Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Azure Migrate appliance is a lightweight tool that discovers on-premises servers and sends their configuration and performance data to Azure. It also performs software inventory, performs agentless dependency analysis, and detects workloads like web apps and instances of SQL Server or MySQL Server.
To use these features, you add server and guest credentials in the appliance configuration manager. Following the principle of least privilege helps keep the setup secure and efficient.
Discovery of the VMware estate
To discover the basic settings of servers running in the VMware estate, you need the following permissions.
vCenter account permissions
Discovery of server metadata
- To discover basic server configurations in a VMware environment, you need these permissions:
- Read-only: Use the built-in read-only role or create a copy of it.
- To discover server metadata and enable software inventory, dependency analysis, and performance assessments, you need these permissions:
- Read-only: Use the built-in read-only role or create a copy of it.
- Guest operations: Add guest operations privileges to the read-only role.
Scoped discovery of VMware servers
- To discover specific virtual machines (VMs), assign read permissions at the individual VMs.
- To discover all VMs in a folder, assign read permissions at the folder level and turn on the Propagate to children option.
- To enable software inventory, dependency analysis, and performance assessments, assign guest operations permissions to the vCenter account along with read permissions.
- Give read-only access to all parent objects that host the virtual machines, such as the host, cluster, host folder, cluster folder, and datacenter. You don't need to apply these permissions to all child objects.
- In the vSphere client, check that read permissions are set on parent objects in both the Hosts and Clusters view and the VMs & Templates view.
Agentless migration
To perform agentless migration, ensure that the vCenter account that the Azure Migrate appliance uses has permissions at all required levels: datacenter, cluster, host, VM, and datastore. Apply permissions at each level to avoid replication errors.
| vSphere privilege name | Privilege purpose | Required | API privilege name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Browse datastore | Allow users to browse VM log files to troubleshoot snapshot creation and deletion | Datastores | Datastore.Browse |
| Low level file operations | Allow read, write, delete, and rename actions in the datastore browser to troubleshoot snapshot creation and deletion | Datastores | Datastore.FileManagement |
| Change Configuration - Toggle disk change tracking | Allow users to enable or disable change tracking of VM disks to pull changed blocks of data between snapshots | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.Config.ChangeTracking |
| Change Configuration - Acquire disk lease | Allow disk lease operations on a VM to read the disk by using the VMware vSphere Virtual Disk Development Kit (VDDK) | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.Config.DiskLease |
| Provisioning - Allow read-only disk access | Allow read-only disk access: opening a disk on a VM to read the disk by using the VDDK | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.Provisioning.DiskRandomRead |
| Provisioning - Allow disk access | Allow opening a disk on a VM to read the disk by using the VDDK | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.Provisioning.DiskRandomAccess |
| Provisioning - Allow virtual machine download | Allow virtual machine download to read VM files, get logs, and troubleshoot failures | Root host or vCenter Server | VirtualMachine.Provisioning.GetVmFiles |
| Snapshot management | Allow discovery, software inventory, and dependency mapping on VMs | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.State.* |
| Guest operations | Allow creation and management of VM snapshots for replication | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.GuestOperations.* |
| Interaction Power Off | Allow the VM to be turned off during migration to Azure | Virtual machines | VirtualMachine.Interact.PowerOff |
Guest discovery of installed software, dependencies, and workloads
To effectively discover software, application dependencies, and workloads on target servers, the Azure Migrate appliance requires guest operating system (OS) credentials. These credentials enable the appliance to securely connect to the servers and collect detailed inventory and performance data.
Quick guest discovery
For quick discovery of software inventory, server dependencies, and database instances, you need the following permissions:
| Use case | Discovered metadata | Credential type | Secure permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick guest discovery | Software inventory Server dependencies (limited data) Inventory of database instances |
Windows Linux |
Local guest user account Any non-Sudo guest user account |
Note
You can use a Windows guest or a Linux non-Sudo user account to get dependency mapping data. But with least privileged accounts, you might not collect process information (like process name or app name) for some processes that run with higher privileges. These processes appear as Unknown under the machine in the single-server view.
