重要
从 2025 年 7 月 28 日起,对应用服务 托管证书 (ASMC)的更改会影响某些情况下证书的颁发和续订方式。 虽然大多数客户不需要采取措施,但我们建议查看 ASMC 的详细博客文章 以了解详细信息。
可以通过为应用启用各种类型的身份验证来限制对 Azure 应用服务应用的访问。 一种设置身份验证的方法是在通过传输层安全性(TLS)/安全套接字层(SSL)发送客户端请求时请求客户端证书,并验证该证书。 此机制称为 相互身份验证 或 客户端证书身份验证。 本文介绍如何将应用设置为使用客户端证书身份验证。
注意
应用代码必须验证客户端证书。 除了将客户端证书转发到应用之外,应用服务不会对客户端证书执行任何作。
如果通过 HTTP 而不是 HTTPS 访问站点,则不会收到任何客户端证书。 如果应用程序需要客户端证书,则不应允许通过 HTTP 向应用程序发出请求。
准备 Web 应用
如果要创建自定义 TLS/SSL 绑定或为应用服务应用启用客户端证书, 应用服务计划 必须位于基本层、标准层、高级层或独立层中。
若要确保 Web 应用位于受支持的定价层中,请执行以下作:
转到 Web 应用
在 Azure 门户 搜索框中,输入 应用服务 ,然后在搜索结果中选择它。
在 “应用服务 ”页上,选择 Web 应用:

现在你位于 Web 应用的管理页上。
检查定价层
在 Web 应用的左侧菜单中,在“设置”下,选择“纵向扩展”(应用服务计划)。
确保 Web 应用不在 F1 或 D1 层中。 这些层不支持自定义 TLS/SSL。
如果需要增加,请按照下一部分中的步骤进行操作。 否则,请关闭 “纵向扩展 ”窗格,并跳过下一部分。
纵向扩展应用服务计划
选择任何非免费层,例如 B1、B2、B3 或“生产”类别中的任何其他层。
完成后,选择“选择”。
当缩放操作完成后,你将看到一条消息,表示计划已更新。
启用客户端证书
为应用启用客户端证书时,应选择客户端证书模式。 该模式定义应用如何处理传入客户端证书。 下表描述了这些模式:
| 客户端证书模式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 必须 | 所有请求均需要提供客户端证书。 |
| 可选 | 请求可以使用客户端证书。 默认情况下,系统会提示客户端输入证书。 例如,浏览器客户端会显示提示以选择证书进行身份验证。 |
| (可选)交互式用户 | 请求可以使用客户端证书。 默认情况下,不会提示客户端输入证书。 例如,浏览器客户端不会显示用于选择证书进行身份验证的提示。 |
若要使用 Azure 门户启用客户端证书,请执行以下作:
- 转到应用管理页面。
- 在左侧菜单中,选择 “配置>常规”设置。
- 对于 客户端证书模式,请选择自己的选择。
- 选择“保存”。
使路径不要求身份验证
为应用程序启用相互身份验证时,应用根目录下的所有路径都需要客户端证书进行访问。 若要针对特定路径去除此要求,请在应用程序配置中定义排除路径。
注意
使用任何客户端证书排除路径都会触发对传入到应用的请求进行 TLS 重新协商。
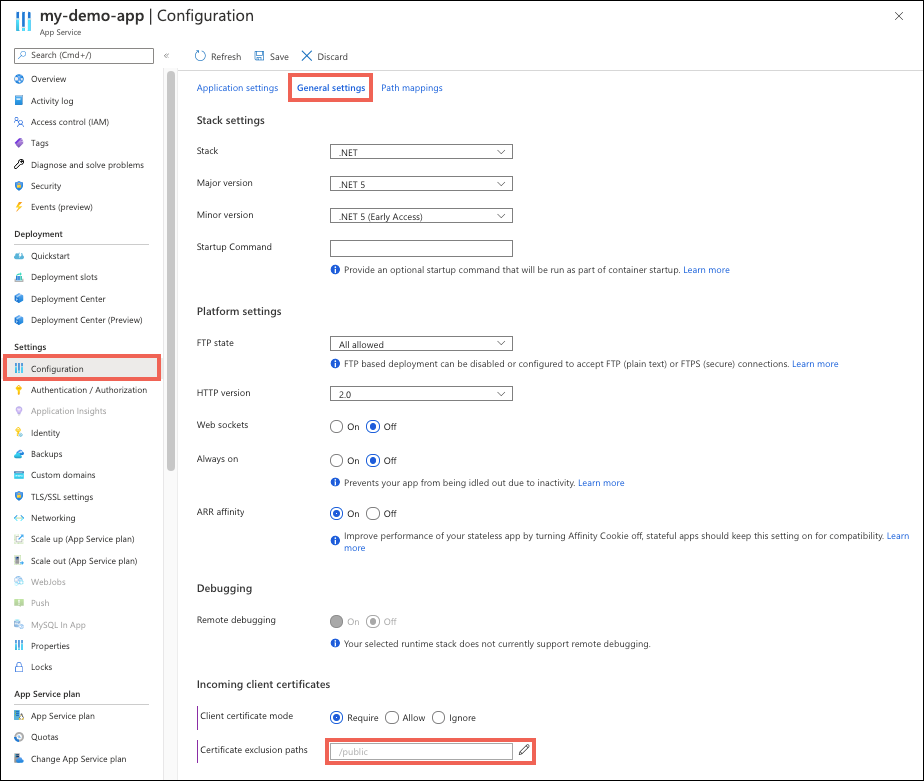
在应用管理页面的左侧菜单中,选择 “设置>配置”。 选择“常规设置”选项卡。
在 证书排除路径旁边,选择铅笔图标。
选择 “新建路径”,指定路径或由
,或;分隔的路径列表,然后选择“ 确定”。选择“保存”。
以下屏幕截图显示了如何设置证书排除路径。 在此示例中,以 /public 客户端证书开头的应用的任何路径都不会请求客户端证书。 路径匹配不区分大小写。
访问客户端证书
在应用服务中,请求的 TLS 终止发生在前端负载均衡器上。 在已启用客户端证书的情况下将请求转发到应用代码时,应用服务会注入包含客户端证书的 X-ARR-ClientCert 请求标头。 应用服务对此客户端证书不做任何操作,只是将其转发到您的应用。 应用代码需要验证客户端证书。
在 ASP.NET 中,客户端证书可通过 HttpRequest.ClientCertificate 属性获得。
在其他应用程序堆栈(Node.js,PHP)中,客户端证书可通过请求标头中的 X-ARR-ClientCert Base64 编码值获得。
ASP.NET Core 示例
