Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial is part one in a series. In this tutorial, learn how to create an Azure Service Fabric application that has an ASP.NET Core Web API front end and a stateful back-end service to store your data. When you're finished, you have a voting application that has an ASP.NET Core web front end that saves voting results in a stateful back-end service in the cluster.
This tutorial series requires a Windows developer computer. If you don't want to manually create the voting application, you can download the source code for the completed application and skip ahead to Walk through the voting sample application. You also can view a video walkthrough of this tutorial.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create an ASP.NET Core Web API service as a stateful reliable service
- Create an ASP.NET Core Web Application service as a stateless web service
- Use reverse proxy to communicate with the stateful service
The tutorial series shows you how to:
- Build a .NET Service Fabric application (this tutorial)
- Deploy the application to a remote cluster
- Add an HTTPS endpoint to an ASP.NET Core front-end service
- Configure CI/CD by using Azure Pipelines
- Set up monitoring and diagnostics for the application
Prerequisites
Before you begin this tutorial:
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial subscription.
- Install Visual Studio 2019 version 15.5 or later, including the Azure development workload and the ASP.NET and web development workload.
- Install the Service Fabric SDK.
Create an ASP.NET Web API service as a reliable service
First, create the web front end of the voting application by using ASP.NET Core. ASP.NET Core is a lightweight, cross-platform web development framework that you can use to create modern web UI and web APIs.
To get a complete understanding of how ASP.NET Core integrates with Service Fabric, we strongly recommend that you review ASP.NET Core in Service Fabric Reliable Services. For now, you can follow this tutorial to get started quickly. To learn more about ASP.NET Core, see the ASP.NET Core documentation.
To create the service:
Open Visual Studio by using the Run as administrator option.
Select File > New > Project to create a new project.
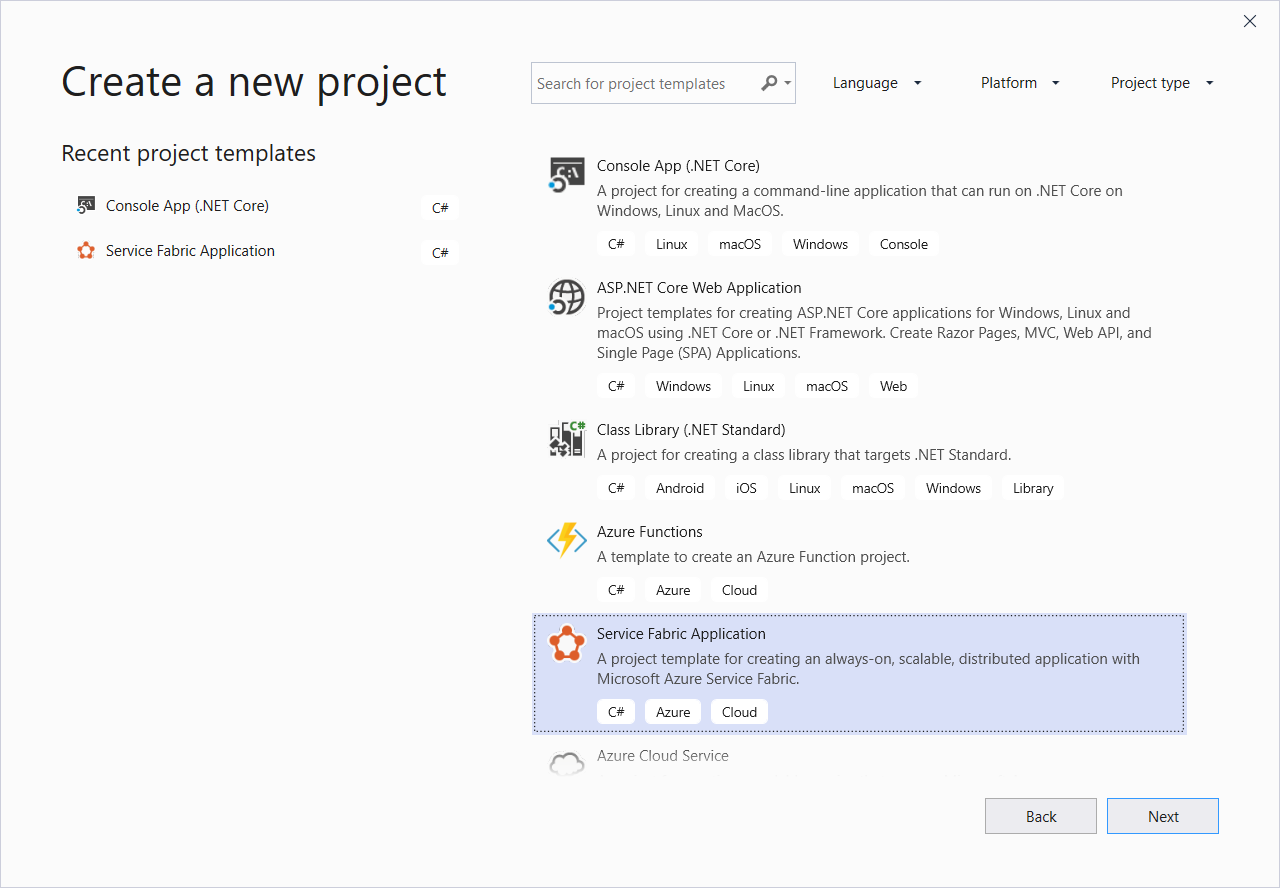
On Create a new project, select Cloud > Service Fabric Application. Select Next.
