Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
 Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
 Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Responsible Artificial Intelligence (Responsible AI) is an approach to developing, assessing, and deploying AI systems safely, ethically, and with trust. AI systems result from many decisions made by their creators. Responsible AI helps guide these decisions—from defining system purpose to user interaction—toward more beneficial and equitable outcomes. It keeps people and their goals at the center of design and respects values like fairness, reliability, and transparency.
Microsoft created a Responsible AI Standard, a framework for building AI systems based on six principles: fairness, reliability and safety, privacy and security, inclusiveness, transparency, and accountability. These principles are the foundation of a responsible and trustworthy approach to AI, especially as intelligent technology becomes more common in everyday products and services.
This article explains how Azure Machine Learning provides tools to help developers and data scientists implement and operationalize these six principles.
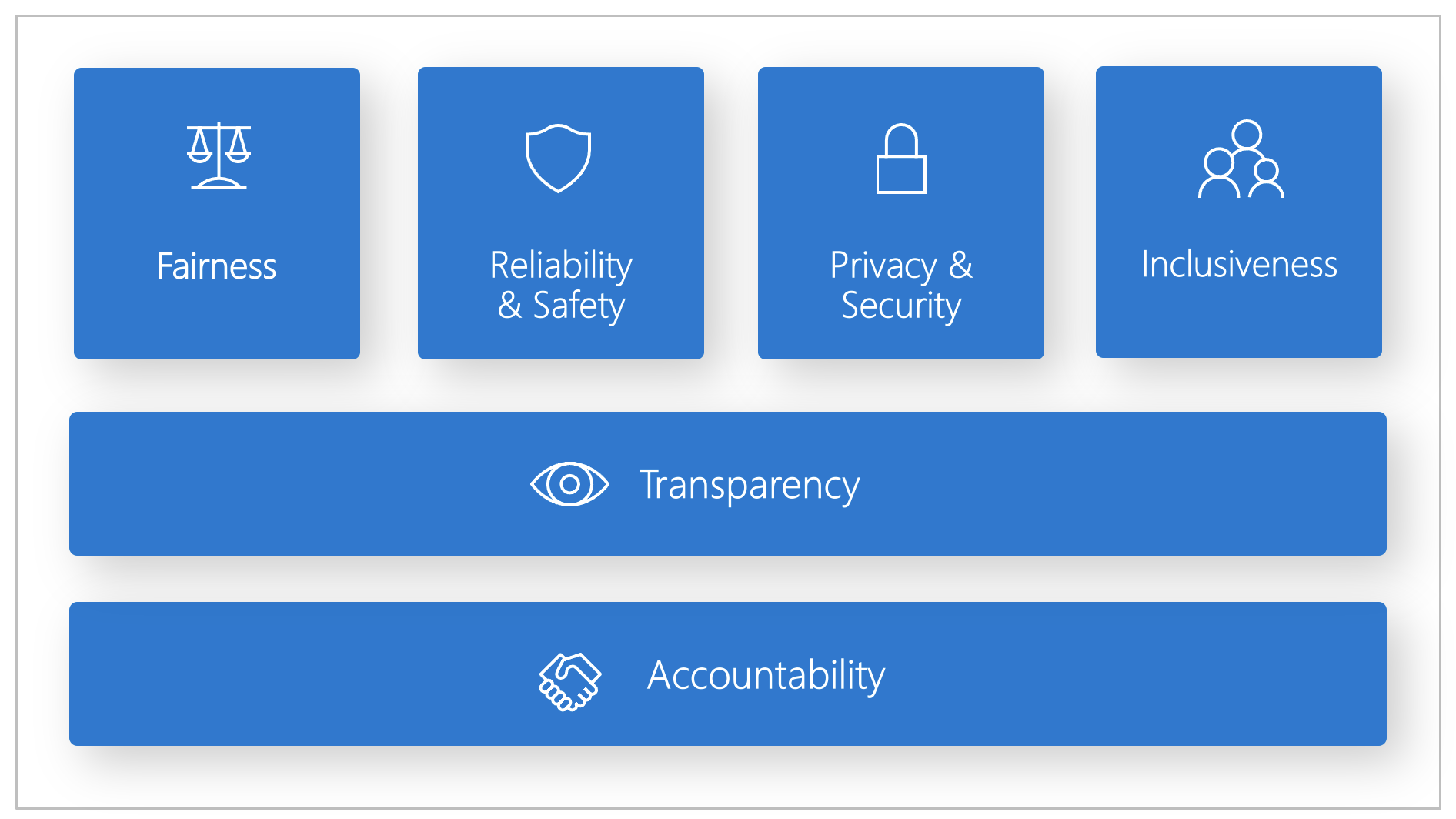
Fairness and inclusiveness
AI systems should treat everyone fairly and avoid affecting similar groups differently. For example, when AI systems provide guidance on medical treatment, loan applications, or employment, they should make the same recommendations to people with similar symptoms, financial circumstances, or qualifications.
Fairness and inclusiveness in Azure Machine Learning: The fairness assessment component of the Responsible AI dashboard helps assess model fairness across sensitive groups, such as gender, ethnicity, age, and other characteristics.
