Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to create a script activity in Azure Data Factory to run custom PostgreSQL queries. With script activity, you can execute various types of PostgreSQL commands, such as Data Manipulation Language (DML) and Data Definition Language (DDL) commands, directly in your pipelines.
DML statements: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT
DDL statements: CREATE, ALTER, and DROP
Prerequisites
- An Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. To learn more, see Create an Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
- (Optional) An Azure integration runtime created within a managed virtual network.
- An Azure Data Factory Linked Service connected to Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
Create a script activity
In Azure Data Factory Studio, select the Author hub. Hover over the Pipelines section, select ... at the left, and select New pipeline to create a new pipeline.
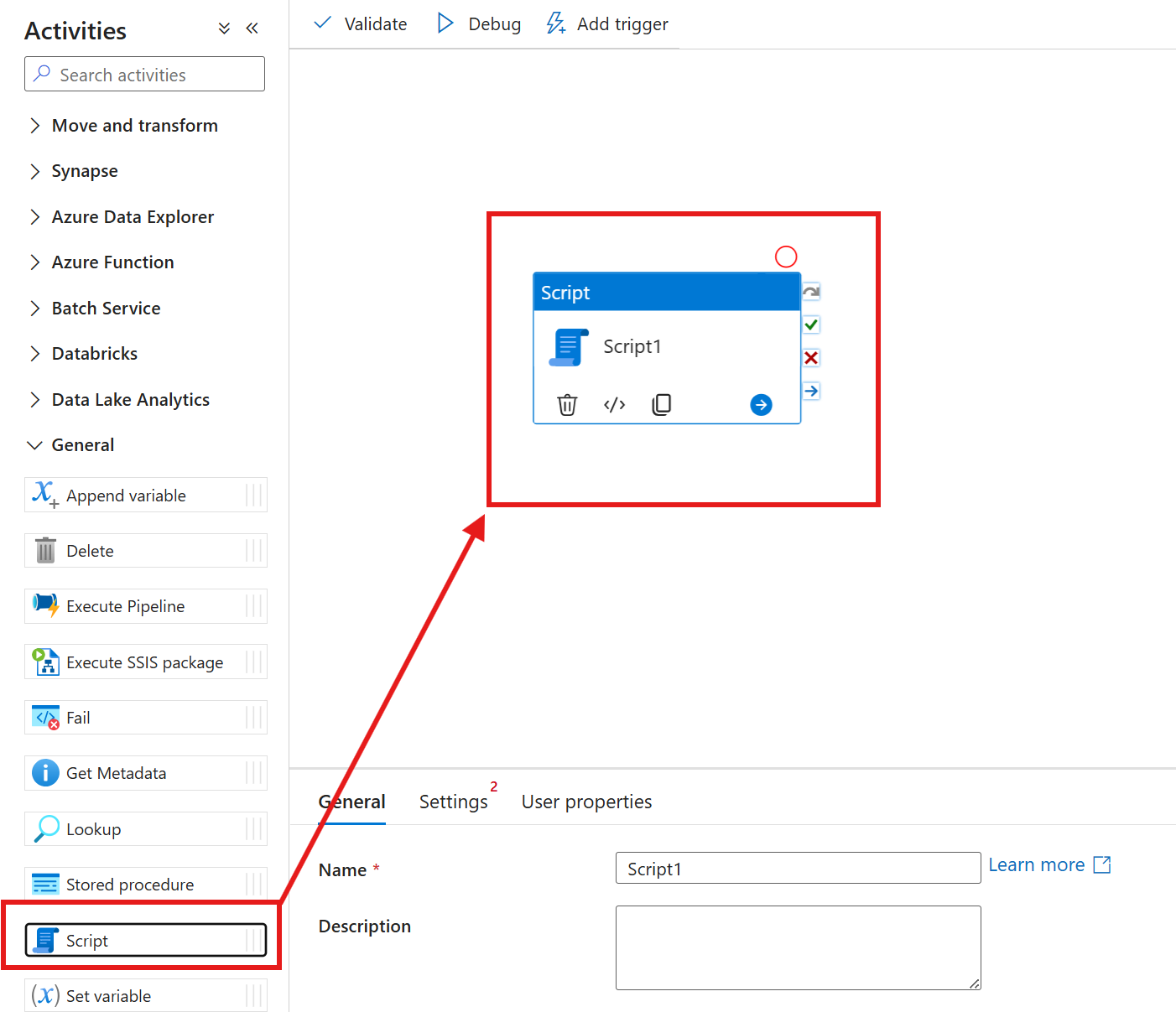
Under General, drag and drop the script activity into the pipeline.
