适用于: SDK v4
分析机器人行为
以下查询集合可用于分析机器人行为。 可以使用该集合在 Azure Monitor Log Analytics 中创作自定义查询,并创建监视和 Power BI 可视化仪表板。
先决条件
对以下内容有基本的了解很有帮助:
- Kusto 查询
- 如何使用 Azure 门户中的 Log Analytics 编写 Azure Monitor 日志查询
- Azure Monitor 中的日志查询的基本概念
提示
如果使用 Copilot Studio 或 Composer 等工具创建机器人,将需要在可用时使用每个查询的自适应对话版本。
仪表板
Azure 仪表板提供了一种很好的方法来查看和共享查询生成的信息。 可将查询与添加到仪表板的磁贴关联起来,从而构建自定义仪表板,以帮助监视机器人活动。 有关仪表板以及如何将查询与仪表板进行关联的详细信息,请参阅创建和共享 Log Analytics 数据的仪表板。 本文的其余部分显示了一些查询示例,这些查询可能对监视机器人行为很有用。
Kusto 查询示例
注意
建议本文中的所有查询都以不同的维度(如时间段、通道和区域设置)为中心。
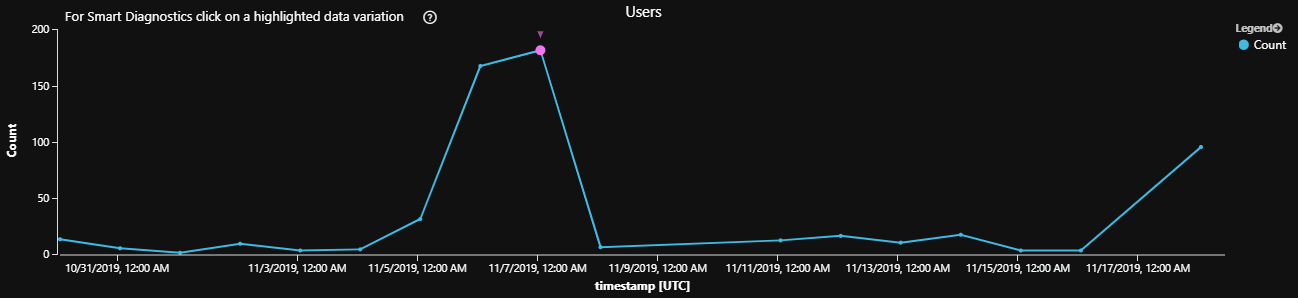
每个时间段的用户数量
此示例将生成一个折线图,该图显示过去 14 天内每日与机器人通信的不同用户的数量。 通过为 queryStartDate、queryEndDate 和 interval 变量分配不同的值,可以轻松地更改时间段。
重要
只有经过身份验证的用户才能在此查询中获得唯一用户的正确计数,结果也可能取决于通道功能。
// number of users per period
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let groupByInterval = 1d;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| summarize uc=dcount(user_Id) by bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| render timechart
提示
Kusto summarize 运算符用于生成聚合输入表内容的表。
Bin 函数是 Kusto 标量函数,当与 summarize operator 结合使用时,会将查询结果分组为指定值。 在上面的示例中,分组方式是按天,Kusto 也可按 h=hours、m=minutes、s=seconds、ms=milliseconds、microsecond=microseconds 分组。
使用 render 运算符能够轻松呈现图表,例如折线图 timechart,其中 x 轴是日期时间,y 轴可以使用任何其他数字列。 即使没有每次都指定数据,它也会自动使 x 轴保持良好的间距。 如果未使用任何 render 语句,则默认为 table。
每周期用户数查询结果示例
每个时间段的活动
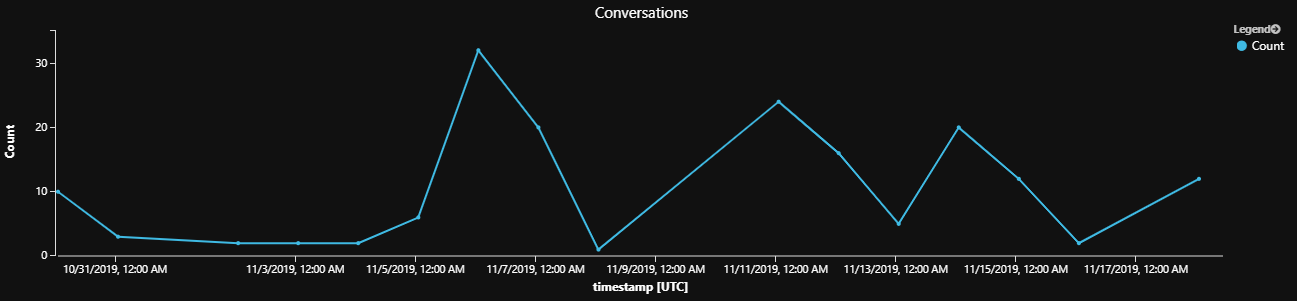
此示例说明了如何测量每个所需维度的活动量,例如过去 14 天内每天的对话、对话或消息数的计数。 通过为 querystartdate、queryEndDate 和 interval 变量分配不同的值,可以轻松地更改时间段。 所需的维度由以下示例中的 extend 子句定义,metric 可设置为 InstanceId、DialogId 或 ActivityId。
将指标分配给要显示的维度:
// Measures the number of activity's (conversations, dialogs, messages) per period.
