Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
The Basic and Standard plans entered a retirement period on March 17, 2025. For more information, see the Azure Spring Apps retirement announcement.
This article explains how to use the AppDynamics Java Agent to monitor Spring Boot applications in Azure Spring Apps.
With the AppDynamics Java Agent, you can:
- Monitor applications
- Configure the AppDynamics Java Agent using environment variables
- Check all monitoring data from the AppDynamics dashboard
Prerequisites
Activate the AppDynamics Java in-process agent
For the whole workflow, you need to:
- Activate the AppDynamics Java in-process agent in Azure Spring Apps to generate application metrics data.
- Connect the AppDynamics Agent to the AppDynamics Controller to collect and visualize the data in the controller.

Activate an application with the AppDynamics Agent using the Azure CLI
To activate an application through the Azure CLI, use the following steps.
Create a resource group.
Create an instance of Azure Spring Apps.
Create an application using the following command. Replace the placeholders
<...>with your own values.az spring app create \ --resource-group "<your-resource-group-name>" \ --service "<your-Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name>" \ --name "<your-app-name>" \ --is-public trueCreate a deployment with the AppDynamics Agent using environment variables.
az spring app deploy \ --resource-group "<your-resource-group-name>" \ --service "<your-Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name>" \ --name "<your-app-name>" \ --artifact-path app.jar \ --jvm-options="-javaagent:/opt/agents/appdynamics/java/javaagent.jar" \ --env APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_APPLICATION_NAME=<your-app-name> \ APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_ACCESS_KEY=<your-agent-access-key> \ APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME=<your-agent-account-name> \ APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME=true \ APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME_PREFIX=<your-agent-node-name> \ APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_TIER_NAME=<your-agent-tier-name> \ APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME=<your-AppDynamics-controller-host-name> \ APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_SSL_ENABLED=true \ APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_PORT=443
Azure Spring Apps pre-installs the AppDynamics Java agent to the path /opt/agents/appdynamics/java/javaagent.jar. You can activate the agent from your applications' JVM options, then configure the agent using environment variables. You can find values for these variables at Monitor Azure Spring Apps with Java Agent. For more information about how these variables help to view and organize reports in the AppDynamics UI, see Tiers and Nodes.
Activate an application with the AppDynamics Agent using the Azure portal
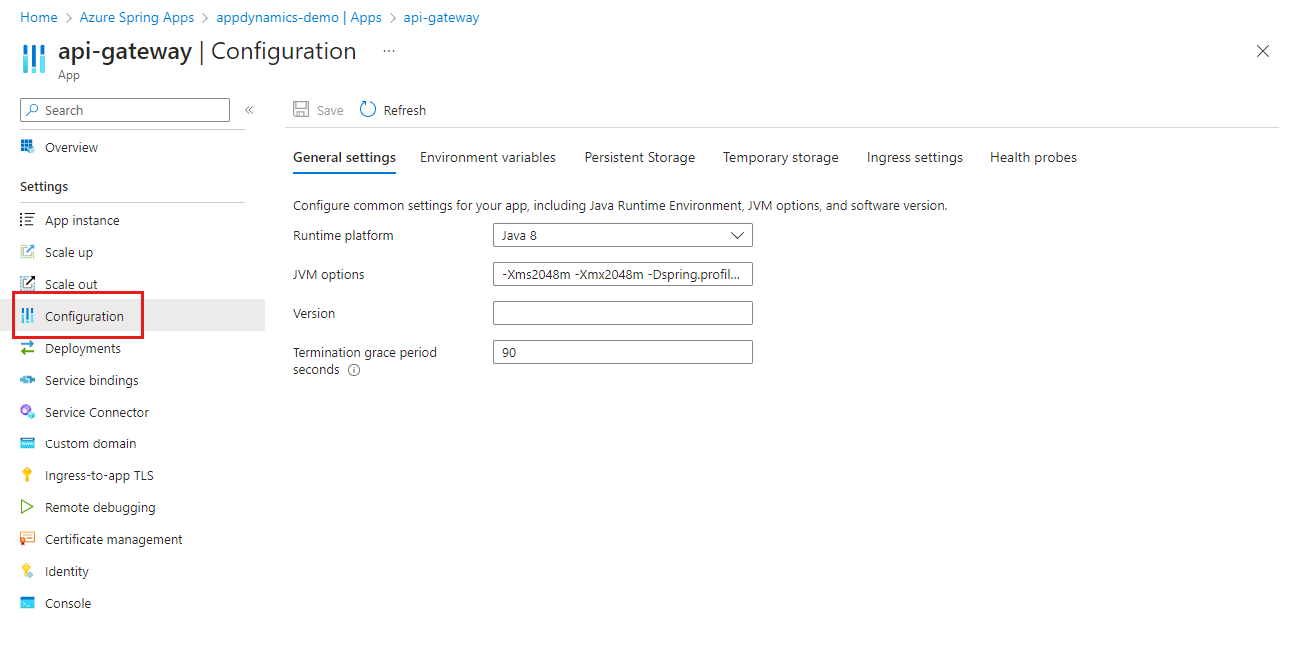
To activate an application through the Azure portal, use the following steps.
