Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
This article provides information on using the Azure Machine Learning SDK v1. SDK v1 is deprecated as of March 31, 2025. Support for it will end on June 30, 2026. You can install and use SDK v1 until that date. Your existing workflows using SDK v1 will continue to operate after the end-of-support date. However, they could be exposed to security risks or breaking changes in the event of architectural changes in the product.
We recommend that you transition to the SDK v2 before June 30, 2026. For more information on SDK v2, see What is Azure Machine Learning CLI and Python SDK v2? and the SDK v2 reference.
This article shows how to access your data with the Azure Machine Learning studio. Connect to your data in Azure storage services with Azure Machine Learning datastores. Then, package that data for ML workflow tasks with Azure Machine Learning datasets.
This table defines and summarizes the benefits of datastores and datasets.
| Object | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Datastores | To securely connect to your storage service on Azure, store your connection information (subscription ID, token authorization, etc.) in the Key Vault associated with the workspace | Because your information is securely stored, you don't put authentication credentials or original data sources at risk, and you no longer need to hard code these values in your scripts |
| Datasets | Dataset creation also creates a reference to the data source location, along with a copy of its metadata. With datasets you can access data during model training, share data, collaborate with other users, and use open-source libraries, like pandas, for data exploration. | Since datasets are lazily evaluated, and the data remains in its existing location, you keep a single copy of data in your storage. Additionally, you incur no extra storage cost, you avoid unintentional changes to your original data sources, and your ML workflow performance speeds improve. |
For more information about where datastores and datasets fit in the overall Azure Machine Learning data access workflow, visit Securely access data.
For more information about the Azure Machine Learning Python SDK and a code-first experience, visit
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial subscription before you begin. Try the trial subscription.
Access to Azure Machine Learning studio
An Azure Machine Learning workspace. Create workspace resources