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let groupByInterval = 1d;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend ActivityId = tostring(customDimensions['activityId'])
| where DialogId != '' and InstanceId != '' and user_Id != ''
| extend metric = InstanceId // DialogId or ActivityId
| summarize Count=dcount(metric) by bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| order by Count desc nulls last
| render timechart
提示
Kusto extend 运算符用于创建计算列并将其追加到结果集中。
每周期活动数查询结果示例
每个用户每个时间段的活动
此示例演示如何对每个用户每个时间段的活动数进行计数。 此查询深入到每个时间段的活动查询,以重点关注每个时间段每个用户的活动。 活动包括对话、聊天或消息。 此查询衡量用户与机器人的交互,这可以帮助发现潜在问题,例如:
- 单个用户进行大量活动的天数可能意味着攻击或测试
- 很少互动的日期可能指示服务运行状况问题
提示
可以按 user_Id 删除以获取常规的机器人活动量,该活动量可以根据时间和对话、消息或聊天进行透视。
// number of users per period per dialogs
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let interval = 6h;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend ActivityId = tostring(customDimensions['activityId'])
| where DialogId != '' and InstanceId != '' and user_Id != ''
| extend metric = ActivityId // InstanceId // DialogId // or InstanceId for conversation count
| summarize Count=dcount(metric) by user_Id, bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| order by Count desc nulls last
每周期每用户活动数查询结果示例
| user_Id | timestamp | 计数 |
|---|---|---|
| User-8107ffd2 | 2019-09-03T00:00:00Z | 14 |
| User-75f2cc8f | 2019-08-30T00:00:00Z | 13 |
| User-75f2cc8d | 2019-09-03T00:00:00Z | 13 |
| User-3060aada | 2019-09-03T00:00:00Z | 10 |
对话完成
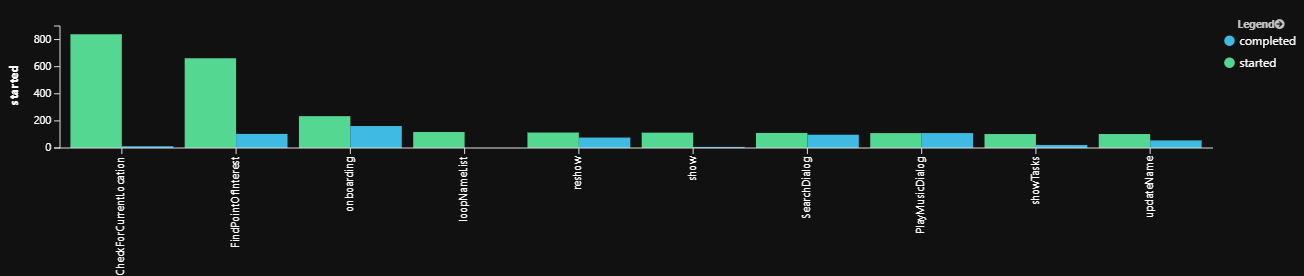
为对话设置遥测客户端后,对话(及其子对话)将发出一些默认遥测数据,例如“已启动”和“已完成”。 该示例可用于度量相对于已启动对话的已完成对话。 如果启动的对话数大于完成的对话数,则表示某些用户未完成对话流。 可以使用此查询来帮助识别和排查任何潜在的对话逻辑问题。 还可以用于识别哪些对话使用频率最高和最低。
提示
如果使用 Copilot Studio 或 Composer 等工具创建机器人,将需要使用每个查询的自适应对话版本。
完成瀑布对话
// % Completed Waterfall Dialog: shows completes relative to starts
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name=="WaterfallStart"
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| join kind=leftouter (
customEvents
| where name=="WaterfallComplete"
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
) on InstanceId
| summarize started=countif(name=='WaterfallStart'), completed=countif(name1=='WaterfallComplete') by tostring(DialogId)
| where started > 100 // filter for sample
// Show starts vs. completes
| project tostring(DialogId), started, completed
| order by started desc, completed asc nulls last
| render barchart with (kind=unstacked, xcolumn=DialogId, ycolumns=completed, started, ysplit=axes)
提示
Kusto 联接运算符用于合并两个表的行,通过匹配每个表中指定列的值组成新表。
项目运算符用于选择要在输出中显示的字段。 类似于添加新字段的 extend operator,project operator 可以从现有的一组字段中进行选择,也可以添加新字段。
自适应对话已启动并完成
// % Completed adaptive dialog: shows completes relative to starts. This type is the default dialog type when using Copilot Studio or Composer.