对于 ASP.NET Core,中间件可用于分析转发的证书。 单独的中间件可用于使用转发的协议标头。 若要接受转发的证书,两者必须同时存在。 可以在 CertificateAuthentication 选项中放置自定义证书验证逻辑:
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
// Configure the application to use the protocol and client IP address forwarded by the front-end load balancer.
services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders =
ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
// By default, only loopback proxies are allowed. Clear that restriction to enable this explicit configuration.
options.KnownNetworks.Clear();
options.KnownProxies.Clear();
});
// Configure the application to use the client certificate forwarded by the front-end load balancer.
services.AddCertificateForwarding(options => { options.CertificateHeader = "X-ARR-ClientCert"; });
// Add certificate authentication so that when authorization is performed the user will be created from the certificate.
services.AddAuthentication(CertificateAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme).AddCertificate();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseForwardedHeaders();
app.UseCertificateForwarding();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthentication()
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
ASP.NET Web 窗体示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Specialized;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Web;
namespace ClientCertificateUsageSample
{
public partial class Cert : System.Web.UI.Page
{
public string certHeader = "";
public string errorString = "";
private X509Certificate2 certificate = null;
public string certThumbprint = "";
public string certSubject = "";
public string certIssuer = "";
public string certSignatureAlg = "";
public string certIssueDate = "";
public string certExpiryDate = "";
public bool isValidCert = false;
//
// Read the certificate from the header into an X509Certificate2 object.
// Display properties of the certificate on the page.