In-depth guest discovery
For in-depth discovery of software inventory, server dependencies, and web apps such as .NET and Java Tomcat, you need the following permissions:
| Use case | Discovered metadata | Credential type | Required permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-depth guest discovery | Software inventory Server dependencies (full data) Inventory of database instances Web apps like .NET and Java Tomcat |
Windows | Administrator |
| In-depth guest discovery | Software inventory Server dependencies (full data) Inventory of database instances Web apps like .NET and Java Tomcat |
Linux | The following Sudo permissions are required to identify server dependencies: /usr/bin/netstat and /usr/bin/ls. If netstat is not available, Sudo permissions on ss are required. For Java web app discovery (Tomcat servers), the user should have read and execute ( r-x) permissions on all Catalina homes. Use the following command to find all Catalina homes: ps -ef \| grep catalina.home. Here's a sample command to set up a least privileged user: setfacl -m u:<username>:rx <catalina/home/path>. |
Discovery of the Hyper-V estate
To find the basic settings of servers running in the Hyper-V estate, you need certain permissions. On all the Hyper-V hosts, create a local user that's part of these three groups:
- Hyper-V administrators
- Performance monitor users
- Remote management users
Use the script to prepare Hyper-V hosts.
For deep discovery of the Hyper-V estate and to perform software inventory and dependency analysis, guest account credentials are required.
Discovery of physical and cloud servers
To discover and assess physical servers or servers hosted in other public clouds, the Azure Migrate appliance requires credentials with least privileged access. These credentials allow the appliance to connect and gather necessary data without overexposing sensitive system permissions.
Quick server discovery
For quick discovery of software inventory, server dependencies, and database instances, you need the following permissions:
| Use case | Discovered metadata | Credential type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick server discovery | Software inventory Agentless dependency analysis (limited data) Workload inventory of databases and web apps |
Windows | Follow these steps |
| Quick server discovery | Software inventory Agentless dependency analysis (full data) Workload inventory of databases and web apps |
Linux | Follow these steps |
Windows servers
For quick discovery of Windows servers, create a Windows user account that belongs to the following user groups:
- Remote management users
- Performance monitor users
- Performance log users
The guest user account needs permission to access the CIMV2 namespace and its sub-namespaces in the WMI Control item in Control Panel. To set the access, use the following steps:
On the target Windows server, go to the Start menu, search for Run, and then select it.
In the Run dialog, type
wmimgmt.mscand then press the Enter key.In the wmimgmt console, right-click WMI Control (Local), and then select Properties.
In the WMI Control (Local) Properties dialog, select the Security tab.
Expand the Root folder in the namespace tree, and then select the CIMV2 namespace.
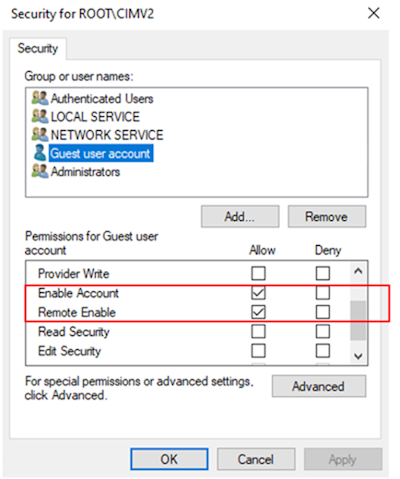
Select Security to open the Security for ROOT\CIMV2 dialog.
In the Group or user names section, select Add to open the Select Users or Groups dialog.
Search for the user account, select it, and then select OK to return to the Security for ROOT\CIMV2 dialog.
In the Group or user names section, select the guest user account. Validate that the following permissions are allowed:
- Enable Account
- Remote Enable
Select Apply to enable the permissions that you set on the user account.
Restart the WinRM service after you add the new guest user.