customEvents
| where name=="AdaptiveDialogStart" or name == "AdaptiveDialogComplete"
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| summarize started=countif(name=='AdaptiveDialogStart'), completed=countif(name=='AdaptiveDialogComplete') by DialogId
| project DialogId, started, completed
| order by started desc, completed asc nulls last
| render barchart with (kind=unstacked, xcolumn=DialogId, ycolumns=completed, started, ysplit=axes)
完成对话查询结果示例
对话未完成
此示例可用于计算在指定的时间段内由于取消或终止而启动但从未完成的对话流的数量。 可以使用它来查看未完成的对话,并检查它们是由于用户混淆而被主动取消,还是由于用户分心或失去兴趣而被放弃。
瀑布对话未完成
// Show incomplete dialogs when using waterfall dialogs.
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name == "WaterfallStart"
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| join kind=leftanti (
customEvents
| where name == "WaterfallComplete"
| extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
) on instanceId
| summarize cnt=count() by tostring(DialogId)
| order by cnt
| render barchart
自适应对话未完成
// Show incomplete dialogs for adaptive dialogs; this type is the default dialog type when using Copilot Studio or Composer.
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where name == "AdaptiveDialogStart"
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| join kind=rightanti (
customEvents
| where name == "AdaptiveDialogComplete"
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
) on name, DialogId
| summarize cnt=count() by DialogId
| order by cnt
| render barchart
提示
Kusto 排序运算符(与 sort operator 相同)用于按一个或多个列对输入表的行进行排序。 注意:如果要从任何查询的结果中排除 null 值,可以在 where 语句中将其筛选掉,例如,可以添加“and isnotnull(Timestamp)”;或者要在开头或结尾返回 null 值,请将 nulls first 或 nulls first 添加到 order 语句的末尾。
未完成对话查询结果示例

对话序列深度探索
聊天中瀑布式对话的开始/步骤/完成
此示例显示了按对话 (instanceId) 分组的对话步骤序列,这对于确定哪些步骤会导致对话中断非常有用。
若要运行此查询,请输入所需 DialogId 的值,代替 <SampleDialogId>
// Drill down: Show waterfall start/step/complete for specific dialog
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let DialogActivity=(dlgid:string) {
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend StepName = customDimensions['StepName']
| extend InstanceId = customDimensions['InstanceId']
| where DialogId == dlgid
| project timestamp, name, StepName, InstanceId
| order by tostring(InstanceId), timestamp asc
};
// For example see SampleDialogId behavior
DialogActivity("<SampleDialogId>")
提示
此查询是使用查询定义函数编写的,该函数是用户定义的函数,在单个查询的范围内定义和使用,由 let 语句定义。 此查询是在不使用 query-defined function 的情况下编写的:
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend StepName = customDimensions['StepName']
| extend InstanceId = customDimensions['InstanceId']
| where DialogId == "<SampleDialogId>"
| project timestamp, name, StepName, InstanceId
| order by tostring(InstanceId), timestamp asc
示例查询结果
