Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you deploy a Java application to Azure Service Fabric using the Eclipse IDE on a Linux developer machine. When you're finished, you have a voting application with a Java web front end that saves voting results in a stateful back-end service in the cluster.
Azure Service Fabric is a distributed systems platform for deploying and managing microservices and containers.
Prerequisites
- Java environment and Yeoman
- Eclipse Neon (4.6)+ and Eclipse plug-in for Service Fabric
- Service Fabric SDK and Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Git
Download the sample
In a command window, run the following command to clone the sample app repository to your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/service-fabric-java-quickstart.git
Run the application locally
Start your local cluster by running the following command:
sudo /opt/microsoft/sdk/servicefabric/common/clustersetup/devclustersetup.shThe startup of the local cluster takes some time. To confirm that the cluster is fully up, access the Service Fabric Explorer at
http://localhost:19080. The five healthy nodes indicate the local cluster is up and running.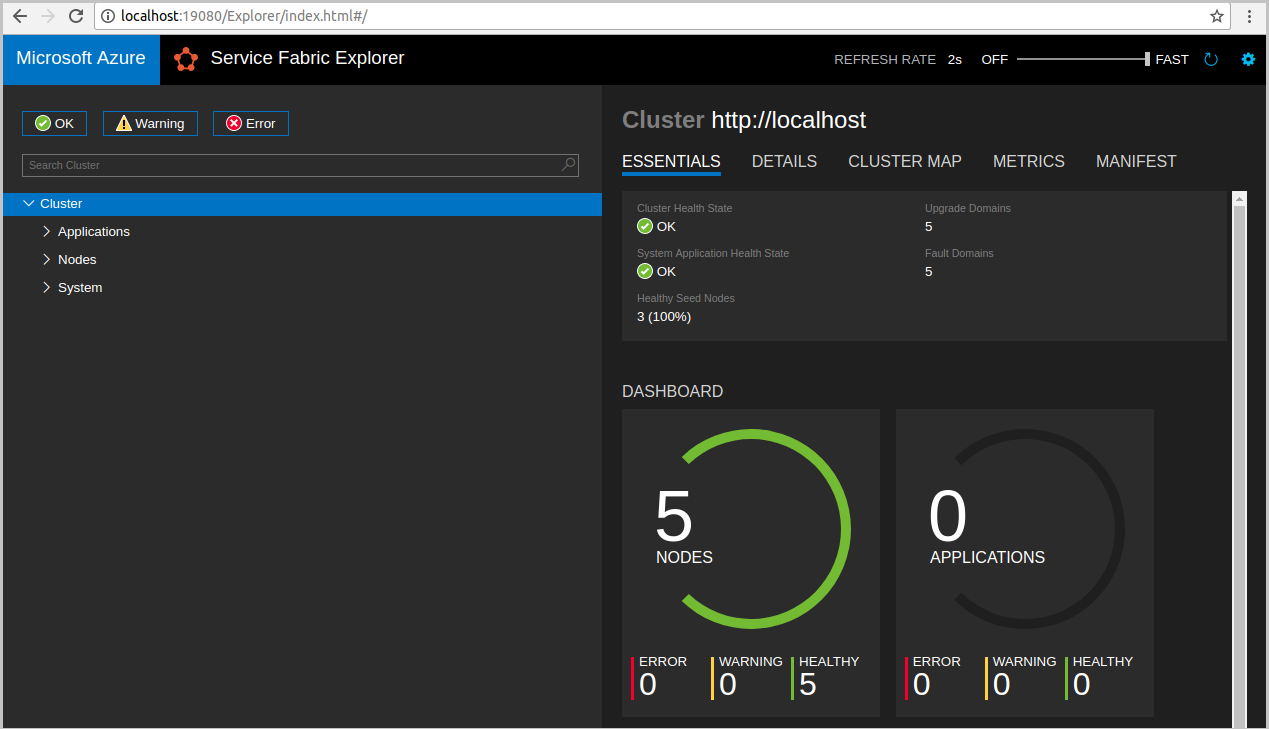
Open Eclipse.
Select File > Import > Gradle > Existing Gradle Project and follow the wizard.
Select Directory and choose the Voting directory from the service-fabric-java-quickstart folder you cloned from GitHub. Select Finish.
