Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In an Interactive Query Cluster, resource management is imperative, especially in a multi-tenant environment. Hive LLAP (low-latency analytical processing) uses workload management to enable users to match specific workload needs and prevent contention for those resources.
Workload Management implements resource pools (also known as query pools) which lets you divide resources available for Hive/LLAP into pools to be used for specific workloads.
It also allows you to configure percentage of resources and query parallelism for each individual resource pool.
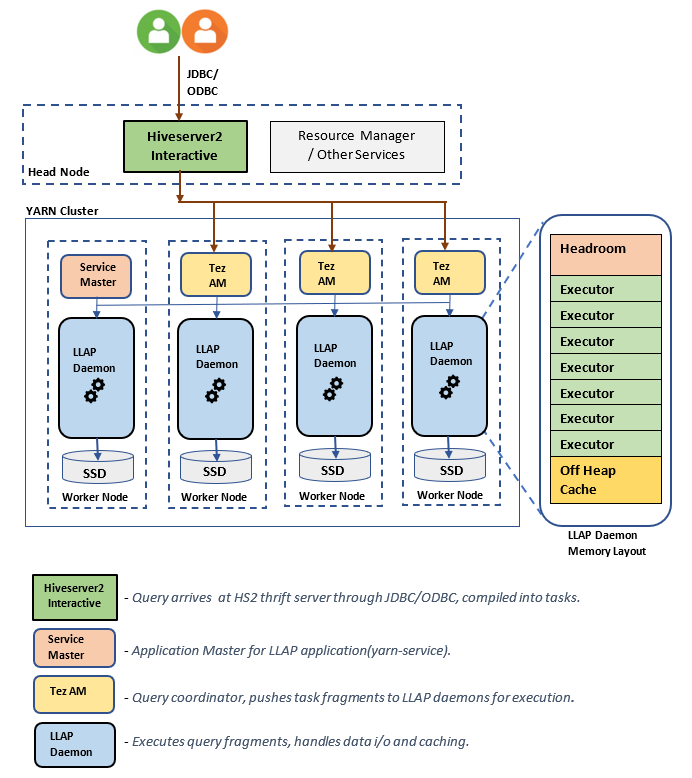
Enable Hive LLAP Workload Management feature for HDInsight clusters
Enable workload management feature in HDInsight Interactive Query clusters by following the steps listed below:
- Create a new yarn queue, which can be used to bring up the workload management Tez AMs.
- Change cluster configs via Ambari to enable the feature in Hive.