Reliability and safety
To build trust, AI systems must operate reliably, safely, and consistently. They should function as designed, respond safely to unexpected conditions, and resist harmful manipulation. Their behavior and ability to handle different conditions reflect the range of situations developers anticipated during design and testing.
Reliability and safety in Azure Machine Learning: The error analysis component of the Responsible AI dashboard helps you:
- Get a deep understanding of how failure is distributed for a model.
- Identify cohorts (subsets) of data with a higher error rate than the overall benchmark.
These discrepancies can occur when the system or model underperforms for specific demographic groups or for rarely observed input conditions in the training data.
Transparency
When AI systems inform decisions that impact people's lives, it's critical that people understand how those decisions are made. For example, a bank might use an AI system to decide if a person is creditworthy, or a company might use one to select job candidates.
A crucial part of transparency is interpretability: providing useful explanations of AI system behavior. Improving interpretability helps stakeholders understand how and why AI systems work, so they can identify performance issues, fairness concerns, exclusionary practices, or unintended outcomes.
Transparency in Azure Machine Learning: The model interpretability and counterfactual what-if components of the Responsible AI dashboard help generate human-understandable descriptions of model predictions.
The model interpretability component provides several views into a model's behavior:
- Global explanations. For example, what features affect the overall behavior of a loan allocation model?
- Local explanations. For example, why was a customer's loan application approved or rejected?
- Model explanations for a selected cohort of data points. For example, what features affect the overall behavior of a loan allocation model for low-income applicants?
The counterfactual what-if component helps you understand and debug a machine learning model by showing how it reacts to feature changes and perturbations.
Azure Machine Learning also supports a Responsible AI scorecard. The scorecard is a customizable PDF report that developers can configure, generate, download, and share with technical and non-technical stakeholders. It helps educate stakeholders about dataset and model health, achieve compliance, and build trust. The scorecard can also support audit reviews by revealing machine learning model characteristics.
Privacy and security
As AI becomes more common, protecting privacy and securing personal and business information is more important and complex. Privacy and data security require close attention because AI systems need data to make accurate predictions and decisions. AI systems must comply with privacy laws that:
- Require transparency about the collection, use, and storage of data.
- Mandate that consumers have appropriate controls to choose how their data is used.
Privacy and security in Azure Machine Learning: Azure Machine Learning enables administrators and developers to create secure configurations that comply with company policies. With Azure Machine Learning and the Azure platform, you can:
- Restrict access to resources and operations by user account or group.
- Restrict incoming and outgoing network communications.
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
- Scan for vulnerabilities.
- Apply and audit configuration policies.
Microsoft also created two open-source packages to help implement privacy and security principles:
SmartNoise: Differential privacy is a set of systems and practices that help keep the data of individuals safe and private. In machine learning solutions, differential privacy might be required for regulatory compliance. SmartNoise is an open-source project (co-developed by Microsoft) that contains components for building differentially private systems that are global.
Counterfit: Counterfit is an open-source project that comprises a command-line tool and generic automation layer to allow developers to simulate cyberattacks against AI systems. Anyone can download the tool and deploy it through Azure CLI to run in a browser, or deploy it locally in an Anaconda Python environment. It can assess AI models hosted in various cloud environments, on-premises, or in the edge. The tool is agnostic to AI models and supports various data types, including text, images, or generic input.
Accountability
People who design and deploy AI systems must be accountable for how those systems operate. Organizations should use industry standards to develop accountability norms. These norms help ensure that AI systems are not the final authority on decisions that affect people's lives and that humans maintain meaningful control over highly autonomous systems.
Accountability in Azure Machine Learning: Machine learning operations (MLOps) is based on DevOps principles and practices that improve AI workflow efficiency. Azure Machine Learning provides these MLOps capabilities for better accountability:
- Register, package, and deploy models from anywhere. You can also track the associated metadata that's required to use the model.
- Capture the governance data for the end-to-end machine learning lifecycle. The logged lineage information can include who is publishing models, why changes were made, and when models were deployed or used in production.
- Notify and alert on events in the machine learning lifecycle. Examples include experiment completion, model registration, model deployment, and data drift detection.
- Monitor applications for operational issues and issues related to machine learning. Compare model inputs between training and inference, explore model-specific metrics, and provide monitoring and alerts on your machine learning infrastructure.
In addition, the Responsible AI scorecard in Azure Machine Learning creates accountability by enabling cross-stakeholder communication. The scorecard empowers developers to configure, download, and share model health insights with both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Sharing these insights helps build trust.
Azure Machine Learning also supports decision-making by informing business decisions through:
- Data-driven insights, which help stakeholders understand causal treatment effects on outcomes using historical data only. For example, "How would a medicine affect a patient's blood pressure?" These insights come from the causal inference component of the Responsible AI dashboard.
- Model-driven insights, which answer user questions (such as "What can I do to get a different outcome from your AI next time?") so they can take action. These insights are provided through the counterfactual what-if component of the Responsible AI dashboard.
Next steps
- For more information on how to implement Responsible AI in Azure Machine Learning, see Responsible AI dashboard.
- Learn how to generate the Responsible AI dashboard via CLI and SDK or Azure Machine Learning studio UI.
- Learn how to generate a Responsible AI scorecard based on the insights observed in your Responsible AI dashboard.
- Learn about the Responsible AI Standard for building AI systems according to six key principles.