Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to set up event-driven applications, processes, or CI/CD workflows based on Azure Machine Learning events. For example, failure notification emails or ML pipeline runs, when certain conditions are detected using Azure Event Grid.
Azure Machine Learning manages the entire lifecycle of machine learning process, including model training, model deployment, and monitoring. You can use Event Grid to react to Azure Machine Learning events, such as the completion of training runs, the registration and deployment of models, and the detection of data drift, by using modern serverless architectures. You can then subscribe and consume events such as run status changed, run completion, model registration, model deployment, and data drift detection within a workspace.
When to use Event Grid for event driven actions:
- Send emails on run failure and run completion
- Use an Azure function after a model is registered
- Streaming events from Azure Machine Learning to various of endpoints
- Trigger an ML pipeline when drift is detected
Important
Items marked (preview) in this article are currently in public preview. The preview version is provided without a service level agreement, and it's not recommended for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Azure Previews.
Prerequisites
To use Event Grid, you need contributor or owner access to the Azure Machine Learning workspace you create events for.
The event model & types
Azure Event Grid reads events from sources, such as Azure Machine Learning and other Azure services. These events are then sent to event handlers such as Azure Event Hubs, Azure Functions, Logic Apps, and others. The following diagram shows how Event Grid connects sources and handlers, but isn't a comprehensive list of supported integrations.
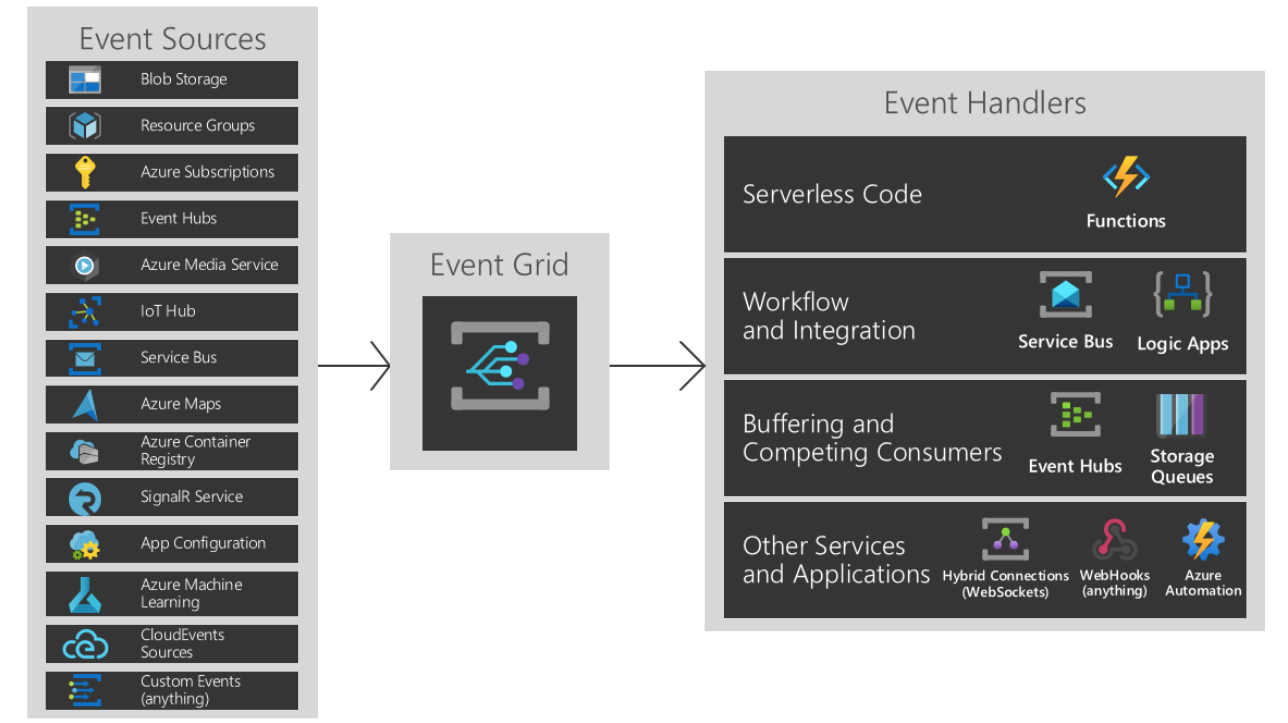
For more information on event sources and event handlers, see What is Event Grid?
