Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
 Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
 Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
This article shows how to create and manage data assets in Azure Machine Learning.
Data assets can help when you need:
- Versioning: Data assets support data versioning.
- Reproducibility: Once you create a data asset version, it is immutable. It cannot be modified or deleted. Therefore, training jobs or pipelines that consume the data asset can be reproduced.
- Auditability: Because the data asset version is immutable, you can track the asset versions, who updated a version, and when the version updates occurred.
- Lineage: For any given data asset, you can view which jobs or pipelines consume the data.
- Ease-of-use: An Azure machine learning data asset resembles web browser bookmarks (favorites). Instead of remembering long storage paths (URIs) that reference your frequently-used data on Azure Storage, you can create a data asset version and then access that version of the asset with a friendly name (for example:
azureml:<my_data_asset_name>:<version>).
Tip
To access your data in an interactive session (for example, a notebook) or a job, you are not required to first create a data asset. You can use Datastore URIs to access the data. Datastore URIs offer a simple way to access data to get started with Azure Machine Learning.
Prerequisites
To create and work with data assets, you need:
An Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a Trial before you begin. Try the trial subscription.
An Azure Machine Learning workspace. Create workspace resources.
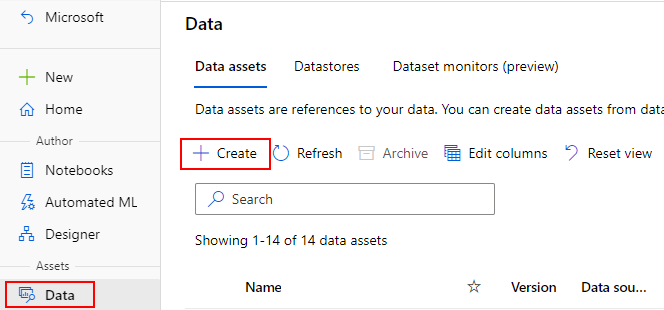
Create data assets
When you create your data asset, you need to set the data asset type. Azure Machine Learning supports three data asset types:
| Type | API | Canonical Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| File Reference a single file |
uri_file |
Read a single file on Azure Storage (the file can have any format). |
| Folder Reference a folder |
uri_folder |
Read a folder of parquet/CSV files into Pandas/Spark. Read unstructured data (images, text, audio, etc.) located in a folder. |
| Table Reference a data table |
mltable |
You have a complex schema subject to frequent changes, or you need a subset of large tabular data. AutoML with Tables. Read unstructured data (images, text, audio, etc.) data that is spread across multiple storage locations. |
Note
Only use embedded newlines in csv files if you register the data as an MLTable. Embedded newlines in csv files might cause misaligned field values when you read the data. MLTable has the support_multi_line parameter available in the read_delimited transformation, to interpret quoted line breaks as one record.
When you consume the data asset in an Azure Machine Learning job, you can either mount or download the asset to the compute nodes. For more information, please visit Modes.
Also, you must specify a path parameter that points to the data asset location. Supported paths include:
| Location | Examples |
|---|---|
| A path on your local computer | ./home/username/data/my_data |
| A path on a Datastore | azureml://datastores/<data_store_name>/paths/<path> |
| A path on a public https server | https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pandas-dev/pandas/main/doc/data/titanic.csv |
| A path on Azure Storage | (Blob) wasbs://<containername>@<accountname>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path_to_data>/(ADLS gen2) abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path> (ADLS gen1) adl://<accountname>.azuredatalakestore.net/<path_to_data>/ |
Note
When you create a data asset from a local path, it will automatically upload to the default Azure Machine Learning cloud datastore.
