Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Speculative execution is a feature in spark that spins up duplicate task when it considers a task taking more time to get completed. This duplicate task spins in a new node other than the one where original task is running. This means that issues caused due to a bad worker node are easily mitigated by enabling speculative execution. This is how Spark completes the job as soon as possible. If either of the tasks gets completed sooner, the other task will be killed.
How to monitor?
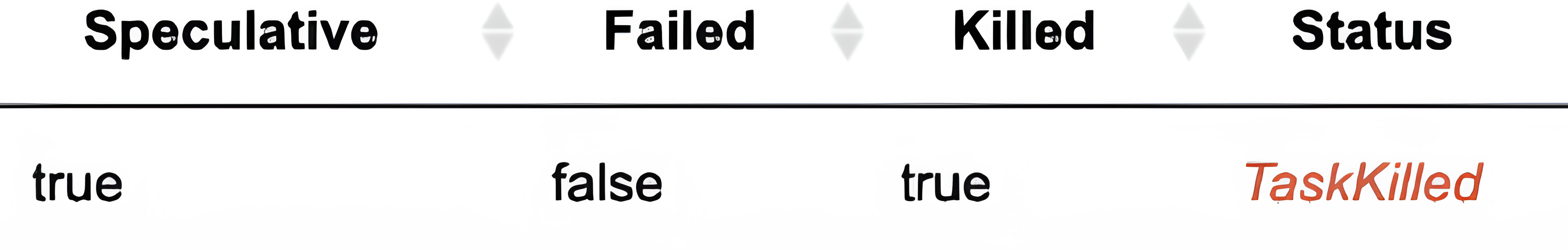
You can monitor this from the spark UI, where a task ID shown Speculative as true.
Configurations that affect this speculative behavior
| Property Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
spark.speculation |
false | If set to "true", performs speculative execution of tasks. This means if one or more tasks are running slowly in a stage, they'll be relaunched. |
spark.speculation.interval |
100 ms | How often Spark will check for tasks to speculate. |
spark.speculation.multiplier |
1.5 | This setting determines how much slower a task can be compared to the median task time before Spark considers it for speculative execution. It's a multiplier of the median task duration. Form example, if the median task time for a stage is 10 seconds, and you set spark.speculation.multiplier = 1.5, Spark will consider any task that is running for more than 15 seconds (1.5 * 10 seconds) to be slow and eligible for speculative execution. |
spark.speculation.quantile |
0.75 | Percentage of tasks completed after which Spark will start to apply speculative execution. The default is speculation starts after 75% of the tasks gets completed in a stage. |
spark.speculation.minTaskRuntime |
100 ms | This setting defines the minimum amount of time a task should run before it's considered for speculative execution. If a task completes faster than this threshold, speculative execution won't be triggered. For example, if spark.speculation.minTaskRuntime = 5 seconds, then tasks that finish in less than 5 seconds won't be speculatively executed, even if they're slower compared to others in the stage. |
Example
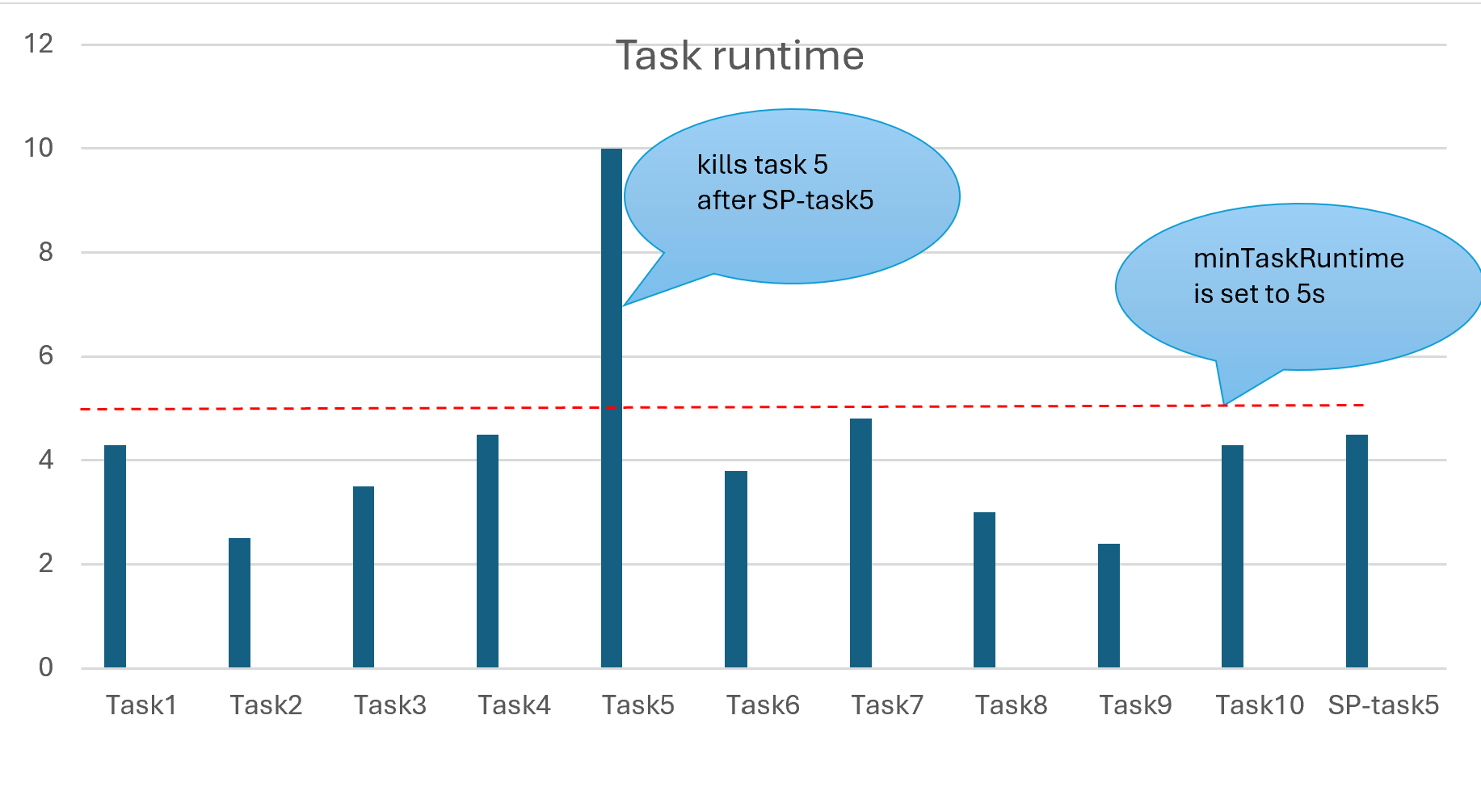
In the below chart, lets consider total 10 tasks in a stage but task 5 takes more than 5 seconds to complete.
When the spark.speculation.minTaskRuntime is set to 5 seconds, it starts a new task SP-task5 on a new node.
When job the finished, the original task 5 is killed by the driver.
When not to run a speculative execution?
- When the data is skewed, the speculated task takes same time as that of the original task increasing the resource consumption and slows the execution time. The data skewness has to be addressed first.
- When speculative execution is enabled, sometimes duplicate records are created if there's any unexpected executor or node failure. Make sure the job is idempotent.
- Enabling speculation can impact performance as duplicate tasks are being created. Make sure it's disabled if the performance is a concern.
- Speculative execution shouldn't be used for a long time period on production jobs. Extended use can result in failed tasks/capacity issues.