Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article helps administrators diagnose and resolve connectivity problems that affect Azure virtual machines (VMs).
Problems
- An Azure VM that’s deployed by using Resource Manager can't connect to another Azure VM in same virtual network.
- An Azure VM can't connect to the second network adapter of an Azure VM in same virtual network.
- An Azure VM can't connect to the internet.
To resolve these problems, follow the steps in the following section.
Note
You can use the following:
netstat -anto list the ports that the VM is listening to- Test-NetConnection module in PowerShell to display diagnostic information for a connection such as ping test and tcp test
- Ensure to utilize tcping or other TCP-based testing tools, as ICMP traffic is deprioritized by many networking devices. Using TCP tests provides more consistent and reliable results, especially in Azure environments.
Resolution
Azure VM can't connect to another Azure VM in same virtual network
Step 1: Verify that VMs can communicate with each other.
Download TCping to your source VM.
Open a Command Prompt window.
Navigate to the folder in which you downloaded TCping.
Ping the destination from the source VM by using the following command:
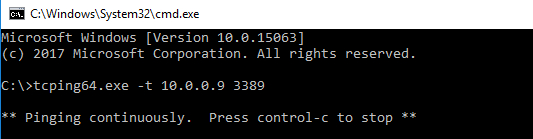
tcping64.exe -t <destination VM address> 3389
Tip
If the ping test is successful, go to Step 3. Otherwise, go to the next step.
Step 2: Check the Network security group settings.
For each VM, check for default Inbound port rules of Allow VNet Inbound and Allow Load Balancer Inbound. Make sure to also check that there are no matching blocking rules that are listed below a lower-priority rule.
Note
Rules that have a lower number are matched first. For example, if you have a rule that has priority 1000 and 6500, the rule that has priority 1000 is matched first.
After that, try to ping the destination from the source VM again:
tcping64.exe -t <destination VM address> 3389
Step 3: Check whether you can connect to the destination VM by using Remote Desktop or SSH.
To connect by using Remote Desktop, follow these steps.
Windows:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- In the left menu, select Virtual Machines.
- Select the virtual machine in the list.
- On the page for the virtual machine, select Connect.
For more information, see How to connect and sign on to an Azure virtual machine running Windows.
Linux:
For more information, see Connect to a Linux VM in Azure.
If the Remote Desktop or SSH connection is successful, go to next step.
Step 4: Perform a connectivity check.
Run a connectivity check on the source VM, and check the response.
Windows: Check connectivity with Azure Network Watcher using PowerShell
Linux: Check connectivity with Azure Network Watcher using Azure CLI 2.0
The following is an example response:
ConnectionStatus : Unreachable
AvgLatencyInMs :
MinLatencyInMs :
MaxLatencyInMs :
ProbesSent : 100
ProbesFailed : 100
Hops : [
{
"Type": "Source",
"Id": "aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb",
"Address": "10.1.1.4",
"ResourceId": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGrou
ps/ContosoRG/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/appNic0/ipConfigurat
ions/ipconfig1",
"NextHopIds": [
"bbbbbbbb-1111-2222-3333-cccccccccccc"
],
"Issues": []
},
{
"Type": "VirtualAppliance",
"Id": "bbbbbbbb-1111-2222-3333-cccccccccccc",
"Address": "10.1.2.4",
"ResourceId": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGrou
ps/ContosoRG/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/fwNic/ipConfiguratio
ns/ipconfig1",
"NextHopIds": [
"cccccccc-2222-3333-4444-dddddddddddd"
],
"Issues": []
},
Step 5: Fix the issue in the connectivity check result.
In the Hops section of the connectivity check response that you received, check the listed issues.

Find the corresponding resolution in the following table, and follow the indicated steps to resolve the issues.
Issue type Value Resolution action NetworkSecurityRule Name of the blocking NSG You can delete the NSG rule or modify the rule as described here. UserDefinedRoute Name of the blocking UDR If you don't require this route, delete the UDR. If you can’t delete the route, update the route by using the appropriate address prefix and next hop. You can also adjust the Network Virtual Appliance to forward traffic appropriately. For more information, see: Virtual network traffic routing and Route network traffic with a route table using PowerShell. CPU Usage Follow these recommendations that describe in Generic performance troubleshooting for Azure Virtual Machine running Linux or Windows. Memory Usage Follow the recommendations that are described in Generic performance troubleshooting for Azure Virtual Machine running Linux or Windows. Guest Firewall Name of the firewall blocking Follow these steps: Turn Windows Firewall on or off. DNS Resolution Name of the DNS Follow these steps: Azure DNS troubleshooting guide and Name resolution for resources in Azure virtual networks. Socket Error Not applicable The specified port is already in use by another application. Try to use a different port. Run the connectivity check again to determine whether the problem is resolved.
Azure VM can't connect to the second network adapter of an Azure VM in same virtual network
Step 1: Make sure that the second network adapter is enabled to talk outside the subnet.
By default, secondary network adapters (also known as network interface cards, or network adapters) aren't configured to have a default gateway. Therefore, the traffic flow on the secondary adapter will be limited to the same subnet.
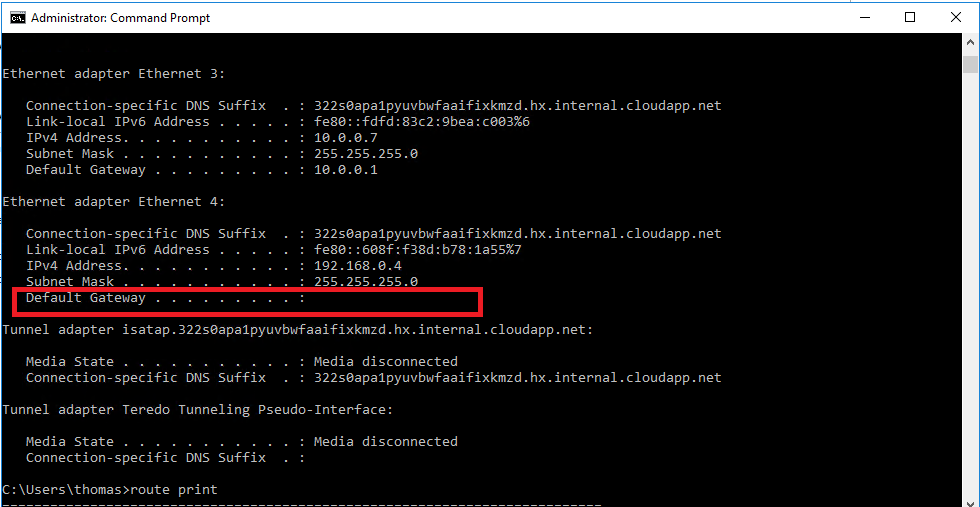
If users want to enable secondary network adapters to talk outside their own subnet, they must add an entry to the routing table to configure the gateway. To do this, follow these steps:
On the VM that has the second network adapter configured, open a Command Prompt window as an administrator.
Run the following command to add the entry in routing table:
Route add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 -p <Gateway IP>For example, if the second IP address is 192.168.0.4, the gateway IP should be 192.168.0.1. You have to run the following command:
Route add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 -p 192.168.0.1Run route print. If the entry is added successfully, you'll see an entry that resembles the following:
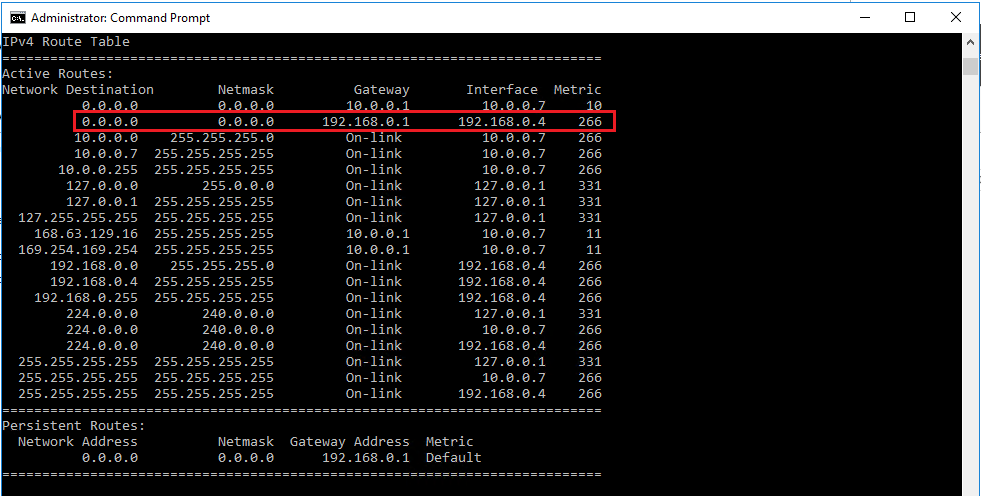
Now, try to connect to secondary network adapter. If the connection is still unsuccessful, go to next step.