- Create and Activate a resource plan.
Create a new yarn queue suitable for Workload Management feature
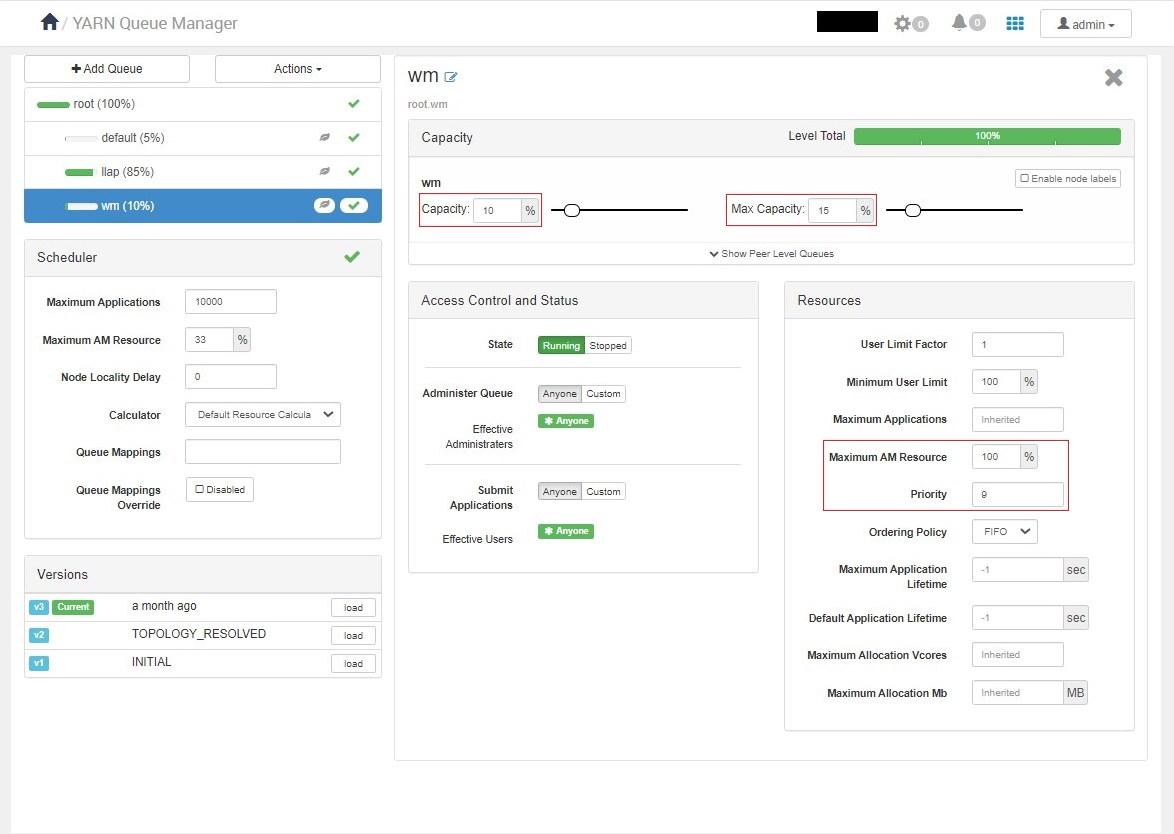
Create a new yarn queue called wm with the help of following guide.
Configure the wm queue on cluster based on following configurations:
| QueueName | Capacity | Max Capacity | Priority | Maximum AM Resource |
|---|---|---|---|---|
default |
5% | 5% | 0 | 33% |
llap |
85% | 100% | 10 | 33% |
wm |
10% | 15% | 9 | 100% |
Confirm if the wm queue configuration looks as shown below.
Enable Workload Management feature in Hive configs
Add the following property to Custom hiveserver2-interactive-site and set its value to the name of newly create yarn queue that is, wm. Restart Interactive HiveServer for configuration changes to take place.
hive.server2.tez.interactive.queue=wm
Create resource plan
Following is an example on how to create a basic resource plan.
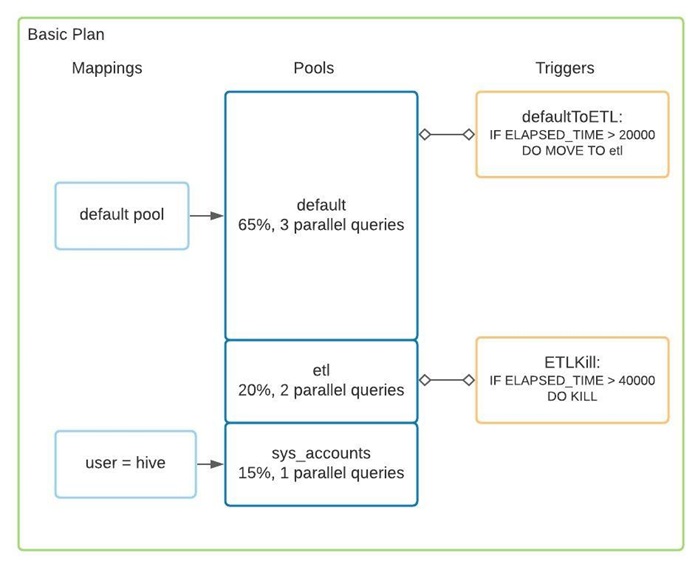
Execute following commands via beeline to create the above resource plan.