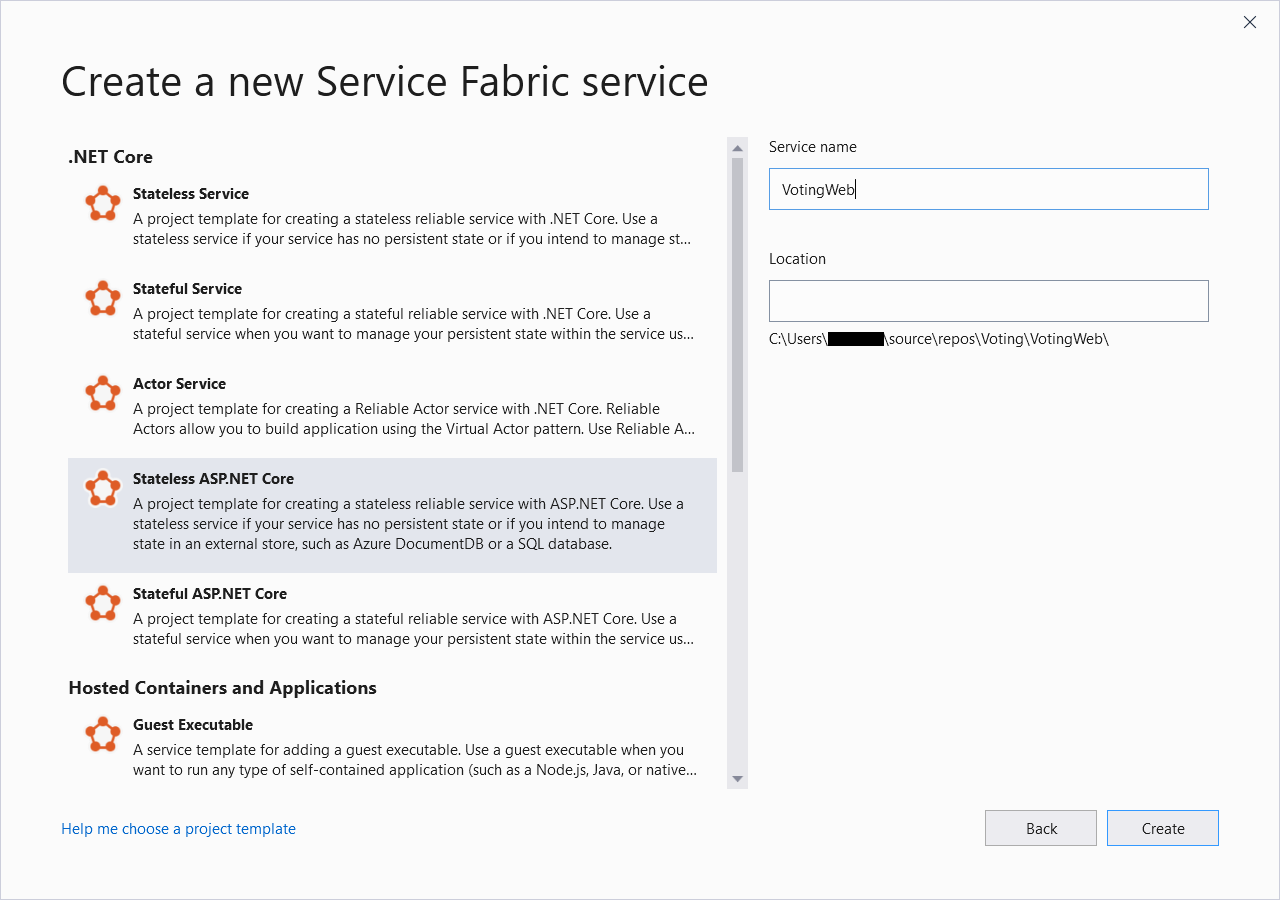
Select Stateless ASP.NET Core for the new project type, name your service VotingWeb, and then select Create.