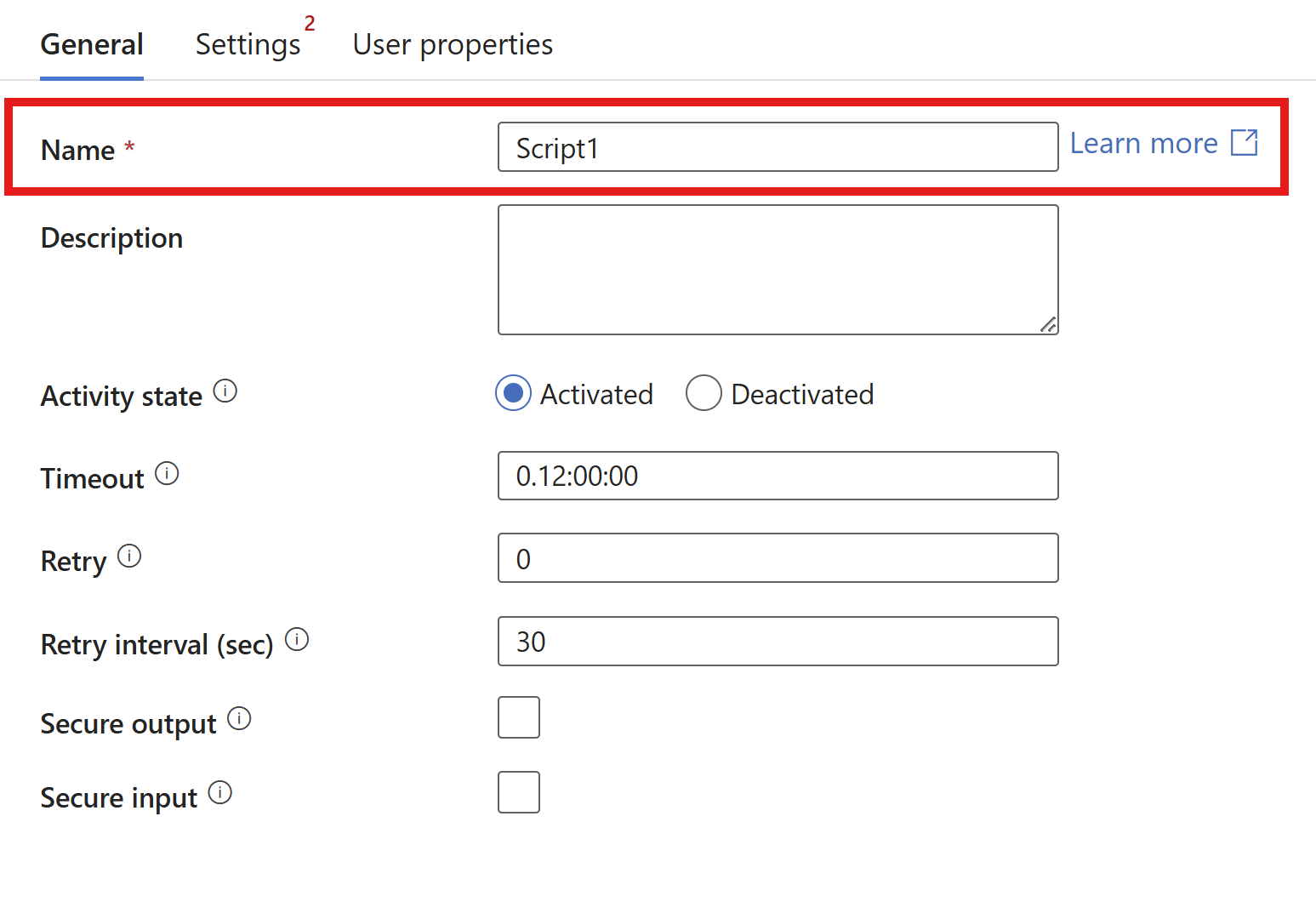
- At the General tab, give your script activity a name.
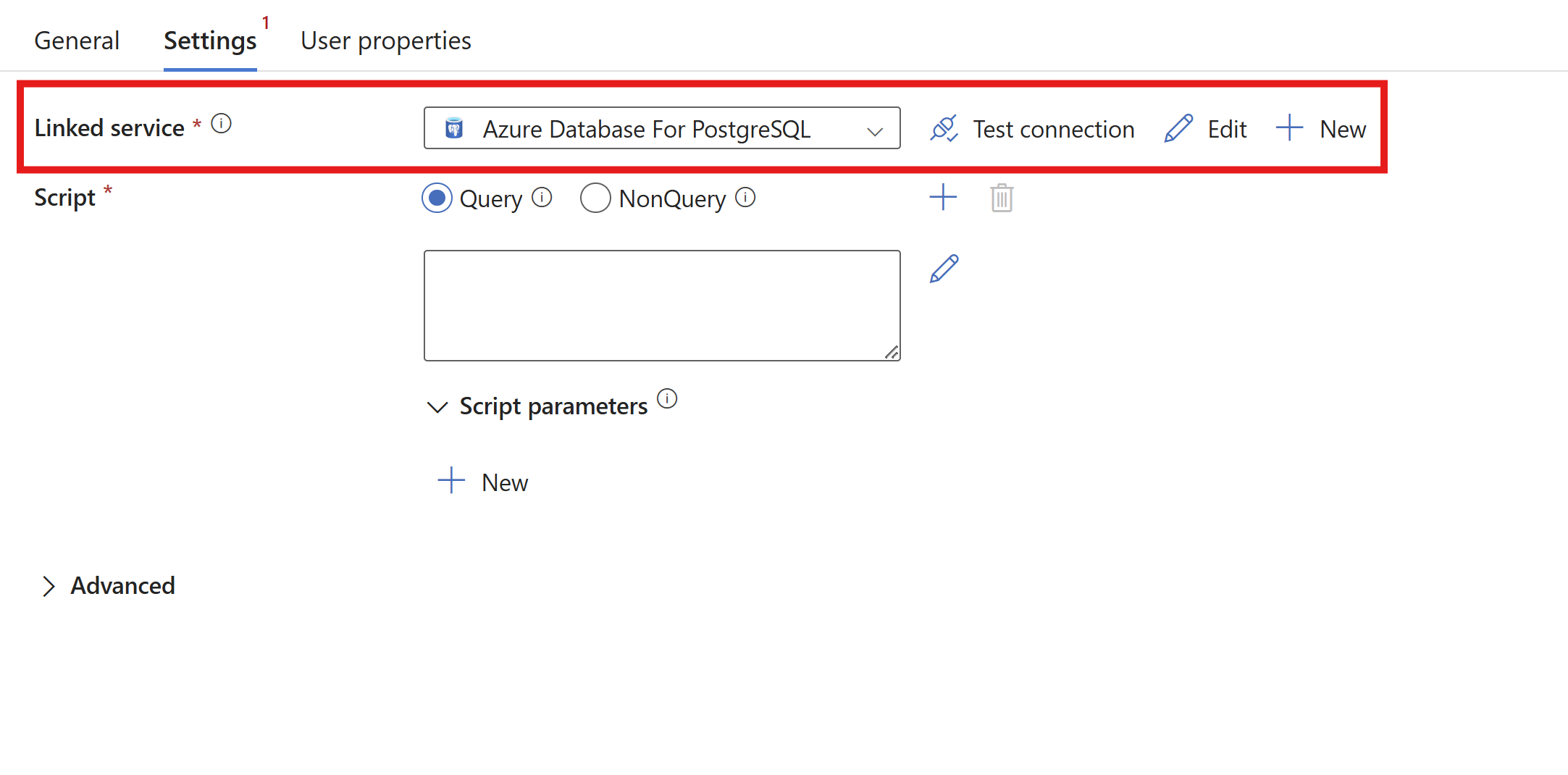
Switch to the Settings tab and select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL linked service, or create a new one. Once added, select Test connection to verify your connection is valid.