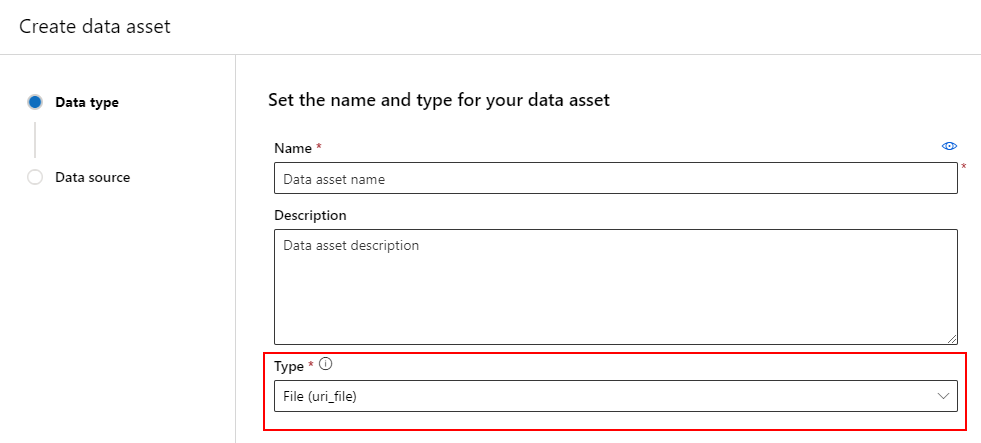
Create a data asset: File type
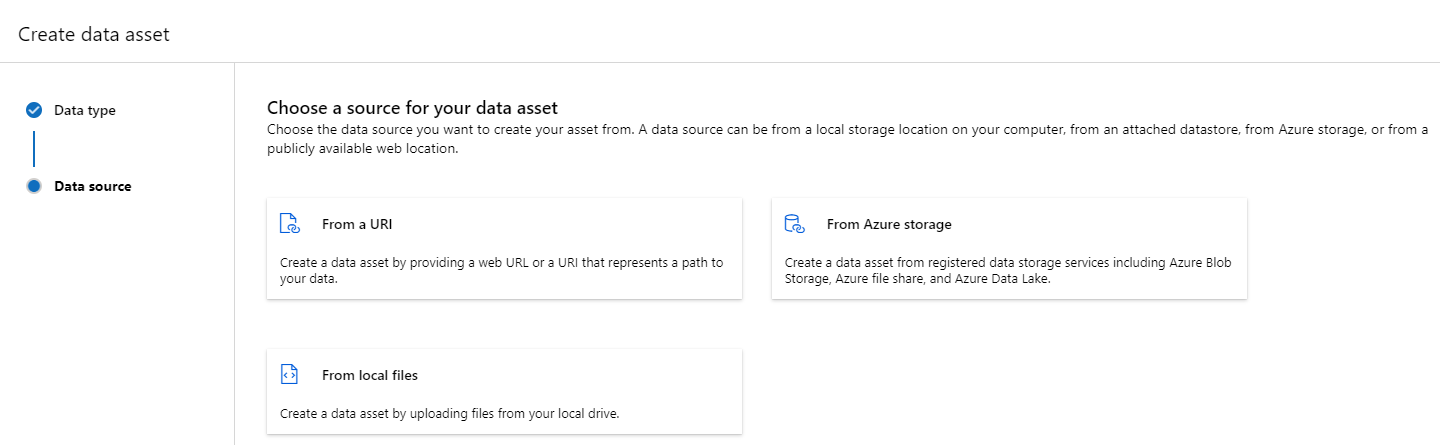
A data asset of a File (uri_file) type points to a single file on storage (for example, a CSV file). You can create a file typed data asset with:
Create a YAML file, and copy-and-paste the following code snippet. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the
- name of your data asset
- the version
- description
- path to a single file on a supported location
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/data.schema.json
# Supported paths include:
# local: './<path>/<file>' (this will be automatically uploaded to cloud storage)
# blob: 'wasbs://<container_name>@<account_name>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>/<file>'
# ADLS gen2: 'abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>/<file>'
# Datastore: 'azureml://datastores/<data_store_name>/paths/<path>/<file>'
type: uri_file
name: <NAME OF DATA ASSET>
version: <VERSION>
description: <DESCRIPTION>
path: <SUPPORTED PATH>
Next, execute the following command in the CLI. Be sure to update the <filename> placeholder to the YAML filename.