- When you create a workspace, an Azure blob container and an Azure file share are automatically registered to the workspace as datastores. They're named
workspaceblobstoreandworkspacefilestore, respectively. For sufficient blob storage resources, theworkspaceblobstoreis set as the default datastore, already configured for use. For more blob storage resources, you need an Azure storage account, with a supported storage type.
- When you create a workspace, an Azure blob container and an Azure file share are automatically registered to the workspace as datastores. They're named
Create datastores
You can create datastores from these Azure storage solutions. For unsupported storage solutions, and to save data egress cost during ML experiments, you must move your data to a supported Azure storage solution. For more information about datastores, visit this resource.
You can create datastores with credential-based access or identity-based access.
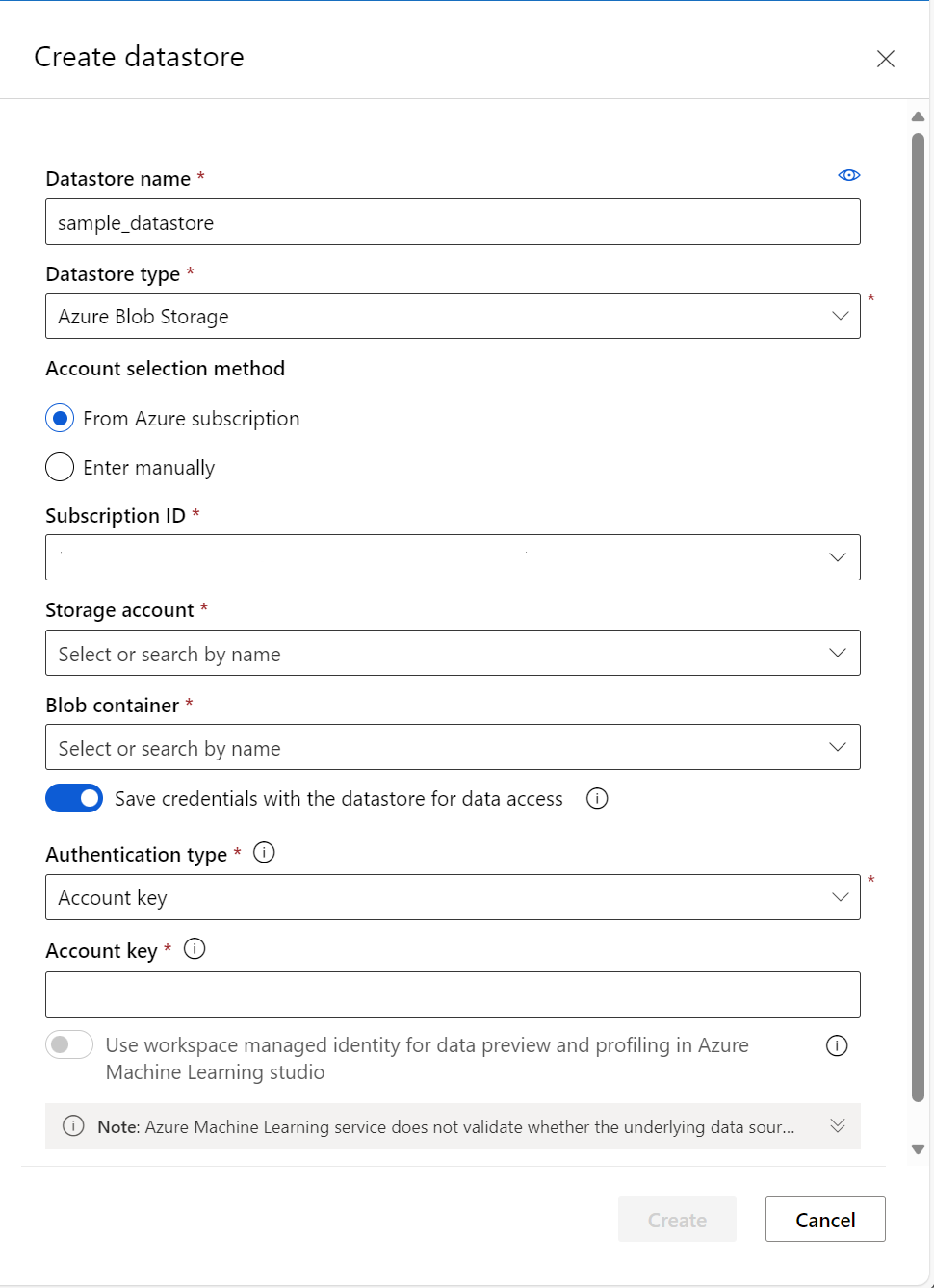
Create a new datastore with the Azure Machine Learning studio.
Important
If your data storage account is located in a virtual network, extra configuration steps are required to ensure that the studio can access your data. Visit Network isolation & privacy for more information about the appropriate configuration steps.
- Sign in to Azure Machine Learning studio.
- Select Data on the left pane under Assets.
- At the top, select Datastores.
- Select +Create.
- Complete the form to create and register a new datastore. The form intelligently updates itself based on your selections for Azure storage type and authentication type. For more information about where to find the authentication credentials needed to populate this form, visit the storage access and permissions section of this document.
The following screenshot shows the Azure blob datastore creation panel:
Create data assets
After you create a datastore, create a dataset to interact with your data. Datasets package your data into a lazily evaluated consumable object for machine learning tasks - for example, training. Visit Create Azure Machine Learning datasets for more information about datasets.
Datasets have two types: FileDataset and TabularDataset. FileDatasets create references to single or multiple files, or public URLs. TabularDatasets represent data in a tabular format. You can create TabularDatasets from
- .csv
- .tsv
- .parquet
- .json files, and from SQL query results.