Event types for Azure Machine Learning
Azure Machine Learning provides events in the various points of machine learning lifecycle:
| Event type | Description |
|---|---|
Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.RunCompleted |
Raised when a machine learning experiment run is completed |
Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelRegistered (preview) |
Raised when a machine learning model is registered in the workspace |
Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelDeployed (preview) |
Raised when a deployment of inference service with one or more models is completed |
Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.DatasetDriftDetected (preview) |
Raised when a data drift detection job for two datasets is completed |
Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.RunStatusChanged |
Raised when a run status is changed |
Filter & subscribe to events
These events are published through Azure Event Grid. From the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI, you can easily subscribe to events by specifying one or more event types, and filtering conditions.
When setting up your events, you can apply filters to only trigger on specific event data. In the following example, for run status changed events, you can filter by run types. The event only triggers when the criteria are met. For more information on the event data you can filter on, see the Azure Machine Learning Event Grid schema.
Subscriptions for Azure Machine Learning events are protected by Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC). Only contributor or owner of a workspace can create, update, and delete event subscriptions. Filters can be applied to event subscriptions either during the creation of the event subscription or at a later time.
Go to the Azure portal, select a new subscription or an existing one.
Select the Events entry from the left pane, and then select + Event subscription.
Select the filters tab and scroll down to Advanced filters. For the Key and Value, provide the property types you want to filter by. Here you can see the event triggers when the run type is a pipeline run or pipeline step run.
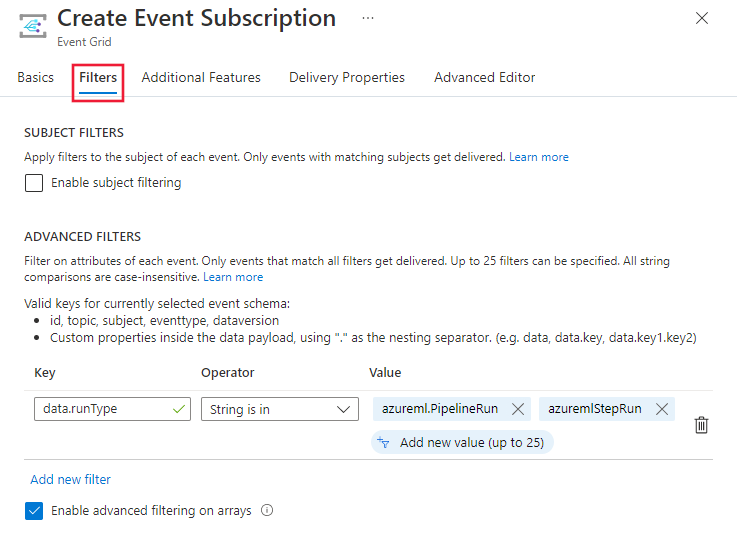
Filter by event type: An event subscription can specify one or more Azure Machine Learning event types.
Filter by event subject: Azure Event Grid supports subject filters based on begins with and ends with matches, so that events with a matching subject are delivered to the subscriber. Different machine learning events have different subject format.
Event type Subject format Sample subject Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.RunCompletedexperiments/{ExperimentId}/runs/{RunId}experiments/b1d7966c-f73a-4c68-b846-992ace89551f/runs/my_exp1_1554835758_38dbaa94Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelRegistered(preview)models/{modelName}:{modelVersion}models/sklearn_regression_model:3Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelDeployed(preview)endpoints/{serviceId}endpoints/my_sklearn_aksMicrosoft.MachineLearningServices.DatasetDriftDetected(preview)datadrift/{data.DataDriftId}/run/{data.RunId}datadrift/4e694bf5-712e-4e40-b06a-d2a2755212d4/run/my_driftrun1_1550564444_fbbcdc0fMicrosoft.MachineLearningServices.RunStatusChangedexperiments/{ExperimentId}/runs/{RunId}experiments/b1d7966c-f73a-4c68-b846-992ace89551f/runs/my_exp1_1554835758_38dbaa94Advanced filtering: Azure Event Grid also supports advanced filtering based on published event schema. Azure Machine Learning event schema details can be found in Azure Event Grid event schema for Azure Machine Learning. For
Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelRegisteredevent, to filter model's tag value:--advanced-filter data.ModelTags.key1 StringIn ('value1')To learn more about how to apply filters, see Filter events for Event Grid.
Consume Machine Learning events
Applications that handle Machine Learning events should follow a few recommended practices:
- As multiple subscriptions can be configured to route events to the same event handler, it is important not to assume events are from a particular source, but to check the topic of the message to ensure that it comes from the machine learning workspace you are expecting.