az ml data create -f <filename>.yml
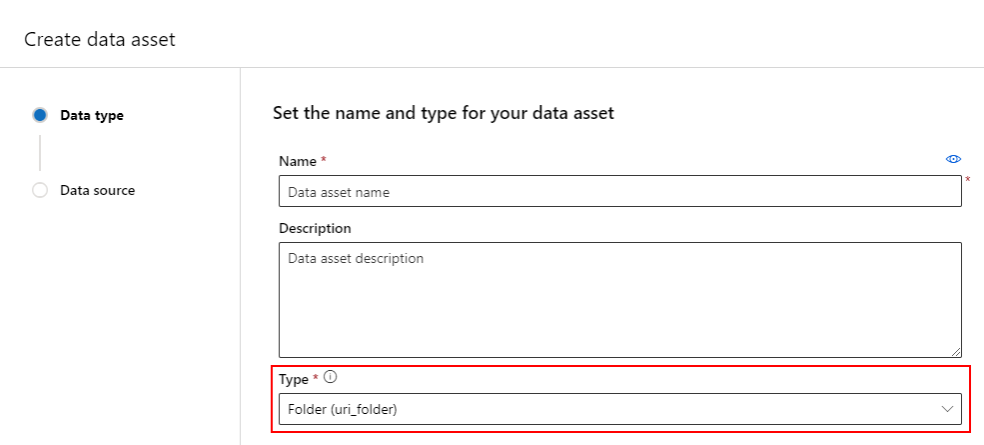
Create a data asset: Folder type
A Folder (uri_folder) type data asset points to a folder in a storage resource - for example, a folder containing several subfolders of images. You can create a folder typed data asset with:
Copy-and-paste the following code into a new YAML file. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the
- Name of your data asset
- The version
- Description
- Path to a folder on a supported location
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/data.schema.json
# Supported paths include:
# local: './<path>/<folder>' (this will be automatically uploaded to cloud storage)
# blob: 'wasbs://<container_name>@<account_name>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>/<folder>'
# ADLS gen2: 'abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>/<folder>'
# Datastore: 'azureml://datastores/<data_store_name>/paths/<path>/<folder>'
type: uri_folder
name: <NAME OF DATA ASSET>
version: <VERSION>
description: <DESCRIPTION>
path: <SUPPORTED PATH>
Next, execute the following command in the CLI. Be sure to update the <filename> placeholder to the YAML filename.
az ml data create -f <filename>.yml
Create a data asset: Table type
Azure Machine Learning Tables (MLTable) have rich functionality, described in more detail at Working with tables in Azure Machine Learning. Instead of repeating that documentation here, read this example that describes how to create a Table-typed data asset, with Titanic data located on a publicly available Azure Blob Storage account.
First, create a new directory called data, and create a file called MLTable:
mkdir data
touch MLTable
Next, copy-and-paste the following YAML into the MLTable file you created in the previous step:
Caution
Do not rename the MLTable file to MLTable.yaml or MLTable.yml. Azure Machine Learning expects an MLTable file.
paths:
- file: wasbs://data@azuremlexampledata.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/titanic.csv
transformations:
- read_delimited:
delimiter: ','
empty_as_string: false
encoding: utf8
header: all_files_same_headers
include_path_column: false
infer_column_types: true
partition_size: 20971520
path_column: Path
support_multi_line: false
- filter: col('Age') > 0
- drop_columns:
- PassengerId
- convert_column_types:
- column_type:
boolean:
false_values:
- 'False'
- 'false'
- '0'
mismatch_as: error
true_values:
- 'True'
- 'true'
- '1'
columns: Survived
type: mltable
Execute the following command in the CLI. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the data asset name and version values.
az ml data create --path ./data --name <DATA ASSET NAME> --version <VERSION> --type mltable
Important
The path should be a folder that contains a valid MLTable file.
Creating data assets from job outputs
You can create a data asset from an Azure Machine Learning job. To do this, set the name parameter in the output. In this example, you submit a job that copies data from a public blob store to your default Azure Machine Learning Datastore and creates a data asset called job_output_titanic_asset.
Create a job specification YAML file (<file-name>.yml):
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/commandJob.schema.json
# path: Set the URI path for the data. Supported paths include
# local: `./<path>
# Blob: wasbs://<container_name>@<account_name>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>
# ADLS: abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>
# Datastore: azureml://datastores/<data_store_name>/paths/<path>
# Data Asset: azureml:<my_data>:<version>
# type: What type of data are you pointing to?
# uri_file (a specific file)
# uri_folder (a folder)
# mltable (a table)
# mode: Set INPUT mode:
# ro_mount (read-only mount)
# download (download from storage to node)
# mode: Set the OUTPUT mode
# rw_mount (read-write mount)
# upload (upload data from node to storage)
type: command
command: cp ${{inputs.input_data}} ${{outputs.output_data}}
compute: azureml:cpu-cluster
environment: azureml://registries/azureml/environments/sklearn-1.1/versions/4
inputs:
input_data:
mode: ro_mount
path: wasbs://data@azuremlexampledata.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/titanic.csv
type: uri_file
outputs:
output_data:
mode: rw_mount
path: azureml://datastores/workspaceblobstore/paths/quickstart-output/titanic.csv
type: uri_file
name: job_output_titanic_asset
Next, submit the job using the CLI:
az ml job create --file <file-name>.yml
Manage data assets
Delete a data asset
Important
By design, data asset deletion is not supported.
If Azure Machine Learning allowed data asset deletion, it would have the following adverse and negative effects:
- Production jobs that consume data assets that were later deleted would fail.
