机器人在本质上是无状态的。 部署机器人后,根据轮次的不同,它不一定会在相同的进程或计算机中运行。 但是,机器人可能需要跟踪聊天上下文,以便可以管理聊天行为并记住先前问题的回答。 使用 Bot Framework SDK 的状态和存储功能可将状态添加到机器人。 机器人使用状态管理和存储对象来管理并持久保存状态。 状态管理器提供一个抽象层,让你可以使用属性访问器来访问状态属性(不考虑基础存储的类型)。
重要
Bot Framework SDK 和 Bot Framework Emulator 已在 GitHub 上存档。 项目不再更新或维护。 自 2025 年 12 月 31 日起,Bot Framework SDK 的支持票证将不再提供服务。
若要使用所选的 AI 服务、业务流程和知识生成代理,请考虑使用 Microsoft 365 代理 SDK。 代理 SDK 对 C#、JavaScript 或 Python 具有语言支持。 可以在 aka.ms/agents 了解有关代理 SDK 的详细信息。
如果现有的机器人是使用 Bot Framework SDK 生成的,则可以将机器人更新到代理 SDK。 查看 Bot Framework SDK 到代理 SDK 迁移指南的核心更改和更新。
如果要查找基于 SaaS 的代理平台,请考虑 Microsoft Copilot Studio。
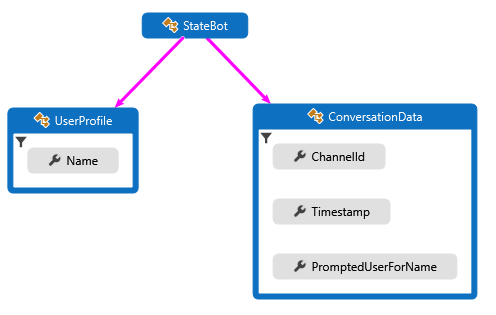
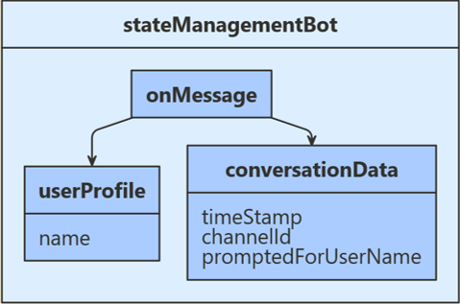
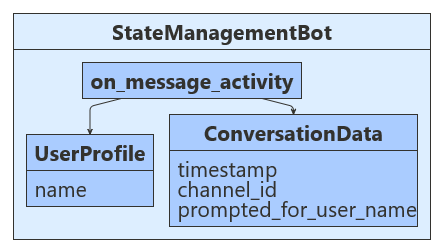
收到用户输入以后,此示例会检查存储的聊天状态,看系统以前是否已提示该用户提供其名称。 如果否,则系统会请求用户的名称,并将该输入存储在用户状态中。 如果是这样,系统会使用用户状态中存储的名称与用户聊天,并将用户的输入数据以及接收时间、输入通道 ID 返回给用户。 将会从用户对话数据中检索时间和通道 ID,然后将其保存到对话状态中。 以下图示显示了机器人、用户配置文件和聊天数据类之间的关系。
设置状态管理时,第一步是定义类,这些类将包含需要在用户和聊天状态中管理的信息。 本文中使用的示例定义以下类:
- 在 UserProfile.cs 中,为机器人将要收集的用户信息定义
UserProfile 类。
- 在 ConversationData.cs 中定义一个
ConversationData 类,用于在收集用户信息时控制聊天状态。
以下代码示例显示了 UserProfile 和 ConversationData 类的定义。
UserProfile.cs
public class UserProfile
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
ConversationData.cs
public class ConversationData
{
// The time-stamp of the most recent incoming message.
public string Timestamp { get; set; }
// The ID of the user's channel.
public string ChannelId { get; set; }
// Track whether we have already asked the user's name
public bool PromptedUserForName { get; set; } = false;
}
设置状态管理时,第一步是定义类,这些类将包含需要在用户和聊天状态中管理的信息。 本文中使用的示例定义以下类:
- 在 UserProfile.java 中,为机器人将要收集的用户信息定义
UserProfile 类。
- 在 ConversationData.java 中定义一个
ConversationData 类,用于在收集用户信息时控制聊天状态。
以下代码示例显示了 UserProfile 和 ConversationData 类的定义。
UserProfile.java
public class UserProfile {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String withName) {
name = withName;
}
}
ConversationData.java
public class ConversationData {
// The time-stamp of the most recent incoming message.