Navigate to your Azure Spring Apps instance in the Azure portal.
Select Apps in the Settings section of the navigation pane.
Select the app, and then select Configuration in the navigation pane.
Use the General settings tab to update values such as the JVM options.
Select Environment variables to add or update the variables used by your application.
Automate provisioning
You can also run a provisioning automation pipeline using Terraform, Bicep, or Azure Resource Manager template (ARM template). This pipeline can provide a complete hands-off experience to instrument and monitor any new applications that you create and deploy.
Automate provisioning using Terraform
To configure the environment variables in a Terraform template, add the following code to the template, replacing the <...> placeholders with your own values. For more information, see Manages an Active Azure Spring Apps Deployment.
resource "azurerm_spring_cloud_java_deployment" "example" {
...
jvm_options = "-javaagent:/opt/agents/appdynamics/java/javaagent.jar"
...
environment_variables = {
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_APPLICATION_NAME" : "<your-app-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_ACCESS_KEY" : "<your-agent-access-key>",
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME" : "<your-agent-account-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME" : "true",
"APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME_PREFIX" : "<your-agent-node-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_TIER_NAME" : "<your-agent-tier-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME" : "<your-AppDynamics-controller-host-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_SSL_ENABLED" : "true",
"APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_PORT" : "443"
}
}
Automate provisioning using Bicep
To configure the environment variables in a Bicep file, add the following code to the file, replacing the <...> placeholders with your own values. For more information, see Microsoft.AppPlatform Spring/apps/deployments.
deploymentSettings: {
environmentVariables: {
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_APPLICATION_NAME : '<your-app-name>'
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_ACCESS_KEY : '<your-agent-access-key>'
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME : '<your-agent-account-name>'
APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME : 'true'
APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME_PREFIX : '<your-agent-node-name>'
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_TIER_NAME : '<your-agent-tier-name>'
APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME : '<your-AppDynamics-controller-host-name>'
APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_SSL_ENABLED : 'true'
APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_PORT : '443'
}
jvmOptions: '-javaagent:/opt/agents/appdynamics/java/javaagent.jar'
}
Automate provisioning using an ARM template
To configure the environment variables in an ARM template, add the following code to the template, replacing the <...> placeholders with your own values. For more information, see Microsoft.AppPlatform Spring/apps/deployments.
"deploymentSettings": {
"environmentVariables": {
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_APPLICATION_NAME" : "<your-app-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_ACCESS_KEY" : "<your-agent-access-key>",
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME" : "<your-agent-account-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME" : "true",
"APPDYNAMICS_JAVA_AGENT_REUSE_NODE_NAME_PREFIX" : "<your-agent-node-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_TIER_NAME" : "<your-agent-tier-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME" : "<your-AppDynamics-controller-host-name>",
"APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_SSL_ENABLED" : "true",
"APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_PORT" : "443"
},
"jvmOptions": "-javaagent:/opt/agents/appdynamics/java/javaagent.jar",
...
}
Review reports in the AppDynamics dashboard
This section shows various reports in AppDynamics.