Linux servers
For quick discovery of Linux servers:
Create a user account; for example,
AzMigrateLeastprivuser.Grant Sudo privileges to the user for only the required commands by adding the following line in the
/etc/sudoersfile:AzMigrateLeastprivuser ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/dmidecode, /usr/sbin/fdisk -l, /usr/sbin/fdisk -l *, /usr/bin/ls -l /proc/*/exe, /usr/bin/netstat -atnp, /usr/sbin/lvdisplay "" Defaults:AzMigrateLeastprivuser !requiretty
In-depth server discovery
For in-depth discovery of software inventory, server dependencies, and web apps such as .NET and Java Tomcat, you need the following permissions:
| Use case | Discovered metadata | Credential type | Commands to configure |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-depth server discovery | In-depth discovery of web apps such as .NET and Java Tomcat Agentless dependency analysis (full data) |
Windows Linux |
Administrator permissions are required. To discover Java web apps on Tomcat servers, the user account needs read and execute ( r-x) permissions on all Catalina home directories.Use the following command to find all Catalina homes: ps -ef \| grep catalina.home.Here's a sample command to set up a least privileged user: setfacl -m u:<username>:rx <catalina/home/path>. |
Database discovery
Software inventory is required for initiating workload discovery. To enable it, ensure that guest credentials are added. The permissions to discover SQL and MySQL databases are the same for all appliance types: VMware, Hyper-V, and physical servers.
Discover SQL Server instances and databases
Create least privileged accounts on individual SQL Server instances. Use Windows authentication and assign only the required permissions.
Windows authentication
-- Create a login to run the assessment.
use master;
DECLARE @SID NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'';
CREATE LOGIN [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT] FROM WINDOWS;
SELECT @SID = N'0x'+CONVERT(NVARCHAR, sid, 2) FROM sys.syslogins where name = 'MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT'
IF (ISNULL(@SID,'') != '')
PRINT N'Created login [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT] with SID = ' + @SID
ELSE
PRINT N'Login creation failed'
GO
-- Create a user in every database other than tempdb, model, and secondary AG databases (with connection_type = ALL) and provide minimal read-only permissions.
USE master;
EXECUTE sp_MSforeachdb '
USE [?];
IF (''?'' NOT IN (''tempdb'',''model''))
BEGIN
DECLARE @is_secondary_replica BIT = 0;
IF CAST(PARSENAME(CAST(SERVERPROPERTY(''ProductVersion'') AS VARCHAR), 4) AS INT) >= 11
BEGIN
DECLARE @innersql NVARCHAR(MAX);
SET @innersql = N''
SELECT @is_secondary_replica = IIF(
EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM sys.availability_replicas a
INNER JOIN sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states b
ON a.replica_id = b.replica_id
WHERE b.is_local = 1
AND b.is_primary_replica = 0
AND a.secondary_role_allow_connections = 2
AND b.database_id = DB_ID()
), 1, 0
);
'';
EXEC sp_executesql @innersql, N''@is_secondary_replica BIT OUTPUT'', @is_secondary_replica OUTPUT;
END
IF (@is_secondary_replica = 0)
BEGIN
CREATE USER [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT] FOR LOGIN [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON sys.sql_expression_dependencies TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
END
END'
GO
-- Provide server-level read-only permissions.
use master;
GRANT SELECT ON sys.sql_expression_dependencies TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT EXECUTE ON OBJECT::sys.xp_regenumkeys TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT EXECUTE ON OBJECT::sys.xp_instance_regread TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GO
-- Provide msdb-specific permissions.
use msdb;
GRANT EXECUTE ON [msdb].[dbo].[agent_datetime] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobsteps] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[syssubsystems] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobhistory] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[syscategories] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobs] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmaintplan_plans] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[syscollector_collection_sets] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmail_profile] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmail_profileaccount] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmail_account] TO [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
GO
-- Clean up
--use master;
-- EXECUTE sp_MSforeachdb 'USE [?]; DROP USER [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT]'
-- DROP LOGIN [MYDOMAIN\MYACCOUNT];
--GO
SQL Server authentication
--- Create a login to run the assessment.
use master;
-- NOTE: SQL Server instances that host replicas of Always On availability groups must use the same SID for the SQL Server login.
-- After the account is created in one of the members, copy the SID output from the script and include this value when executing against the remaining replicas.
-- When the SID needs to be specified, add the value to the following @SID variable definition.