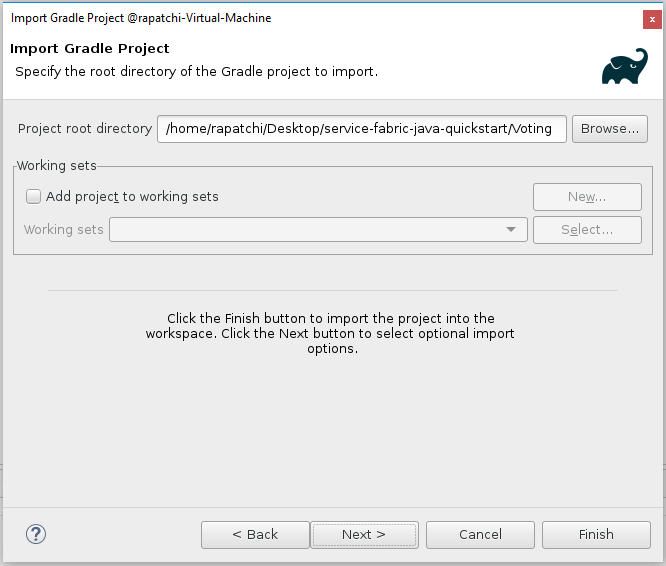
You now have the
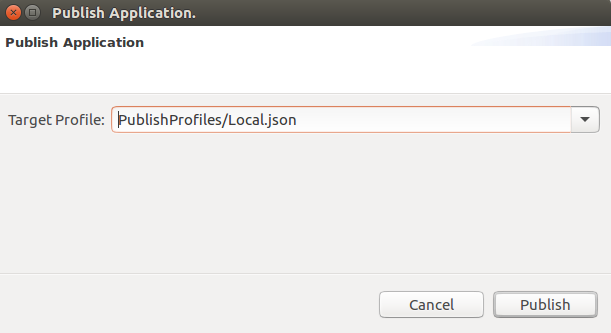
Votingproject in the Package Explorer for Eclipse.Right-click on the project and select Publish Application under the Service Fabric dropdown. Choose PublishProfiles/Local.json as the Target Profile and select Publish.
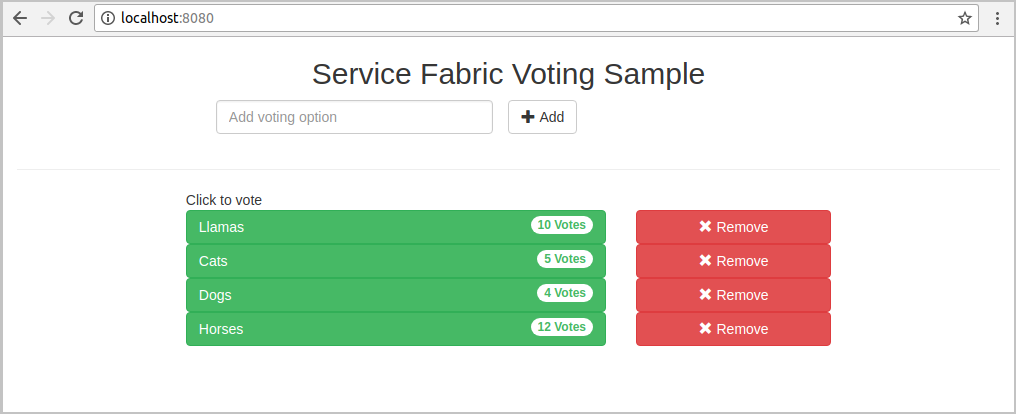
Open your favorite web browser and access the application by accessing
http://localhost:8080.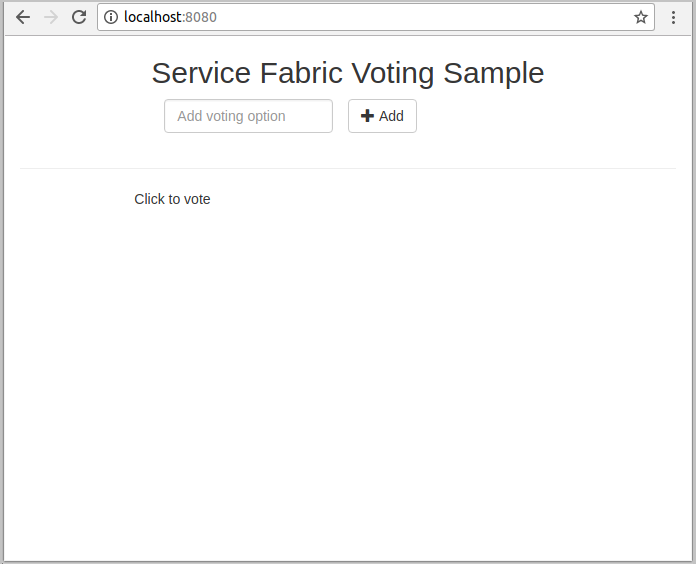
You can now add a set of voting options, and start taking votes. The application runs and stores all data in your Service Fabric cluster, without the need for a separate database.