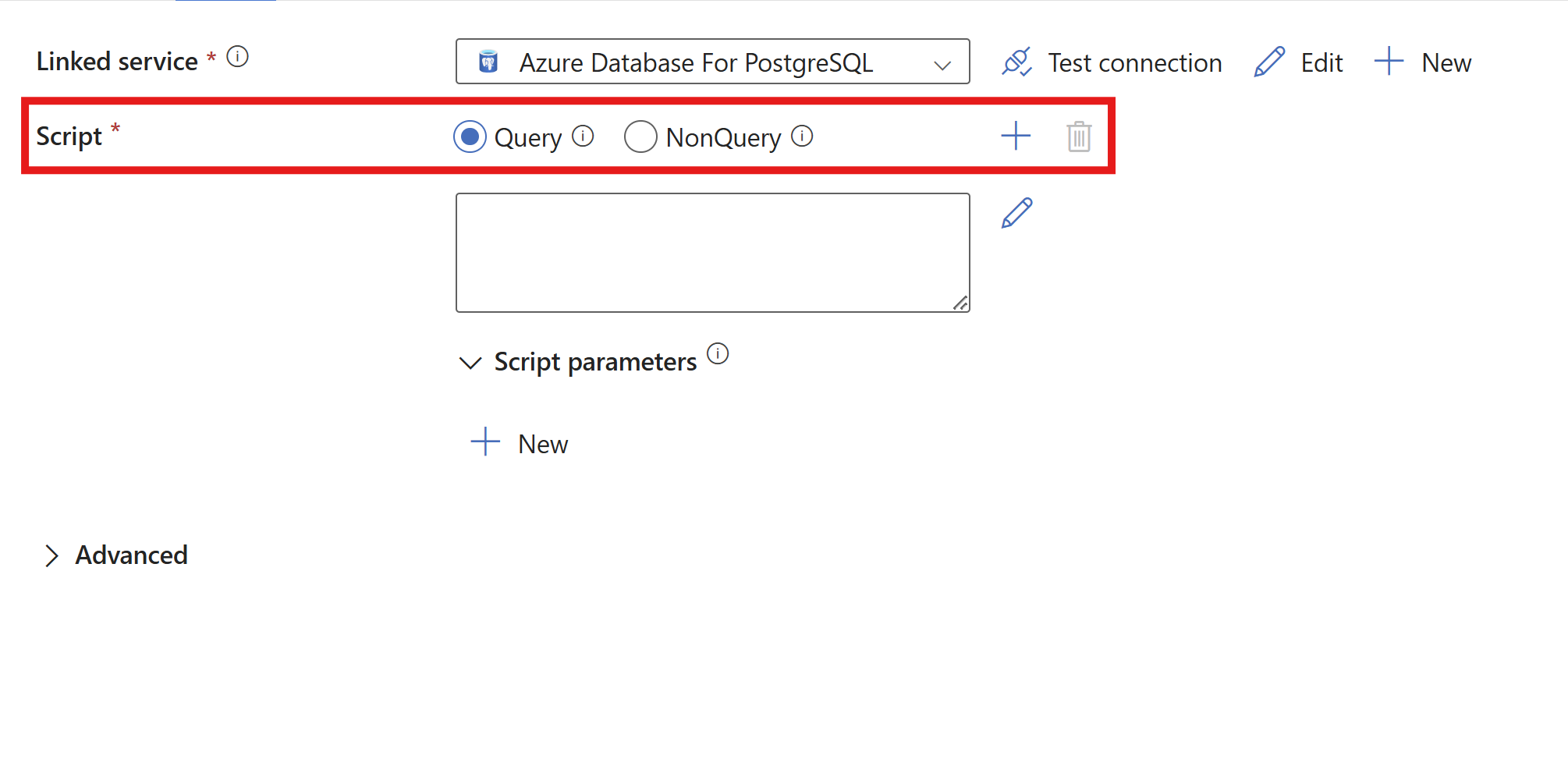
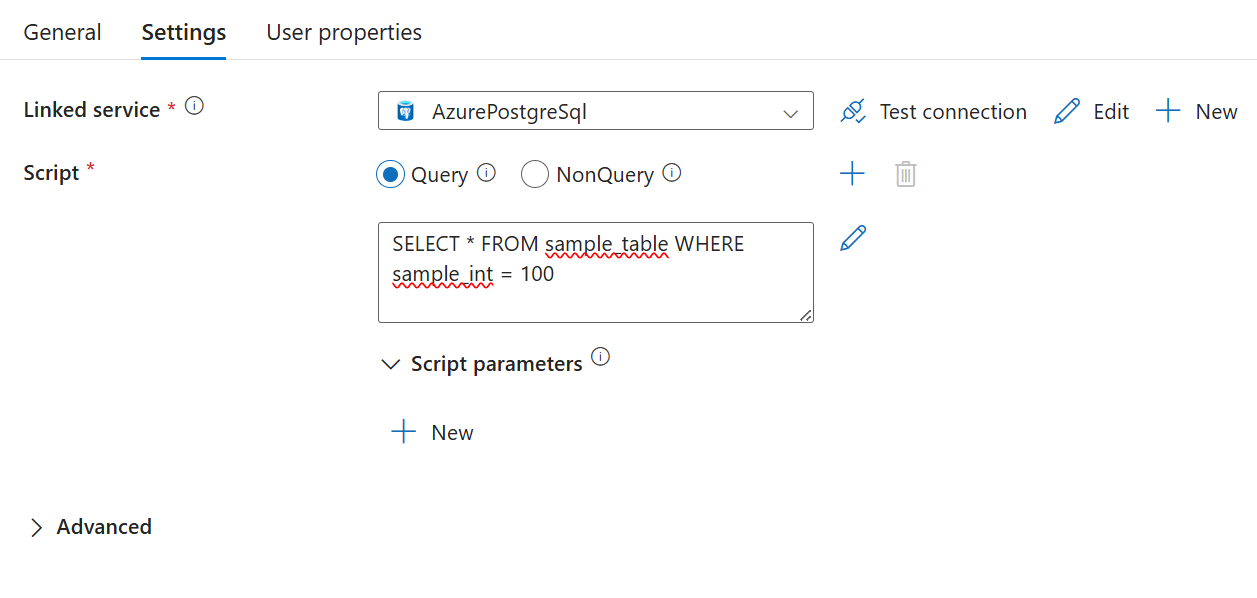
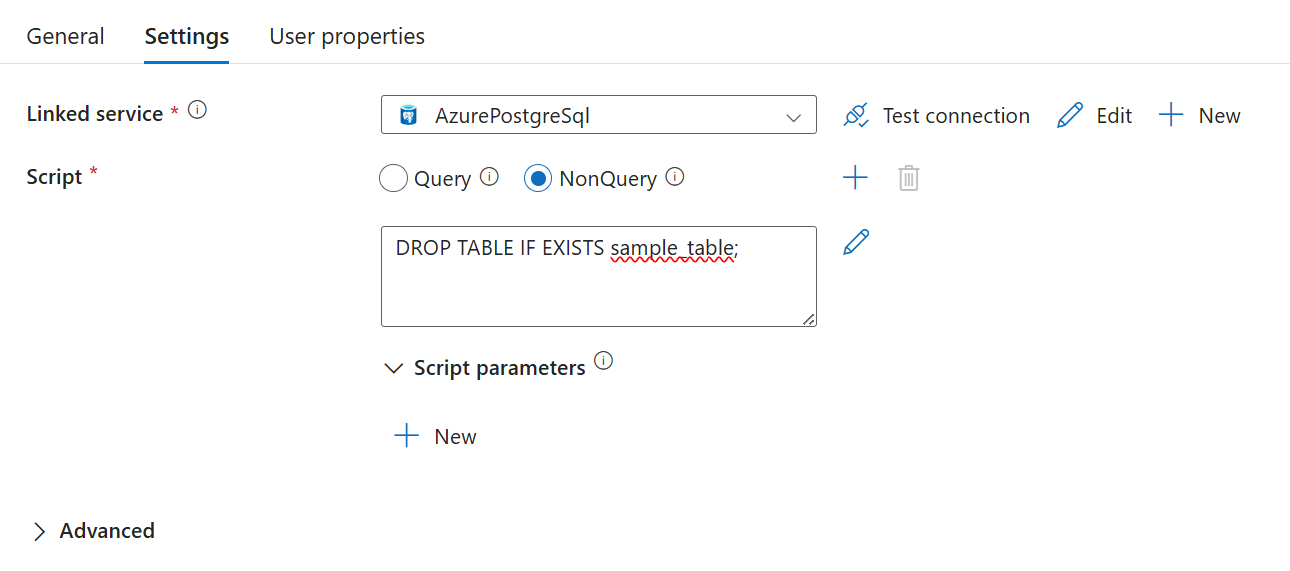
Select either the Query or NonQuery option depending on your script.
The script activity supports both query and nonquery statements.
Query statements execute PostgreSQL statements that return results. Often
SELECTstatements. A Query statement returns records of data.Sample of a payload with a Query.
{ "name": "Sample of select statement", "type": "Script", "dependsOn": [], "policy": { "timeout": "1.12:00:00", "retry": 0, "retryIntervalInSeconds": 30, "secureOutput": false, "secureInput": false }, "userProperties": [], "linkedServiceName": { "referenceName": "AzurePostgreSQL", "type": "LinkedServiceReference" }, "typeProperties": { "scripts": [ { "type": "Query", "text": "SELECT * FROM sample_table WHERE sample_int = 100; " } ], "scriptBlockExecutionTimeout": "02:00:00" } }
Create multiple scripts inside one script activity
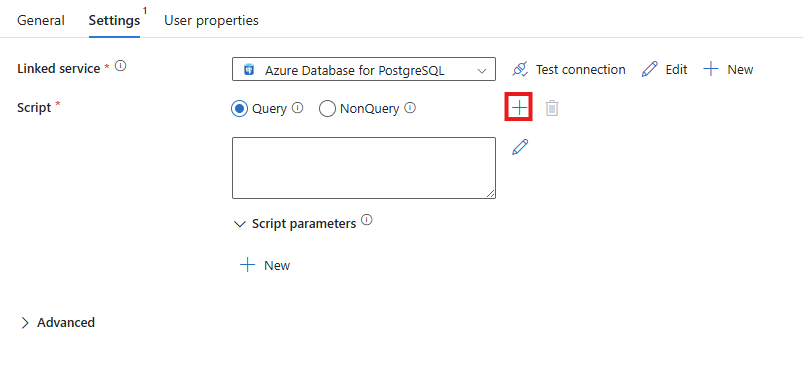
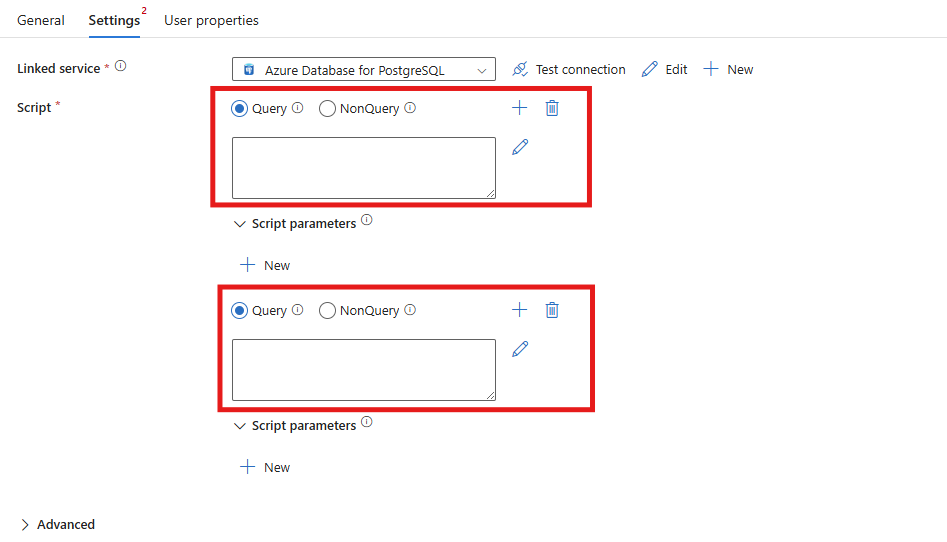
You can include multiple queries in one script activity by selecting the + sign next to Script to add a new script input.
You can delete query input boxes by using the delete icon next to Script.
