Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Managed Redis has different SKU and tier offerings that provide flexibility in the choice of cache size and performance. You can scale to a larger memory size or change to a tier with more compute performance. You can also scale down to a smaller or more appropriate tier. This article shows you how to scale your cache using the Azure portal, plus tools such as Azure PowerShell and Azure CLI.
Note
Because each tier of Azure Managed Redis has almost the same features, scaling is typically used just to change memory and performance characteristics. Scaling geo-replicated Azure Managed Redis caches remains in Public Preview.
Types of scaling
Azure Managed Redis supports scaling in two dimensions:
Memory Increasing memory increases the size of the Redis instance, allowing you to store more data. When reducing the memory, you need to ensure that your current memory usage is less than new memory size you want to use.
vCPUs Azure Managed Redis offers three tiers (Memory Optimized, Balanced, and Compute Optimized) that have an increasing number of vCPUs for each level of memory. Scaling to a tier with more vCPUs increases the performance of your instance without requiring you to increase memory. Unlike the Basic, Standard, and Premium tiers of Azure Cache for Redis that only utilize a single vCPU, Azure Managed Redis uses the Redis Enterprise stack. The Redis Enterprise stack is able to use multiple vCPUs, which means that the number of vCPUs used by your Redis instance directly correlates with throughput and latency performance.
Performance tiers
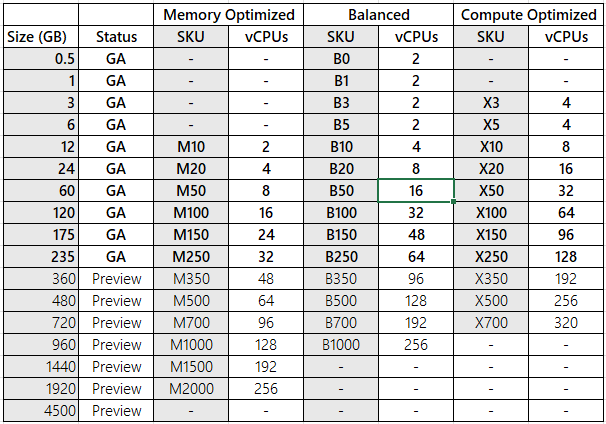
There are four tiers of Azure Managed Redis available, each with different performance characteristics and price levels.
Important
All in-memory tiers that use over 235 GB of storage are in Public Preview, including Memory Optimized M350 and higher; Balanced B350 and higher; and Compute Optimized X350 and higher. All these tiers and higher are in Public Preview.
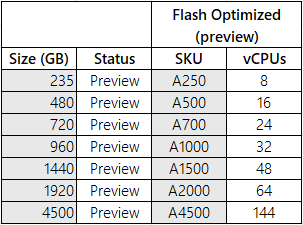
All Flash Optimized tiers are in Public Preview.
Tiers and SKUs at a glance
Here are three tiers store that store data in memory:
Memory Optimized Ideal for memory-intensive use cases that require a high memory-to-vCPU ratio (8:1) but don't need the highest throughput performance. It provides a lower price point for scenarios where less processing power or throughput is necessary, making it an excellent choice for development and testing environments.
Balanced (Memory + Compute) Offers a balanced memory-to-vCPU (4:1) ratio, making it ideal for standard workloads. This tier provides a healthy balance of memory and compute resources.
Compute Optimized Designed for performance-intensive workloads requiring maximum throughput, with a low memory-to-vCPU (2:1) ratio. It's ideal for applications that demand the highest performance.
Here's the tier that stores data both in-memory and on-disk:
Flash Optimized (preview) Enables Redis clusters to automatically move less frequently accessed data from memory (RAM) to NVMe storage. This reduces performance, but allows for cost-effective scaling of caches with large datasets.
Performance (Throughput and Latency)
For performance benchmarks and more information on how to measure the performance of each SKU and tier, see Performance testing with Azure Managed Redis
When to scale
You can use the monitoring features of Azure Managed Redis to monitor the health and performance of your cache. Use that information to determine when to scale the cache.
You can monitor the following metrics to determine if you need to scale.
- CPU
- High CPU usage means that the Redis server is unable to keep pace with requests from all the clients. Scaling to more vCPUs helps distribute requests across multiple Redis processes. Scaling also helps distribute TLS encryption/decryption and connection/disconnection, speeding up cache instances using TLS.
- Memory Usage
- High memory usage indicates that your data size is too large for the current cache size. Consider scaling to a cache size with larger memory. When reducing the memory, you need to ensure that your memory usage of your current cache is lower than new memory size you want to use. You can't put a large data set into a smaller cache size.
- Client connections
- Each cache size has a limit to the number of client connections it can support. If your client connections are close to the limit for the cache size, consider scaling to a larger memory size or a higher performance tier.