- Similarly, check that the eventType is one you are prepared to process, and do not assume that all events you receive will be the types you expect.
- As messages can arrive out of order and after some delay, use the etag fields to understand if your information about objects is still up-to-date. Also, use the sequencer fields to understand the order of events on any particular object.
- Ignore fields you don't understand. This practice will help keep you resilient to new features that might be added in the future.
- Failed or cancelled Azure Machine Learning operations will not trigger an event. For example, if a model deployment fails Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelDeployed won't be triggered. Consider such failure mode when design your applications. You can always use Azure Machine Learning SDK, CLI or portal to check the status of an operation and understand the detailed failure reasons.
Azure Event Grid allows customers to build decoupled message handlers, which can be triggered by Azure Machine Learning events. Some notable examples of message handlers are:
- Azure Functions
- Azure Logic Apps
- Azure Event Hubs
- Azure Data Factory Pipeline
- Generic webhooks, which might be hosted on the Azure platform or elsewhere
Set up in Azure portal
Open the Azure portal and go to your Azure Machine Learning workspace.
From the left bar, select Events and then select Event Subscriptions.
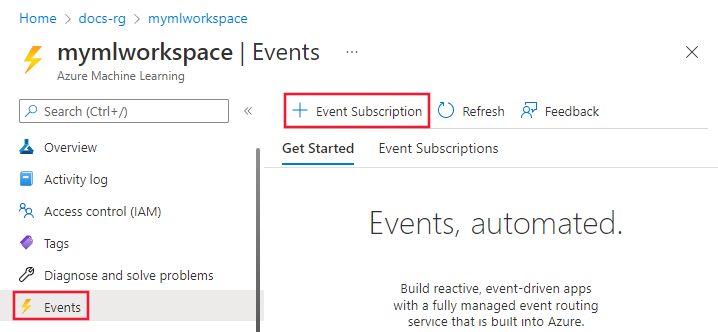
Select the event type to consume.
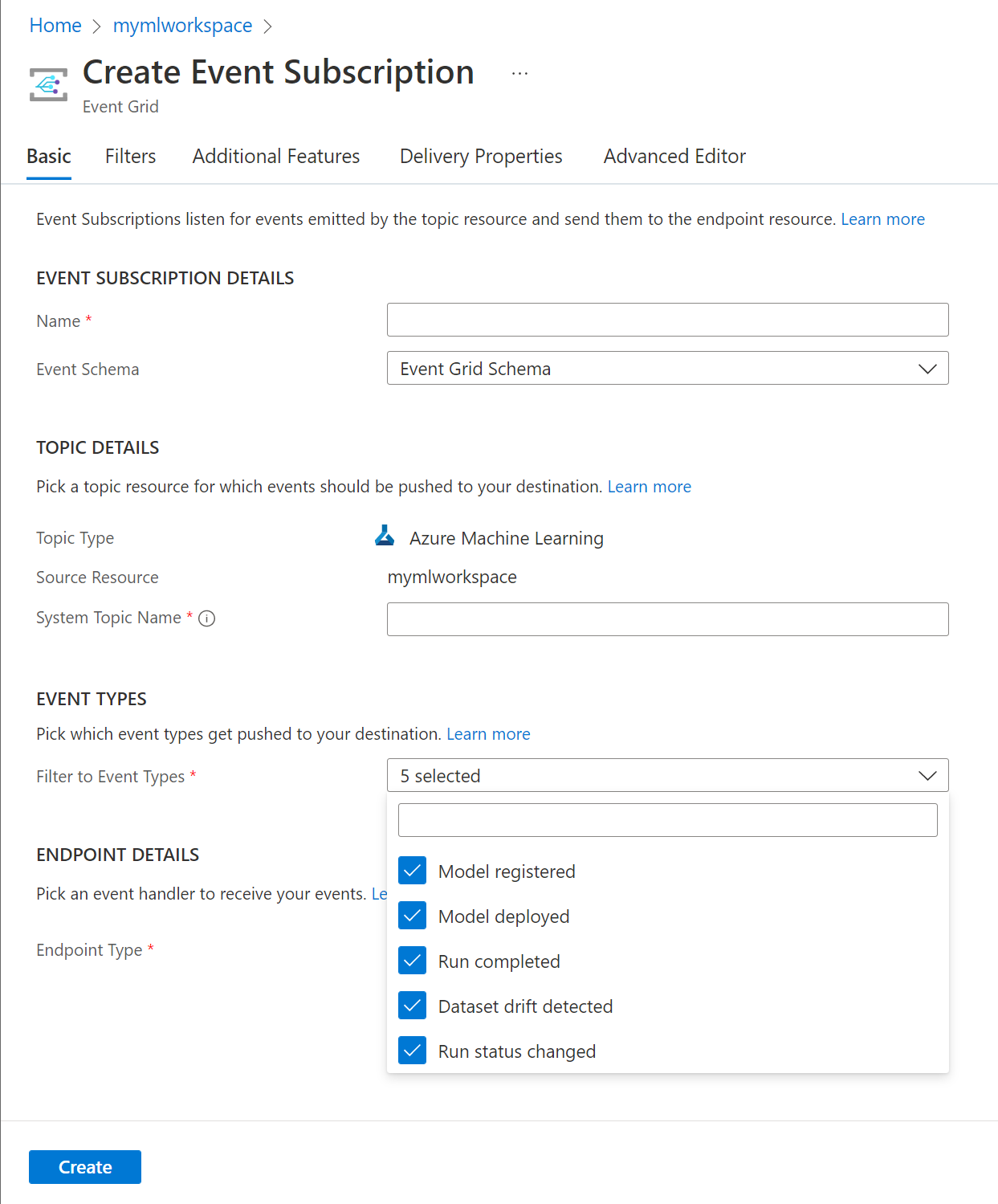
Select the endpoint to publish the event to. In the following screenshot, Event hub is the selected endpoint:
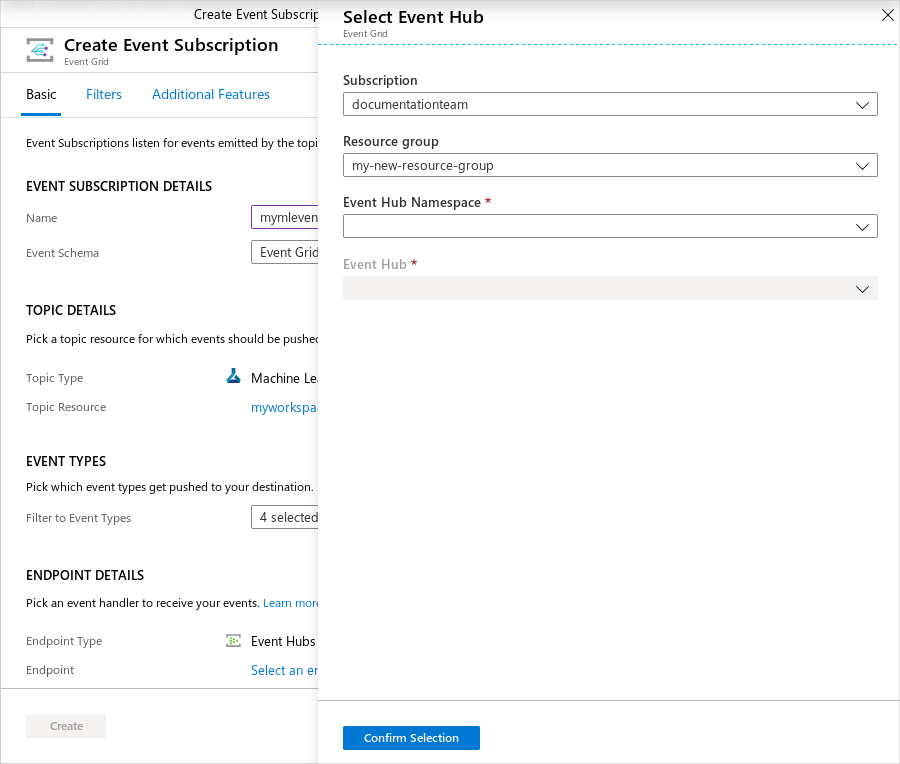
Once you confirm your selection, select Create. After configuration, these events will be pushed to your endpoint.
Set up with the CLI
You can install the latest Azure CLI.
