-critical workloads or predictable traffic spikes , you can configure greater control to ensure consistent performance.
Prescaling allows you to proactively set minimum and maximum capacity units. This configuration provides predictable performance while autoscaling occurs within the defined range.
Key benefits
With prescaling, you can:
- Pre-provision capacity for high-traffic events or known traffic spikes
- Maintain consistent performance by setting a baseline capacity
- Observe live capacity with the Observed Capacity metric
How prescaling works
You can configure two properties in the autoscaleConfiguration setting:
| Property | Description | Allowed range |
|---|---|---|
| minCapacity | The minimum number of capacity units always provisioned | 2 to 50 |
| maxCapacity | The maximum number of capacity units the firewall can scale to | 2 to 50 |
When minCapacity and maxCapacity are set to the same value, the firewall runs at a fixed capacity with no autoscaling.
Important
The minimum and maximum capacity values must either be equal, or their difference must be greater than 1. For example, if minCapacity is 5, maxCapacity must be at least 7.
Configuration options
You can configure prescaling using the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, ARM templates, or Bicep.
Portal example
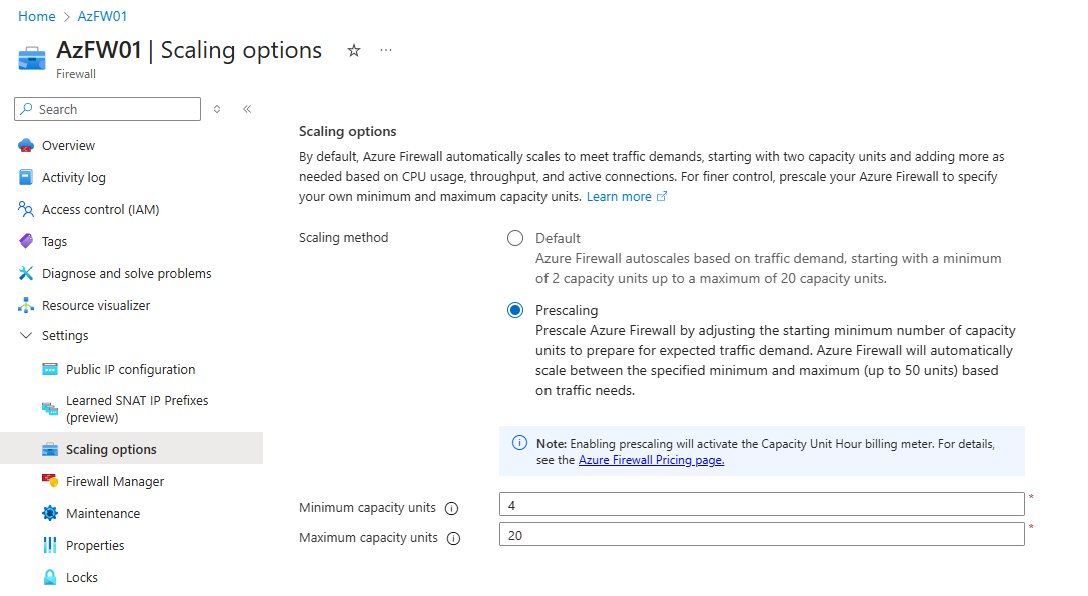
To configure prescaling in the Azure portal:
- Navigate to your Azure Firewall resource.
- Under Settings, select Scaling options.
- Select Prescaling.
- Set your desired minimum and maximum capacity values.
PowerShell example
New-AzFirewall `
-Name "MyFirewall" `
-ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup" `
-Location "chinaeast" `
-VirtualNetwork (Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name "MyVNet" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup") `
-PublicIpAddress (Get-AzPublicIpAddress -Name "MyFW-PublicIP" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup") `
-MinCapacity 4 `
-MaxCapacity 10
Bicep Example
For reference, here's an example configuration using a Bicep template where you can see the new autoscaleConfiguration property: Azure Firewall Bicep template
Choosing capacity values
To determine the optimal minCapacity and maxCapacity values:
- Set a reasonable minimum to avoid unnecessary scaling: Start with a minimum capacity that handles your typical peak traffic comfortably so scaling events are rare under normal conditions.
- Leave headroom with a higher maximum: Set maxCapacity higher than your expected peak to handle unexpected surges. Azure Firewall autoscaling increases capacity up to your maxCapacity value.
- Monitor the Observed Capacity metric to see how often scaling occurs and adjust minimum and maximum values as needed. If scaling happens frequently, consider raising minCapacity.
- Configure alerts on the Observed Capacity metric to get notified when scaling events occur, so you can evaluate if adjustments are needed.
Monitoring
Prescaling introduces new observability:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Observed Capacity | Shows the number of capacity units currently provisioned and tracks scaling activity over time. Updates can take up to 30 minutes to appear. |
| Alerts | You can configure an alert for autoscaling events using the Observed Capacity metric. |
Handling performance issues
If you experience packet drops or connectivity issues:
- Review Observed Capacity to assess capacity trends.
- Consider increasing minimum capacity to provide more capacity support or if frequent upward scales occur.
- Use key telemetry metrics such as Latency Probe, Throughput, and Observed Capacity to optimize scaling strategies.
Limitations
Keep the following considerations in mind when using prescaling:
- No region-level capacity guarantees: Scaling might fail or be delayed if the region lacks capacity.
- Fixed capacity disables autoscaling: When minCapacity equals maxCapacity, autoscaling is disabled.
- Retention of previous settings: If your firewall already has autoscaleConfiguration values set, and you deploy or update the resource without specifying the autoscaleConfiguration property (such as via Bicep, ARM template, or other templates), the firewall keeps using the existing autoscaleConfiguration values. This behavior helps prevent accidental overwriting or loss of your scaling settings.
- Configuration resets on resource changes: Deleting, re-creating, or migrating the firewall might reset capacity values to defaults.
- Active scaling or maintenance events: Prescaling changes might fail if the firewall is midscale or during an upgrade. Retry after completion.
Known issues
The following known issues exist when using prescaling:
| Known issue | Description | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Prescaling is not supported with Customer Provided PIP in Secured Virtual Hubs | Configuring prescaling will result in a Failed State. | Avoid prescaling when using Customer Provided PIP in Secured Virtual Hubs. Alternatively, revert back to default autoscaling mode. |
Next steps
- Learn about Monitoring Azure Firewall
- Review Azure Firewall best practices