- For more information on connection limits by cache size, see Performance testing with Azure Managed Redis.
- Network Bandwidth
- If the Redis server exceeds the available bandwidth, clients requests could time out because the server can't push data to the client fast enough. To see how much server-side bandwidth is being used, check "Cache Read" and "Cache Write" metrics. If your Redis server is exceeding available network bandwidth, consider scaling to a higher performance tier or a larger cache size.
- The choice of cluster policy affects network bandwidth available. Generally, the OSS cluster policy has higher network bandwidth than the Enterprise cluster policy. For more information, see Cluster policy
- For more information on network available bandwidth by cache size, see Performance testing with Azure Managed Redis.
For more information on determining the cache pricing tier to use, see Choosing the right tier.
For more information on how to optimize the scaling process, see the best practices for scaling guide.
Limitations of scaling Azure Managed Redis
- You can't scale from the Memory Optimized, Balanced, or Compute Optimized tiers to the Flash Optimized tier, or vice-versa.
- When reducing the memory for your Redis instance, the current memory usage of your Redis instance should be less than the intended new memory size. For more information, see What happens to my data if I scale to smaller memory size?
- When reducing the memory or vCPU for your Redis instance, you can only scale to SKUs, which have a vCPU and shard configuration that's compatible with the configuration on your current instance.
- In some cases when scaling, the underlying IP address of the Redis instance can change. The DNS record for the instance changes and is transparent to most applications. However, if you use an IP address to configure the connection to your Redis instance, or to configure NSGs, or firewalls allowing traffic to the Redis instance, your application might have trouble connecting sometime after the DNS record updates.
- Scaling an instance in a geo-replication group has some more limitations. See Are there scaling limitations with geo-replication? for more information.
- When you scale down, you can only scale to certain tiers. For more information, see Why can only I scale down to a subset of smaller SKUs?
How to scale
In this section, we describe how to scale an Azure Managed Redis cache.
Scale using the Azure portal
Note
Scaling geo-replicated Azure Managed Redis caches remains in Public Preview.
To scale your cache, browse to the cache in the Azure portal and select Scale from the Resource menu.
To scale your vCPUs, choose a different Cache type and then choose Save.
Important
If you select a SKU that can't be scaled to, the Save option is disabled. Review the Limitations of scaling Azure Managed Redis section for details on which scaling options are allowed.
When scaling is complete, the status changes from Scaling to Running when viewing the Overview section of the Resource menu.
Scale using PowerShell
You can scale your Azure Managed Redis instances with PowerShell by using the Update-AzRedisEnterpriseCache cmdlet. You can modify the Sku property to select the tier and SKU you need. The following example shows how to scale a cache named myCache to a Compute Optimized X20 (24 GB) instance.
Update-AzRedisEnterpriseCache -ResourceGroupName <your-group> -Name <your-cache-name> -Sku <sku-name>
Scale using Azure CLI
To scale your Azure Managed Redis instances using Azure CLI, call the az redisenterprise update command. You can modify the sku property to select the tier and SKU you need. The following example shows how to scale a cache named myCache to a Compute Optimized X20 (24 GB) instance.
az redisenterprise update --cluster-name <your-cache-name> --resource-group <your-resource-group> --sku <name-of-sku>
Scaling FAQ
The following list contains answers to commonly asked questions about Azure Managed Redis scaling.
- Can I scale within or across tiers?
- What happens to my data if I scale to smaller memory size?
- After scaling, do I have to change my cache name or access keys?
- How does scaling work?
- Do I lose data from my cache during scaling?
- Is my cache available during scaling?
- Are there scaling limitations with geo-replication?
- How long does scaling take?
- How can I tell when scaling is complete?
- Does Azure Managed Redis use clustering? How many shards does each Azure Managed Redis SKU use?
- How are keys distributed in a cluster?
- What is the largest cache size I can create?
- Why can only I scale down to a subset of smaller SKUs?
- Can the Clustering Policy be changed after selecting OSS or Enterprise Cluster?
Can I scale within or across tiers?
You can always scale to a higher performance tier at the same memory size or a larger memory size within the same performance tier. For scaling to a lower performance tier or smaller memory size, we recommend you run the "listskusforscaling" REST API to get the list of SKUs that you can scale to.
az redisenterprise list-skus-for-scaling --cluster-name <your-redis-instance> --resource-group <your-resource-group>
What happens to my data if I scale to smaller memory size?
You can scale to a smaller memory size only if the current memory usage is less than the intended smaller memory size. If the current memory usage is higher than the intended smaller size, your scaling request fails. You can reduce the current memory usage by deleted unwanted key value pairs or by running the flush operation.
az redisenterprise database flush --cluster-name <your-redis-instance> --resource-group <your-resource-group>
After scaling, do I have to change my cache name or access keys?
No, your cache name and access keys aren't changed during a scaling operation.
