变量资产是可供自动化帐户中的所有 Runbook 和 DSC 配置使用的值。 你可以在 Azure 门户、PowerShell、Runbook 或 DSC 配置中管理它们。
自动化变量可用于以下方案:
在多个 Runbook 或 DSC 配置之间共享某个值。
在同一 Runbook 或 DSC 配置中的多个作业之间共享某个值。
通过门户或 PowerShell 命令行管理 Runbook 或 DSC 配置使用的值。 例如,一组常用配置项,包括特定的 VM 名称列表、特定资源组、AD 域名等。
Azure 自动化会持久保存变量,因此即使 Runbook 或 DSC 配置失败,变量也仍然可用。 此行为允许一个 Runbook 或 DSC 配置设置的值随后由另一个 Runbook 使用,或由同一 Runbook 或 DSC 配置在下次运行时使用。
Azure 自动化会安全存储每个加密的变量。 创建变量时,可以指定将其加密,并由 Azure 自动化将其作为安全资产进行存储。 创建变量后,除非重新创建变量,否则将无法更改其加密状态。 如果你拥有存储了尚未加密的敏感数据的自动化帐户变量,需要删除这些变量并将其重新创建为加密变量。 Microsoft Defender for Cloud 建议加密所有 Azure 自动化变量,如应加密自动化帐户变量中所述。
注释
Azure 自动化中的安全资产包括凭据、证书、连接和加密的变量。 这些资产已使用针对每个自动化帐户生成的唯一密钥进行加密并存储在 Azure 自动化中。 Azure 自动化将密钥存储在系统管理的 Key Vault 中。 在存储安全资产之前,自动化会从 Key Vault 加载密钥,然后使用该密钥加密资产。
变量类型
使用 Azure 门户创建变量时,必须从下拉列表指定一个数据类型,使门户能够显示用于输入变量值的相应控件。 下面是可在 Azure 自动化中使用的变量类型:
- 字符串
- 整数
- 日期和时间
- 布尔型
- 零
该变量并不局限于指定的数据类型。 但如果要指定不同类型的值,则必须使用 Windows PowerShell 设置该变量。 如果指示 Not defined,则变量的值将设置为 Null。 必须使用 Set-AzAutomationVariable cmdlet 或内部 Set-AutomationVariable cmdlet 来设置值。 可以在要在 Azure 沙盒环境中或 Windows 混合 Runbook 辅助角色上运行的 runbook 中使用 Set-AutomationVariable。
不能使用 Azure 门户来创建或更改复杂变量类型的值。 但是,可以使用 Windows PowerShell 提供任何类型的值。 复杂类型会作为 Complex 对象类型的 Newtonsoft.Json.Linq.JProperty(而不是 PSObject 类型 PSCustomObject)进行检索。
可以通过创建一个数组或哈希表并将其保存到变量,来将多个值存储到单一变量。
注释
VM 名称变量最多可以包含 80 个字符。 资源组变量最多可以包含 90 个字符。 请参阅 Azure 资源的命名规则和限制。
用于访问变量的 PowerShell cmdlet
下表中的 cmdlet 使用 PowerShell 创建和管理自动化变量。 它们作为 Az 模块的一部分提供。
| Cmdlet (命令行工具) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Get-AzAutomationVariable | 检索现有变量的值。 如果该值为简单类型,则检索相同的类型。 如果为复杂类型,则检索 PSCustomObject 类型。
1 |
| New-AzAutomationVariable | 创建新变量并设置变量值。 |
| Remove-AzAutomationVariable | 删除现有变量。 |
| Set-AzAutomationVariable(设置Az自动化变量) | 设置现有变量的值。 |
1 不能使用此 cmdlet 来检索已加密变量的值。 只能在 runbook 或 DSC 配置中使用内部 Get-AutomationVariable cmdlet 来执行此操作。 例如,若要查看某个加密变量的值,可以创建一个 runbook 来获取该变量,然后将其写入到输出流:
$encryptvar = Get-AutomationVariable -Name TestVariable
Write-output "The encrypted value of the variable is: $encryptvar"
用于访问变量的内部 cmdlet
下表中的内部 cmdlet 用于访问 Runbook 和 DSC 配置中的变量。 这些 cmdlet 附带全局模块 Orchestrator.AssetManagement.Cmdlets。 有关详细信息,请参阅内部 cmdlet。
| 内部 Cmdlet | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
Get-AutomationVariable |
检索现有变量的值。 |
Set-AutomationVariable |
设置现有变量的值。 |
注释
避免在 runbook 或 DSC 配置中的 Name cmdlet 的 Get-AutomationVariable 参数中使用变量。 使用变量可能会使在设计时发现 runbook 与自动化变量之间的依赖项变得复杂。
用于访问变量的 Python 函数
下表中的函数用于在 Python 2 和 3 Runbook 中访问变量。 Python 3 Runbook 目前处于预览阶段。
| Python 函数 | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
automationassets.get_automation_variable |
检索现有变量的值。 |
automationassets.set_automation_variable |
设置现有变量的值。 |