private String timestamp;
// The ID of the user's channel.
private String channelId;
// Track whether we have already asked the user's name.
private boolean promptedUserForName = false;
public String getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public void setTimestamp(String withTimestamp) {
timestamp = withTimestamp;
}
public String getChannelId() {
return channelId;
}
public void setChannelId(String withChannelId) {
channelId = withChannelId;
}
public boolean getPromptedUserForName() {
return promptedUserForName;
}
public void setPromptedUserForName(boolean withPromptedUserForName) {
设置状态管理时,第一步是定义类,这些类将包含需要在用户和聊天状态中管理的信息。 本文中使用的示例定义以下类:
-
user_profile.py 包含
UserProfile 类,用于存储机器人收集的用户信息。
-
conversation_data.py 包含
ConversationData 类,用于控制收集用户信息时的对话状态。
以下代码示例显示了 UserProfile 和 ConversationData 类的定义。
user_profile.py
class UserProfile:
def __init__(self, name: str = None):
self.name = name
conversation_data.py
class ConversationData:
def __init__(
self,
timestamp: str = None,
channel_id: str = None,
prompted_for_user_name: bool = False,
):
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.channel_id = channel_id
self.prompted_for_user_name = prompted_for_user_name
接下来,注册用于创建 MemoryStorage 和 UserState 对象的 ConversationState。 用户和聊天状态对象在Startup时创建,依赖项会注入机器人构造函数中。 机器人的其他已注册服务:凭据提供程序、适配器和机器人实现。
Startup.cs
// {
// TypeNameHandling = TypeNameHandling.All,
// var storage = new BlobsStorage("<blob-storage-connection-string>", "bot-state");
// With a custom JSON SERIALIZER, use this instead.
// var storage = new BlobsStorage("<blob-storage-connection-string>", "bot-state", jsonSerializer);
/* END AZURE BLOB STORAGE */
Bots/StateManagementBot.cs
private BotState _conversationState;
private BotState _userState;
public StateManagementBot(ConversationState conversationState, UserState userState)
{
_conversationState = conversationState;
_userState = userState;
}
接下来,注册随后用于创建 MemoryStorage 和 UserState 对象的 ConversationState。 这些项在 index.js 创建,在创建机器人后使用。
index.js
// Define state store for your bot.
// See https://aka.ms/about-bot-state to learn more about bot state.
const memoryStorage = new MemoryStorage();
// Create conversation and user state with in-memory storage provider.
const conversationState = new ConversationState(memoryStorage);
const userState = new UserState(memoryStorage);
// Create the bot.
const bot = new StateManagementBot(conversationState, userState);
bots/stateManagementBot.js
// The accessor names for the conversation data and user profile state property accessors.
const CONVERSATION_DATA_PROPERTY = 'conversationData';
const USER_PROFILE_PROPERTY = 'userProfile';
class StateManagementBot extends ActivityHandler {
constructor(conversationState, userState) {
super();
// Create the state property accessors for the conversation data and user profile.
this.conversationDataAccessor = conversationState.createProperty(CONVERSATION_DATA_PROPERTY);
this.userProfileAccessor = userState.createProperty(USER_PROFILE_PROPERTY);
// The state management objects for the conversation and user state.
this.conversationState = conversationState;
this.userState = userState;
接下来,在 Application.java 中注册 StateManagementBot。 默认情况下,ConversationState 和 UserState 都是从 BotDependencyConfiguration 类提供的,Spring 会将它们注入到 getBot 方法中。
Application.java
@Bean
public Bot getBot(
ConversationState conversationState,
UserState userState
) {
return new StateManagementBot(conversationState, userState);
}
接下来,注册用于创建 MemoryStorage 和 UserState 对象的 ConversationState。 这些项在 app.py 创建,在创建机器人后使用。
app.py
CONVERSATION_STATE = ConversationState(MEMORY)
# Create Bot
BOT = StateManagementBot(CONVERSATION_STATE, USER_STATE)