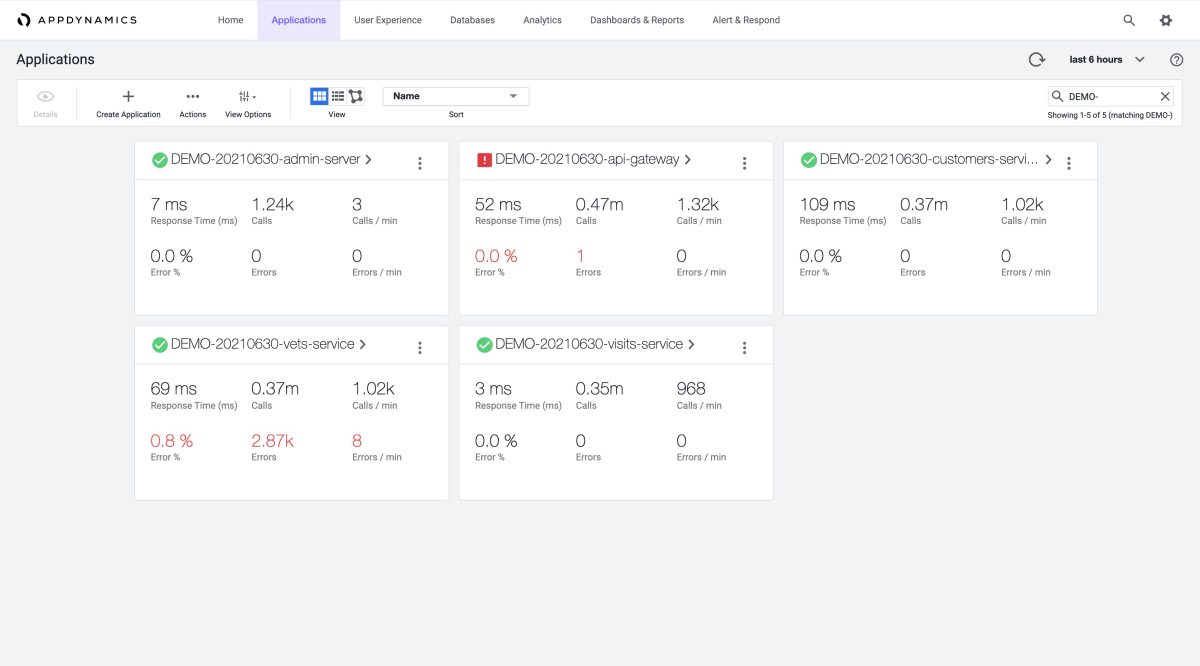
The following screenshot shows an overview of your apps in the AppDynamics dashboard:
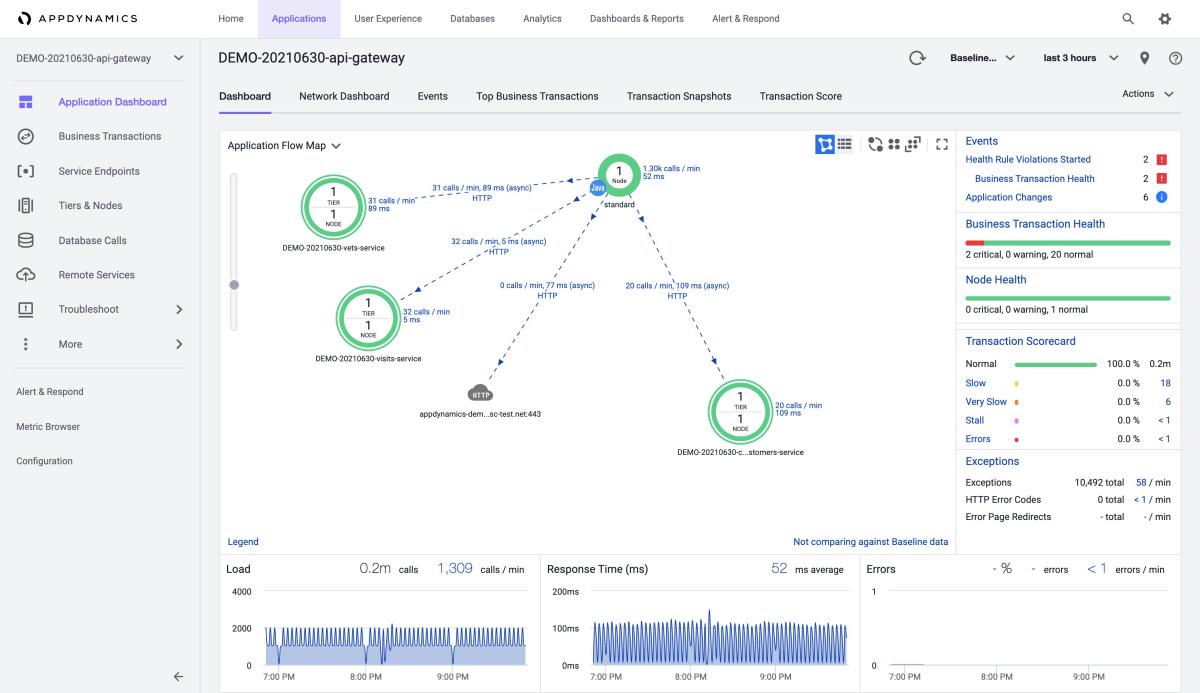
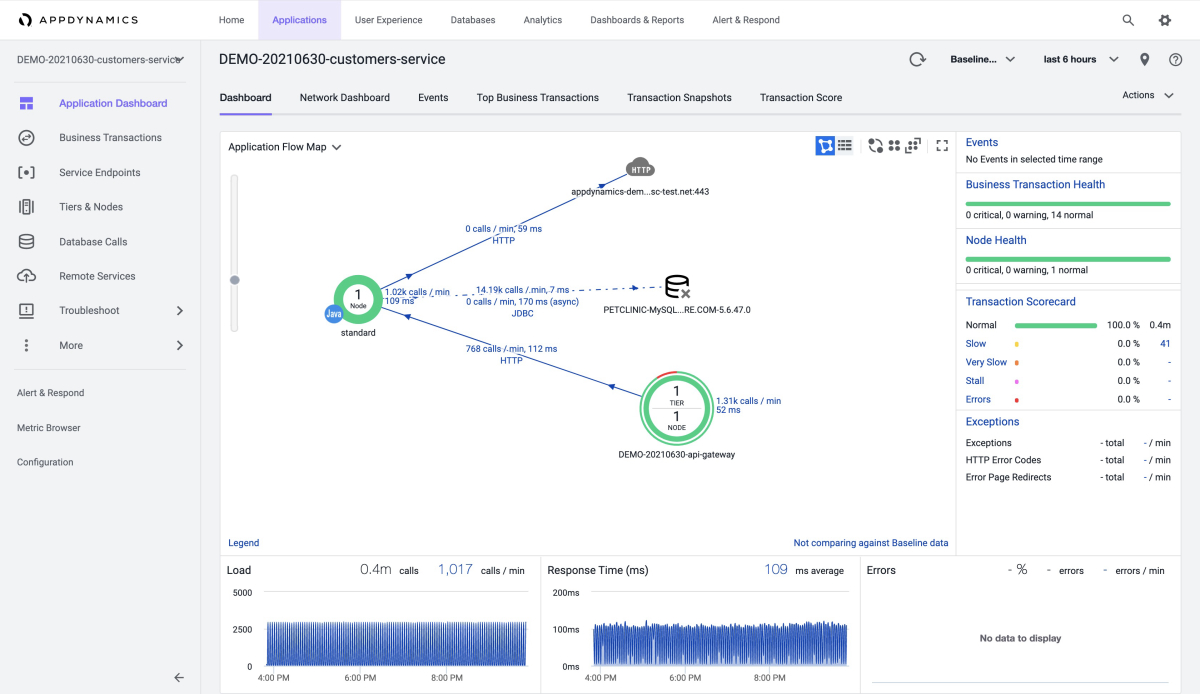