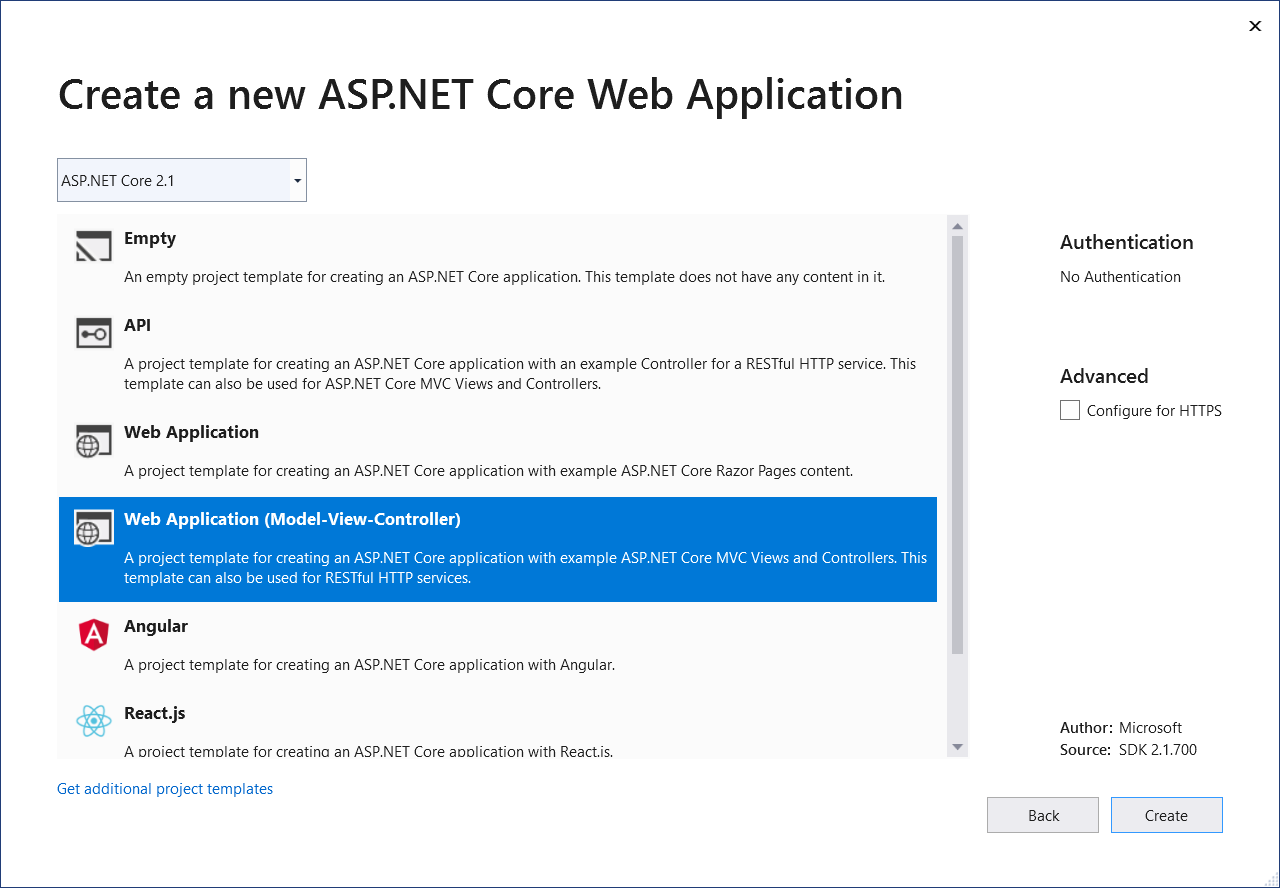
The next pane shows a set of ASP.NET Core project templates. For this tutorial, select Web Application (Model-View-Controller), and then select OK.