# Listen for incoming requests on /api/messages.
bots/state_management_bot.py
def __init__(self, conversation_state: ConversationState, user_state: UserState):
if conversation_state is None:
raise TypeError(
"[StateManagementBot]: Missing parameter. conversation_state is required but None was given"
)
if user_state is None:
raise TypeError(
"[StateManagementBot]: Missing parameter. user_state is required but None was given"
)
self.conversation_state = conversation_state
self.user_state = user_state
self.conversation_data_accessor = self.conversation_state.create_property(
"ConversationData"
)
self.user_profile_accessor = self.user_state.create_property("UserProfile")
现在,使用 CreateProperty 方法来创建属性访问器,该方法提供 BotState 对象的句柄。 每个状态属性访问器允许获取或设置关联状态属性的值。 在使用状态属性之前,使用每个访问器从存储加载属性,并从状态缓存获取该属性。 为了将范围设置适当的密钥与状态属性相关联,请调用 GetAsync 方法。
Bots/StateManagementBot.cs
var conversationStateAccessors = _conversationState.CreateProperty<ConversationData>(nameof(ConversationData));
var userStateAccessors = _userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>(nameof(UserProfile));
现在,为 UserState 和 ConversationState 创建属性访问器。 每个状态属性访问器允许获取或设置关联状态属性的值。 使用每个访问器从存储加载关联的属性,并从缓存中检索其当前状态。
bots/stateManagementBot.js
constructor(conversationState, userState) {
super();
// Create the state property accessors for the conversation data and user profile.
this.conversationDataAccessor = conversationState.createProperty(CONVERSATION_DATA_PROPERTY);
this.userProfileAccessor = userState.createProperty(USER_PROFILE_PROPERTY);
现在,使用 createProperty 方法创建属性访问器。 每个状态属性访问器允许获取或设置关联状态属性的值。 在使用状态属性之前,使用每个访问器从存储加载属性,并从状态缓存获取该属性。 为了将范围设置适当的密钥与状态属性相关联,请调用 get 方法。
StateManagementBot.java
StatePropertyAccessor<ConversationData> dataAccessor =
conversationState.createProperty("data");
CompletableFuture<ConversationData> dataFuture =
dataAccessor.get(turnContext, ConversationData::new);
现在,为 UserProfile 和 ConversationData 创建属性访问器。 每个状态属性访问器允许获取或设置关联状态属性的值。 使用每个访问器从存储加载关联的属性,并从缓存中检索其当前状态。
bots/state_management_bot.py
self.conversation_data_accessor = self.conversation_state.create_property(
"ConversationData"
)
self.user_profile_accessor = self.user_state.create_property("UserProfile")
- 如果
userProfile.Name 为空且 conversationData.PromptedUserForName 为 true,请检索提供的用户名并将其存储在用户状态中。
- 如果
userProfile.Name 为空且 conversationData.PromptedUserForName 为 false,请索要用户名。
- 如果之前已存储
userProfile.Name,请从用户输入中检索消息时间和通道 ID,将所有数据回显给用户,然后将检索的数据存储在对话状态中。
Bots/StateManagementBot.cs
protected override async Task OnMessageActivityAsync(ITurnContext<IMessageActivity> turnContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// Get the state properties from the turn context.
var conversationStateAccessors = _conversationState.CreateProperty<ConversationData>(nameof(ConversationData));
var conversationData = await conversationStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new ConversationData());
var userStateAccessors = _userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>(nameof(UserProfile));
var userProfile = await userStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new UserProfile());
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(userProfile.Name))
{
// First time around this is set to false, so we will prompt user for name.
if (conversationData.PromptedUserForName)
{
// Set the name to what the user provided.
userProfile.Name = turnContext.Activity.Text?.Trim();
// Acknowledge that we got their name.
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Thanks {userProfile.Name}. To see conversation data, type anything.");
// Reset the flag to allow the bot to go through the cycle again.
conversationData.PromptedUserForName = false;
}
else
{
// Prompt the user for their name.
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"What is your name?");
// Set the flag to true, so we don't prompt in the next turn.
conversationData.PromptedUserForName = true;
}
}
else
{
// Add message details to the conversation data.
// Convert saved Timestamp to local DateTimeOffset, then to string for display.
var messageTimeOffset = (DateTimeOffset)turnContext.Activity.Timestamp;
var localMessageTime = messageTimeOffset.ToLocalTime();
conversationData.Timestamp = localMessageTime.ToString();
conversationData.ChannelId = turnContext.Activity.ChannelId.ToString();
// Display state data.