The Applications tab shows the overall information for each of your apps, as shown in the following screenshots using example applications:
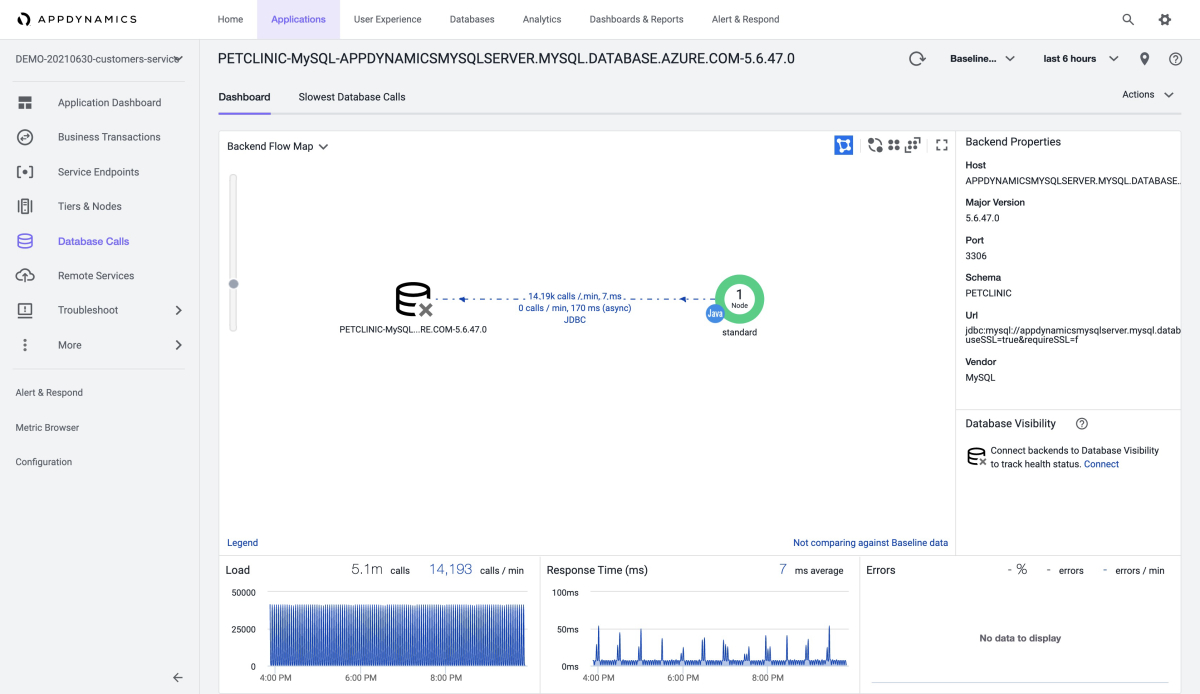
The following screenshot shows how you can get basic information from the Database Calls dashboard.