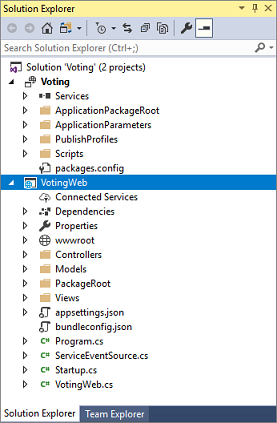
Visual Studio creates an application and a service project, and then displays them in Visual Studio Solution Explorer:
Update the site.js file
Go to wwwroot/js/site.js and open the file. Replace the file contents with the following JavaScript that's used by the Home views, and then save your changes.
var app = angular.module('VotingApp', ['ui.bootstrap']);
app.run(function () { });
app.controller('VotingAppController', ['$rootScope', '$scope', '$http', '$timeout', function ($rootScope, $scope, $http, $timeout) {
$scope.refresh = function () {
$http.get('api/Votes?c=' + new Date().getTime())
.then(function (data, status) {
$scope.votes = data;
}, function (data, status) {
$scope.votes = undefined;
});
};
$scope.remove = function (item) {
$http.delete('api/Votes/' + item)
.then(function (data, status) {
$scope.refresh();
})
};
$scope.add = function (item) {
var fd = new FormData();
fd.append('item', item);
$http.put('api/Votes/' + item, fd, {
transformRequest: angular.identity,
headers: { 'Content-Type': undefined }
})
.then(function (data, status) {
$scope.refresh();
$scope.item = undefined;
})
};
}]);
Update the Index.cshtml file
Go to Views/Home/Index.cshtml and open the file. This file has the view that's specific to the Home controller. Replace its contents with the following code, and then save your changes.
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Service Fabric Voting Sample";
}
<div ng-controller="VotingAppController" ng-init="refresh()">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-8 col-xs-offset-2 text-center">
<h2>Service Fabric Voting Sample</h2>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-8 col-xs-offset-2">
<form class="col-xs-12 center-block">
<div class="col-xs-6 form-group">
<input id="txtAdd" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Add voting option" ng-model="item"/>
</div>
<button id="btnAdd" class="btn btn-default" ng-click="add(item)">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus" aria-hidden="true"></span>
Add
</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<hr/>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-8 col-xs-offset-2">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-4">
Click to vote
</div>
</div>
<div class="row top-buffer" ng-repeat="vote in votes.data">
<div class="col-xs-8">
<button class="btn btn-success text-left btn-block" ng-click="add(vote.Key)">
<span class="pull-left">
{{vote.key}}
</span>
<span class="badge pull-right">
{{vote.value}} Votes
</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-4">
<button class="btn btn-danger pull-right btn-block" ng-click="remove(vote.Key)">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-remove" aria-hidden="true"></span>
Remove
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Update the _Layout.cshtml file
Go to Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml and open the file. This file has the default layout for the ASP.NET app. Replace its contents with the following code, and then save your changes.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html ng-app="VotingApp" xmlns:ng="https://angularjs.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"/>
<title>@ViewData["Title"]</title>
<link href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
<link href="~/css/site.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container body-content">
@RenderBody()
</div>
<script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.js"></script>
<script src="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/angular.js/1.7.2/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/angular-ui-bootstrap/2.5.0/ui-bootstrap-tpls.js"></script>
<script src="~/js/site.js"></script>
@RenderSection("Scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
Update the VotingWeb.cs file
Open the VotingWeb.cs file. This file creates the ASP.NET Core WebHost inside the stateless service by using the WebListener web server.
At the beginning of the file, add the using System.Net.Http; directive.
Replace the CreateServiceInstanceListeners() function with the following code, and then save your changes.