To install the Event Grid extension, use the following command from the CLI:
az extension add --name eventgrid
The following example demonstrates how to select an Azure subscription and creates e a new event subscription for Azure Machine Learning:
# Select the Azure subscription that contains the workspace
az account set --subscription "<name or ID of the subscription>"
# Subscribe to the machine learning workspace. This example uses EventHub as a destination.
az eventgrid event-subscription create --name {eventGridFilterName} \
--source-resource-id /subscriptions/{subId}/resourceGroups/{RG}/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/{wsName} \
--endpoint-type eventhub \
--endpoint /subscriptions/{SubID}/resourceGroups/TestRG/providers/Microsoft.EventHub/namespaces/n1/eventhubs/EH1 \
--included-event-types Microsoft.MachineLearningServices.ModelRegistered \
--subject-begins-with "models/mymodelname"
Examples
Example: Send email alerts
Use Azure Logic Apps to configure emails for all your events. Customize with conditions and specify recipients to enable collaboration and awareness across teams working together.
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure Machine Learning workspace and select the events tab from the left bar. From here, select Logic apps.
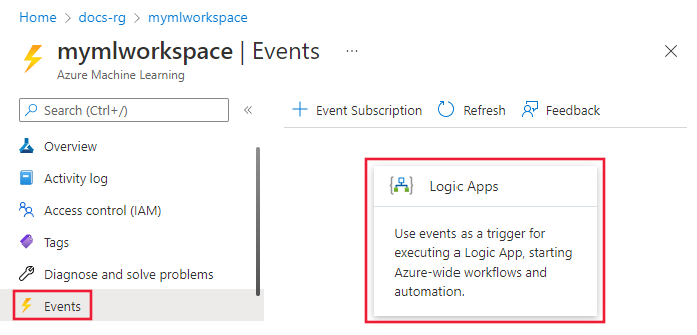
Sign into the Logic App UI and select Machine Learning service as the topic type.
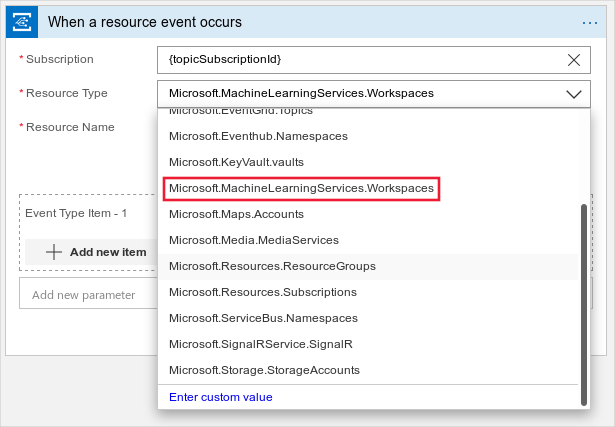
Select which event to be notified for. For example, the following screenshot RunCompleted.
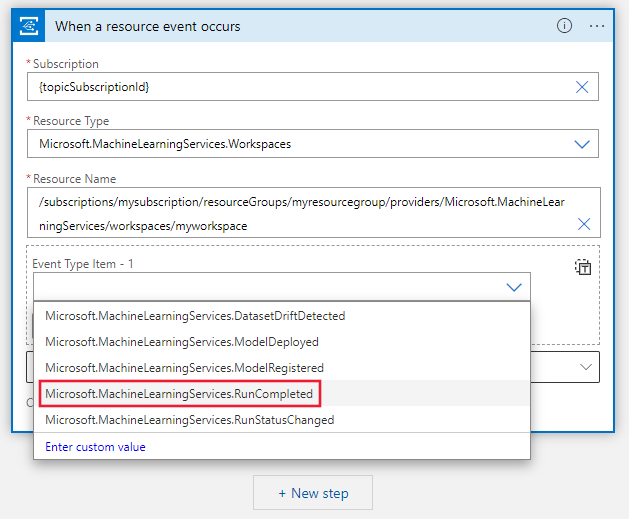
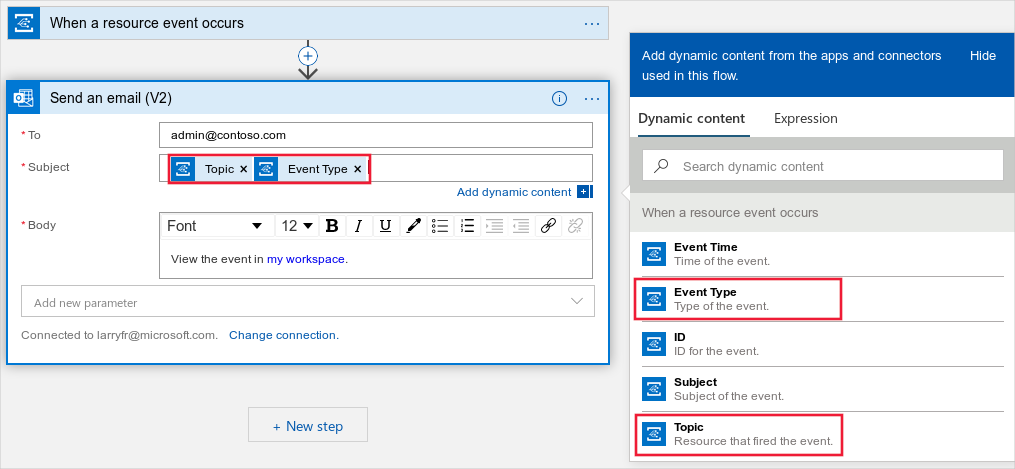
Next, add a step to consume this event and search for email. There are several different mail accounts you can use to receive events. You can also configure conditions on when to send an email alert.