//
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
NameValueCollection headers = base.Request.Headers;
certHeader = headers["X-ARR-ClientCert"];
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(certHeader))
{
try
{
byte[] clientCertBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(certHeader);
certificate = new X509Certificate2(clientCertBytes);
certSubject = certificate.Subject;
certIssuer = certificate.Issuer;
certThumbprint = certificate.Thumbprint;
certSignatureAlg = certificate.SignatureAlgorithm.FriendlyName;
certIssueDate = certificate.NotBefore.ToShortDateString() + " " + certificate.NotBefore.ToShortTimeString();
certExpiryDate = certificate.NotAfter.ToShortDateString() + " " + certificate.NotAfter.ToShortTimeString();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
errorString = ex.ToString();
}
finally
{
isValidCert = IsValidClientCertificate();
if (!isValidCert) Response.StatusCode = 403;
else Response.StatusCode = 200;
}
}
else
{
certHeader = "";
}
}
//
// This is a sample verification routine. You should modify this method to suit your application logic and security requirements.
//
//
private bool IsValidClientCertificate()
{
// In this example, the certificate is accepted as a valid certificate only if these conditions are met:
// - The certificate isn't expired and is active for the current time on the server.
// - The subject name of the certificate has the common name nildevecc.
// - The issuer name of the certificate has the common name nildevecc and the organization name Microsoft Corp.
// - The thumbprint of the certificate is 30757A2E831977D8BD9C8496E4C99AB26CB9622B.
//
// This example doesn't test that the certificate is chained to a trusted root authority (or revoked) on the server.
// It allows self-signed certificates.
//
if (certificate == null || !String.IsNullOrEmpty(errorString)) return false;
// 1. Check time validity of the certificate.
if (DateTime.Compare(DateTime.Now, certificate.NotBefore) < 0 || DateTime.Compare(DateTime.Now, certificate.NotAfter) > 0) return false;
// 2. Check the subject name of the certificate.
bool foundSubject = false;
string[] certSubjectData = certificate.Subject.Split(new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (string s in certSubjectData)
{
if (String.Compare(s.Trim(), "CN=nildevecc") == 0)
{
foundSubject = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundSubject) return false;
// 3. Check the issuer name of the certificate.
bool foundIssuerCN = false, foundIssuerO = false;
string[] certIssuerData = certificate.Issuer.Split(new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (string s in certIssuerData)
{
if (String.Compare(s.Trim(), "CN=nildevecc") == 0)
{
foundIssuerCN = true;
if (foundIssuerO) break;
}
if (String.Compare(s.Trim(), "O=Microsoft Corp") == 0)
{
foundIssuerO = true;
if (foundIssuerCN) break;
}
}
if (!foundIssuerCN || !foundIssuerO) return false;
// 4. Check the thumbprint of the certificate.
if (String.Compare(certificate.Thumbprint.Trim().ToUpper(), "30757A2E831977D8BD9C8496E4C99AB26CB9622B") != 0) return false;
return true;
}
}
}
Node.js 示例
以下 Node.js 示例代码获取 X-ARR-ClientCert 标头,并使用 node-forge 将 Base64 编码的隐私增强邮件 (PEM) 字符串转换为证书对象并对其进行验证:
import { NextFunction, Request, Response } from 'express';
import { pki, md, asn1 } from 'node-forge';
export class AuthorizationHandler {
public static authorizeClientCertificate(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction): void {
try {
// Get header.
const header = req.get('X-ARR-ClientCert');
if (!header) throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Convert from PEM to PKI certificate.
const pem = `-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----${header}-----END CERTIFICATE-----`;
const incomingCert: pki.Certificate = pki.certificateFromPem(pem);
// Validate certificate thumbprint.
const fingerPrint = md.sha1.create().update(asn1.toDer(pki.certificateToAsn1(incomingCert)).getBytes()).digest().toHex();
if (fingerPrint.toLowerCase() !== 'abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12') throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Validate time validity.
const currentDate = new Date();
if (currentDate < incomingCert.validity.notBefore || currentDate > incomingCert.validity.notAfter) throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Validate issuer.
if (incomingCert.issuer.hash.toLowerCase() !== 'abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12') throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Validate subject.
if (incomingCert.subject.hash.toLowerCase() !== 'abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12') throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
next();
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof Error && e.message === 'UNAUTHORIZED') {
res.status(401).send();
} else {
next(e);
}
}
}
}
Java 示例
以下 Java 类将证书从 X-ARR-ClientCert 编码为 X509Certificate 实例。
certificateIsValid() 验证证书的指纹是否与构造函数中给定的指纹匹配,并且证书未过期。
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.cert.*;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import sun.security.provider.X509Factory;
import javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.Date;
public class ClientCertValidator {
private String thumbprint;
private X509Certificate certificate;
/**
* Constructor.
