Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Front Door traffic routing takes place over multiple stages. First, traffic is routed from the client to the Front Door. Then, Front Door uses your configuration to determine the origin to send the traffic to. The Front Door web application firewall, routing rules, rules engine, and caching configuration can all affect the routing process.
The following diagram illustrates the routing architecture:
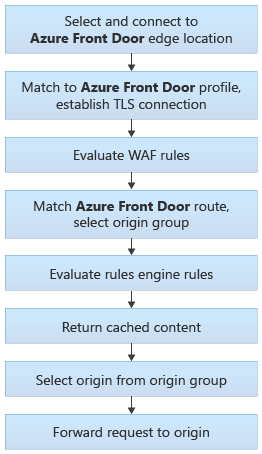
The following sections describe these steps in detail.
Select and connect to the Front Door edge location
The user or client application initiates a connection to the Front Door. The connection terminates at an edge location closest to the end user. Front Door's edge location processes the request.
For more information about how requests are made to Front Door, see Front Door traffic acceleration.
Match request to a Front Door profile
When Front Door receives an HTTP request, it uses the request's Host header to match the request to the correct customer's Front Door profile. If the request is using a custom domain name, the domain name must be registered with Front Door to enable requests to get matched to your profile.
The client and server perform a TLS handshake using the TLS certificate you configured for your custom domain name, or by using the Front Door certificate when the Host header ends with *.azurefd.net.
Evaluate WAF rules
If your domain has Web Application Firewall enabled, WAF rules are evaluated.
If a rule gets violated, Front Door returns an error to the client and the request processing stops.
Match a route
Front Door matches the request to a route. Learn more about the route matching process.
The route specifies the origin group that the request should be sent to.
Evaluate rule sets
If you define rule sets for the route, they get process in the order configured. Rule sets can override the origin group specified in a route. Rule sets can also trigger a redirection response to the request instead of forwarding it to an origin.
Return cached response
If the Front Door routing rule has caching enabled, and the Front Door edge location's cache includes a valid response for the request, then Front Door returns the cached response.
If caching is disabled or no response is available, the request is forwarded to the origin.
Select origin
Front Door selects an origin to use within the origin group. Origin selection is based on several factors, including:
- Health of each origin, which Front Door monitors by using health probes.
- Routing method for your origin group.
- If you enable session affinity
Forward the request to the origin
Finally, the request is forwarded to the origin.