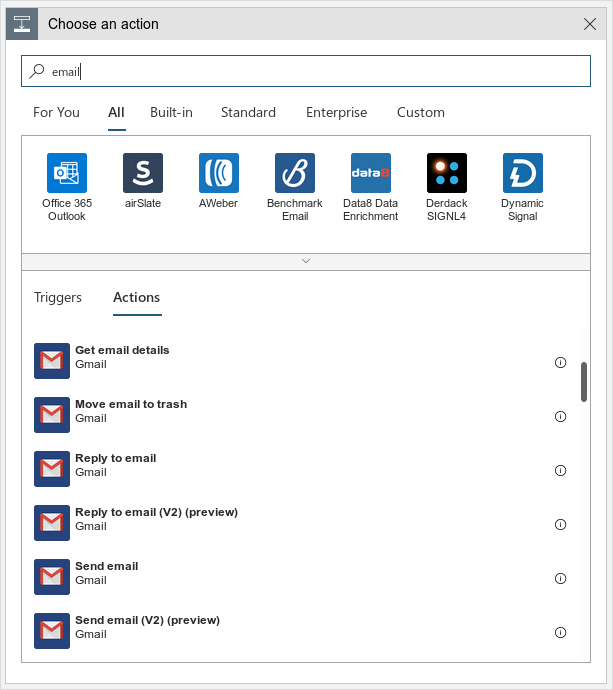
Select Send an email and fill in the parameters. In the subject, you can include the Event Type and Topic to help filter events. You can also include a link to the workspace page for runs in the message body.
To save this action, select Save As on the left corner of the page.
Example: Data drift triggers retraining
Important
This example relies on a feature (data drift) that is only available when using Azure Machine Learning SDK v1 or Azure CLI extension v1 for Azure Machine Learning. For more information, see What is Azure Machine Learning CLI & SDK v2.
Important
This article provides information on using the Azure Machine Learning SDK v1. SDK v1 is deprecated as of March 31, 2025. Support for it will end on June 30, 2026. You can install and use SDK v1 until that date. Your existing workflows using SDK v1 will continue to operate after the end-of-support date. However, they could be exposed to security risks or breaking changes in the event of architectural changes in the product.
We recommend that you transition to the SDK v2 before June 30, 2026. For more information on SDK v2, see What is Azure Machine Learning CLI and Python SDK v2? and the SDK v2 reference.
Important
Some of the Azure CLI commands in this article use the azure-cli-ml, or v1, extension for Azure Machine Learning. Support for CLI v1 ended on September 30, 2025. Microsoft will no longer provide technical support or updates for this service. Your existing workflows using CLI v1 will continue to operate after the end-of-support date. However, they could be exposed to security risks or breaking changes in the event of architectural changes in the product.
We recommend that you transition to the ml, or v2, extension as soon as possible. For more information on the v2 extension, see Azure Machine Learning CLI extension and Python SDK v2.
Models go stale over time, and not remain useful in the context it's running in. One way to tell if it's time to retrain the model is detecting data drift.
This example shows how to use Event Grid with an Azure Logic App to trigger retraining. The example triggers an Azure Data Factory pipeline when data drift occurs between a model's training and serving datasets.