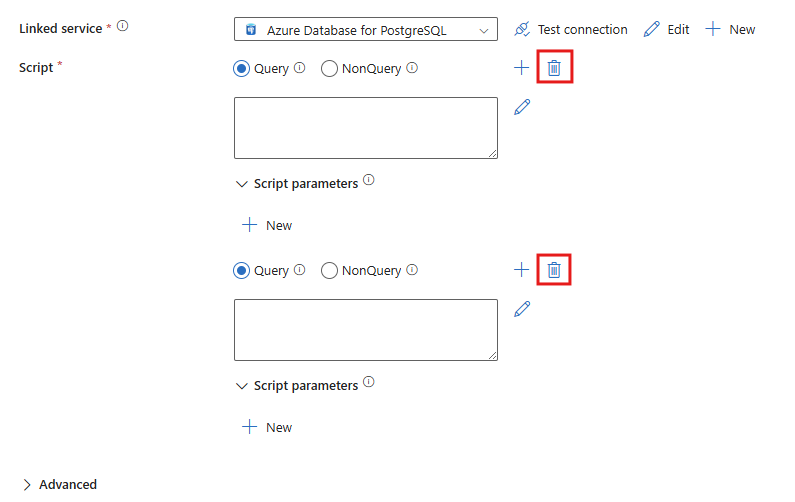
Here's a sample of a payload with two separate queries.
{
"name": "Sample of multiple select statements",
"type": "Script",
"dependsOn": [],
"policy": {
"timeout": "1.12:00:00",
"retry": 0,
"retryIntervalInSeconds": 30,
"secureOutput": false,
"secureInput": false
},
"userProperties": [],
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "AzurePostgreSQL1",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"typeProperties": {
"scripts": [
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "SELECT * FROM sample_table WHERE sample_int = 100; "
},
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "SELECT * FROM sample_table WHERE sample_int > 250; "
}
],
"scriptBlockExecutionTimeout": "02:00:00"
}
}
Script parameters
Important
Multi-query statements using output parameters aren't supported. Split any output queries into separate script blocks within the same or different script activity.
Script activity supports two types of script parameters: positional and named parameters. Named parameters use the name of the parameters and are specified as @<name> in the queries. Positional parameters use the index of the parameters and are specified in the query in order as $<position number> with a starting index of 1.
Named parameters (recommended)
Named parameters use an @ prefix to the name of the parameter.
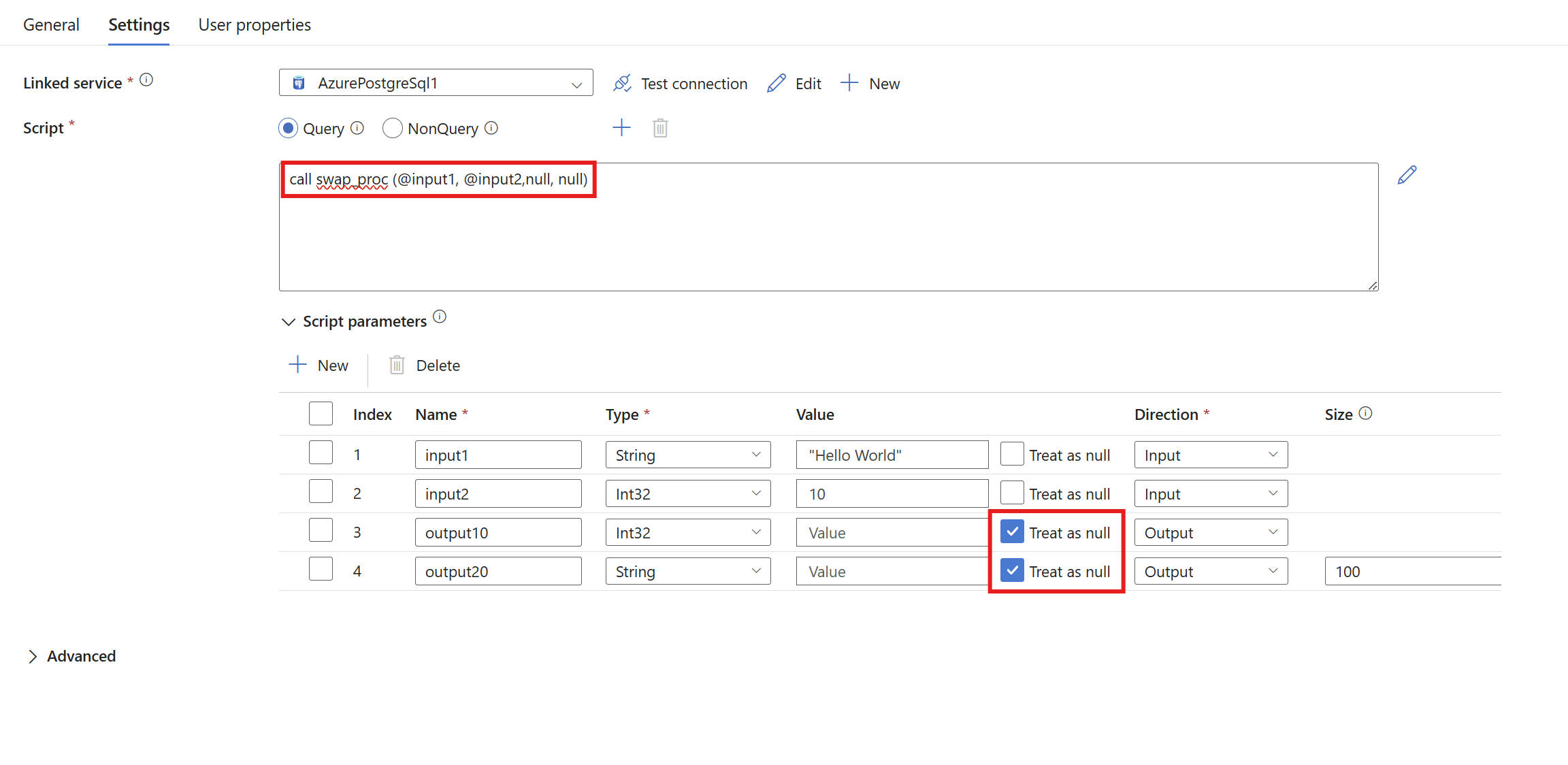
Set named parameters as output parameters by setting the value to null with the Treat as null box checked in the UI, and with the payload left blank or null. The value in the text should be null.
The name set within the procedure for output is the name used within the resultSets data output. The name set in the UI output row is used for the name of outputParameters.
Sample result from the UI execution
"resultSetCount": 1,
"recordsAffected": 0,
"resultSets": [
{
"rowCount": 1,
"rows": [
{
"output1": 10,
"output2": "\"Hello World\""
}
]
}
],
"outputParameters": {
"output10": 10,
"output20": "\"Hello World\""
}
Payload sample for output parameter.