- It would become more difficult to reproduce an ML experiment.
- Job lineage would break, because it would become impossible to view the deleted data asset version.
- You wouldn't be able to track and audit correctly, since versions could be missing.
Therefore, the immutability of data assets provides a level of protection when working in a team creating production workloads.
For a mistakenly created data asset - for example, with an incorrect name, type or path - Azure Machine Learning offers solutions to handle the situation without the negative consequences of deletion:
| I want to delete this data asset because... | Solution |
|---|---|
| The name is incorrect | Archive the data asset |
| The team no longer uses the data asset | Archive the data asset |
| It clutters the data asset listing | Archive the data asset |
| The path is incorrect | Create a new version of the data asset (same name) with the correct path. For more information, visit Create data assets. |
| It has an incorrect type | At this time, Azure Machine Learning doesn't allow the creation of a new version with a different type compared to the initial version. (1) Archive the data asset (2) Create a new data asset under a different name with the correct type. |
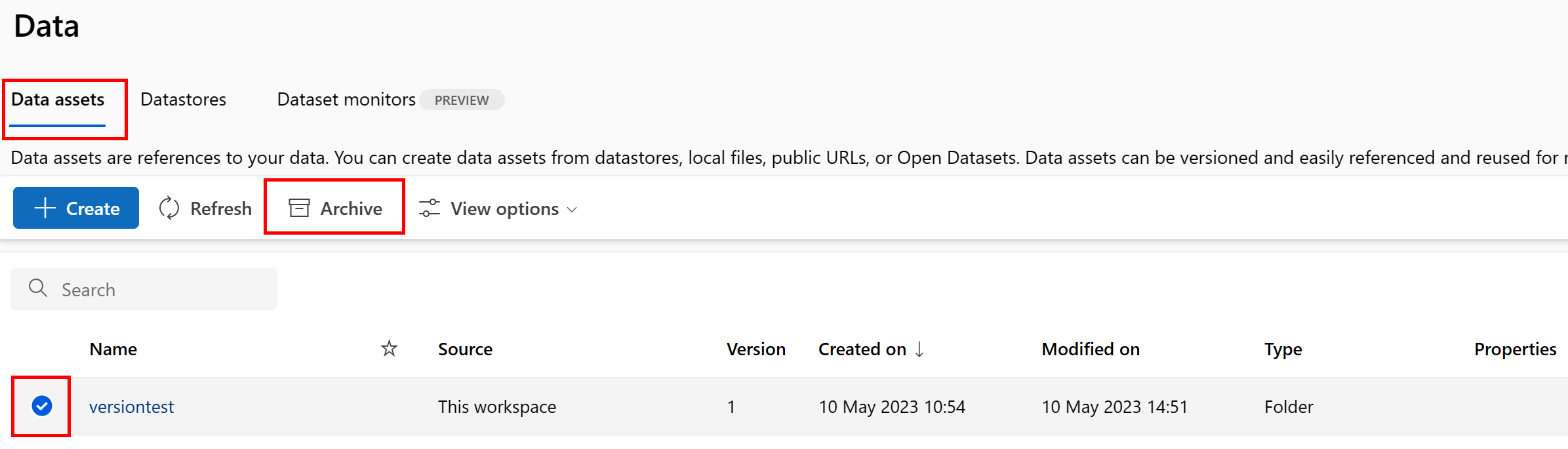
Archive a data asset
Archiving a data asset hides it by default from both list queries (for example, in the CLI az ml data list) and the data asset listing in the Studio UI. You can still continue to reference and use an archived data asset in your workflows. You can archive either:
- All versions of the data asset under a given name
Or
- A specific data asset version
Archive all versions of a data asset
To archive all versions of the data asset under a given name, use:
Execute the following command. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with your information.
az ml data archive --name <NAME OF DATA ASSET>
Archive a specific data asset version
To archive a specific data asset version, use:
Execute the following command. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the name of your data asset and version.