Scale applications and services in a cluster
Services can be scaled across a cluster to accommodate for a change in the load on the services. You scale a service by changing the number of instances running in the cluster. There are many ways of scaling your services. For example, you can use scripts or commands from Service Fabric CLI (sfctl). The following steps use Service Fabric Explorer.
Service Fabric Explorer runs in all Service Fabric clusters and can be accessed from a browser by browsing to the cluster's HTTP management port (19080). For example, http://localhost:19080.
To scale the web front-end service, do the following:
Open Service Fabric Explorer in your cluster. For example,
https://localhost:19080.Select the ellipsis (...) next to the fabric:/Voting/VotingWeb node in the treeview and select Scale Service.
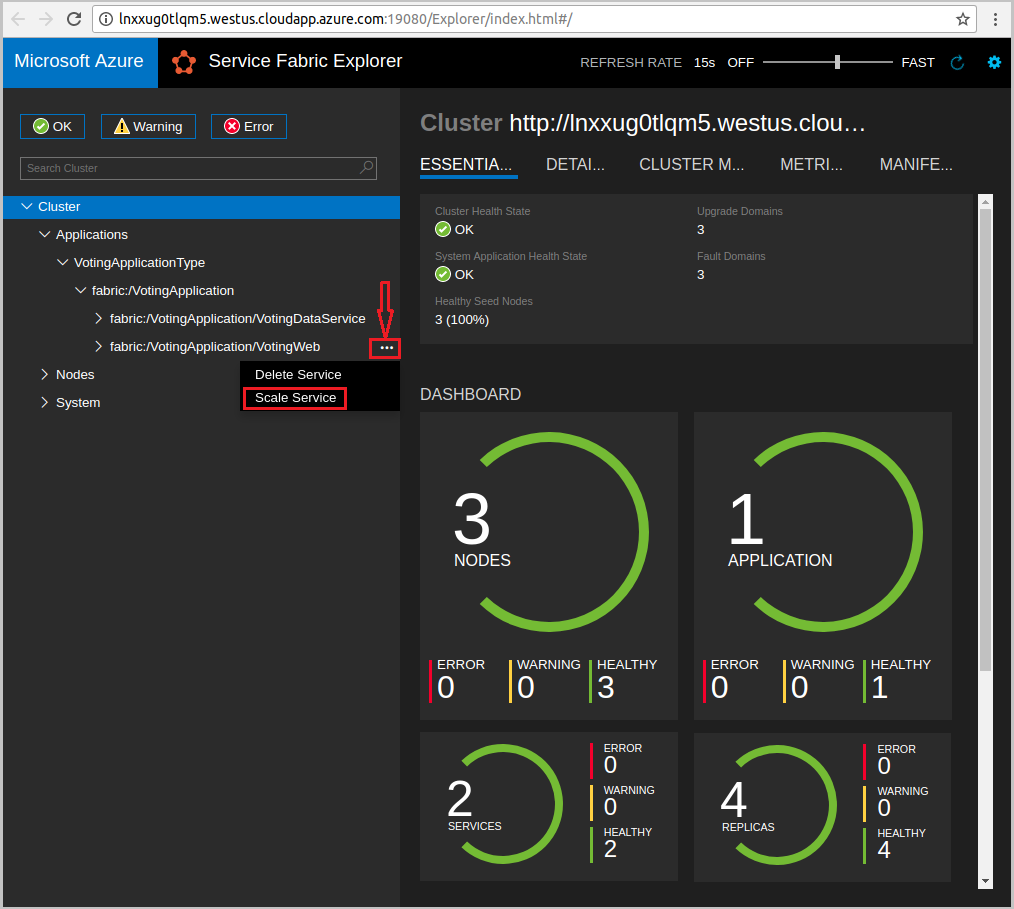
You can now choose to scale the number of instances of the web front-end service.