"scripts": [
{
"text": "CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE swap_proc (input1 IN TEXT, input2 IN BIGINT, output1 OUT BIGINT, output2 OUT TEXT) LANGUAGE plpgsql AS $$ DECLARE BEGIN output2 := input1; output1 := input2; END $$",
"type": "NonQuery"
},
{
"text": "CALL swap_proc(@input1, @input2, null, null)",
"type": "Query",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "input1",
"type": "String",
"value": "Hello world",
"direction": "Input",
"size": 100
},
{
"name": "input2",
"type": "INT32",
"value": 1234,
"direction": "Input"
},
{
"name": "output1",
"type": "INT32",
"direction": "Output"
},
{
"name": "output2",
"type": "String",
"direction": "Output",
"size": 100
}
]
}
]
Positional parameters
Important
Multi-query statements using positional parameters aren't supported. Ensure that any queries with positional parameters are in separate script blocks within the same or different script activity.
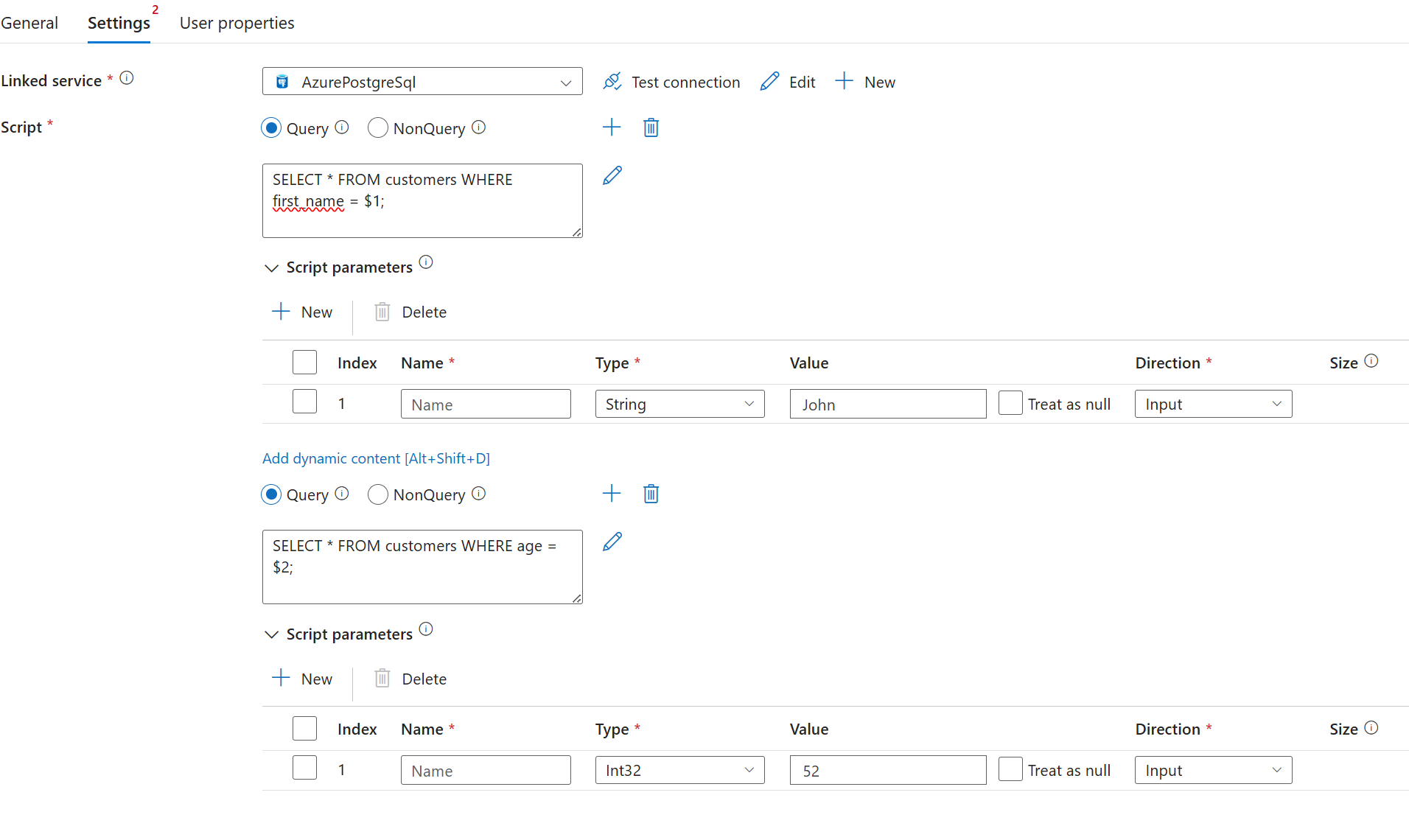
To use positional parameters, use a placeholder of $<positional number> in your query. Under parameters the name field must be left blank in the UI and specified as null in the payload.
"scripts": [
{
"text": "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE first_name = $1 AND age = $2;",
"type": "Query",
"parameters": [
{
"name": null,
"type": "String",
"value": "John",
"direction": "Input",
"size": 256
},
{
"name": null,
"type": "INT32",
"value": 52,
"direction": "Input"
}
]
}
]
Example of valid positional parameter
"scripts": [
{
"text": "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE first_name = $1;",
"type": "Query",
"parameters": [
{
"name": null,
"type": "String",
"value": "John",
"direction": "Input",
"size": 256
}
]
},
{
"text": "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE age = $2;",
"type": "Query",
"parameters": [
{
"name": null,
"type": "INT32",
"value": 52,
"direction": "Input"
}
]
}
]
Example of invalid positional parameter
"scripts": [
{
"text": "SELECT * FROM customers WHERE first_name = $1; SELECT * FROM customers WHERE age = $2;",
"type": "Query",
"parameters": [
{
"name": null,
"type": "String",
"value": "John",
"direction": "Input",
"size": 256
},
{
"name": null,
"type": "INT32",
"value": 52,
"direction": "Input"
}
]
}
]
Advanced settings
The advanced settings in Azure Data Factory's script activity for PostgreSQL let you fine-tune execution and logging options for your data workflows. You can set script block timeouts to stop long-running queries from affecting pipeline reliability, and turn on detailed logging to track PostgreSQL notices and activity outputs. These features help keep data operations strong and give you more visibility into your pipeline executions in Azure.
