Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In most cases, a role assignment grants the permissions you need to Azure resources. However, in some cases you might want to provide more granular access control by adding a role assignment condition.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Add a condition to a role assignment
- Restrict access to blobs based on a blob index tag
Important
Azure attribute-based access control (Azure ABAC) is generally available (GA) for controlling access to Azure Blob Storage, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, and Azure Queues using request, resource, environment, and principal attributes in both the standard and premium storage account performance tiers. Currently, the list blob include request attribute and snapshot request attribute for hierarchical namespace are in PREVIEW. For complete feature status information of ABAC for Azure Storage, see Status of condition features in Azure Storage.
See the Supplemental Terms of Use for Azure Previews for legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
Prerequisites
For information about the prerequisites to add or edit role assignment conditions, see Conditions prerequisites.
Condition
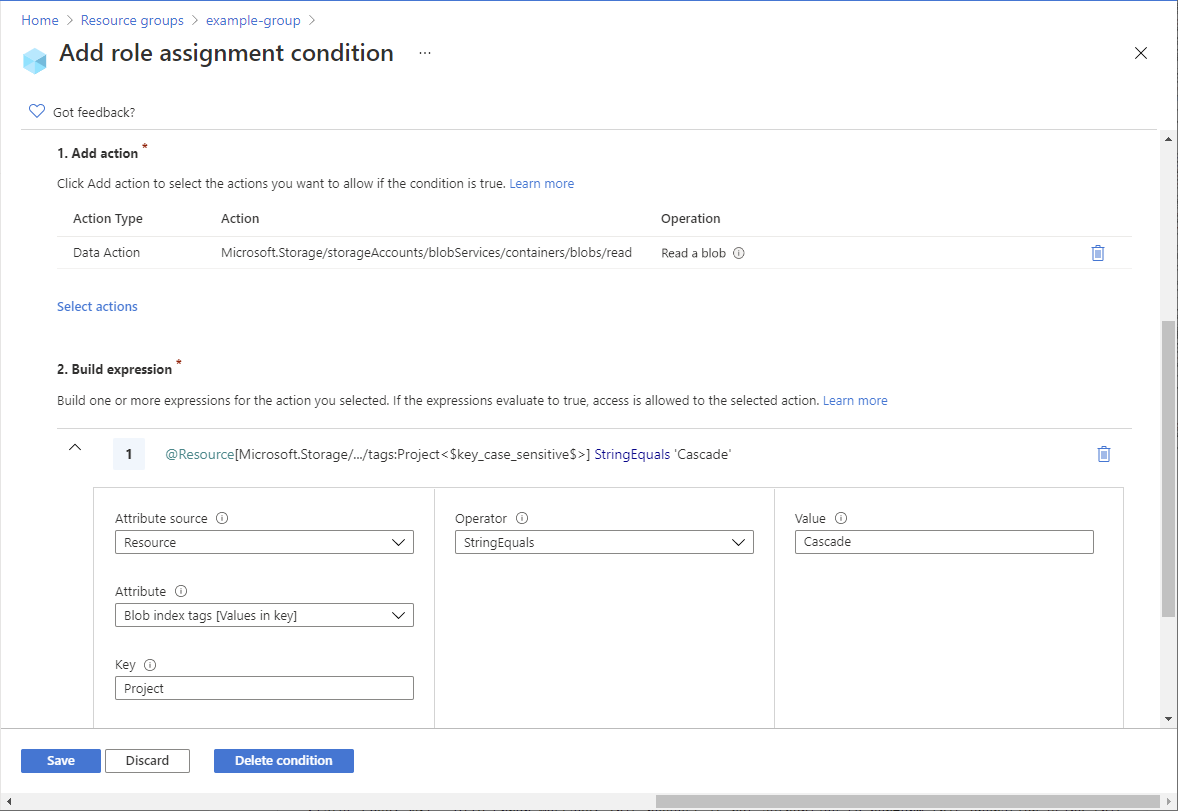
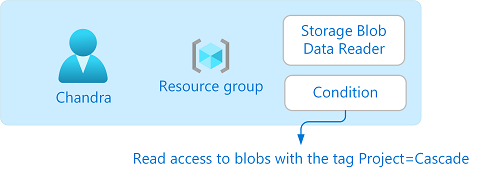
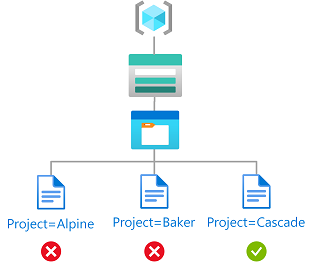
In this tutorial, you restrict access to blobs with a specific tag. For example, you add a condition to a role assignment so that Chandra can only read files with the tag Project=Cascade.