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceInstanceListener> CreateServiceInstanceListeners()
{
return new ServiceInstanceListener[]
{
new ServiceInstanceListener(
serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(
serviceContext,
"ServiceEndpoint",
(url, listener) =>
{
ServiceEventSource.Current.ServiceMessage(serviceContext, $"Starting Kestrel on {url}");
return new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.ConfigureServices(
services => services
.AddSingleton<HttpClient>(new HttpClient())
.AddSingleton<FabricClient>(new FabricClient())
.AddSingleton<StatelessServiceContext>(serviceContext))
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None)
.UseUrls(url)
.Build();
}))
};
}
Then add the following GetVotingDataServiceName method after CreateServiceInstanceListeners(), and then save your changes. GetVotingDataServiceName returns the service name when polled.
internal static Uri GetVotingDataServiceName(ServiceContext context)
{
return new Uri($"{context.CodePackageActivationContext.ApplicationName}/VotingData");
}
Add the VotesController.cs file
Add a controller to define voting actions. Right-click the Controllers folder, and then select Add > New item > Visual C# > ASP.NET Core > Class. Name the file VotesController.cs, and then select Add.
Replace the VotesController.cs file contents with the following code, and then save your changes. Later, in Update the VotesController.cs file, this file is modified to read and write voting data from the back-end service. For now, the controller returns static string data to the view.
namespace VotingWeb.Controllers
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Fabric;
using System.Fabric.Query;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
[Produces("application/json")]
[Route("api/Votes")]
public class VotesController : Controller
{
private readonly HttpClient httpClient;
public VotesController(HttpClient httpClient)
{
this.httpClient = httpClient;
}
// GET: api/Votes
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get()
{
List<KeyValuePair<string, int>> votes= new List<KeyValuePair<string, int>>();
votes.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, int>("Pizza", 3));
votes.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, int>("Ice cream", 4));
return Json(votes);
}
}
}
Configure the listening port
When the VotingWeb front-end service is created, Visual Studio randomly selects a port for the service to listen on. The VotingWeb service acts as the front end for this application and accepts external traffic. In this section, you bind that service to a fixed and well-known port. The service manifest declares the service endpoints.
In Solution Explorer, open VotingWeb/PackageRoot/ServiceManifest.xml. In the Resources section, find the Endpoint element, and then change the Port value to 8080.
To deploy and run the application locally, the application listening port must be open and available on your computer.
<Resources>
<Endpoints>
<!-- This endpoint is used by the communication listener to obtain the port on which to
listen. Please note that if your service is partitioned, this port is shared with
replicas of different partitions that are placed in your code. -->
<Endpoint Protocol="http" Name="ServiceEndpoint" Type="Input" Port="8080" />
</Endpoints>
</Resources>
Then update the Application URL property value in the Voting project so that a web browser opens to the correct port when you debug your application. In Solution Explorer, select the Voting project, and then update the Application URL property to 8080.
Deploy and run the Voting application locally
You can now run the Voting application to debug it. In Visual Studio, select F5 to deploy the application to your local Service Fabric cluster in debug mode. The application fails if you didn't previously open Visual Studio by using the Run as administrator option.
Note
The first time you run and deploy the application locally, Visual Studio creates a local Service Fabric cluster to use for debugging. The process to create a cluster might take some time. The cluster creation status is displayed in the Visual Studio Output window.
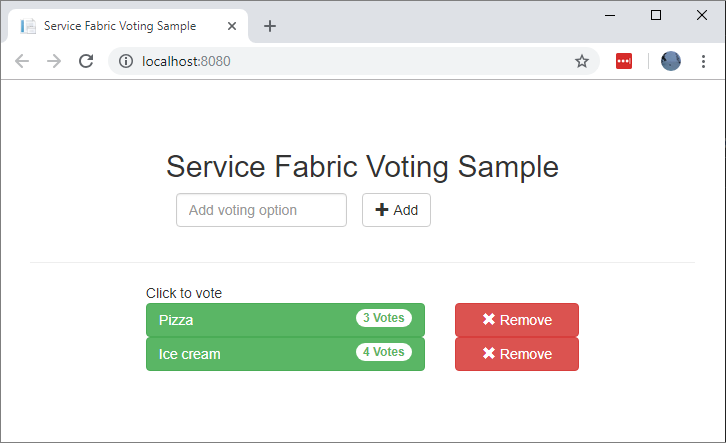
After the Voting application is deployed to your local Service Fabric cluster, your web app automatically opens in a browser tab. It looks similar to this example:
To stop debugging the application, go back to Visual Studio and select Shift+F5.
Add a stateful back-end service to your application
Now that an ASP.NET Web API service is running in the application, add a stateful reliable service to store some data in the application.
You can use Service Fabric to consistently and reliably store your data right inside your service by using reliable collections. Reliable collections are a set of highly available and reliable collection classes that are familiar to anyone who has experience using C# collections.
