Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Use a combination of internal and external standard load balancers to create outbound connectivity for VMs behind an internal load balancer.
This configuration provides outbound NAT for an internal load balancer scenario, producing an "egress only" setup for your backend pool.
Note
Azure NAT Gateway is the recommended configuration for outbound connectivity in production deployments. For more information about NAT Gateway, see What is Azure NAT Gateway?.
To deploy an outbound only load balancer configuration with Azure NAT Gateway, see Tutorial: Integrate NAT gateway with an internal load balancer - Azure portal.
For more information about outbound connections in Azure and default outbound access, see Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) for outbound connections and Default outbound access.
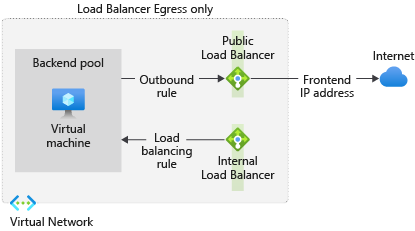
Figure: Egress only load balancer configuration
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create a trial subscription.
Create a virtual network and bastion host
Create a virtual network and bastion host
The following procedure creates a virtual network with a resource subnet, an Azure Bastion subnet, and an Azure Bastion host.
In the portal, search for and select Virtual networks.
On the Virtual networks page, select + Create.
On the Basics tab of Create virtual network, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select Create new.
Enter load-balancer-rg in Name.
Select OK.Instance details Name Enter lb-vnet. Region Select China East. Select the Security tab or Next button at the bottom of the page.
Under Azure Bastion, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Azure Bastion Enable Azure Bastion Select checkbox. Azure Bastion host name Enter lb-bastion. Azure Bastion public IP address Select Create new.
Enter lb-bastion-ip in Name.
Select OK.Select the IP addresses tab, or Next at the bottom of the page.
On Create virtual network page, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Add IPv4 address space IPv4 address space Enter 10.0.0.0/16 (65,356 addresses). Subnets Select the default subnet link to edit. Subnet template Leave the default Default. Name Enter backend-subnet. Starting address Enter 10.0.0.0. Subnet size Enter /24(256 addresses). Security NAT Gateway Select None. Select Save.
Select Review + create at the bottom of the screen, and when validation passes, select Create.
Create internal load balancer
In this section, you'll create the internal load balancer.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Load balancer. Select Load balancers in the search results.
In the Load balancer page, select Create.
In the Basics tab of the Create load balancer page, enter, or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select lb-resource-group. Instance details Name Enter lb-internal Region Select China North 3. SKU Leave the default Standard. Type Select Internal. Select Next: Frontend IP configuration at the bottom of the page.
In Frontend IP configuration, select + Add a frontend IP configuration.
Enter lb-int-frontend in Name.
Select lb-vnet in Virtual Network.
Select backend-subnet in Subnet.
Select Dynamic for Assignment.
Select Zone-redundant in Availability zone.
Note
In regions with Availability Zones, you have the option to select no-zone (default option), a specific zone, or zone-redundant. The choice will depend on your specific domain failure requirements. In regions without Availability Zones, this field won't appear.
For more information on availability zones, see Availability zones overview.Select Add.
Select Next: Backend pools at the bottom of the page.
In the Backend pools tab, select + Add a backend pool.
Enter lb-int-backend-pool for Name in Add backend pool.
Select NIC or IP Address for Backend Pool Configuration.
Select Save.
Select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
Select Create.
Create public load balancer
In this section, you'll create the public load balancer.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Load balancer. Select Load balancers in the search results.
In the Load balancer page, select Create.
In the Basics tab of the Create load balancer page, enter, or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select lb-resource-group. Instance details Name Enter lb-public Region Select China North 3. SKU Leave the default Standard. Type Select Public. Tier Leave the default Regional. Select Next: Frontend IP configuration at the bottom of the page.
In Frontend IP configuration, select + Add a frontend IP.
Enter lb-ext-frontend in Name.
Select IPv4 or IPv6 for the IP version.
Select IP address for the IP type.
Note
For more information on IP prefixes, see Azure Public IP prefix.
Select Create new in Public IP address.
In Add a public IP address, enter lb-public-ip for Name.
Select Zone-redundant in Availability zone.