Before you begin, perform the following actions:
- Set up a dataset monitor to detect data drift (SDK/CLI v1) in a workspace
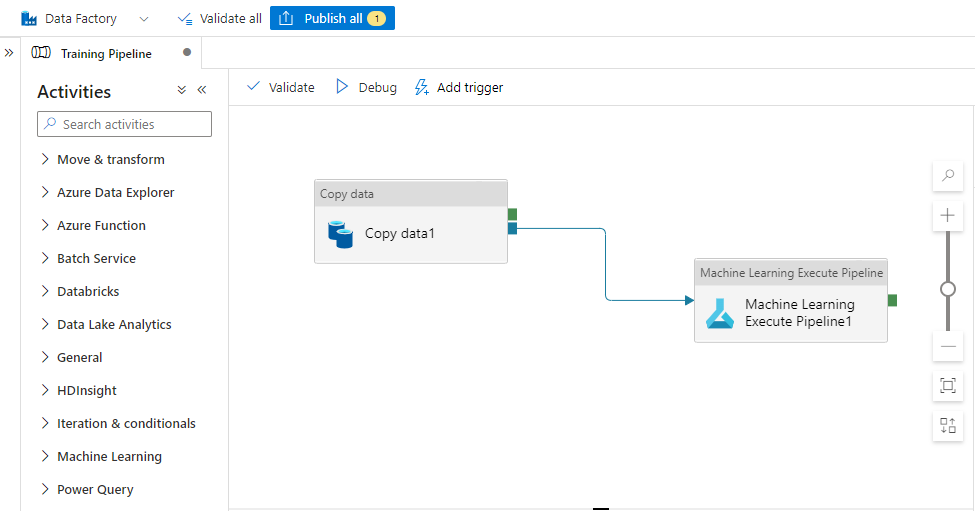
- Create a published Azure Data Factory pipeline.
In this example, a simple Data Factory pipeline is used to copy files into a blob store and run a published Machine Learning pipeline. For more information on this scenario, see how to set up a Machine Learning step in Azure Data Factory.
Start with creating the logic app. Go to the Azure portal, search for Logic Apps, and select create.

Fill in the requested information. To simplify the experience, use the same subscription and resource group as your Azure Data Factory Pipeline and Azure Machine Learning workspace.
Once you create the logic app, select When an Event Grid resource event occurs.
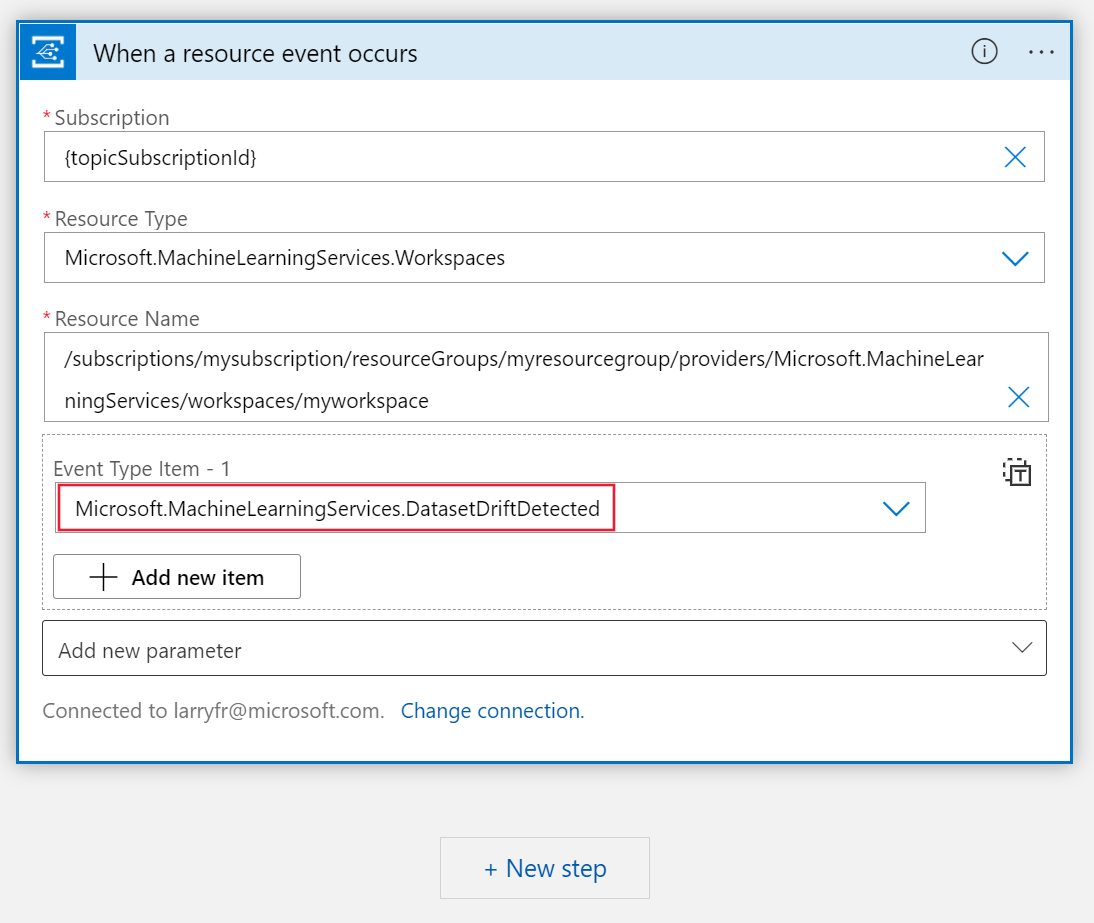
Login and fill in the details for the event. Set the Resource Name to the workspace name. Set the Event Type to DatasetDriftDetected.
