Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Attention: All Microsoft Sentinel features will be officially retired in Azure in China regions on August 18, 2026 per the announcement posted by 21Vianet.
One of the primary activities of a security team is to search logs for specific events. For example, you might search logs for the activities of a specific user within a given time-frame.
In Microsoft Sentinel, you can search across long time periods in extremely large datasets by using a search job. While you can run a search job on any type of log, search jobs are ideally suited to search logs in a long-term retention (formerly known as archive) state. If you need to do a full investigation on such data, you can restore that data into an interactive retention state—like your regular Log Analytics tables— to run high performing queries and deeper analysis.
Search large datasets
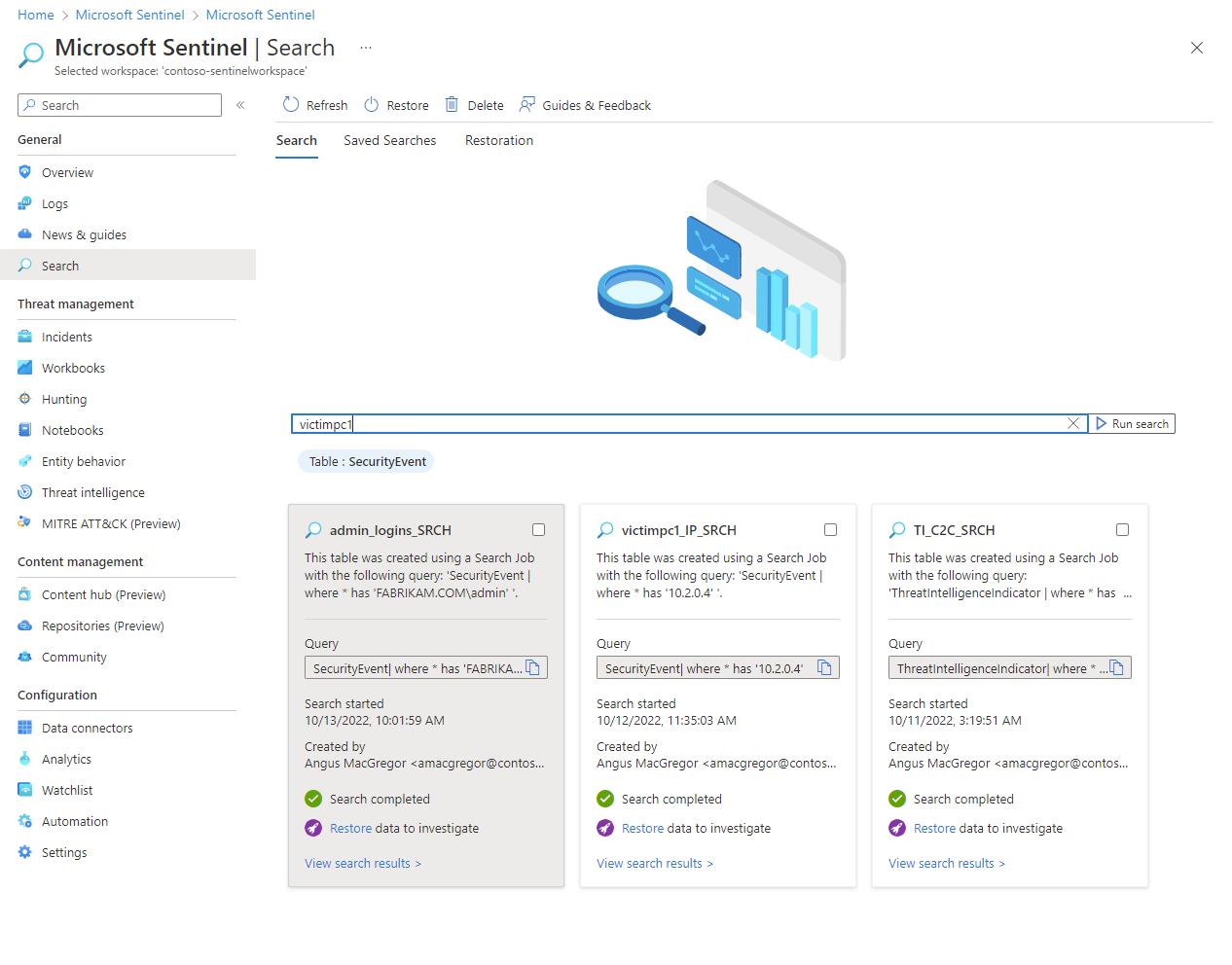
Use a search job to retrieve data stored in long-term retention, or to scan through large volumes of data, if the log query time-out of 10 minutes isn't sufficient. Search jobs are asynchronous queries that fetch records into a search table in your Log Analytics workspace. The search job uses parallel processing to search across long time spans in extremely large datasets, so search jobs don't impact the workspace's performance or availability.