If Chandra tries to read a blob without the tag Project=Cascade, access isn't allowed.
Here's what the condition looks like in code:
(
(
!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'}
AND NOT
SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})
)
OR
(
@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<$key_case_sensitive$>] StringEquals 'Cascade'
)
)
Step 1: Sign in to Azure
Use the az login command and follow the instructions that appear to sign in to your directory as User Access Administrator or Owner.
az loginUse az account show to get the ID of your subscriptions.
az account showDetermine the subscription ID and initialize the variable.
subscriptionId="<subscriptionId>"
Step 2: Create a user
Use az ad user create to create a user or find an existing user. This tutorial uses Chandra as the example.
Initialize the variable for the object ID of the user.
userObjectId="<userObjectId>"
Step 3: Set up storage
You can authorize access to Blob storage from the Azure CLI either with Microsoft Entra credentials or by using the storage account access key. This article shows how to authorize Blob storage operations using Microsoft Entra ID. For more information, see Quickstart: Create, download, and list blobs with Azure CLI
Use az storage account to create a storage account that is compatible with the blob index feature. For more information, see Manage and find Azure Blob data with blob index tags.
Use az storage container to create a new blob container within the storage account and set the anonymous access level to Private (no anonymous access).
Use az storage blob upload to upload a text file to the container.
Add the following blob index tag to the text file. For more information, see Use blob index tags to manage and find data on Azure Blob Storage.
Note
Blobs also support the ability to store arbitrary user-defined key-value metadata. Although metadata is similar to blob index tags, you must use blob index tags with conditions.
Key Value Project Cascade Upload a second text file to the container.
Add the following blob index tag to the second text file.
Key Value Project Baker Initialize the following variables with the names you used.
resourceGroup="<resourceGroup>" storageAccountName="<storageAccountName>" containerName="<containerName>" blobNameCascade="<blobNameCascade>" blobNameBaker="<blobNameBaker>"
Step 4: Assign a role with a condition
Initialize the Storage Blob Data Reader role variables.
roleDefinitionName="Storage Blob Data Reader" roleDefinitionId="2a2b9908-6ea1-4ae2-8e65-a410df84e7d1"Initialize the scope for the resource group.
scope="/subscriptions/$subscriptionId/resourceGroups/$resourceGroup"Initialize the condition.
condition="((!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'} AND NOT SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})) OR (@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<\$key_case_sensitive\$>] StringEquals 'Cascade'))"In Bash, if history expansion is enabled, you might see the message
bash: !: event not foundbecause of the exclamation point (!). In this case, you can disable history expansion with the commandset +H. To re-enable history expansion, useset -H.In Bash, a dollar sign ($) has special meaning for expansion. If your condition includes a dollar sign ($), you might need to prefix it with a backslash (\). For example, this condition uses dollar signs to delineate the tag key name. For more information about rules for quotation marks in Bash, see Double Quotes.
Initialize the condition version and description.
conditionVersion="2.0" description="Read access to blobs with the tag Project=Cascade"Use az role assignment create to assign the Storage Blob Data Reader role with a condition to the user at a resource group scope.
az role assignment create --assignee-object-id $userObjectId --scope $scope --role $roleDefinitionId --description "$description" --condition "$condition" --condition-version $conditionVersionHere's an example of the output:
{ "canDelegate": null, "condition": "((!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'} AND NOT SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})) OR (@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<$key_case_sensitive$>] StringEquals 'Cascade'))", "conditionVersion": "2.0", "description": "Read access to blobs with the tag Project=Cascade", "id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/{roleAssignmentId}", "name": "{roleAssignmentId}", "principalId": "{userObjectId}", "principalType": "User", "resourceGroup": "{resourceGroup}", "roleDefinitionId": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/2a2b9908-6ea1-4ae2-8e65-a410df84e7d1", "scope": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup}", "type": "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments" }
Step 5: (Optional) View the condition in the Azure portal
In the Azure portal, open the resource group.
