Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article explains how to enable role-based access control (RBAC) for data plane operations on Azure AI Search. With RBAC enabled, you can use Microsoft Entra ID authentication instead of API keys.
Important
When you create a search service, key-based authentication is the default, but it's not the most secure option. We recommend that you replace it with role-based access as described in this article.
Before you can assign roles for authorized data plane access to Azure AI Search, you must enable role-based access control on your search service. Roles for service administration (control plane) are built in and can't be enabled or disabled.
If you observe key-related activity, such as Get Admin Keys, in the Activity Log on a roles-only search service, those actions are initiated on the control plane and don't affect your content or content-related operations.
Prerequisites
A search service in any region, on any tier, including free.
Owner, User Access Administrator, or a custom role with Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write permissions.
After enabling RBAC, you need data plane roles to access content: Search Service Contributor, Search Index Data Contributor, and Search Index Data Reader. See Assign roles for details.
Enable role-based access for data plane operations
Configure your search service to recognize an authorization header on data requests that provide an OAuth2 access token.
When you enable roles for the data plane, the change is effective immediately, but wait a few seconds before assigning roles.
The default failure mode for unauthorized requests is http401WithBearerChallenge. Alternatively, you can set the failure mode to http403.
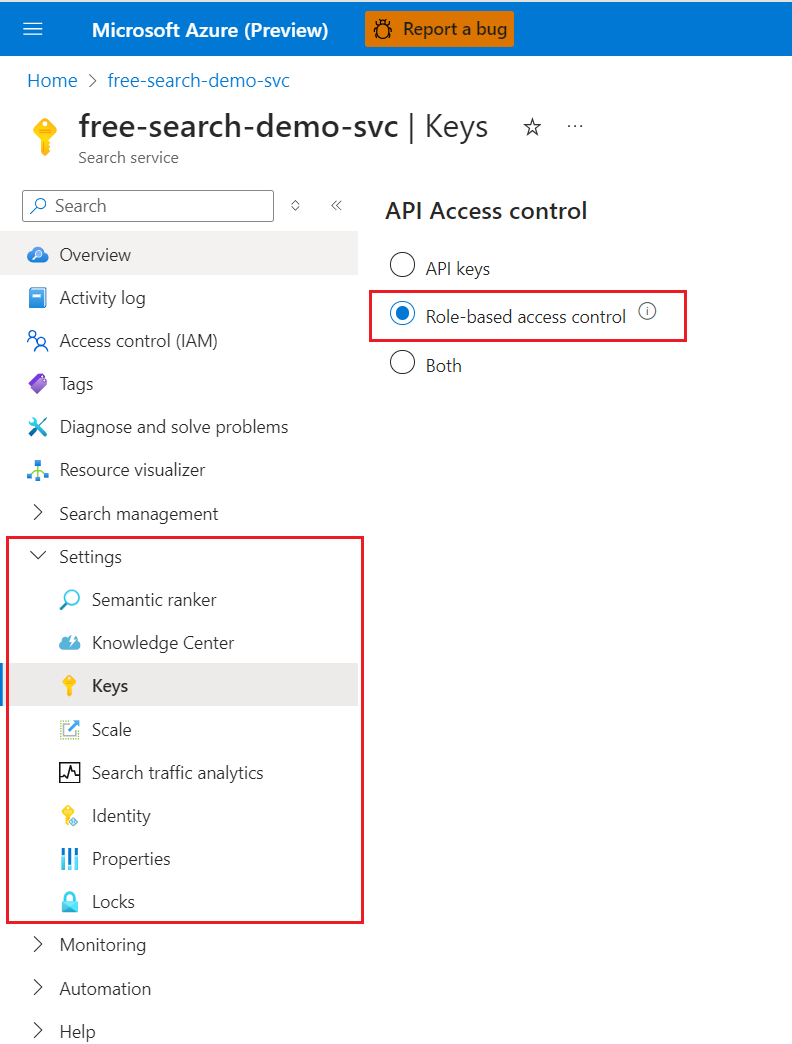
Sign in to the Azure portal and navigate to your search service.
Select Settings and then select Keys in the left pane.
Choose Role-based control. Only choose Both if you're currently using keys and need time to transition clients to role-based access control.
Option Description API Key (default) Requires API keys on the request header for authorization. Role-based access control (recommended) Requires membership in a role assignment to complete the task. It also requires an authorization header on the request. Both Requests are valid using either an API key or role-based access control, but if you provide both in the same request, the API key is used. As an administrator, if you choose a roles-only approach, assign data plane roles to your user account to restore full administrative access over data plane operations in the Azure portal. Roles include Search Service Contributor, Search Index Data Contributor, and Search Index Data Reader. You need the first two roles if you want equivalent access.
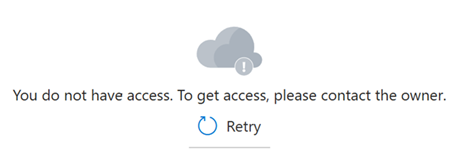
Sometimes it can take five to ten minutes for role assignments to take effect. Until that happens, the following message appears in the Azure portal pages used for data plane operations.
Disable role-based access control
It's possible to disable role-based access control for data plane operations and use key-based authentication instead. You might do this as part of a test workflow, for example to rule out permission issues.
To disable role-based access control in the Azure portal:
Sign in to the Azure portal and open the search service page.
Select Settings and then select Keys in the left pane.
Select API Keys.
Disable API key authentication
Key access, or local authentication, can be disabled on your service if you're exclusively using the built-in roles and Microsoft Entra authentication. Disabling API keys causes the search service to refuse all data-related requests that pass an API key in the header.
Admin API keys can be disabled, but not deleted. Query API keys can be deleted.
Owner or Contributor permissions are required to disable security features.
In the Azure portal, navigate to your search service.
In the left-navigation pane, select Keys.
Select Role-based access control.
The change is effective immediately, but wait a few seconds before testing. Assuming you have permission to assign roles as a member of Owner, service administrator, or coadministrator, you can use portal features to test role-based access.