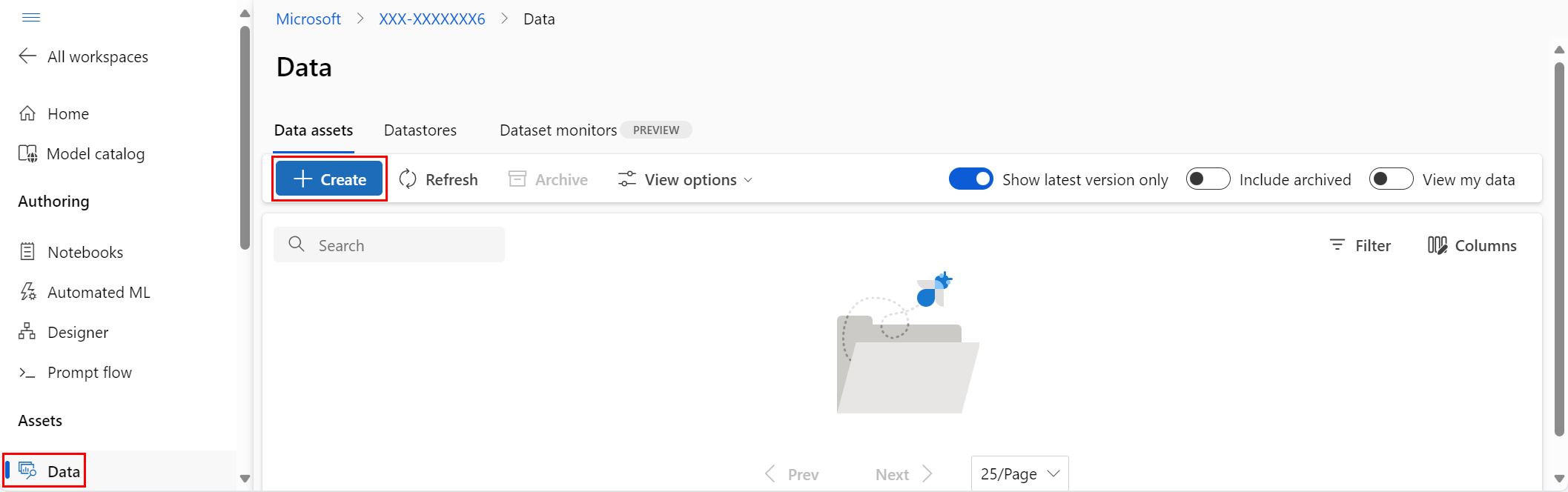
The following steps describe how to create a dataset in Azure Machine Learning studio.
Note
Datasets created through Azure Machine Learning studio are automatically registered to the workspace.
Navigate to Azure Machine Learning studio
Under Assets in the left navigation, select Data. On the Data assets tab, select Create, as shown in the following screenshot:
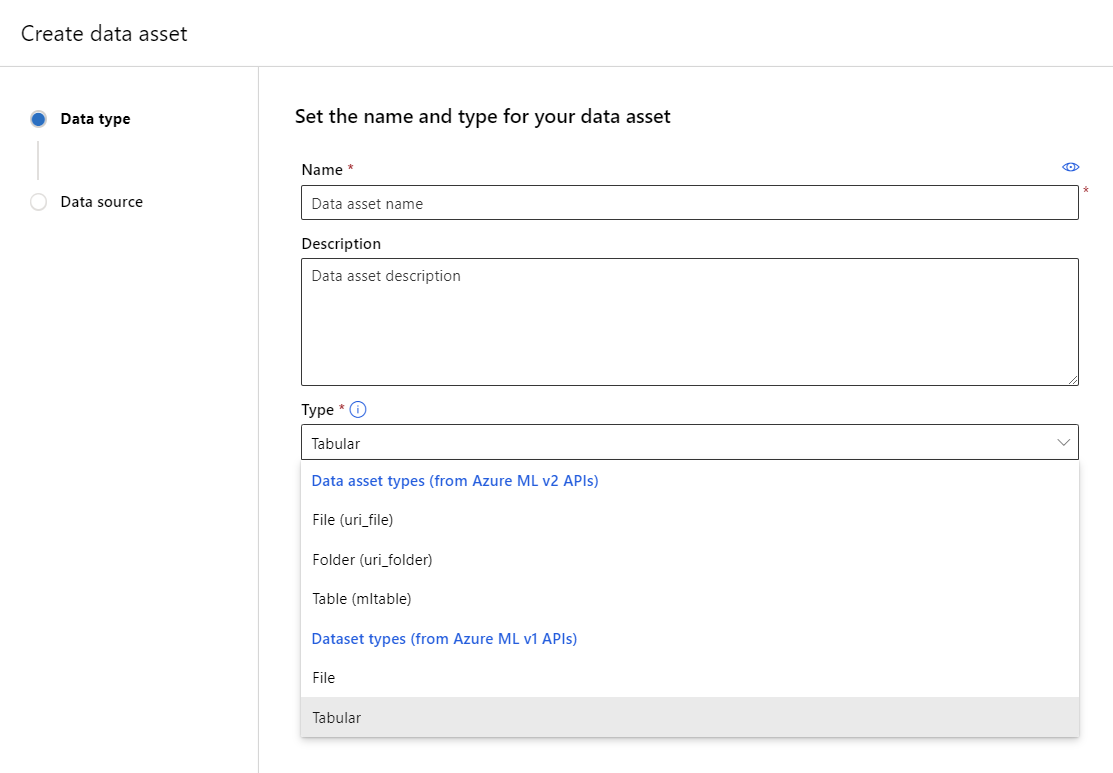