DECLARE @SID NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'';
IF (@SID = N'')
BEGIN
CREATE LOGIN [evaluator]
WITH PASSWORD = '<provide a strong password>'
END
ELSE
BEGIN
DECLARE @SQLString NVARCHAR(500) = 'CREATE LOGIN [evaluator]
WITH PASSWORD = ''<provide a strong password>''
, SID = ' + @SID
EXEC SP_EXECUTESQL @SQLString
END
SELECT @SID = N'0x'+CONVERT(NVARCHAR(100), sid, 2) FROM sys.syslogins where name = 'evaluator'
IF (ISNULL(@SID,'') != '')
PRINT N'Created login [evaluator] with SID = '''+ @SID +'''. If this instance hosts any Always On Availability Group replica, use this SID value when executing the script against the instances hosting the other replicas'
ELSE
PRINT N'Login creation failed'
GO
-- Create a user in every database other than tempdb, model, and secondary AG databases (with connection_type = ALL) and provide minimal read-only permissions.
USE master;
EXECUTE sp_MSforeachdb '
USE [?];
IF (''?'' NOT IN (''tempdb'',''model''))
BEGIN
DECLARE @is_secondary_replica BIT = 0;
IF CAST(PARSENAME(CAST(SERVERPROPERTY(''ProductVersion'') AS VARCHAR), 4) AS INT) >= 11
BEGIN
DECLARE @innersql NVARCHAR(MAX);
SET @innersql = N''
SELECT @is_secondary_replica = IIF(
EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM sys.availability_replicas a
INNER JOIN sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states b
ON a.replica_id = b.replica_id
WHERE b.is_local = 1
AND b.is_primary_replica = 0
AND a.secondary_role_allow_connections = 2
AND b.database_id = DB_ID()
), 1, 0
);
'';
EXEC sp_executesql @innersql, N''@is_secondary_replica BIT OUTPUT'', @is_secondary_replica OUTPUT;
END
IF (@is_secondary_replica = 0)
BEGIN
CREATE USER [evaluator] FOR LOGIN [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON sys.sql_expression_dependencies TO [evaluator];
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [evaluator];
END
END'
GO
-- Provide server-level read-only permissions.
USE master;
GRANT SELECT ON sys.sql_expression_dependencies TO [evaluator];
GRANT EXECUTE ON OBJECT::sys.xp_regenumkeys TO [evaluator];
GRANT EXECUTE ON OBJECT::sys.xp_instance_regread TO [evaluator];
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [evaluator];
GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO [evaluator];
GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO [evaluator];
GO
-- Provide msdb-specific permissions.
USE msdb;
GRANT EXECUTE ON [msdb].[dbo].[agent_datetime] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobsteps] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[syssubsystems] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobhistory] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[syscategories] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobs] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmaintplan_plans] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[syscollector_collection_sets] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmail_profile] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmail_profileaccount] TO [evaluator];
GRANT SELECT ON [msdb].[dbo].[sysmail_account] TO [evaluator];
GO
-- Clean up
--use master;
-- EXECUTE sp_MSforeachdb 'USE [?]; BEGIN TRY DROP USER [evaluator] END TRY BEGIN CATCH PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE() END CATCH;'
-- BEGIN TRY DROP LOGIN [evaluator] END TRY BEGIN CATCH PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE() END CATCH;
--GO
For information on how to set up custom SQL accounts with least privilege at scale, see Provision custom accounts with least privileges for SQL Server discovery and assessment.
Discovery of MySQL Server instances and databases
To discover MySQL databases, add MySQL database credentials to the appliance.
Ensure that the user who corresponds to the added MySQL credentials has the following privileges:
- Select permission on
information_schematables - Select permission on
mysql.userstables
For MySQL discovery, ensure the appliance's IP or domain is allowed by configuring the necessary firewall rules and MySQL user privileges. The bind-address in my.cnf should also be set to allow external connections if needed.
Use the following commands to grant the necessary privileges to the MySQL user:
GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'username'@'ip';
GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO 'username'@'ip';
GRANT SELECT (User, Host, Super_priv, File_priv, Create_tablespace_priv, Shutdown_priv) ON mysql.user TO 'username'@'ip';
GRANT SELECT ON information_schema.* TO 'username'@'ip';
GRANT SELECT ON performance_schema.* TO 'username'@'ip';
Related content
- Learn how to discover the VMware estate.
- Learn how to discover the Hyper-V estate.
- Learn how to discover physical servers or servers running in a public cloud.