Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article shows you how to use Azure Storage Explorer to create and manage directories and files in storage accounts that have hierarchical namespace (HNS) enabled.
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription. See Get Azure trial.
A storage account that has hierarchical namespace (HNS) enabled. Follow these instructions to create one.
Azure Storage Explorer installed on your local computer. To install Azure Storage Explorer for Windows, Macintosh, or Linux, see Azure Storage Explorer.
Note
Storage Explorer makes use of both the Blob (blob) & Data Lake Storage (dfs) endpoints when working with Azure Data Lake Storage. If access to Azure Data Lake Storage is configured using private endpoints, ensure that two private endpoints are created for the storage account: one with the target sub-resource blob and the other with the target sub-resource dfs.
Sign in to Storage Explorer
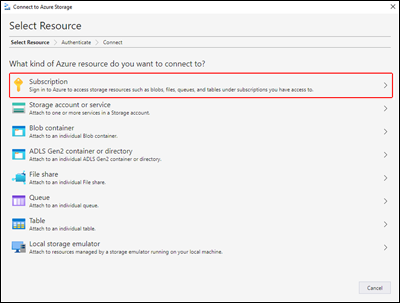
When you first start Storage Explorer, the Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer - Connect to Azure Storage window appears. While Storage Explorer provides several ways to connect to storage accounts, only one way is currently supported for managing ACLs.
In the Select Resource panel, select Subscription.
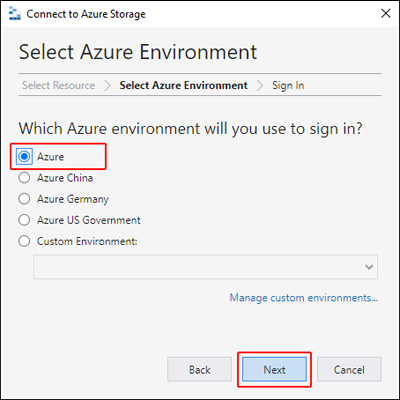
In the Select Azure Environment panel, select an Azure environment to sign in to. You can sign in to global Azure, a national cloud or an Azure Stack instance. Then select Next.
Storage Explorer opens a webpage for you to sign in.
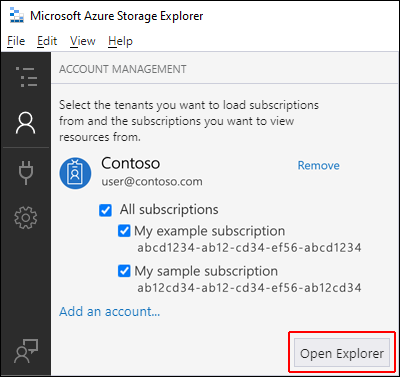
After you successfully sign in with an Azure account, the account and the Azure subscriptions associated with that account appear under ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT. Select the Azure subscriptions that you want to work with, and then select Open Explorer.
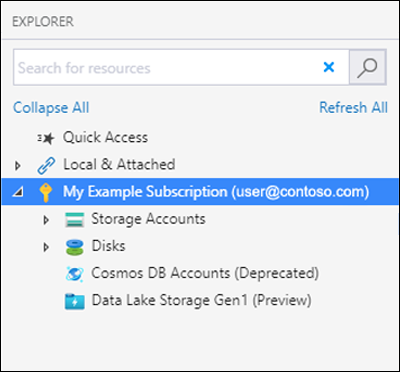
When it completes connecting, Azure Storage Explorer loads with the Explorer tab shown. This view gives you insight to all of your Azure storage accounts as well as local storage configured through the Azurite storage emulator or Azure Stack environments.
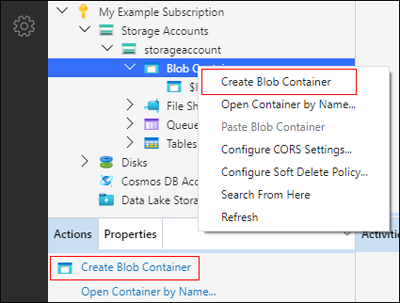
Create a container
A container holds directories and files. To create one, expand the storage account you created in the proceeding step. Select Blob Containers, right-click, and select Create Blob Container. Alternatively, you can select Blob Containers, then select Create Blob Container in the Actions pane.
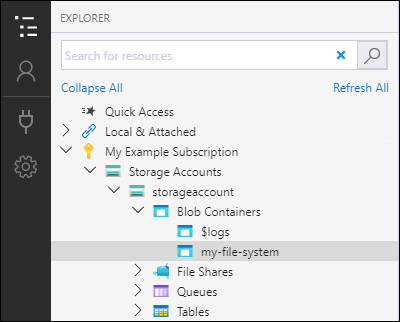
Enter the name for your container. See the Create a container section for a list of rules and restrictions on naming containers. When complete, press Enter to create the container. After the container has been successfully created, it's displayed under the Blob Containers folder for the selected storage account.
Create a directory
To create a directory, select the container that you created in the proceeding step. In the container ribbon, choose the New Folder button. Enter the name for your directory. When complete, press Enter to create the directory. After the directory has been successfully created, it appears in the editor window.
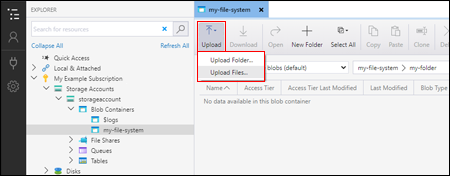
Upload blobs to the directory
On the directory ribbon, choose the Upload button. This operation gives you the option to upload a folder or a file.
Choose the files or folder to upload.
When you select Upload, the files selected are queued, and each file is uploaded. When the upload is complete, the results are shown in the Activities window.
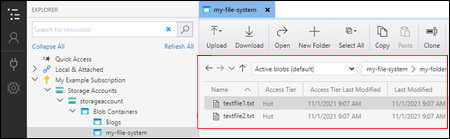
View blobs in a directory
In the Azure Storage Explorer application, select a directory under a storage account. The main pane shows a list of the blobs in the selected directory.
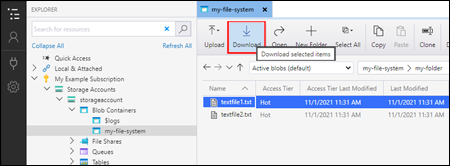
Download blobs
To download files by using Azure Storage Explorer, with a file selected, select Download from the ribbon. A file dialog opens and provides you with the ability to enter a file name. Select Select Folder to start the download of a file to the local location.
Next steps
Learn how to manage file and directory permission by setting access control lists (ACLs)