| timestamp | name | StepName | InstanceId |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-08-23T20:04… | WaterfallStart | null | …79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:04… | WaterfallStep | GetPointOfInterestLocations | …79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:04… | WaterfallStep | ProcessPointOfInterestSelection | …79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:04… | WaterfallStep | GetRoutesToDestination | …79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:05… | WaterfallStep | ResponseToStartRoutePrompt | …79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-23T20:05… | WaterfallComplete 1 | Null | …79c0f03d8701 |
| 2019-08-28T23:35… | WaterfallStart | Null | …6ac8b3211b99 |
| 2019-08-28T23:35… | WaterfallStep 2 | GetPointOfInterestLocations | …6ac8b3211b99 |
| 2019-08-28T19:41… | WaterfallStart | Null | …8137d76a5cbb |
| 2019-08-28T19:41… | WaterfallStep 2 | GetPointOfInterestLocations | …8137d76a5cbb |
| 2019-08-28T19:41… | WaterfallStart | Null | …8137d76a5cbb |
1 已完成
2 已终止
解释:用户似乎在 GetPointOfInterestLocations 步骤终止了聊天。
注意
瀑布式对话的执行序列(开始、多个步骤、完成)。 如果序列显示开始但未完成,则表示该对话由于用户终止或取消对话而被中断。 在此详细分析中,可以看到此行为(请参阅已完成步骤与已放弃的步骤)。
瀑布式对话的开始/步骤/完成/取消步骤的汇总数据
此示例显示了以下内容的汇总数据:开始对话序列的总次数、瀑布式步骤的组合总数、已成功完成的次数、已取消的次数,以及 WaterfallStart 和 WaterfallComplete 加上 WaterfallCancel 的组合总数之间的差值,通过这些信息可了解终止的总次数。
// Drill down: Aggregate view of waterfall start/step/complete/cancel steps totals for specific dialog
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let DialogSteps=(dlgid:string) {
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| where DialogId == dlgid
| project name
| summarize count() by name
};
// For example see SampleDialogId behavior
DialogSteps("<SampleDialogId>")
瀑布聚合查询结果示例
| name | count |
|---|---|
| WaterfallStart | 21 |
| WaterfallStep | 47 |
| WaterfallComplete | 11 |
| WaterfallCancel | 1 |
解释:在对话序列的 21 次调用中,只有 11 次完成,9 次被放弃,1 次被用户取消。
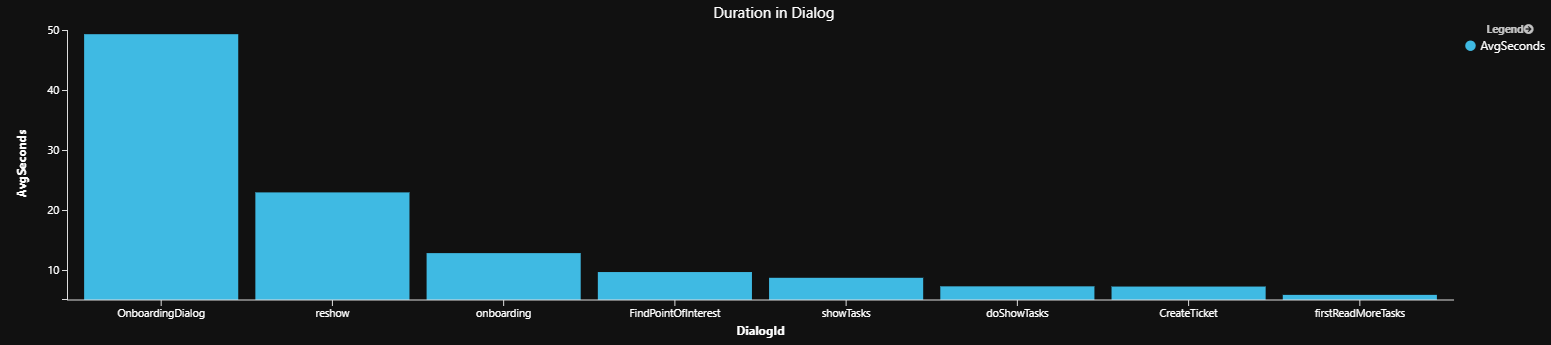
对话的平均持续时间
此示例测量用户在给定对话中花费的平均时间。 机器人可能会从简化用户需要很长时间才能完成的对话中受益。
// Average dialog duration
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name=="WaterfallStart"
| extend DialogId = customDimensions['DialogId']
| extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| join kind=leftouter (customEvents | where name=="WaterfallCancel" | extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])) on instanceId
| join kind=leftouter (customEvents | where name=="WaterfallComplete" | extend instanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])) on instanceId
| extend duration = case(not(isnull(timestamp1)), timestamp1 - timestamp,
not(isnull(timestamp2)), timestamp2 - timestamp, 0s) // Abandoned aren't counted. Alternate: now()-timestamp
| extend seconds = round(duration / 1s)