- Give the data asset a name and optional description. Then, under Type, select a Dataset type, either File or Tabular, as shown in the following screenshot:
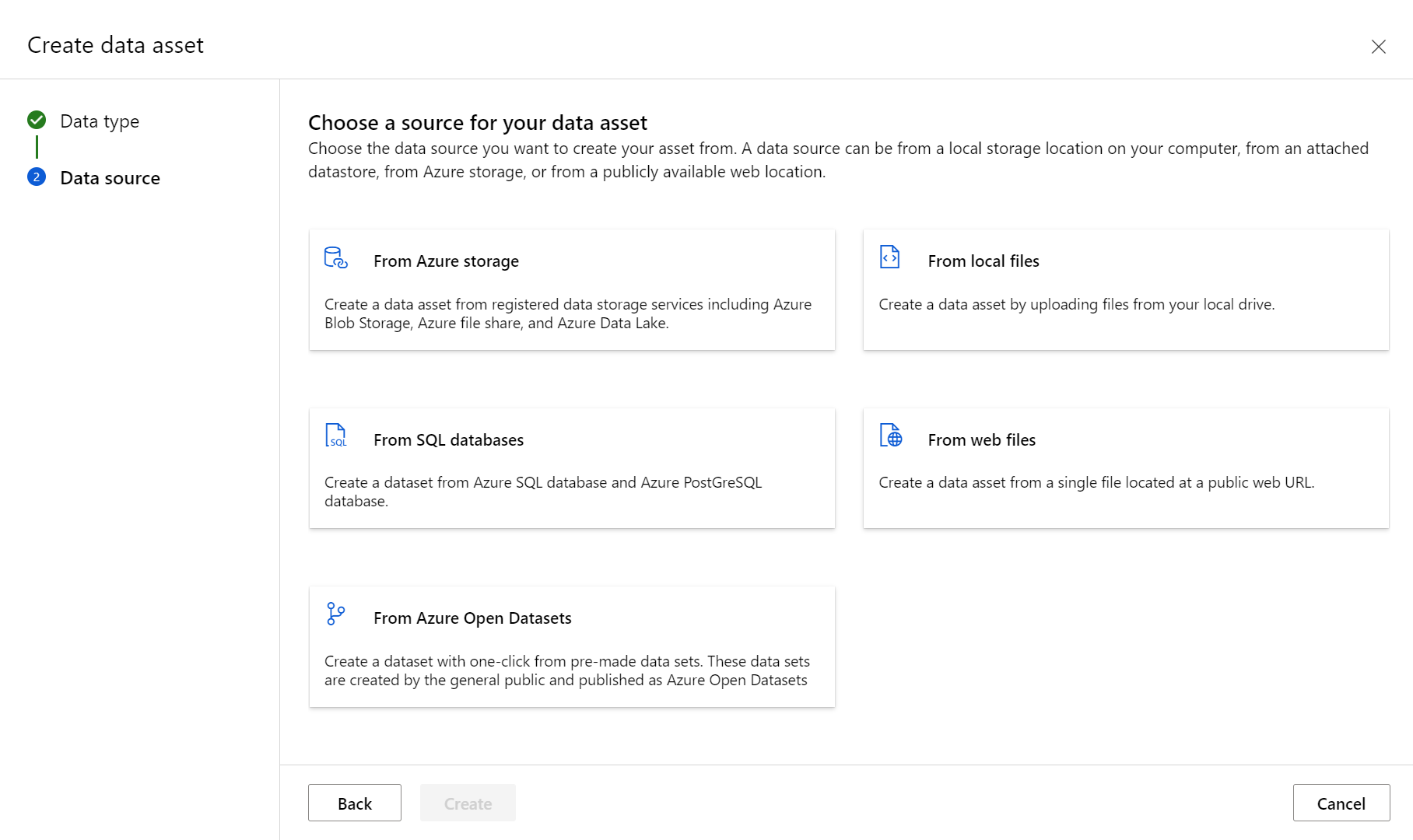
- The Data source pane opens next, as shown in the following screenshot:
You have different options for your data source. For data already stored in Azure, choose "From Azure storage." To upload data from your local drive, choose "From local files." For data stored at a public web location, choose "From web files." You can also create a data asset from a SQL database.