To create a service that stores a counter value in a reliable collection:
In Solution Explorer, right-click Services in the Voting application project and select Add > New Service Fabric Service.
In the New Service Fabric Service dialog, select Stateful ASP.NET Core, name the service VotingData, and then select OK.
After your service project is created, you have two services in your application. As you continue to build your application, you can add more services the same way. Each service can be independently versioned and upgraded.
The next pane shows a set of ASP.NET Core project templates. For this tutorial, select API.
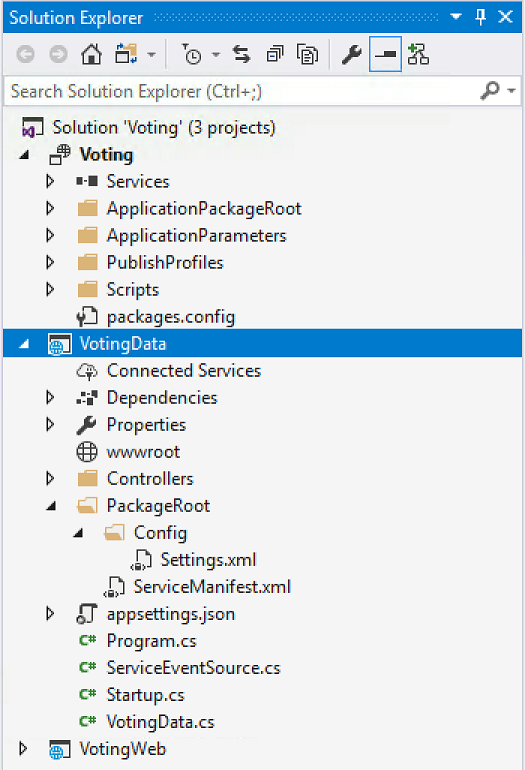
Visual Studio creates the VotingData service project and displays it in Solution Explorer:
Add the VoteDataController.cs file
In the VotingData project, right-click the Controllers folder, and then select Add > New item > Class. Name the file VoteDataController.cs and select Add. Replace the file contents with the following code, and then save your changes.
namespace VotingData.Controllers
{
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Data;
using Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Data.Collections;
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class VoteDataController : Controller
{
private readonly IReliableStateManager stateManager;
public VoteDataController(IReliableStateManager stateManager)
{
this.stateManager = stateManager;
}
// GET api/VoteData
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get()
{
CancellationToken ct = new CancellationToken();
IReliableDictionary<string, int> votesDictionary = await this.stateManager.GetOrAddAsync<IReliableDictionary<string, int>>("counts");
using (ITransaction tx = this.stateManager.CreateTransaction())
{
Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Data.IAsyncEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, int>> list = await votesDictionary.CreateEnumerableAsync(tx);
Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Data.IAsyncEnumerator<KeyValuePair<string, int>> enumerator = list.GetAsyncEnumerator();
List<KeyValuePair<string, int>> result = new List<KeyValuePair<string, int>>();
while (await enumerator.MoveNextAsync(ct))
{
result.Add(enumerator.Current);
}
return this.Json(result);
}
}
// PUT api/VoteData/name
[HttpPut("{name}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Put(string name)
{
IReliableDictionary<string, int> votesDictionary = await this.stateManager.GetOrAddAsync<IReliableDictionary<string, int>>("counts");
using (ITransaction tx = this.stateManager.CreateTransaction())
{
await votesDictionary.AddOrUpdateAsync(tx, name, 1, (key, oldvalue) => oldvalue + 1);
await tx.CommitAsync();
}
return new OkResult();
}
// DELETE api/VoteData/name
[HttpDelete("{name}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(string name)
{
IReliableDictionary<string, int> votesDictionary = await this.stateManager.GetOrAddAsync<IReliableDictionary<string, int>>("counts");
using (ITransaction tx = this.stateManager.CreateTransaction())
{
if (await votesDictionary.ContainsKeyAsync(tx, name))
{
await votesDictionary.TryRemoveAsync(tx, name);
await tx.CommitAsync();
return new OkResult();
}
else
{
return new NotFoundResult();
}
}
}
}
}
Connect the services
In this section, you connect two services. You make the front-end web application get voting information from the back-end service, and then set the information in the app.
Service Fabric gives you complete flexibility in the way that you communicate with reliable services. Within a single application, you might have services that are accessible via TCP/IP, via an HTTP REST API, or via WebSocket protocol. For background on the options that are available and their tradeoffs, see Communicating with services.