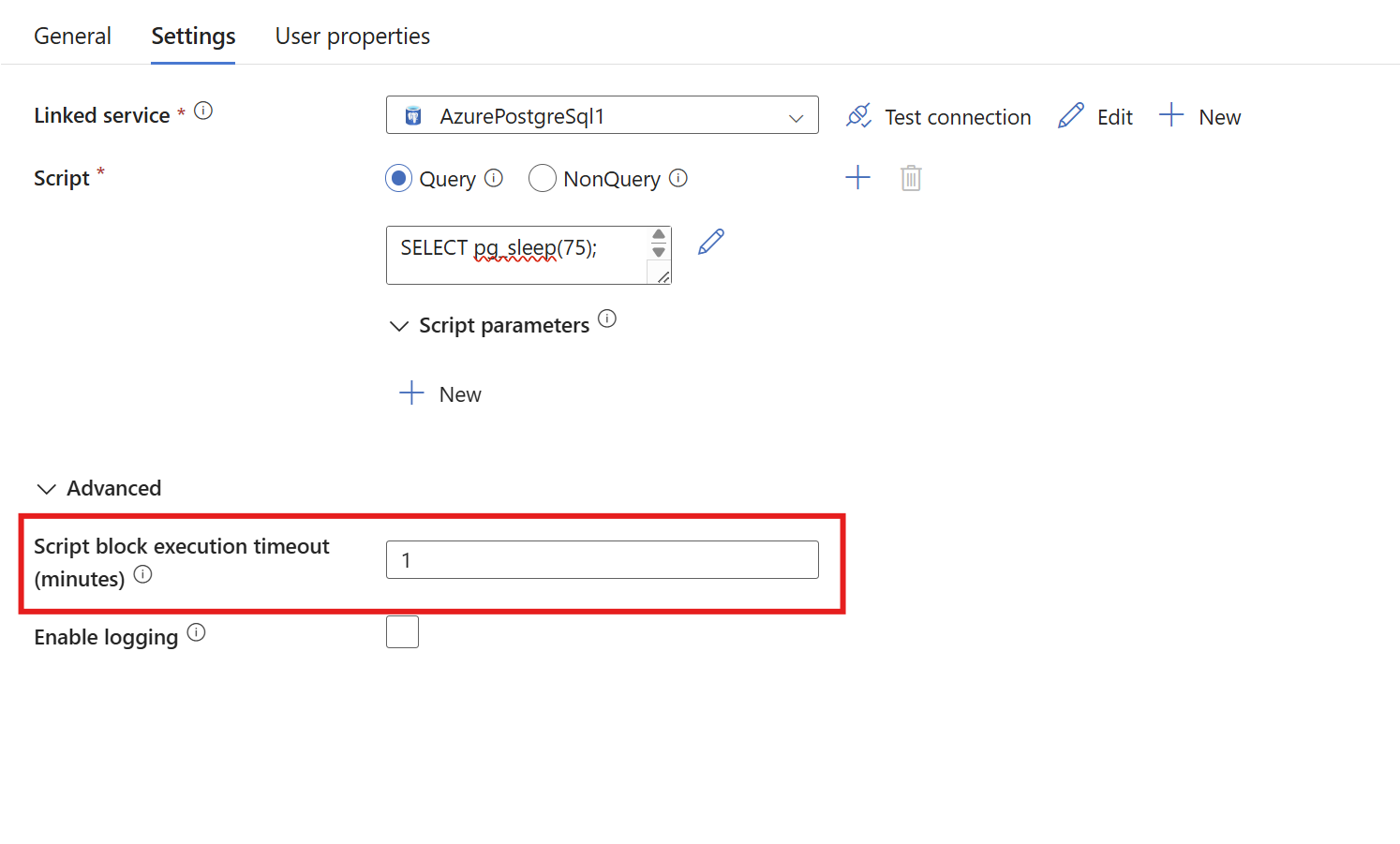
Script block execution timeout
Set a timeout in minutes for each script block run. If any script block in your script activity goes over the timeout, the whole activity fails.
"typeProperties": {
"scripts": [
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "SELECT pg_sleep(40);"
},
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "SELECT pg_sleep(40);"
},
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "SELECT pg_sleep(40);"
}
],
"scriptBlockExecutionTimeout": "00:01:00"
}
Logging
Use logging to send PostgreSQL Notices to an external Blob Storage or to internal storage.
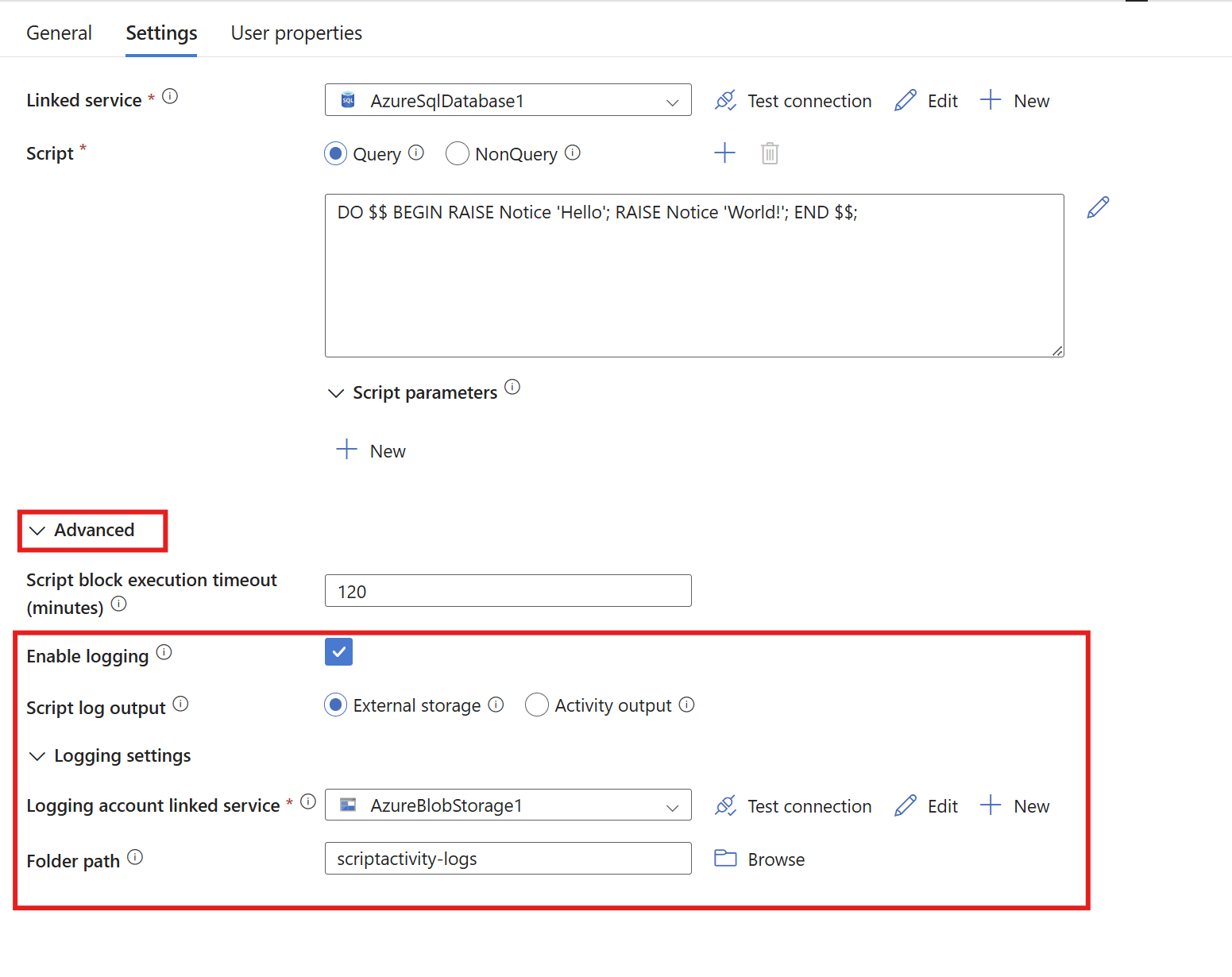
External storage
For external logging, open the Advanced tab, then select Enable logging and External storage. Add a blob storage account by creating a new linked service for your blob storage account. You can optionally enter a folder path. If you leave it blank, the logs go under the scriptactivity-logs folder.