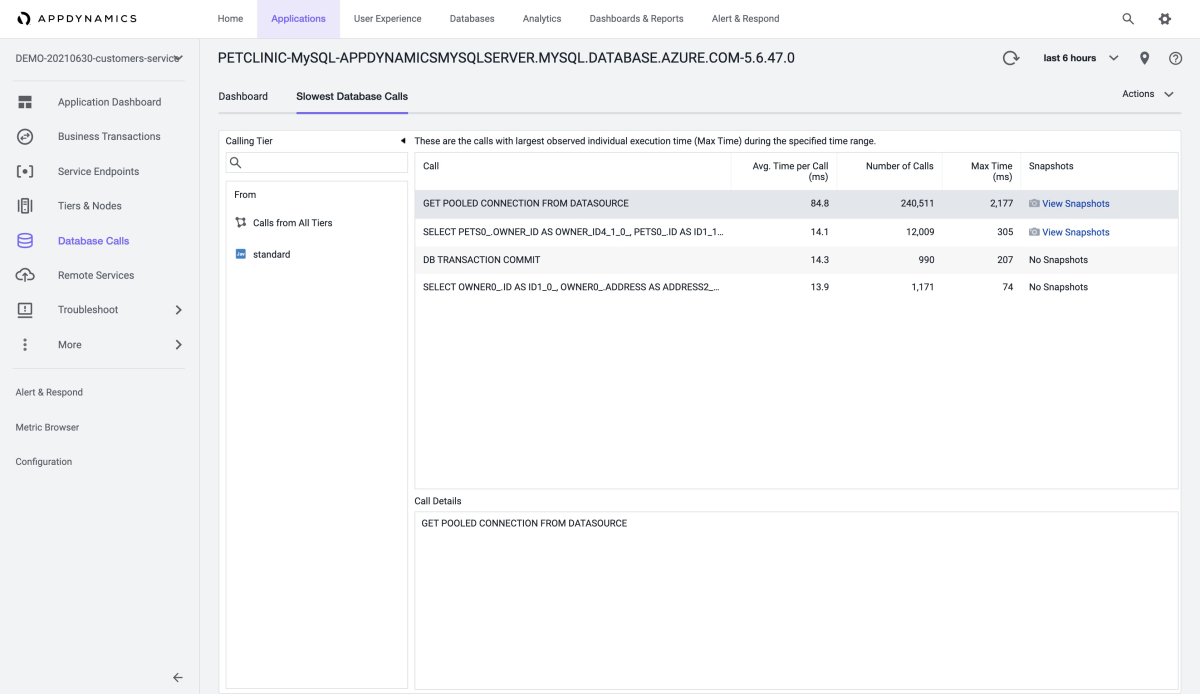
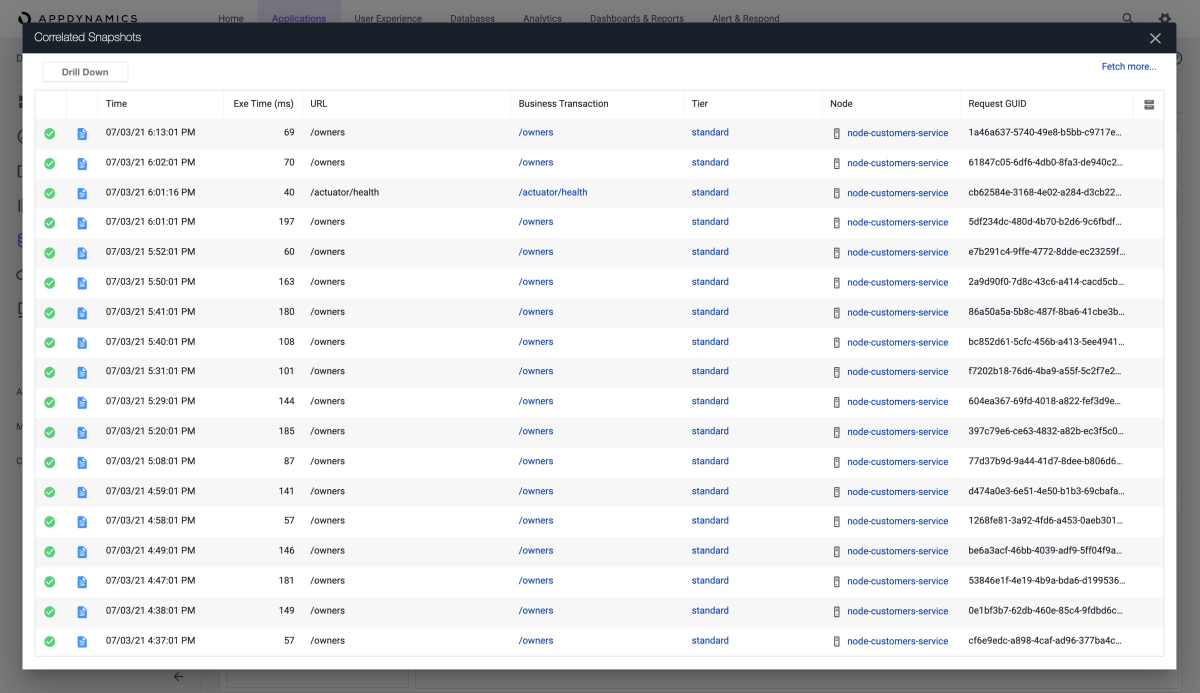
You can also get information about the slowest database calls, as shown in these screenshots:
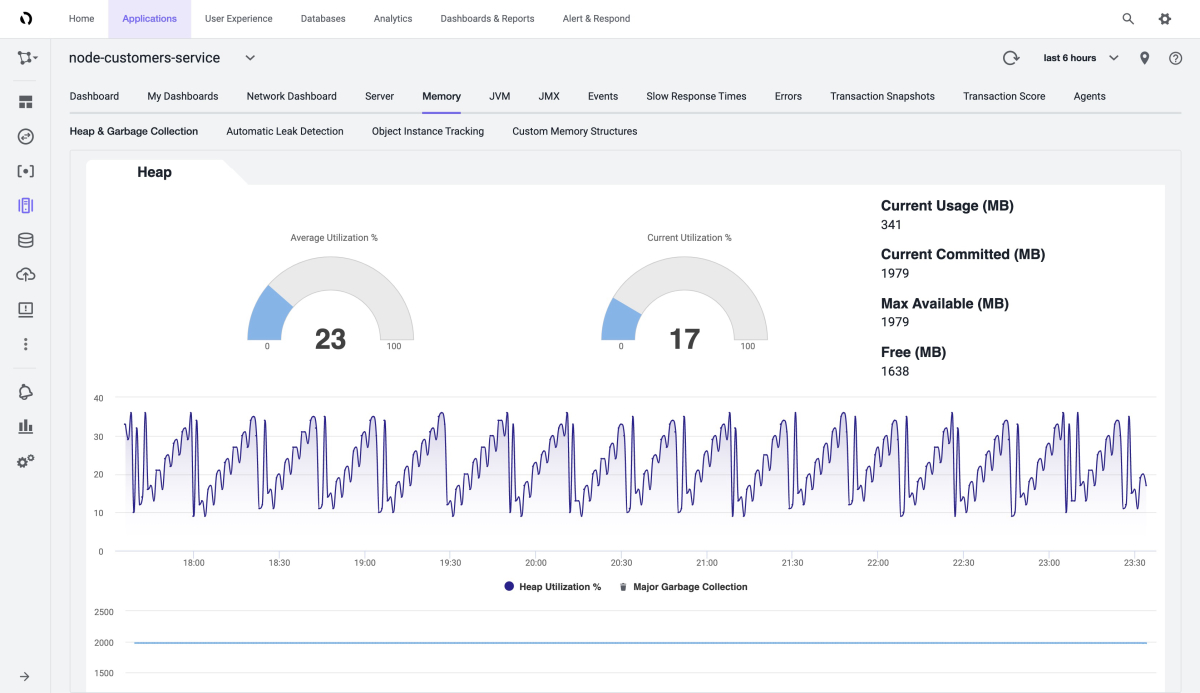
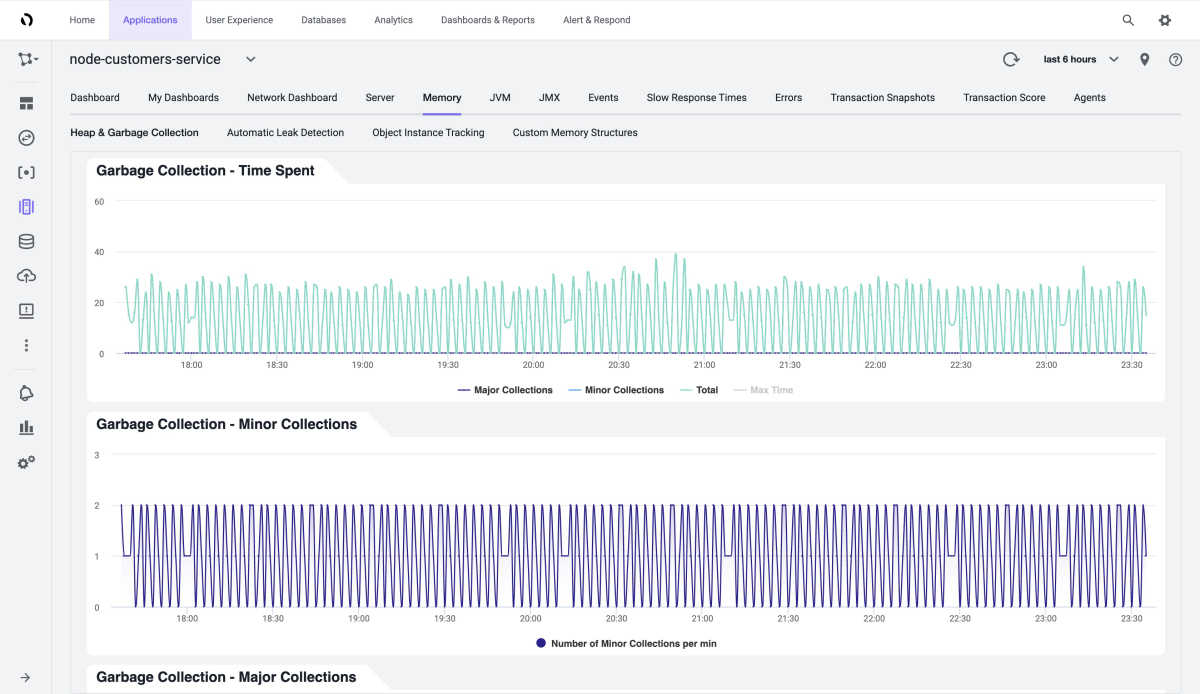
The following screenshot shows memory usage analysis in the Heap section of the Memory page:
You can also see the garbage collection process, as shown in this screenshot:
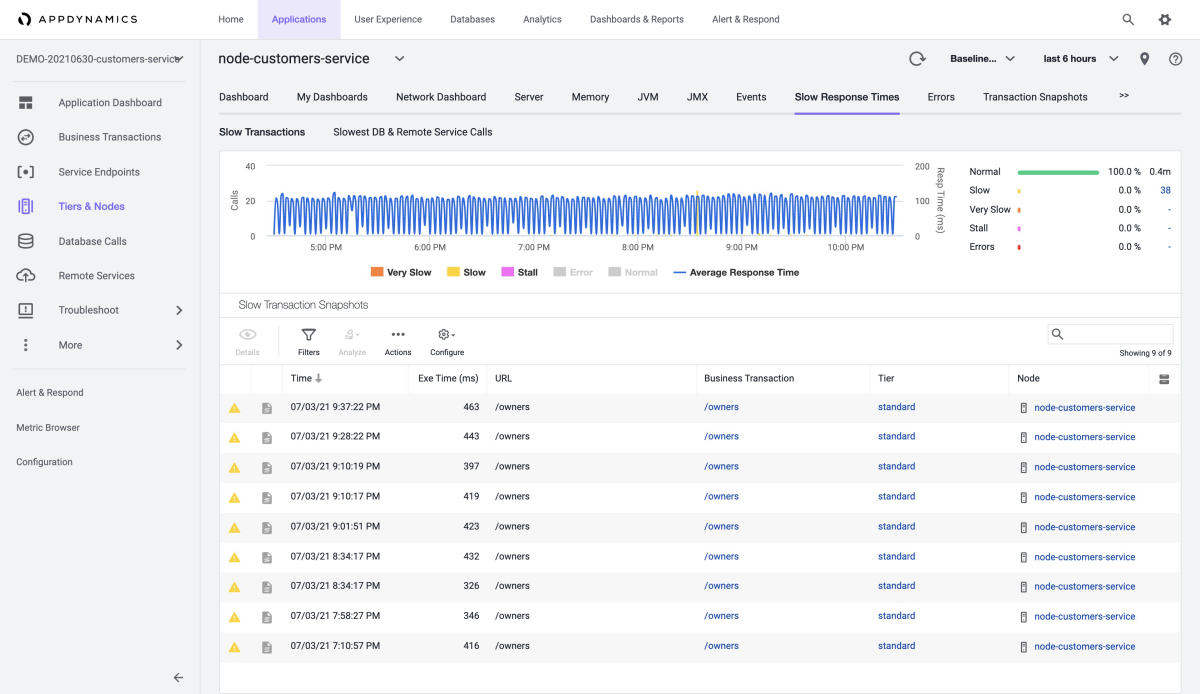
The following screenshot shows the Slow Transactions page:
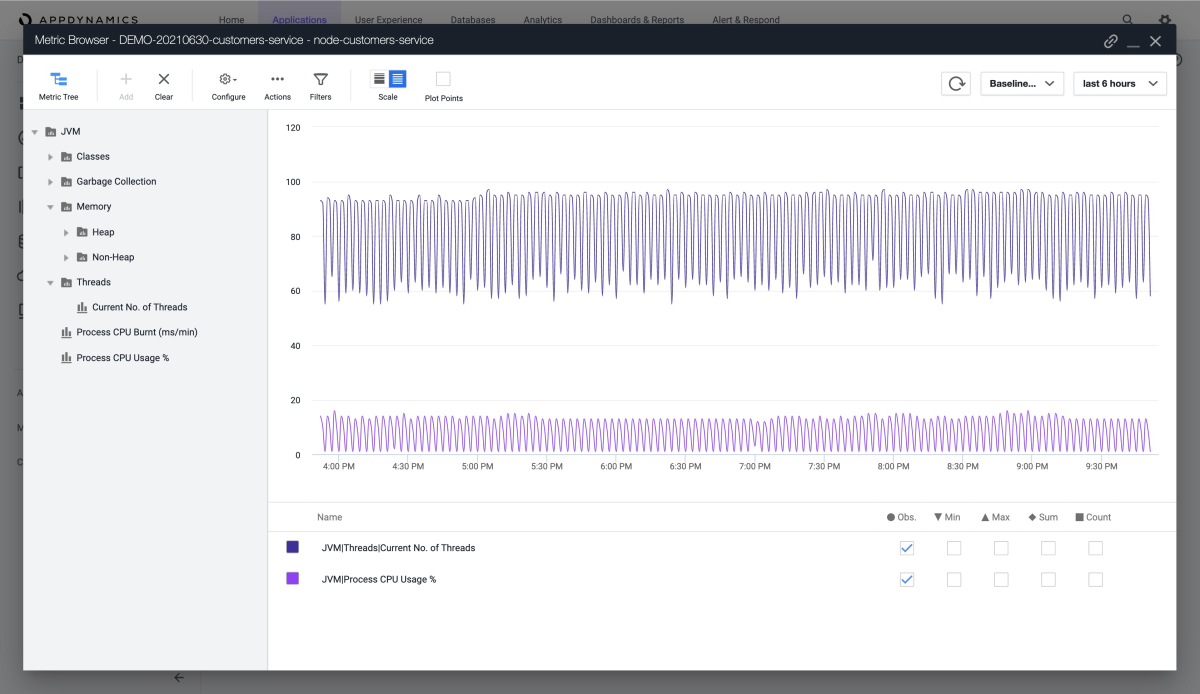
You can define more metrics for the JVM, as shown in this screenshot of the Metric Browser:
View AppDynamics Agent logs
By default, Azure Spring Apps prints the info level logs of the AppDynamics Agent to STDOUT. The logs are mixed with the application logs. You can find the explicit agent version from the application logs.
You can also get the logs of the AppDynamics Agent from the following locations:
- Azure Spring Apps logs
- Azure Spring Apps Application Insights
- Azure Spring Apps LogStream
Learn about AppDynamics Agent upgrade
The AppDynamics Agent is upgraded regularly with JDK (quarterly). Agent upgrade might affect the following scenarios:
- Existing applications using AppDynamics Agent before upgrade are unchanged, but require restart or redeploy to engage the new version of AppDynamics Agent.
- Applications created after upgrade use the new version of AppDynamics Agent.
Configure virtual network injection instance outbound traffic
For virtual network injection instances of Azure Spring Apps, make sure the outbound traffic is configured correctly for AppDynamics Agent. For details, see Cisco AppDynamics SaaS Domains and IP Ranges and Customer responsibilities for running Azure Spring Apps in a virtual network.
Understand the limitations
To understand the limitations of the AppDynamics Agent, see Monitor Azure Spring Apps with Java Agent.
Next steps
Use Application Insights Java In-Process Agent in Azure Spring Apps