az ml data archive --name <NAME OF DATA ASSET> --version <VERSION TO ARCHIVE>
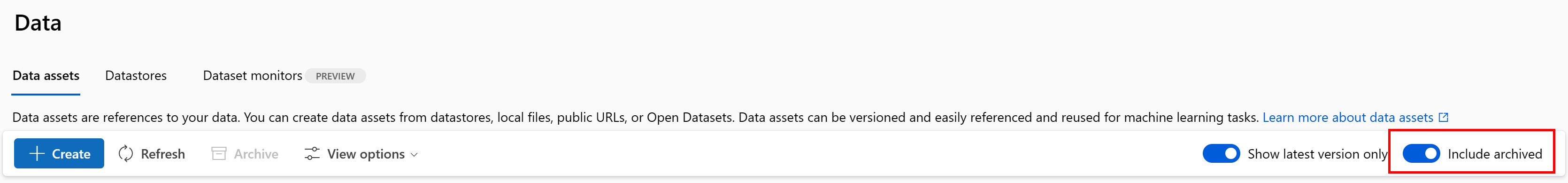
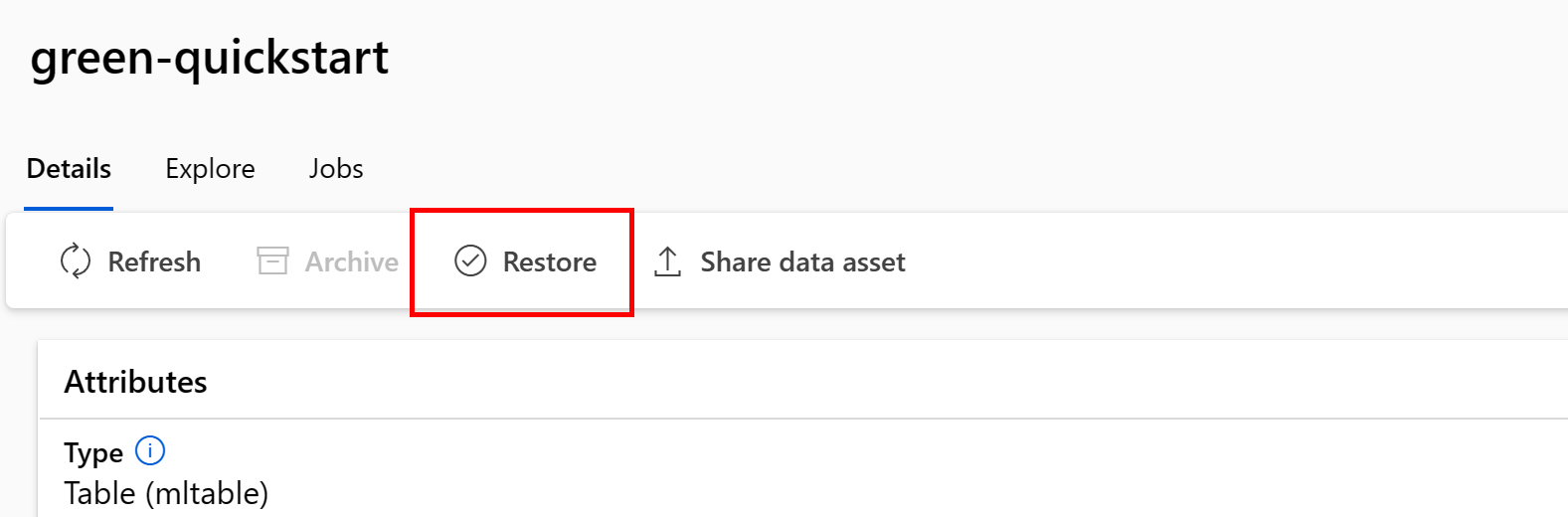
Restore an archived data asset
You can restore an archived data asset. If all of versions of the data asset are archived, you can't restore individual versions of the data asset - you must restore all versions.
Restore all versions of a data asset
To restore all versions of the data asset under a given name, use:
Execute the following command. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the name of your data asset.
az ml data restore --name <NAME OF DATA ASSET>
Restore a specific data asset version
Important
If all data asset versions were archived, you can't restore individual versions of the data asset - you must restore all versions.
To restore a specific data asset version, use:
Execute the following command. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the name of your data asset and version.
az ml data restore --name <NAME OF DATA ASSET> --version <VERSION TO ARCHIVE>
Data lineage
Data lineage is broadly understood as the lifecycle that spans the origin of the data, and where it moves over time across storage. Different kinds of backwards-looking scenarios use it, for example
- Troubleshooting
- Tracing root causes in ML pipelines
- Debugging
Data quality analysis, compliance and "what if" scenarios also use lineage. Lineage is represented visually to show data moving from source to destination, and additionally covers data transformations. Given the complexity of most enterprise data environments, these views can become hard to understand without consolidation or masking of peripheral data points.