Note
In regions with Availability Zones, you have the option to select no-zone (default option), a specific zone, or zone-redundant. The choice will depend on your specific domain failure requirements. In regions without Availability Zones, this field won't appear.
For more information on availability zones, see Availability zones overview.Select OK.
Select Add.
Select Next: Backend pools at the bottom of the page.
In the Backend pools tab, select + Add a backend pool.
Enter lb-pub-backend-pool for Name in Add backend pool.
Select lb-VNet in Virtual network.
Select NIC or IP Address for Backend Pool Configuration.
Select Save.
Select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
Select Create.
Create virtual machine
You'll create a virtual machine in this section. During creation, you'll add it to the backend pool of the internal load balancer. After the virtual machine is created, you'll add the virtual machine to the backend pool of the public load balancer.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual machine. Select Virtual machines in the search results.
In Virtual machines, select + Create > Virtual machine.
In Create a virtual machine, enter or select the values in the Basics tab:
Setting Value Project Details Subscription Select your Azure subscription Resource Group Select lb-resource-group Instance details Virtual machine name Enter lb-VM Region Select China North 3 Availability Options Select No infrastructure redundancy required Security type Select Standard. Image Select Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition - Gen2 Size Choose VM size or take default setting Administrator account Username Enter a username Password Enter a password Confirm password Reenter password Inbound port rules Public inbound ports Select None Select the Networking tab, or select Next: Disks, then Next: Networking.
In the Networking tab, select or enter:
Setting Value Network interface Virtual network lb-VNet Subnet backend-subnet Public IP Select None. NIC network security group Select Advanced Configure network security group Leave the default of vm-NSG. This might be different if you choose a different name for your VM. Under Load balancing, select the following:
Setting Value Load-balancing options Select Azure load balancing Select a load balancer Select lb-internal Select a backend pool Select lb-int-backend-pool Select Review + create.
Review the settings, and then select Create.
Add VM to backend pool of public load balancer
In this section, you'll add the virtual machine you created previously to the backend pool of the public load balancer.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Load balancer. Select Load balancers in the search results.
Select lb-public.
Select Backend pools in Settings in lb-public.
Select lb-pub-backend-pool under Backend pool in the Backend pools page.
In lb-pub-backend-pool, select lb-VNet in Virtual network.
In Virtual machines, select the blue + Add button.
Select the box next to lb-VM in Add virtual machines to backend pool.
Select Add.
Select Save.
Test connectivity before outbound rule
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual machine. Select Virtual machines in the search results.
Select lb-VM.
In the Overview page, select Connect, then Bastion.
Enter the username and password entered during VM creation.
Select Connect.
Open Microsoft Edge browser.
Enter https://whatsmyip.org in the address bar.
The connection should fail. By default, standard public load balancer doesn't allow outbound traffic without a defined outbound rule.
Create a public load balancer outbound rule
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Load balancer. Select Load balancers in the search results.
Select lb-public.
Select Outbound rules in Settings in lb-public.
Select + Add in Outbound rules.
Enter or select the following information to configure the outbound rule.
Setting Value Name Enter myOutboundRule. Frontend IP address Select lb-ext-frontend. Protocol Leave the default of All. Idle timeout (minutes) Move slider to 15 minutes. TCP Reset Select Enabled. Backend pool Select lb-pub-backend-pool. Port allocation Port allocation Select Manually choose number of outbound ports. Outbound ports Choose by Select Ports per instance. Ports per instance Enter 10000 Select Add.
Test connectivity after outbound rule
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual machine. Select Virtual machines in the search results.
Select lb-VM.
On the Overview page, select Connect, then Bastion.
Enter the username and password entered during VM creation.
Select Connect.
Open Microsoft Edge browser.
Enter https://whatsmyip.org in the address bar.
The connection should succeed.
The IP address displayed should be the frontend IP address of lb-public.
Clean up resources
When no longer needed, delete the resource group, load balancers, VM, and all related resources.
To do so, select the resource group lb-resource-group and then select Delete.
Next steps
In this article, you created an "egress only" configuration with a combination of public and internal load balancers.
This configuration allows you to load balance incoming internal traffic to your backend pool while still preventing any public inbound connections.
For more information about Azure Load Balancer and Azure Bastion, see What is Azure Load Balancer? and What is Azure Bastion?.