At the file selection step, select the location where Azure should store your data, and the data files you want to use.
- Enable skip validation if your data is in a virtual network. For more information about virtual network isolation and privacy, visit this resource.
Follow the steps to set the data parsing settings and schema for your data asset. The settings prepopulate based on file type, and you can further configure your settings before the creation of the data asset.
Once you reach the Review step, select Create on the last page
Data preview and profile
After you create your dataset, verify that you can view the preview and profile in the studio:
- Sign in to the Azure Machine Learning studio
- Under Assets in the left navigation, select Data as shown in the following screenshot:
- Select the name of the dataset you want to view.
- Select the Explore tab.
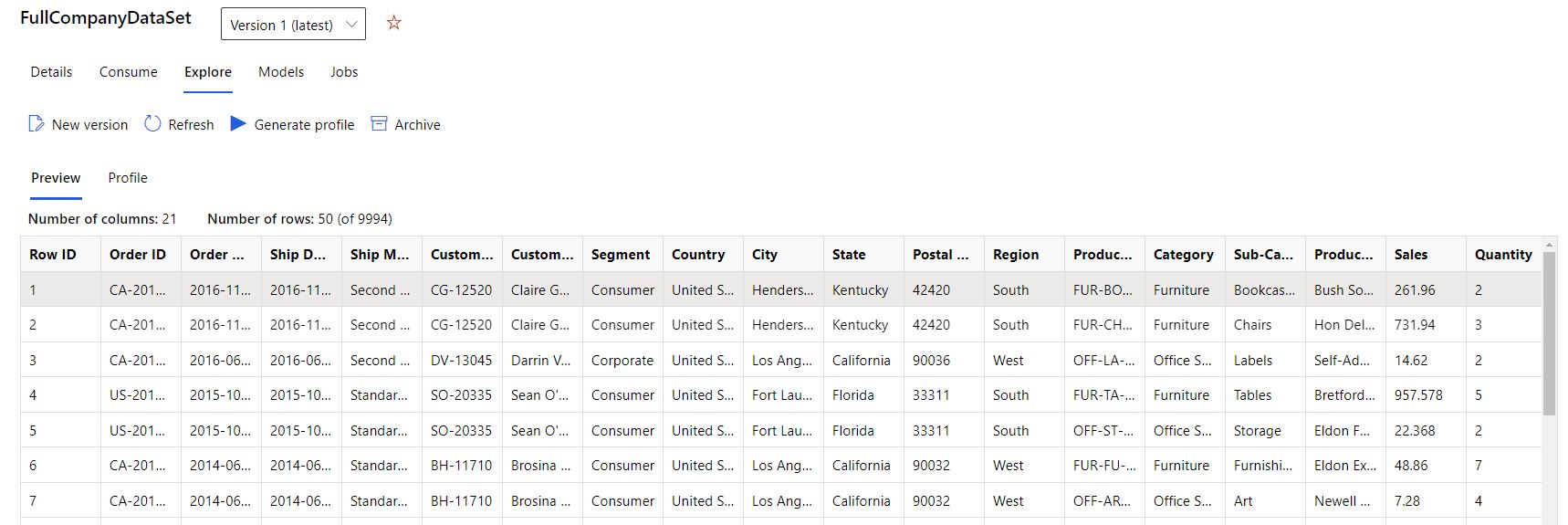
- Select the Preview tab, as shown in the following screenshot:
- Select the Profile tab, as shown in the following screenshot:
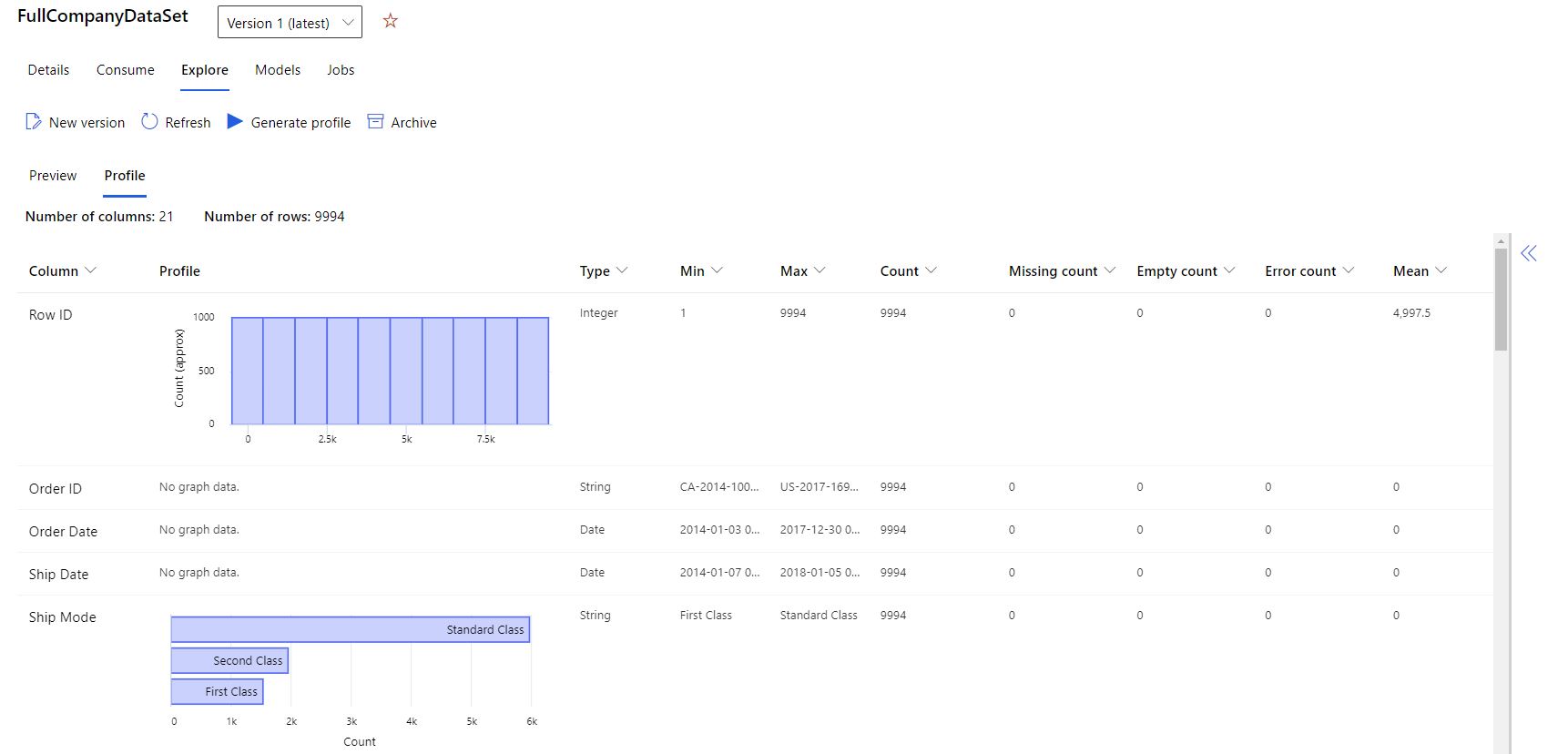
To verify whether your data set is ML-ready, you can use summary statistics across your data set. For non-numeric columns, these statistics include only basic statistical measures - for example, min, max, and error count. Numeric columns offer statistical moments and estimated quantiles.