Change the number to 2 and select Scale Service.
Select the fabric:/Voting/VotingWeb node in the tree-view and expand the partition node (represented by a GUID).
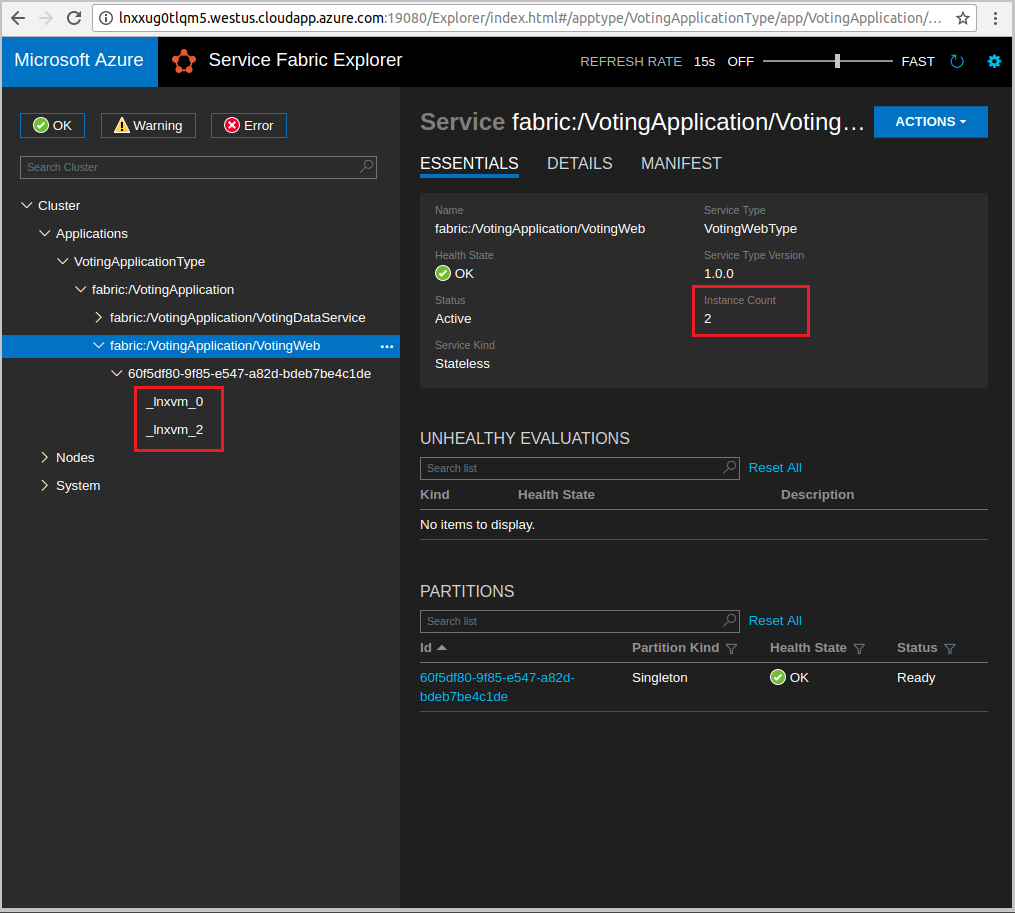
You can now see that the service has two instances, and in the tree view you see which nodes the instances run on.
Through this simple management task, you've doubled the resources available for the front-end service to process user load. It's important to understand that you don't need multiple instances of a service for it to run reliably. If a service fails, Service Fabric makes sure that a new service instance runs in the cluster.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to:
- Use Eclipse as a tool for your Service Fabric Java applications
- Deploy Java applications to your local cluster
- Scale out the application across multiple nodes
To learn more about working with Java apps in Service Fabric, continue to the tutorial for Java apps.