This tutorial uses ASP.NET Core Web API and the Service Fabric reverse proxy so that the VotingWeb front-end web service can communicate with the back-end VotingData service. A reverse proxy is configured by default to use port 19081. The reverse proxy port is set in the Azure Resource Manager template that sets up the cluster. To find which port is used, look in the cluster template in the Microsoft.ServiceFabric/clusters resource:
"nodeTypes": [
{
...
"httpGatewayEndpointPort": "[variables('nt0fabricHttpGatewayPort')]",
"isPrimary": true,
"vmInstanceCount": "[parameters('nt0InstanceCount')]",
"reverseProxyEndpointPort": "[parameters('SFReverseProxyPort')]"
}
],
To find the reverse proxy port that's used in your local development cluster, view the HttpApplicationGatewayEndpoint element in the local Service Fabric cluster manifest:
- To open the Service Fabric Explorer tool, open a browser and go to
http://localhost:19080. - Select Cluster > Manifest.
- Make a note of the
HttpApplicationGatewayEndpointelement port. By default, the port is 19081. If it isn't 19081, change the port in theGetProxyAddressmethod of the VotesController.cs code as described in the next section.
Update the VotesController.cs file
In the VotingWeb project, open the Controllers/VotesController.cs file. Replace the VotesController class definition contents with the following code, and then save your changes. If the reverse proxy port you discovered in the pervious step isn't 19081, change the port in the GetProxyAddress method from 19081 to the port that you discovered.
public class VotesController : Controller
{
private readonly HttpClient httpClient;
private readonly FabricClient fabricClient;
private readonly StatelessServiceContext serviceContext;
public VotesController(HttpClient httpClient, StatelessServiceContext context, FabricClient fabricClient)
{
this.fabricClient = fabricClient;
this.httpClient = httpClient;
this.serviceContext = context;
}
// GET: api/Votes
[HttpGet("")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get()
{
Uri serviceName = VotingWeb.GetVotingDataServiceName(this.serviceContext);
Uri proxyAddress = this.GetProxyAddress(serviceName);
ServicePartitionList partitions = await this.fabricClient.QueryManager.GetPartitionListAsync(serviceName);
List<KeyValuePair<string, int>> result = new List<KeyValuePair<string, int>>();
foreach (Partition partition in partitions)
{
string proxyUrl =
$"{proxyAddress}/api/VoteData?PartitionKey={((Int64RangePartitionInformation) partition.PartitionInformation).LowKey}&PartitionKind=Int64Range";
using (HttpResponseMessage response = await this.httpClient.GetAsync(proxyUrl))
{
if (response.StatusCode != System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
continue;
}
result.AddRange(JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<KeyValuePair<string, int>>>(await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()));
}
}
return this.Json(result);
}
// PUT: api/Votes/name
[HttpPut("{name}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Put(string name)
{
Uri serviceName = VotingWeb.GetVotingDataServiceName(this.serviceContext);
Uri proxyAddress = this.GetProxyAddress(serviceName);
long partitionKey = this.GetPartitionKey(name);
string proxyUrl = $"{proxyAddress}/api/VoteData/{name}?PartitionKey={partitionKey}&PartitionKind=Int64Range";
StringContent putContent = new StringContent($"{{ 'name' : '{name}' }}", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
putContent.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json");
using (HttpResponseMessage response = await this.httpClient.PutAsync(proxyUrl, putContent))
{
return new ContentResult()
{
StatusCode = (int) response.StatusCode,
Content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()
};
}
}
// DELETE: api/Votes/name
[HttpDelete("{name}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(string name)
{
Uri serviceName = VotingWeb.GetVotingDataServiceName(this.serviceContext);
Uri proxyAddress = this.GetProxyAddress(serviceName);
long partitionKey = this.GetPartitionKey(name);
string proxyUrl = $"{proxyAddress}/api/VoteData/{name}?PartitionKey={partitionKey}&PartitionKind=Int64Range";
using (HttpResponseMessage response = await this.httpClient.DeleteAsync(proxyUrl))
{
if (response.StatusCode != System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
return this.StatusCode((int) response.StatusCode);
}
}
return new OkResult();
}
/// <summary>
/// Constructs a reverse proxy URL for a given service.