The Azure Machine Learning dataset data profile includes:
Note
Blank entries appear for features with irrelevant types.
| Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
| Feature | The summarized column name |
| Profile | In-line visualization based on the inferred type. Strings, booleans, and dates have value counts. Decimals (numerics) have approximated histograms. These visualizations offer a quick understanding of the data distribution |
| Type distribution | In-line value count of types within a column. Nulls are their own type, so this visualization can detect odd or missing values |
| Type | Inferred column type. Possible values include: strings, booleans, dates, and decimals |
| Min | Minimum value of the column. Blank entries appear for features whose type doesn't have an inherent ordering (for example, booleans) |
| Max | Maximum value of the column. |
| Count | Total number of missing and nonmissing entries in the column |
| Not missing count | Number of entries in the column that aren't missing. Empty strings and errors are treated as values, so they don't contribute to the "not missing count." |
| Quantiles | Approximated values at each quantile, to provide a sense of the data distribution |
| Mean | Arithmetic mean or average of the column |
| Standard deviation | Measure of the amount of dispersion or variation for the data of this column |
| Variance | Measure of how far the data of this column spreads out from its average value |
| Skewness | Measures the difference of this column's data from a normal distribution |
| Kurtosis | Measures the degree of "tailness" of this column's data, compared to a normal distribution |
Storage access and permissions
To ensure that you securely connect to your Azure storage service, Azure Machine Learning requires that you have permission to access the corresponding data storage. This access depends on the authentication credentials used to register the datastore.
Virtual network
If your data storage account is in a virtual network, extra configuration steps are required to ensure that Azure Machine Learning has access to your data. Visit Use Azure Machine Learning studio in a virtual network to ensure the appropriate configuration steps are applied when you create and register your datastore.
Access validation
Warning
Cross-tenant access to storage accounts isn't supported. If your scenario needs cross-tenant access, reach out to the (Azure Machine Learning Data Support team) for assistance with a custom code solution.
As part of the initial datastore creation and registration process, Azure Machine Learning automatically validates that the underlying storage service exists and that the user-provided principal (username, service principal, or SAS token) has access to the specified storage.
After datastore creation, this validation is only performed for methods that require access to the underlying storage container. The validation is not performed each time datastore objects are retrieved. For example, validation happens when you download files from your datastore. However, if you want to change your default datastore, validation doesn't occur.
To authenticate your access to the underlying storage service, provide either your account key, shared access signatures (SAS) tokens, or service principal, according to the datastore type you want to create. The storage type matrix lists the supported authentication types that correspond to each datastore type.
You can find account key, SAS token, and service principal information at your Azure portal.
To obtain an account key for authentication, select Storage Accounts in the left pane, and choose the storage account that you want to register
- The Overview page provides information such as the account name, container, and file share name
- Expand the Security + networking node in the left nav
- Select Access keys
- The available key values serve as Account key values
To obtain an SAS token for authentication, select Storage Accounts in the left pane, and choose the storage account that you want
- To obtain an Access key value, expand the Security + networking node in the left nav
- Select Shared access signature
- Complete the process to generate the SAS value
To use a service principal for authentication, go to your App registrations and select which app you want to use
- Its corresponding Overview page contains required information like tenant ID and client ID
Important
- To change your access keys for an Azure Storage account (account key or SAS token), be sure to sync the new credentials with both your workspace and the datastores connected to it. For more information, visit sync your updated credentials.
- If you unregister and then re-register a datastore with the same name, and that re-registration fails, the Azure Key Vault for your workspace might not have soft-delete enabled. By default, soft-delete is enabled for the key vault instance created by your workspace. However, it might not be enabled if you used an existing key vault or have a workspace created before October 2020. For more information about how to enable soft-delete, visit Turn on Soft Delete for an existing key vault.
Permissions
For Azure blob container and Azure Data Lake Gen 2 storage, ensure that your authentication credentials have Storage Blob Data Reader access. Learn more about Storage Blob Data Reader. By default, an account SAS token has no permissions.
For data read access, your authentication credentials must have a minimum of list and read permissions for containers and objects.
For data write access, write and add permissions also are required.
Train with datasets
Use your datasets in your machine learning experiments for training ML models. Learn more about how to train with datasets.
Next steps
- A step-by-step example of training with TabularDatasets and automated machine learning
- Train a model
- For more dataset training examples, see the sample notebooks