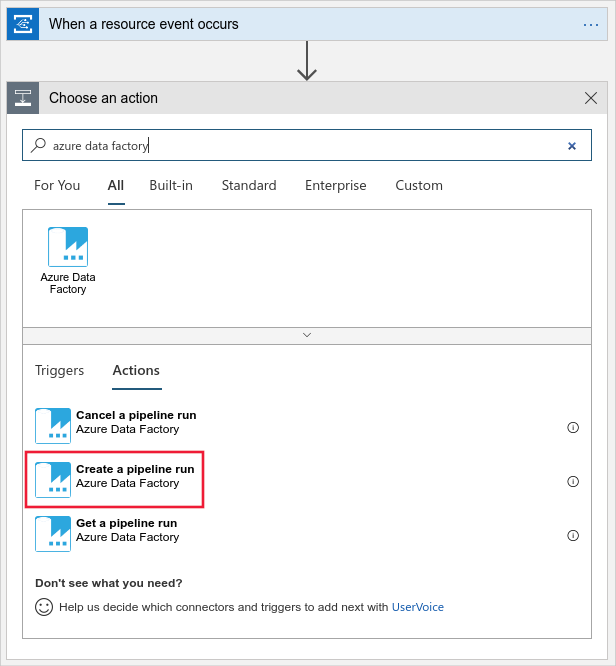
Add a new step, and search for Azure Data Factory. Select Create a pipeline run.
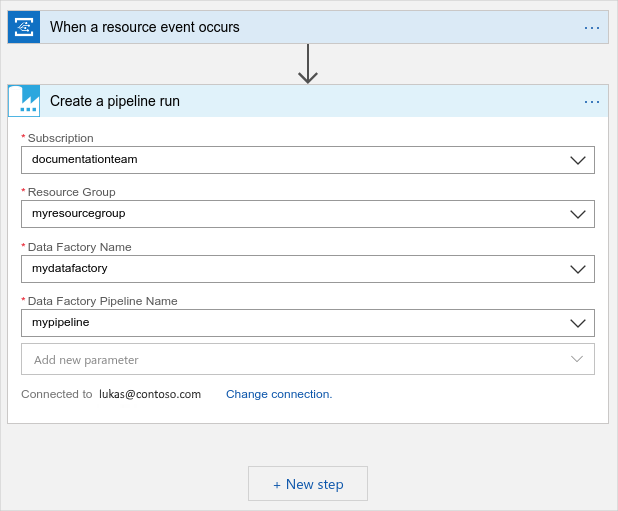
Login and specify the published Azure Data Factory pipeline to run.
Save and create the logic app using the save button on the top left of the page. To view your app, go to your workspace in the Azure portal and select Events.
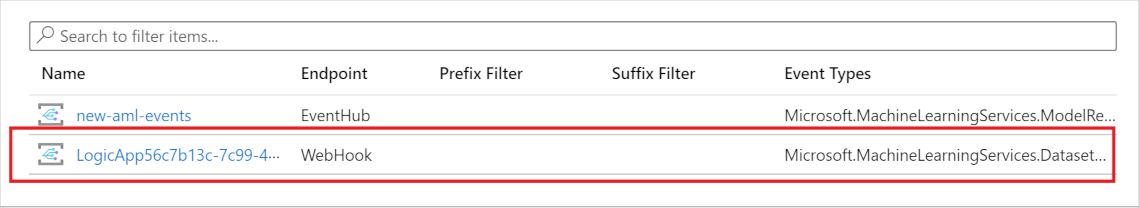
Now the data factory pipeline is triggered when drift occurs. View details on your data drift run and machine learning pipeline in Azure Machine Learning studio.
Next steps
Learn more about Event Grid and give Azure Machine Learning events a try: