适用于:SDK v4
机器人与用户之间的聊天通常涉及到请求(提示)用户输入信息、分析用户的响应,然后对该信息采取措施。 机器人应该跟踪聊天上下文,以便可以管理聊天行为并记住先前问题的回答。 机器人的状态是它为了正确响应传入消息而跟踪的信息。
提示
对话库提供内置提示,这些提示提供的功能超出用户能够使用的功能。 有关这些提示的示例,可参阅实现顺序聊天流一文。
重要
Bot Framework SDK 和 Bot Framework Emulator 已在 GitHub 上存档。 项目不再更新或维护。 自 2025 年 12 月 31 日起,Bot Framework SDK 的支持票证将不再提供服务。
若要使用所选的 AI 服务、业务流程和知识生成代理,请考虑使用 Microsoft 365 代理 SDK。 代理 SDK 对 C#、JavaScript 或 Python 具有语言支持。 可以在 aka.ms/agents 了解有关代理 SDK 的详细信息。 如果现有的机器人是使用 Bot Framework SDK 生成的,则可以将机器人更新到代理 SDK。 查看 Bot Framework SDK 到代理 SDK 迁移指南的核心更改和更新。
如果要查找基于 SaaS 的代理平台,请考虑 Microsoft Copilot Studio。
先决条件
关于示例代码
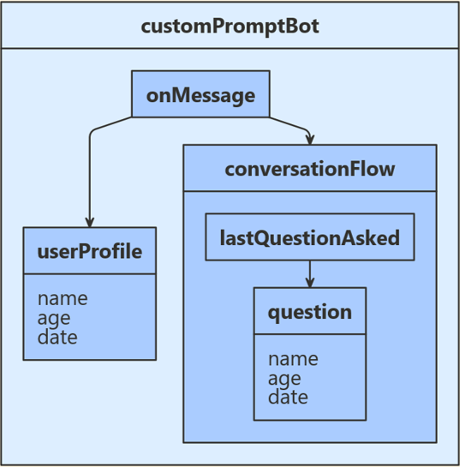
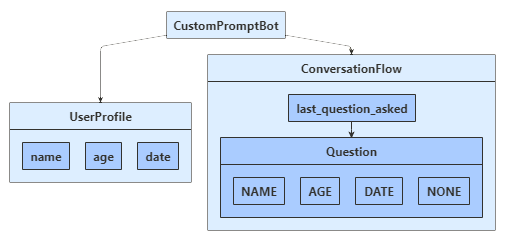
示例机器人会向用户提出一系列问题,验证他们的某些回答,然后保存其输入。 以下图示显示了机器人、用户配置文件和聊天流类之间的关系。
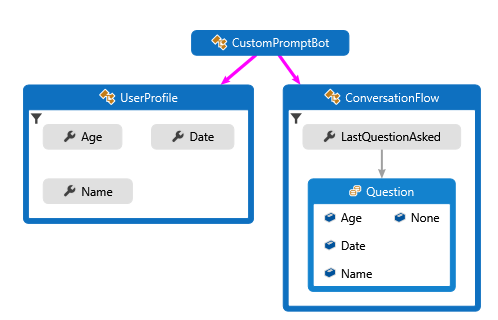
- 一个
UserProfile类,用于跟踪机器人要收集的用户信息。 - 一个
ConversationFlow类,用于在收集用户信息时控制聊天状态。 - 一个内部
ConversationFlow.Question枚举,用于跟踪你在聊天中所处的位置。
用户状态会跟踪用户的姓名、年龄和所选日期,而对话状态则会跟踪你上次提问用户的内容。 由于你不打算部署此机器人,因此需将用户和对话状态配置为使用“内存存储”。
你将使用机器人的消息轮次处理程序以及用户和聊天状态属性来管理聊天流与输入的收集。 在机器人中,需记录消息轮次处理程序的每次迭代期间收到的状态属性信息。
创建聊天和用户对象
在启动时创建用户和聊天状态对象,并通过在机器人构造函数中进行依赖项注入来使用它们。
Startup.cs
// Create the Bot Adapter with error handling enabled.
services.AddSingleton<IBotFrameworkHttpAdapter, AdapterWithErrorHandler>();
// Create the storage we'll be using for User and Conversation state. (Memory is great for testing purposes.)
services.AddSingleton<IStorage, MemoryStorage>();
// Create the User state.
services.AddSingleton<UserState>();
// Create the Conversation state.
services.AddSingleton<ConversationState>();
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
private readonly BotState _userState;
private readonly BotState _conversationState;
public CustomPromptBot(ConversationState conversationState, UserState userState)
{
_conversationState = conversationState;
_userState = userState;
}
创建属性访问器
为用户配置文件和聊天流属性创建属性访问器,然后通过调用 GetAsync 从状态检索属性值。
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
protected override async Task OnMessageActivityAsync(ITurnContext<IMessageActivity> turnContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var conversationStateAccessors = _conversationState.CreateProperty<ConversationFlow>(nameof(ConversationFlow));
var flow = await conversationStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new ConversationFlow(), cancellationToken);
var userStateAccessors = _userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>(nameof(UserProfile));
var profile = await userStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new UserProfile(), cancellationToken);
在此轮聊天结束之前,调用 SaveChangesAsync 将任何状态更改写入存储。
await _conversationState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
await _userState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
}
消息轮次处理程序
处理消息活动时,消息处理程序使用帮助程序方法来管理聊天并提示用户。 以下部分介绍了帮助程序方法。
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
protected override async Task OnMessageActivityAsync(ITurnContext<IMessageActivity> turnContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var conversationStateAccessors = _conversationState.CreateProperty<ConversationFlow>(nameof(ConversationFlow));
var flow = await conversationStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new ConversationFlow(), cancellationToken);
var userStateAccessors = _userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>(nameof(UserProfile));
var profile = await userStateAccessors.GetAsync(turnContext, () => new UserProfile(), cancellationToken);
await FillOutUserProfileAsync(flow, profile, turnContext, cancellationToken);
// Save changes.
await _conversationState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
await _userState.SaveChangesAsync(turnContext, false, cancellationToken);
}
填写用户个人资料
机器人会根据自己在上一轮提问的问题(如果有)来提示用户输入信息。 使用验证方法对输入进行分析。
每个验证方法都遵循类似的设计:
- 返回值将指示输入是否为此问题的有效回答。
- 如果通过了验证,则生成可保存的已分析规范化值。
- 如果未通过验证,则生成一条消息,机器人可凭此再次请求提供信息。
以下部分介绍验证方法。
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
{
var input = turnContext.Activity.Text?.Trim();
string message;
switch (flow.LastQuestionAsked)
{
case ConversationFlow.Question.None:
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync("Let's get started. What is your name?", null, null, cancellationToken);
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.Name;
break;
case ConversationFlow.Question.Name:
if (ValidateName(input, out var name, out message))
{
profile.Name = name;
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Hi {profile.Name}.", null, null, cancellationToken);
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync("How old are you?", null, null, cancellationToken);
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.Age;
break;
}
else
{
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync(message ?? "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.", null, null, cancellationToken);
break;
}
case ConversationFlow.Question.Age:
if (ValidateAge(input, out var age, out message))
{
profile.Age = age;
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"I have your age as {profile.Age}.", null, null, cancellationToken);
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync("When is your flight?", null, null, cancellationToken);
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.Date;
break;
}
else
{
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync(message ?? "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.", null, null, cancellationToken);
break;
}
case ConversationFlow.Question.Date:
if (ValidateDate(input, out var date, out message))
{
profile.Date = date;
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Your cab ride to the airport is scheduled for {profile.Date}.");
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Thanks for completing the booking {profile.Name}.");
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync($"Type anything to run the bot again.");
flow.LastQuestionAsked = ConversationFlow.Question.None;
profile = new UserProfile();
break;
}
else
{
await turnContext.SendActivityAsync(message ?? "I'm sorry, I didn't understand that.", null, null, cancellationToken);
break;
}
}
}
分析和验证输入
机器人使用以下条件来验证输入。
- 姓名必须为非空字符串。 通过剪裁空格来规范化它。
- 年龄必须介于 18 与 120 之间。 通过返回整数来规范化它。
- 日期必须是将来至少一小时后的任何日期或时间。 通过只返回已分析输入的日期部分来规范化它。
注意
对于年龄和日期输入,示例使用 Microsoft/Recognizers-Text 库来执行初始分析。 这只是分析输入的方法之一。 有关这些库的详细信息,请参阅项目的 README。
Bots/CustomPromptBot.cs
private static bool ValidateName(string input, out string name, out string message)
{
name = null;
message = null;
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input))
{
message = "Please enter a name that contains at least one character.";
}
else
{
name = input.Trim();
}
return message is null;
}
private static bool ValidateAge(string input, out int age, out string message)
{
age = 0;
message = null;
// Try to recognize the input as a number. This works for responses such as "twelve" as well as "12".
try
{
// Attempt to convert the Recognizer result to an integer. This works for "a dozen", "twelve", "12", and so on.
// The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
var results = NumberRecognizer.RecognizeNumber(input, Culture.English);
foreach (var result in results)
{
// The result resolution is a dictionary, where the "value" entry contains the processed string.
if (result.Resolution.TryGetValue("value", out var value))
{
age = Convert.ToInt32(value);
if (age >= 18 && age <= 120)
{
return true;
}
}
}
message = "Please enter an age between 18 and 120.";
}
catch
{
message = "I'm sorry, I could not interpret that as an age. Please enter an age between 18 and 120.";
}
return message is null;
}
private static bool ValidateDate(string input, out string date, out string message)
{
date = null;
message = null;
// Try to recognize the input as a date-time. This works for responses such as "11/14/2018", "9pm", "tomorrow", "Sunday at 5pm", and so on.
// The recognizer returns a list of potential recognition results, if any.
try
{
var results = DateTimeRecognizer.RecognizeDateTime(input, Culture.English);
// Check whether any of the recognized date-times are appropriate,
// and if so, return the first appropriate date-time. We're checking for a value at least an hour in the future.
var earliest = DateTime.Now.AddHours(1.0);
foreach (var result in results)
{
// The result resolution is a dictionary, where the "values" entry contains the processed input.
var resolutions = result.Resolution["values"] as List<Dictionary<string, string>>;
foreach (var resolution in resolutions)
{
// The processed input contains a "value" entry if it is a date-time value, or "start" and
// "end" entries if it is a date-time range.
if (resolution.TryGetValue("value", out var dateString)
|| resolution.TryGetValue("start", out dateString))
{
if (DateTime.TryParse(dateString, out var candidate)
&& earliest < candidate)
{
date = candidate.ToShortDateString();
return true;
}
}
}
}
message = "I'm sorry, please enter a date at least an hour out.";
}
catch
{
message = "I'm sorry, I could not interpret that as an appropriate date. Please enter a date at least an hour out.";
}
return false;
}
在本地测试机器人
下载并安装用于在本地测试机器人的 Bot Framework Emulator。
其他资源
对话库提供的某些类可以从多个方面将聊天管理自动化。