* @param certificate. The certificate from the "X-ARR-ClientCert" HTTP header.
* @param thumbprint. The thumbprint to check against.
* @throws CertificateException if the certificate factory can't be created.
*/
public ClientCertValidator(String certificate, String thumbprint) throws CertificateException {
certificate = certificate
.replaceAll(X509Factory.BEGIN_CERT, "")
.replaceAll(X509Factory.END_CERT, "");
CertificateFactory cf = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
byte [] base64Bytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(certificate);
X509Certificate X509cert = (X509Certificate) cf.generateCertificate(new ByteArrayInputStream(base64Bytes));
this.setCertificate(X509cert);
this.setThumbprint(thumbprint);
}
/**
* Check that the certificate's thumbprint matches the one given in the constructor, and that the
* certificate isn't expired.
* @return True if the certificate's thumbprint matches and isn't expired. False otherwise.
*/
public boolean certificateIsValid() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, CertificateEncodingException {
return certificateHasNotExpired() && thumbprintIsValid();
}
/**
* Check certificate's timestamp.
* @return True if the certificate isn't expired. It returns False if it is expired.
*/
private boolean certificateHasNotExpired() {
Date currentTime = new java.util.Date();
try {
this.getCertificate().checkValidity(currentTime);
} catch (CertificateExpiredException | CertificateNotYetValidException e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Check whether the certificate's thumbprint matches the given one.
* @return True if the thumbprints match. False otherwise.
*/
private boolean thumbprintIsValid() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, CertificateEncodingException {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
byte[] der = this.getCertificate().getEncoded();
md.update(der);
byte[] digest = md.digest();
String digestHex = DatatypeConverter.printHexBinary(digest);
return digestHex.toLowerCase().equals(this.getThumbprint().toLowerCase());
}
// Getters and setters.
public void setThumbprint(String thumbprint) {
this.thumbprint = thumbprint;
}
public String getThumbprint() {
return this.thumbprint;
}
public X509Certificate getCertificate() {
return certificate;
}
public void setCertificate(X509Certificate certificate) {
this.certificate = certificate;
}
}
Python 示例
以下 Flask 和 Django Python 代码示例实现了一个名为 authorize_certificate 的装饰器,该装饰器可在视图函数上使用,以仅允许提供有效客户端证书的调用方进行访问。 它预期标头中包含 PEM 格式的 X-ARR-ClientCert 证书,并使用 Python 加密 包根据证书的指纹(指纹)、使用者公用名、颁发者公用名以及开始和到期日期来验证证书。 如果验证失败,该修饰器可确保将状态代码为 403(禁止)的 HTTP 响应返回到客户端。
from functools import wraps
from datetime import datetime, timezone
from flask import abort, request
from cryptography import x509
from cryptography.x509.oid import NameOID
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
def validate_cert(request):
try:
cert_value = request.headers.get('X-ARR-ClientCert')
if cert_value is None:
return False
cert_data = ''.join(['-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n', cert_value, '\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n',])
cert = x509.load_pem_x509_certificate(cert_data.encode('utf-8'))
fingerprint = cert.fingerprint(hashes.SHA1())
if fingerprint != b'12345678901234567890':
return False
subject = cert.subject
subject_cn = subject.get_attributes_for_oid(NameOID.COMMON_NAME)[0].value
if subject_cn != "contoso.com":
return False
issuer = cert.issuer
issuer_cn = issuer.get_attributes_for_oid(NameOID.COMMON_NAME)[0].value
if issuer_cn != "contoso.com":
return False
current_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
if current_time < cert.not_valid_before_utc:
return False
if current_time > cert.not_valid_after_utc:
return False
return True
except Exception as e:
# Handle any errors encountered during validation.
print(f"Encountered the following error during certificate validation: {e}")
return False
def authorize_certificate(f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
if not validate_cert(request):
abort(403)
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
以下代码片段演示如何在 Flask 视图函数上使用修饰器。
@app.route('/hellocert')
@authorize_certificate
def hellocert():
print('Request for hellocert page received')
return render_template('index.html')