How does scaling work?
- When you scale a Redis instance, one of the nodes in the Redis cluster is shut down and reprovisioned to the new size. Then data transfers over, and the other node does a similar failover next, before reprovisioning. The shutdown and reprovisioning is similar to the process that occurs during patching or a failure of one of the nodes of a cache.
- When you scale to an instance with more vCPUs, new shards are provisioned and added to the Redis server cluster. Data is then resharded across all shards.
For more information on how Azure Managed Redis handles sharding, see Sharding configuration.
Do I lose data from my cache during scaling?
- If high availability mode is enabled, all data should be preserved during scaling operations.
- If you're scaling to a smaller memory level, you need to ensure that the current memory usage is smaller than the intended new memory size. If the current memory usage is more than the intended SKU memory size, you can flush your data using Flush operation or manually choose key values to delete.
- If high availability mode is disabled, all data is lost and the cache is unavailable during the scaling operation.
Is my cache available during scaling?
- Azure Managed Redis instances with high availability mode enabled remain available during the scaling operation. However, connection blips can occur while scaling these caches. These connection blips are typically short and Redis clients can generally re-establish their connection instantly.
- If high availability mode is disabled, the Azure Managed Redis instance is offline during scaling operations.
Are there scaling limitations with geo-replication?
Scaling geo-replicated caches is in Public Preview. With active geo-replication configured, you can't mix and match cache sizes in a geo-replication group. As a result, scaling the caches in a geo-replication group requires a few more steps. See Scaling instances in a geo-replication group for instructions.
Scaling down to a smaller memory size or smaller shard count isn't supported for geo-replicated caches. For more information, see How many shards does each Azure Managed Redis SKU use to find out shards in your cluster.
How long does scaling take?
Scaling time depends on a few factors. Here are some factors that can affect how long scaling takes.
- Amount of data: Larger amounts of data take a longer time to be replicated
- High write requests: Higher number of writes mean more data replicates across nodes or shards
- High CPU usage: Higher CPU usage means the Redis server is busy and limited CPU cycles are available to complete data redistribution
Generally, when you scale an instance with no data, it takes approximately 10 minutes.
How can I tell when scaling is complete?
In the Azure portal, you can see the scaling operation in progress. When scaling is complete, the status of the cache changes to Running when viewing Overview on the Resource menu.
Does Azure Managed Redis use clustering?
Unlike Azure Cache for Redis, Azure Managed Redis uses clustering across all tiers and SKUs. Clustering enables significant performance optimizations. Each SKU of Azure Managed Redis is configured for an optimized number of shards for the number of vCPUs available. The number of shards isn't user configurable.
How many shards does each Azure Managed Redis SKU use?
Because Azure Managed Redis runs on Redis Enterprise software, shards can be used in a denser configuration than in community Redis. To learn about the specific number of shards used in each SKU, see Sharding configuration.
How are keys distributed in a cluster?
Per the Redis documentation on Keys distribution model: The key space is split into 16,384 slots. Each key is hashed and assigned to one of these slots, which are distributed across the nodes of the cluster. You can configure which part of the key is hashed to ensure that multiple keys are located in the same shard using hash tags.
- Keys with a hash tag - if any part of the key is enclosed in
{and}, only that part of the key is hashed for the purposes of determining the hash slot of a key. For example, the following three keys would be located in the same shard:{key}1,{key}2, and{key}3since only thekeypart of the name is hashed. For a complete list of keys hash tag specifications, see Keys hash tags. - Keys without a hash tag - the entire key name is used for hashing, resulting in a statistically even distribution across the shards of the cache.
For best performance and throughput, we recommend distributing the keys evenly. If you're using keys with a hash tag, it's the application's responsibility to ensure the keys are distributed evenly.
For more information, see Keys distribution model, Redis Cluster data sharding, and Keys hash tags.
What is the largest cache size I can create?
The largest cache size you can have is 4.5 TB, called Flash Optimized A4500 instance. Azure Cache for Redis Pricing.
Why can only I scale down to a subset of smaller SKUs?
To maintain compatibility with number of shards and vCPU, you're allowed to scale down only to certain SKUs. You can see which SKUs your Redis instance can scale down to by checking the available options in the Scale section of the Azure portal. You can also run the following CLI command.
You can see which SKUs your Redis instance can scale down to by checking the available options in the Scale section of the Azure portal.
az redisenterprise list-skus-for-scaling --cluster-name <your-redis-instance> --resource-group <your-resource-group>
Can the Clustering Policy be changed after selecting OSS or Enterprise Cluster?
Once you set a clustering policy to either OSSCluster or EnterpriseCluster when you create a cache, you can't change it. To switch to a different clustering policy, you must delete the Redis cache and recreate it with the desired configuration. Only caches with the Noncluster policy can be updated to a clustered configuration after deployment.