注释
必须在 Python Runbook 顶部导入 automationassets 模块才能访问资产函数。
创建并获取变量
注释
如果要删除对变量的加密,则必须删除该变量,并将其重新创建为未加密的变量。
使用 Azure 门户创建并获取变量
- 在自动化帐户的左侧窗格中,选择“共享资源”下的“变量” 。
- 在“变量”页上,选择“添加变量”。
- 完成“新建变量”页上的选项,然后选择“创建”保存新变量。
注释
保存加密的变量后,就不能在门户中查看它。 只能更新它。
在 Windows PowerShell 中创建并获取变量
Runbook 或 DSC 配置使用 New-AzAutomationVariable cmdlet 创建新的变量并设置其初始值。 如果变量已加密,则调用应使用 Encrypted 参数。 脚本可以使用 Get-AzAutomationVariable 检索变量的值。
注释
PowerShell 脚本无法检索加密的值。 只能使用内部 Get-AutomationVariable cmdlet 执行此操作。
下面的示例演示如何创建字符串变量,然后返回其值。
$rgName = "ResourceGroup01"
$accountName = "MyAutomationAccount"
$variableValue = "My String"
New-AzAutomationVariable -ResourceGroupName "ResourceGroup01"
-AutomationAccountName "MyAutomationAccount" -Name 'MyStringVariable' `
-Encrypted $false -Value 'My String'
$string = (Get-AzAutomationVariable -ResourceGroupName "ResourceGroup01" `
-AutomationAccountName "MyAutomationAccount" -Name 'MyStringVariable').Value
下面的示例演示如何创建复杂类型的变量,并检索其属性。 在本例中,我们使用了 Get-AzVM 返回的虚拟机对象(通过指定其属性的子集)。
$rgName = "ResourceGroup01"
$accountName = "MyAutomationAccount"
$vm = Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName "ResourceGroup01" -Name "VM01" | Select Name, Location, Extensions
New-AzAutomationVariable -ResourceGroupName "ResourceGroup01" -AutomationAccountName "MyAutomationAccount" -Name "MyComplexVariable" -Encrypted $false -Value $vm
$vmValue = Get-AzAutomationVariable -ResourceGroupName "ResourceGroup01" `
-AutomationAccountName "MyAutomationAccount" -Name "MyComplexVariable"
$vmName = $vmValue.Value.Name
$vmTags = $vmValue.Value.Tags
文本 Runbook 示例
下面的示例演示如何设置和检索文本 Runbook 中的变量。 此示例假设要创建名为 numberOfIterations 和 numberOfRunnings 的整数变量,以及名为 sampleMessage 的字符串变量 。
$rgName = "ResourceGroup01"
$accountName = "MyAutomationAccount"
$numberOfIterations = Get-AutomationVariable -Name "numberOfIterations"
$numberOfRunnings = Get-AutomationVariable -Name "numberOfRunnings"
$sampleMessage = Get-AutomationVariable -Name "sampleMessage"
Write-Output "Runbook has been run $numberOfRunnings times."
for ($i = 1; $i -le $numberOfIterations; $i++) {
Write-Output "$i`: $sampleMessage"
}
Set-AutomationVariable -Name numberOfRunnings -Value ($numberOfRunnings += 1)
图形 Runbook 示例
在图形 runbook 中,可以为内部 cmdlet Get-AutomationVariable 或 Set-AutomationVariable 添加活动 。 只需在图形编辑器的“库”窗格中右键单击每个变量,然后选择所需的活动即可。
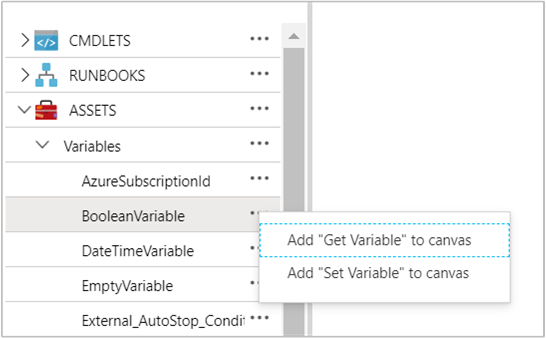
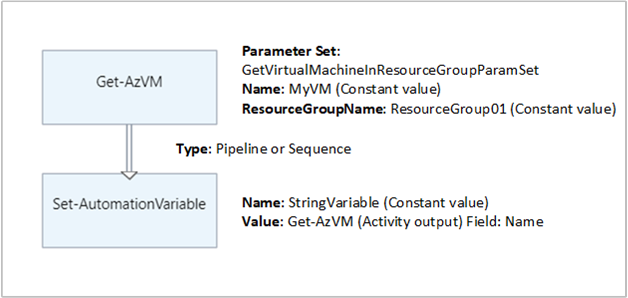
下图显示了在图形 Runbook 中用于更新具有简单值的变量的示例活动。 在此示例中,Get-AzVM 的活动检索单个 Azure 虚拟机,并将计算机名保存到现有的自动化字符串变量中。
链接是管道还是序列并不重要,因为代码只需要输出中的单个对象。
后续步骤
若要了解有关用于访问变量的 cmdlet 的详细信息,请参阅在 Azure 自动化中管理模块。
有关 Runbook 的常规信息,请参阅在 Azure 自动化中执行 Runbook。
有关 DSC 配置的详细信息,请参阅 Azure 自动化 State Configuration 概述。