Step 2: Check NSG settings for the network adapters.
For both the primary and secondary network adapters, check the default Inbound port rules of Allow VNet Inbound and Allow Load Balancer allow inbound on both network adapters. You should also make sure that there are no matching blocking rules that have a lower-priority rule above them.
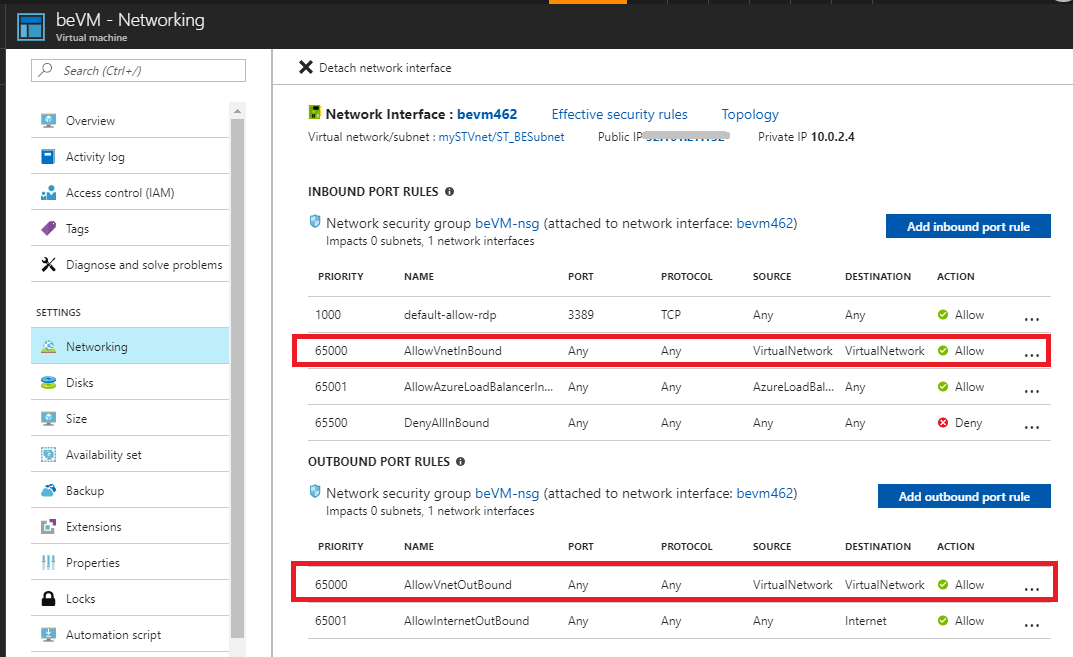
Step 3: Run a connectivity check to the secondary network adapter.
- Run a connectivity check to the secondary network adapter.
- Run a connectivity check across the environment to make sure that the process works end to end.
For more information about how to run the connectivity check, see the following articles:
Windows: Check connectivity with Azure Network Watcher using PowerShell
Linux: Check connectivity with Azure Network Watcher using Azure CLI 2.0.
The following is an example response:
ConnectionStatus : Unreachable
AvgLatencyInMs :
MinLatencyInMs :
MaxLatencyInMs :
ProbesSent : 100
ProbesFailed : 100
Hops : [
{
"Type": "Source",
"Id": "aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb",
"Address": "10.1.1.4",
"ResourceId": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGrou
ps/ContosoRG/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/appNic0/ipConfigurat
ions/ipconfig1",
"NextHopIds": [
"bbbbbbbb-1111-2222-3333-cccccccccccc"
],
"Issues": []
},
{
"Type": "VirtualAppliance",
"Id": "bbbbbbbb-1111-2222-3333-cccccccccccc",
"Address": "10.1.2.4",
"ResourceId": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGrou
ps/ContosoRG/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/fwNic/ipConfiguratio
ns/ipconfig1",
"NextHopIds": [
"cccccccc-2222-3333-4444-dddddddddddd"
],
"Issues": []
},