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"{userProfile.Name} sent: {turnContext.Activity.Text}");
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Message received at: {conversationData.Timestamp}");
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Message received from: {conversationData.ChannelId}");
}
}
在退出轮次处理程序之前,使用状态管理对象的 SaveChangesAsync() 方法将所有状态更改写回到存储中。
Bots/StateManagementBot.cs
public override async Task OnTurnAsync(ITurnContext turnContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
{
await base.OnTurnAsync(turnContext, cancellationToken);
// Save any state changes that might have occurred during the turn.
await _conversationState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
await _userState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
}
- 如果
userProfile.Name 为空且 conversationData.PromptedUserForName 为 true,请检索提供的用户名并将其存储在用户状态中。
- 如果
userProfile.Name 为空且 conversationData.PromptedUserForName 为 false,请索要用户名。
- 如果之前已存储
userProfile.Name,请从用户输入中检索消息时间和通道 ID,将所有数据回显给用户,然后将检索的数据存储在对话状态中。
bots/stateManagementBot.js
this.userState = userState;
this.onMessage(async (turnContext, next) => {
// Get the state properties from the turn context.
const userProfile = await this.userProfileAccessor.get(turnContext, {});
const conversationData = await this.conversationDataAccessor.get(
turnContext, { promptedForUserName: false });
if (!userProfile.name) {
// First time around this is undefined, so we will prompt user for name.
if (conversationData.promptedForUserName) {
// Set the name to what the user provided.
userProfile.name = turnContext.activity.text;
// Acknowledge that we got their name.
await turnContext.sendActivity(`Thanks ${ userProfile.name }. To see conversation data, type anything.`);
// Reset the flag to allow the bot to go though the cycle again.
conversationData.promptedForUserName = false;
} else {
// Prompt the user for their name.
await turnContext.sendActivity('What is your name?');
// Set the flag to true, so we don't prompt in the next turn.
conversationData.promptedForUserName = true;
}
} else {
// Add message details to the conversation data.
conversationData.timestamp = turnContext.activity.timestamp?.toLocaleString();
conversationData.channelId = turnContext.activity.channelId;
// Display state data.
await turnContext.sendActivity(`${ userProfile.name } sent: ${ turnContext.activity.text }`);
await turnContext.sendActivity(`Message received at: ${ conversationData.timestamp }`);
await turnContext.sendActivity(`Message received from: ${ conversationData.channelId }`);
}
// By calling next() you ensure that the next BotHandler is run.
await next();
});
在退出每个对话轮次之前,使用状态管理对象的 saveChanges() 方法来持久保存所有更改,方法是将状态写回到存储中。
bots/stateManagementBot.js
}
/**
* Override the ActivityHandler.run() method to save state changes after the bot logic completes.
*/
async run(context) {
await super.run(context);
// Save any state changes. The load happened during the execution of the Dialog.
await this.conversationState.saveChanges(context, false);
await this.userState.saveChanges(context, false);
}
- 如果
userProfile.getName() 为空且 conversationData.getPromptedUserForName() 为 true,请检索提供的用户名并将其存储在用户状态中。
- 如果
userProfile.getName() 为空且 conversationData.getPromptedUserForName() 为 false,请索要用户名。
- 如果之前已存储
userProfile.getName(),请从用户输入中检索消息时间和通道 ID,将所有数据回显给用户,然后将检索的数据存储在对话状态中。
StateManagementBot.java
@Override
protected CompletableFuture<Void> onMessageActivity(TurnContext turnContext) {
// Get state data from ConversationState.
StatePropertyAccessor<ConversationData> dataAccessor =
conversationState.createProperty("data");
CompletableFuture<ConversationData> dataFuture =
dataAccessor.get(turnContext, ConversationData::new);
// Get profile from UserState.
StatePropertyAccessor<UserProfile> profileAccessor = userState.createProperty("profile");
CompletableFuture<UserProfile> profileFuture =
profileAccessor.get(turnContext, UserProfile::new);
return dataFuture.thenCombine(profileFuture, (conversationData, userProfile) -> {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(userProfile.getName())) {
// First time around this is set to false, so we will prompt user for name.
if (conversationData.getPromptedUserForName()) {
// Reset the flag to allow the bot to go though the cycle again.
conversationData.setPromptedUserForName(false);
// Set the name to what the user provided and reply.
userProfile.setName(turnContext.getActivity().getText());
// Acknowledge that we got their name.
return turnContext.sendActivity(
MessageFactory.text(
"Thanks " + userProfile.getName()
+ ". To see conversation data, type anything."