"typeProperties": {
"scripts": [
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "DO $$ BEGIN RAISE Notice 'Hello'; RAISE Notice 'World!'; END $$;"
}
],
"scriptBlockExecutionTimeout": "02:00:00",
"logSettings": {
"logDestination": "ExternalStore",
"logLocationSettings": {
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Blob Storage linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"path": "<Azure Blob Storage folder path>"
}
}
}
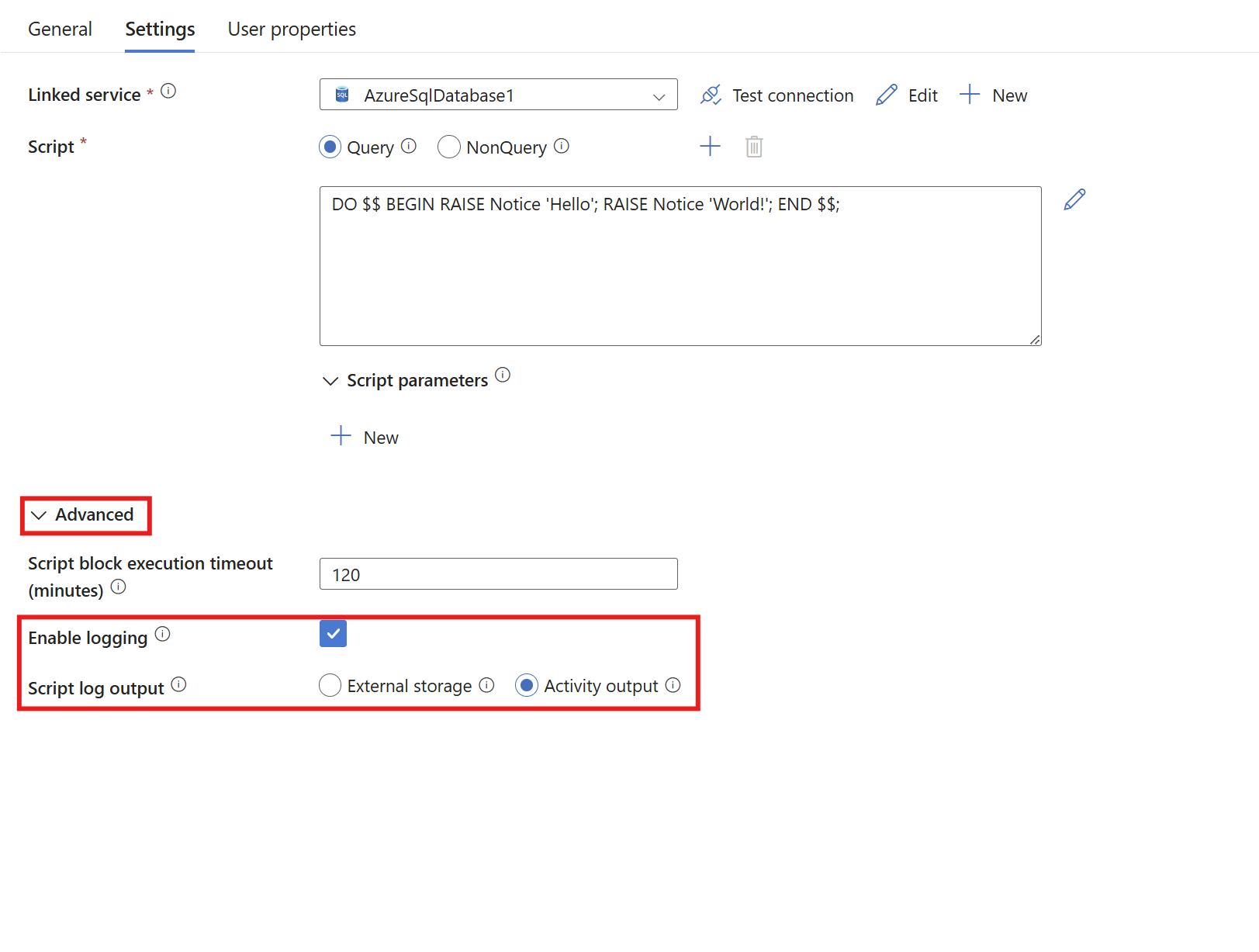
Activity output
For activity output logging, expand the Advanced section and select Enable logging and Activity output. These options turn on logging in the activity output.
"typeProperties": {
"scripts": [
{
"type": "Query",
"text": "DO $$ BEGIN RAISE Notice 'Hello'; RAISE Notice 'World!'; END $$;"
}
],
"scriptBlockExecutionTimeout": "02:00:00",
"logSettings": {
"logDestination": "ActivityOutput"
}
}