Commands to create, view, and drop the resource plan
# CREATE RESOURCE PLAN
CREATE RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan;
# CREATE POOLS
ALTER POOL demo_plan.default SET ALLOC_FRACTION = 0.65, QUERY_PARALLELISM = 2;
CREATE POOL demo_plan.etl WITH ALLOC_FRACTION = 0.20, QUERY_PARALLELISM = 2;
CREATE POOL demo_plan.sys_accounts WITH ALLOC_FRACTION = 0.15, QUERY_PARALLELISM = 1;
# CREATE MAPPING
CREATE USER MAPPING 'hive' IN demo_plan TO sys_accounts WITH ORDER 1;
# CREATE TRIGGERS
CREATE TRIGGER demo_plan.defaultToETL WHEN ELAPSED_TIME > 20000 DO MOVE TO etl;
ALTER TRIGGER demo_plan.defaultToETL ADD TO POOL default;
CREATE TRIGGER demo_plan.ETLKill WHEN ELAPSED_TIME > 40000 DO KILL;
ALTER TRIGGER demo_plan.ETLKill ADD TO POOL etl;
# VALIDATE PLAN
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan VALIDATE;
# ENABLE PLAN
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan ENABLE;
# ACTIVATE PLAN
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan ACTIVATE;
# SHOW RESOURCE PLAN
SHOW RESOURCE PLANS;
SHOW RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan;
# VALIDATE PLAN
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan VALIDATE;
# ENABLE PLAN
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan ENABLE;
# ACTIVATE PLAN
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan ACTIVATE;
# SHOW RESOURCE PLAN
SHOW RESOURCE PLANS;
SHOW RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan;
# DISABLE PLAN
-- In case plan is in active state first run:
-- DISABLE WORKLOAD MANAGEMENT;
ALTER RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan DISABLE;
# DROP RESOURCE PLAN
DROP RESOURCE PLAN demo_plan;
Understanding resource plan
To have an optimal resource plan, one needs to have a thorough understanding of the workload requirements.
Number of pools
The number of pools is limited by total query parallelism (Minimum one query per pool). Most of the workloads rarely require more than three pools.
- default, for interactive queries
- etl/batch, for long running queries
- sys, for system administrators
Total QUERY_PARALLELISM
Total QUERY_PARALLELISM or Number of total concurrent queries can be obtained with following formula:
Number of total concurrent queries(Tez AMs) = Math.floor( (total cluster memory capacity / size of Tez AM container) x percentage of wm queue capacity)
For example:
Let's assume Tez AM container size is 4 GB and total memory capacity of yarn cluster is 400 GB, out of which 10% is allocated for wm queue then,
Number of total concurrent queries = floor((400/4) x 0.10) = 10
Tip
Have a slightly more capacity in wm queue than required to avoid tez AMs getting stuck in accepted state that is, wm queue capacity can be made to 10.01% and default queue capacity can be reduced to 4.99%.
Mappings
Mappings provide a mechanism to direct queries to certain pools. As number of mappings increase, multiple rules may apply for a given query. To establish which rule should take precedence:
If ordering is specified with the optional WITH ORDER clause, lower-order rule takes priority. Else, user rules take precedence over application rules and application rules take precedence over group rules.
The order of group rules with the same priority is undefined.
Note
- Tez AMs in
llapqueue will remain unused when WLM plan is active. These Tez AMs inllapqueue will be readily available in case the WLM resource plan is disabled. - Enabling WLM resource plan launches number of Tez AMs equal to total
QUERY_PARALLELISMconfigured for the given resource plan.wmqueue size should be tuned to avoid these Tez AM getting stuck in ACCEPTED state. - We only support the use of following two counters for use in resource plans:
- EXECUTION_TIME
- ELAPSED_TIME