/// Example: http://localhost:19081/VotingApplication/VotingData/
/// </summary>
/// <param name="serviceName"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private Uri GetProxyAddress(Uri serviceName)
{
return new Uri($"http://localhost:19081{serviceName.AbsolutePath}");
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a partition key from the given name.
/// Uses the zero-based numeric position in the alphabet of the first letter of the name (0-25).
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private long GetPartitionKey(string name)
{
return Char.ToUpper(name.First()) - 'A';
}
}
Walk through the voting sample application
The voting application consists of two services:
- A web front-end service (VotingWeb): An ASP.NET Core web front-end service that serves the webpage and exposes web APIs to communicate with the back-end service.
- A back-end service (VotingData): An ASP.NET Core web service that exposes an API to store the vote results in a reliable dictionary that's persisted on disk.

When you vote in the application, the following events occur:
A JavaScript file sends the vote request to the web API in the web front-end service as an HTTP PUT request.
The web front-end service uses a proxy to locate and forward an HTTP PUT request to the back-end service.
The back-end service takes the incoming request and stores the updated result in a reliable dictionary. The dictionary is replicated to multiple nodes in the cluster and persisted on disk. All the application's data is stored in the cluster, so no database is needed.
Debug in Visual Studio
When you debug an application in Visual Studio, you use a local Service Fabric development cluster. You can adjust your debugging experience to your scenario.
In this application, store data in the back-end service by using a reliable dictionary. Visual Studio removes the application by default when you stop the debugger. Removing the application causes the data in the back-end service to also be removed. To persist the data between debugging sessions, you can change the Application Debug Mode as a property on the Voting project in Visual Studio.
To see what happens in the code, complete the following steps:
Open the VotingWeb\VotesController.cs file and set a breakpoint in the web API's
Putmethod (line 72).Open the VotingData\VoteDataController.cs file and set a breakpoint in this web API's
Putmethod (line 54).Select F5 to start the application in debug mode.
Go back to the browser and select a voting option or add a new voting option. You hit the first breakpoint in the web front-end's API controller.
The JavaScript in the browser sends a request to the web API controller in the front-end service:
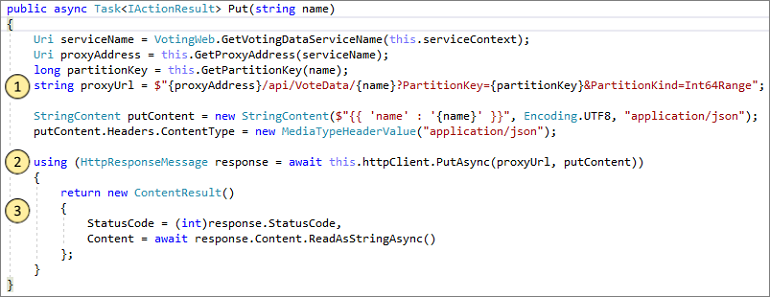
- First, construct the URL to the reverse proxy for the back-end service. (1)
- Then send the HTTP PUT request to the reverse proxy. (2)
- Finally, return the response from the back-end service to the client. (3)
Select F5 to continue.
You're now at the breakpoint in the back-end service:
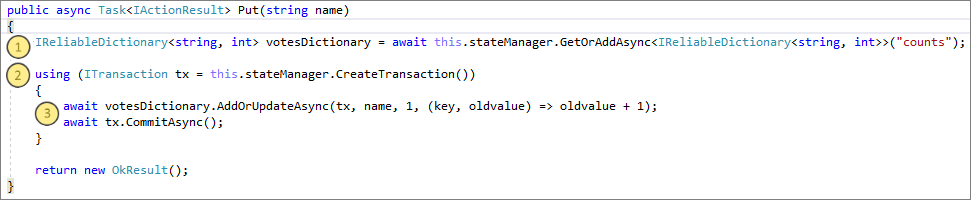
- In the first line in the method, use
stateManagerto get or add a reliable dictionary calledcounts. (1) - All interactions that have values in a reliable dictionary require a transaction. This
usingstatement creates that transaction. (2) - In the transaction, update the value of the relevant key for the voting option and commit the operation. When the
commitmethod returns, the data is updated in the dictionary. It then replicates to other nodes in the cluster. The data is now safely stored in the cluster, and the back-end service can fail over to other nodes and still have the data available. (3)
- In the first line in the method, use
Select F5 to continue.
To stop the debugging session, select Shift+F5.