In an Azure Machine Learning Pipeline, data assets show the origin of the data and how the data was processed, for example:
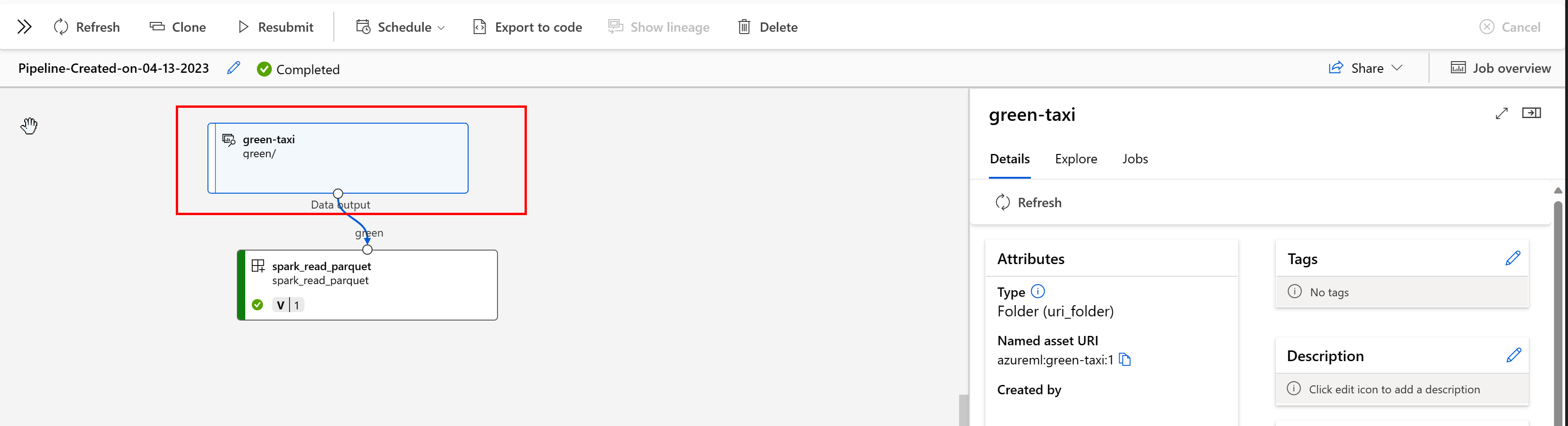
You can view the jobs that consume the data asset in the Studio UI. First, select Data from the left-hand menu, and then select the data asset name. Note the jobs consuming the data asset:
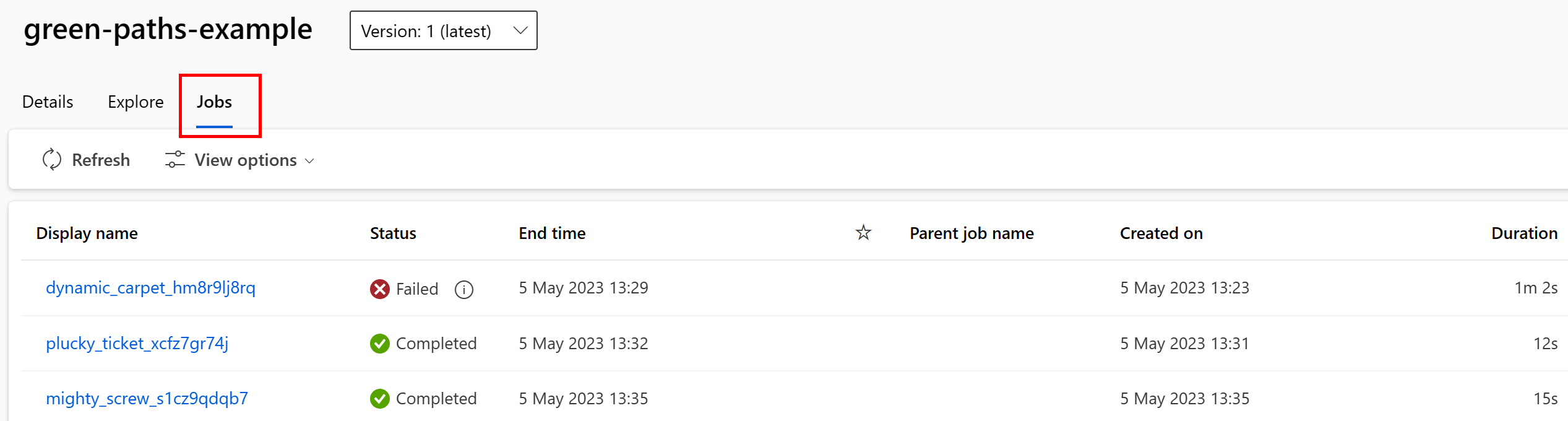
The jobs view in Data assets makes it easier to find job failures and do root-cause analysis in your ML pipelines and debugging.