Select Access control (IAM).
On the Role assignments tab, find the role assignment.
In the Condition column, select View/Edit to view the condition.
Step 6: Test the condition
Open a new command window.
Use az login to sign in as Chandra.
az loginInitialize the following variables with the names you used.
storageAccountName="<storageAccountName>" containerName="<containerName>" blobNameBaker="<blobNameBaker>" blobNameCascade="<blobNameCascade>"Use az storage blob show to try to read the properties of the file for the Baker project.
az storage blob show --account-name $storageAccountName --container-name $containerName --name $blobNameBaker --auth-mode loginHere's an example of the output. Notice that you can't read the file because of the condition you added.
You do not have the required permissions needed to perform this operation. Depending on your operation, you may need to be assigned one of the following roles: "Storage Blob Data Contributor" "Storage Blob Data Reader" "Storage Queue Data Contributor" "Storage Queue Data Reader" If you want to use the old authentication method and allow querying for the right account key, please use the "--auth-mode" parameter and "key" value.Read the properties of the file for the Cascade project.
az storage blob show --account-name $storageAccountName --container-name $containerName --name $blobNameCascade --auth-mode loginHere's an example of the output. Notice that you can read the properties of the file because it has the tag Project=Cascade.
{ "container": "<containerName>", "content": "", "deleted": false, "encryptedMetadata": null, "encryptionKeySha256": null, "encryptionScope": null, "isAppendBlobSealed": null, "isCurrentVersion": null, "lastAccessedOn": null, "metadata": {}, "name": "<blobNameCascade>", "objectReplicationDestinationPolicy": null, "objectReplicationSourceProperties": [], "properties": { "appendBlobCommittedBlockCount": null, "blobTier": "Hot", "blobTierChangeTime": null, "blobTierInferred": true, "blobType": "BlockBlob", "contentLength": 7, "contentRange": null, ... }
Step 7: (Optional) Edit the condition
In the other command window, use az role assignment list to get the role assignment you added.
az role assignment list --assignee $userObjectId --resource-group $resourceGroupThe output is similar to the following:
[ { "canDelegate": null, "condition": "((!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'} AND NOT SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})) OR (@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<$key_case_sensitive$>] StringEquals 'Cascade'))", "conditionVersion": "2.0", "description": "Read access to blobs with the tag Project=Cascade", "id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/{roleAssignmentId}", "name": "{roleAssignmentId}", "principalId": "{userObjectId}", "principalName": "chandra@contoso.com", "principalType": "User", "resourceGroup": "{resourceGroup}", "roleDefinitionId": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/2a2b9908-6ea1-4ae2-8e65-a410df84e7d1", "roleDefinitionName": "Storage Blob Data Reader", "scope": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup}", "type": "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments" } ]Create a JSON file with the following format and update the
conditionanddescriptionproperties.{ "canDelegate": null, "condition": "((!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'} AND NOT SubOperationMatches{'Blob.List'})) OR (@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<$key_case_sensitive$>] StringEquals 'Cascade' OR @Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/tags:Project<$key_case_sensitive$>] StringEquals 'Baker'))", "conditionVersion": "2.0", "description": "Read access to blobs with the tag Project=Cascade or Project=Baker", "id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/{roleAssignmentId}", "name": "{roleAssignmentId}", "principalId": "{userObjectId}", "principalName": "chandra@contoso.com", "principalType": "User", "resourceGroup": "{resourceGroup}", "roleDefinitionId": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions/2a2b9908-6ea1-4ae2-8e65-a410df84e7d1", "roleDefinitionName": "Storage Blob Data Reader", "scope": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup}", "type": "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments" }Use az role assignment update to update the condition for the role assignment.
az role assignment update --role-assignment "./path/roleassignment.json"
Step 8: Clean up resources
Use az role assignment delete to remove the role assignment and condition you added.
az role assignment delete --assignee $userObjectId --role "$roleDefinitionName" --resource-group $resourceGroupDelete the storage account you created.
Delete the user you created.