)
);
} else {
// Set the flag to true, so we don't prompt in the next turn.
conversationData.setPromptedUserForName(true);
// Prompt the user for their name.
return turnContext.sendActivity(MessageFactory.text("What is your name?"));
}
} else {
OffsetDateTime messageTimeOffset = turnContext.getActivity().getTimestamp();
LocalDateTime localMessageTime = messageTimeOffset.toLocalDateTime();
//Displaying current date and time in 12 hour format with AM/PM
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeAMPMFormat = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("MM/dd/yyyy, hh:mm:ss a");
conversationData.setTimestamp(dateTimeAMPMFormat.format(localMessageTime));
conversationData.setChannelId(turnContext.getActivity().getChannelId());
List<Activity> sendToUser = new ArrayList<>();
sendToUser.add(
MessageFactory.text(
userProfile.getName() + " sent: " + turnContext.getActivity().getText()
)
);
sendToUser.add(
MessageFactory.text("Message received at: " + conversationData.getTimestamp()
)
);
sendToUser.add(
MessageFactory.text("Message received from: " + conversationData.getChannelId()
)
);
return turnContext.sendActivities(sendToUser);
}
})
// make the return value happy.
.thenApply(resourceResponse -> null);
}
在退出轮次处理程序之前,使用状态管理对象的 saveChanges() 方法将所有状态更改写回到存储中。
StateManagementBot.java
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Void> onTurn(TurnContext turnContext) {
return super.onTurn(turnContext)
// Save any state changes that might have occurred during the turn.
.thenCompose(turnResult -> conversationState.saveChanges(turnContext))
.thenCompose(saveResult -> userState.saveChanges(turnContext));
}
- 如果
user_profile.name 为空且 conversation_data.prompted_for_user_name 为 true,则机器人会检索用户提供的名称,然后将其存储在用户的状态中。
- 如果
user_profile.name 为空且 conversation_data.prompted_for_user_name 为 false,则机器人会索要用户名。
- 如果之前已存储
user_profile.name,机器人会从用户输入中检索“消息时间”和“通道 ID”,将数据回显给用户,然后将检索的数据存储在对话状态中。
bots/state_management_bot.py
async def on_message_activity(self, turn_context: TurnContext):
# Get the state properties from the turn context.
user_profile = await self.user_profile_accessor.get(turn_context, UserProfile)
conversation_data = await self.conversation_data_accessor.get(
turn_context, ConversationData
)
if user_profile.name is None:
# First time around this is undefined, so we will prompt user for name.
if conversation_data.prompted_for_user_name:
# Set the name to what the user provided.
user_profile.name = turn_context.activity.text
# Acknowledge that we got their name.
await turn_context.send_activity(
f"Thanks { user_profile.name }. To see conversation data, type anything."
)
# Reset the flag to allow the bot to go though the cycle again.
conversation_data.prompted_for_user_name = False
else:
# Prompt the user for their name.
await turn_context.send_activity("What is your name?")
# Set the flag to true, so we don't prompt in the next turn.
conversation_data.prompted_for_user_name = True
else:
# Add message details to the conversation data.
conversation_data.timestamp = self.__datetime_from_utc_to_local(
turn_context.activity.timestamp
)
conversation_data.channel_id = turn_context.activity.channel_id
# Display state data.
await turn_context.send_activity(
f"{ user_profile.name } sent: { turn_context.activity.text }"
)
await turn_context.send_activity(
f"Message received at: { conversation_data.timestamp }"
)
await turn_context.send_activity(
f"Message received from: { conversation_data.channel_id }"
)
在每个对话轮次结束之前,机器人会使用状态管理对象的 save_changes 方法来持久保存所有更改,方法是在存储中写入状态信息。
bots/state_management_bot.py
async def on_turn(self, turn_context: TurnContext):
await super().on_turn(turn_context)
await self.conversation_state.save_changes(turn_context)
await self.user_state.save_changes(turn_context)