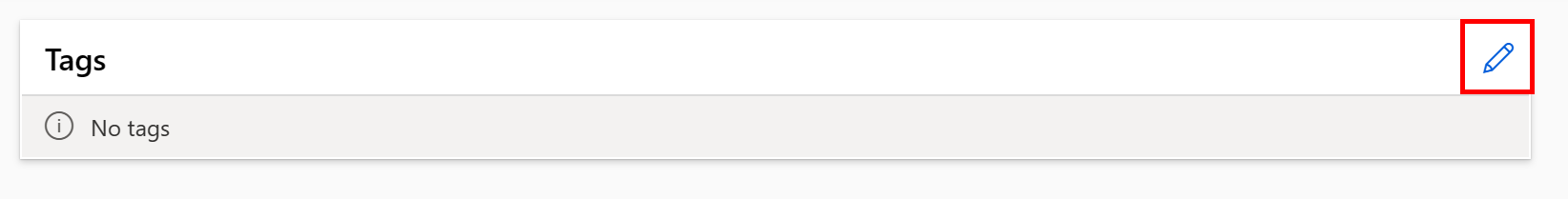
Data asset tagging
Data assets support tagging, which is extra metadata applied to the data asset as a key-value pair. Data tagging provides many benefits:
- Data quality description. For example, if your organization uses a medallion lakehouse architecture, you can tag assets with
medallion:bronze(raw),medallion:silver(validated), andmedallion:gold(enriched). - Efficient searching and filtering of data, to help data discovery.
- Identification of sensitive personal data, to properly manage and govern data access. For example,
sensitivity:PII/sensitivity:nonPII. - Determination of whether or not data is approved by a responsible AI (RAI) audit. For example,
RAI_audit:approved/RAI_audit:todo.
You can add tags to data assets as part of their creation flow, or you can add tags to existing data assets. This section shows both:
Add tags as part of the data asset creation flow
Create a YAML file, and copy-and-paste the following code into that YAML file. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the
- name of your data asset
- the version
- description
- tags (key-value pairs)
- path to a single file on a supported location
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/data.schema.json
# Supported paths include:
# local: './<path>/<file>' (this will be automatically uploaded to cloud storage)
# blob: 'wasbs://<container_name>@<account_name>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>/<file>'
# ADLS gen2: 'abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<path>/<file>'
# Datastore: 'azureml://datastores/<data_store_name>/paths/<path>/<file>'
# Data asset types, use one of:
# uri_file, uri_folder, mltable
type: uri_file
name: <NAME OF DATA ASSET>
version: <VERSION>
description: <DESCRIPTION>
tags:
<KEY1>: <VALUE>
<KEY2>: <VALUE>
path: <SUPPORTED PATH>
Execute the following command in the CLI. Be sure to update the <filename> placeholder to the YAML filename.
az ml data create -f <filename>.yml
Add tags to an existing data asset
Execute the following command in the Azure CLI. Be sure to update the <> placeholders with the
- Name of your data asset
- The version
- Key-value pair for the tag
az ml data update --name <DATA ASSET NAME> --version <VERSION> --set tags.<KEY>=<VALUE>
Versioning best practices
Typically, your ETL processes organize your folder structure on Azure storage by time, for example:
/
└── 📁 mydata
├── 📁 year=2022
│ ├── 📁 month=11
│ │ └── 📄 file1
│ │ └── 📄 file2
│ └── 📁 month=12
│ └── 📄 file1
│ │ └── 📄 file2
└── 📁 year=2023
└── 📁 month=1
└── 📄 file1
│ │ └── 📄 file2
The combination of time/version structured folders and Azure Machine Learning Tables (MLTable) allows you to construct versioned datasets. A hypothetical example shows how to achieve versioned data with Azure Machine Learning Tables. Suppose you have a process that uploads camera images to Azure Blob storage every week, in this structure:
/myimages
└── 📁 year=2022
├── 📁 week52
│ ├── 📁 camera1
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
│ └── 📁 camera2
│ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
└── 📁 year=2023
├── 📁 week1
│ ├── 📁 camera1
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
│ └── 📁 camera2
│ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
Note
While we show how to version image (jpeg) data, the same approach works for any file type (for example, Parquet, CSV).