Search results are stored in a table named with a _SRCH suffix.
This image shows example search criteria for a search job.
Restore log data from long-term retention
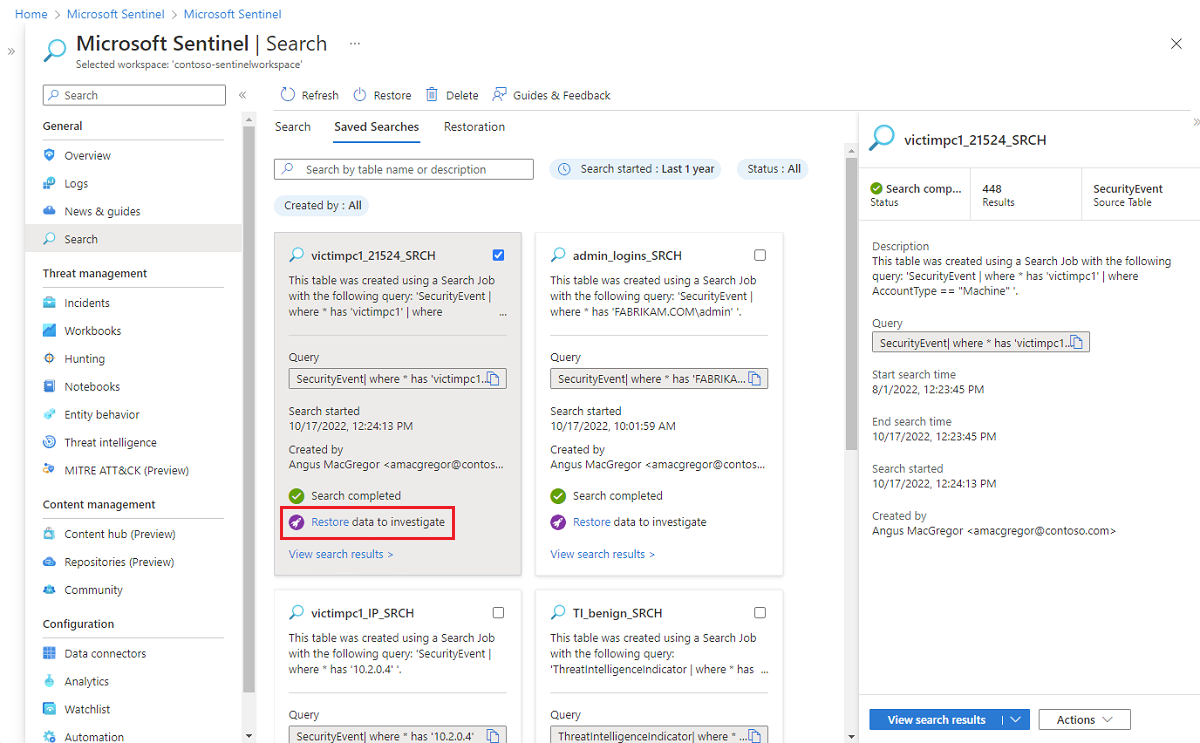
When you need to do a full investigation on log data in long-term retention, restore a table from the Search page in Microsoft Sentinel. Specify a target table and time range for the data you want to restore. Within a few minutes, the log data is restored and available within the Log Analytics workspace. Then you can use the data in high-performance queries that support full KQL.
A restored log table is available in a new table that has a *_RST suffix. The restored data is available as long as the underlying source data is available. But you can delete restored tables at any time without deleting the underlying source data. To save costs, we recommend you delete the restored table when you no longer need it.
The following image shows the restore option on a saved search.
Limitations of log restore
See Restore limitations in the Azure Monitor documentation.
Bookmark search results or restored data rows
Similar to the threat hunting dashboard, bookmark rows that contain information you find interesting so you can attach them to an incident or refer to them later. For more information, see Create bookmarks.