With Azure Machine Learning Tables (mltable), construct a Table of paths that include the data up to the end of the first week in 2023. Then create a data asset:
import mltable
from mltable import MLTableHeaders, MLTableFileEncoding, DataType
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient
from azure.ai.ml.entities import Data
from azure.ai.ml.constants import AssetTypes
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
# The ** in the pattern below will glob all sub-folders (camera1, ..., camera2)
paths = [
{
"pattern": "abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/myimages/year=2022/week=52/**/*.jpeg"
},
{
"pattern": "abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/myimages/year=2023/week=1/**/*.jpeg"
},
]
tbl = mltable.from_paths(paths)
tbl.save("./myimages")
# Connect to the AzureML workspace
subscription_id = "<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>"
resource_group = "<RESOURCE_GROUP>"
workspace = "<AZUREML_WORKSPACE_NAME>"
ml_client = MLClient(
DefaultAzureCredential(), subscription_id, resource_group, workspace
)
# Define the Data asset object
my_data = Data(
path=mltable_folder,
type=AssetTypes.MLTABLE,
description="My images. Version includes data through to 2023-Jan-08.",
name="myimages",
version="20230108",
)
# Create the data asset in the workspace
ml_client.data.create_or_update(my_data)
At the end of the following week, your ETL updated the data to include more data:
/myimages
└── 📁 year=2022
├── 📁 week52
│ ├── 📁 camera1
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
│ └── 📁 camera2
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
└── 📁 year=2023
├── 📁 week1
│ ├── 📁 camera1
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
│ └── 📁 camera2
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
├── 📁 week2
│ ├── 📁 camera1
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
│ └── 📁 camera2
│ │ └── 🖼️ file1.jpeg
│ │ └── 🖼️ file2.jpeg
The first version (20230108) continues to only mount/download files from year=2022/week=52 and year=2023/week=1 because the paths are declared in the MLTable file. This ensures reproducibility for your experiments. To create a new version of the data asset that includes year=2023/week2, use:
import mltable
from mltable import MLTableHeaders, MLTableFileEncoding, DataType
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient
from azure.ai.ml.entities import Data
from azure.ai.ml.constants import AssetTypes
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
# The ** in the pattern below will glob all sub-folders (camera1, ..., camera2)
paths = [
{
"pattern": "abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/myimages/year=2022/week=52/**/*.jpeg"
},
{
"pattern": "abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/myimages/year=2023/week=1/**/*.jpeg"
},
{
"pattern": "abfss://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/myimages/year=2023/week=2/**/*.jpeg"
},
]
# Save to an MLTable file on local storage
tbl = mltable.from_paths(paths)
tbl.save("./myimages")
# Next, you create a data asset - the MLTable file will automatically be uploaded
# Connect to the AzureML workspace
subscription_id = "<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>"
resource_group = "<RESOURCE_GROUP>"
workspace = "<AZUREML_WORKSPACE_NAME>"
ml_client = MLClient(
DefaultAzureCredential(), subscription_id, resource_group, workspace
)
# Define the Data asset object
my_data = Data(
path=mltable_folder,
type=AssetTypes.MLTABLE,
description="My images. Version includes data through to 2023-Jan-15.",
name="myimages",
version="20230115", # update version to the date
)
# Create the data asset in the workspace
ml_client.data.create_or_update(my_data)
You now have two versions of the data, where the name of the version corresponds to the date the images were uploaded to storage:
- 20230108: The images up to 2023-Jan-08.
- 20230115: The images up to 2023-Jan-15.
In both cases, MLTable constructs a table of paths that only include the images up to those dates.
In an Azure Machine Learning job you can mount or download those paths in the versioned MLTable to your compute target using either the eval_download or eval_mount modes:
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient, command, Input
from azure.ai.ml.entities import Environment
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from azure.ai.ml.constants import InputOutputModes
# connect to the AzureML workspace
ml_client = MLClient.from_config(
DefaultAzureCredential()
)
# Get the 20230115 version of the data
data_asset = ml_client.data.get(name="myimages", version="20230115")
input = {
"images": Input(type="mltable",
path=data_asset.id,
mode=InputOutputModes.EVAL_MOUNT
)
}
cmd = """
ls ${{inputs.images}}/**
"""
job = command(
command=cmd,
inputs=input,
compute="cpu-cluster",
environment="azureml://registries/azureml/environments/sklearn-1.1/versions/4"
)
ml_client.jobs.create_or_update(job)
Note
The eval_mount and eval_download modes are unique to MLTable. In this case, the Azure Machine Learning data runtime capability evaluates the MLTable file and mounts the paths on the compute target.