| summarize AvgSeconds=avg(seconds) by tostring(DialogId)
| order by AvgSeconds desc nulls last
| render barchart with (title="Duration in Dialog")
平均持续时间查询结果示例
对话的平均步骤
此示例显示了每个被调用的对话的“长度”,由平均值、最小值、最大值和标准偏差计算得出。 此内容有助于分析对话质量。 例如:
- 应评估步骤过多的对话是否有简化的机会。
- 如果对话的最小值/最大值/平均值之间存在很大差异,则可能意味着用户在试图完成任务时陷入了停顿。 你可能需要评估用较短路径完成任务的可能性,或者减少对话复杂性的方法。
- 具有大型标准偏差的对话表示路径复杂或经验不足(终止/取消)。
- 很少步骤的对话可能是这样的,因为它们从未完成。 分析完成/终止率可能有助于进行确定。
// min/max/std/avg steps per dialog
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend StepName = tostring(customDimensions['StepName'])
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| where name == "WaterfallStart" or name == "WaterfallStep" or name == "WaterfallComplete"
| order by InstanceId, timestamp asc
| project timestamp, DialogId, name, InstanceId, StepName
| summarize cnt=count() by InstanceId, DialogId
| summarize avg=avg(cnt), minsteps=min(cnt),maxsteps=max(cnt), std=stdev(cnt) by DialogId
| extend avgsteps = round(avg, 1)
| extend avgshortbysteps=maxsteps-avgsteps
| extend avgshortbypercent=round((1.0 - avgsteps/maxsteps)*100.0, 1)
| project DialogId, avgsteps, minsteps, maxsteps, std, avgshortbysteps, avgshortbypercent
| order by std desc nulls last
平均步骤数查询结果示例
| 对话框 ID | 平均步骤数 | 最少步骤数 | 最多步骤数 | std | 平均简化步骤数 | 平均简化百分比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FindArticlesDialog | 6.2 | 2 | 7 | 2.04 | 0.8 | 11.4% |
| CreateTicket | 4.3 | 2 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 14% |
| CheckForCurrentLocation | 3.9 | 2 | 5 | 1.41 | 1.1 | 22% |
| BaseAuth | 3.3 | 2 | 4 | 1.03 | 0.7 | 17.5% |
| 加入 | 2.7 | 2 | 4 | 0.94 | 1.3 | 32.5% |
__解释:例如,FindArticlesDialog 在最小/最大值之间有很大的差异,应进行调查,并可能需要重新设计和优化。
按活动指标划分的通道活动
此示例测量了在给定时间段内机器人接收每个通道的活动量。 它通过对以下任一指标进行计数来实现此操作:传入消息、用户、聊天或对话。 这对于服务运行状况分析或衡量通道受欢迎程度非常有用。
// number of metric: messages, users, conversations, dialogs by channel
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
let groupByInterval = 1d;
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| extend InstanceId = tostring(customDimensions['InstanceId'])
| extend DialogId = tostring(customDimensions['DialogId'])
| extend ActivityId = tostring(customDimensions['activityId'])
| extend ChannelId = tostring(customDimensions['channelId'])
| where DialogId != '' and InstanceId != '' and user_Id != ''
| extend metric = user_Id // InstanceId or ActivityId or user_Id
| summarize Count=count(metric) by ChannelId, bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)
| order by Count desc nulls last
| render barchart with (title="Users", kind=stacked) // or Incoming Messages or Conversations or Users
提示
建议考虑尝试以下变体:
- 在没有时间戳 Bucket 存储的情况下运行查询:
bin(timestamp, groupByInterval)。 - 还可以将
dcount用于不同的用户,将count用于所有用户事件活动。 这也适用于重复用户。
通过通道逐个活动进行查询的结果示例
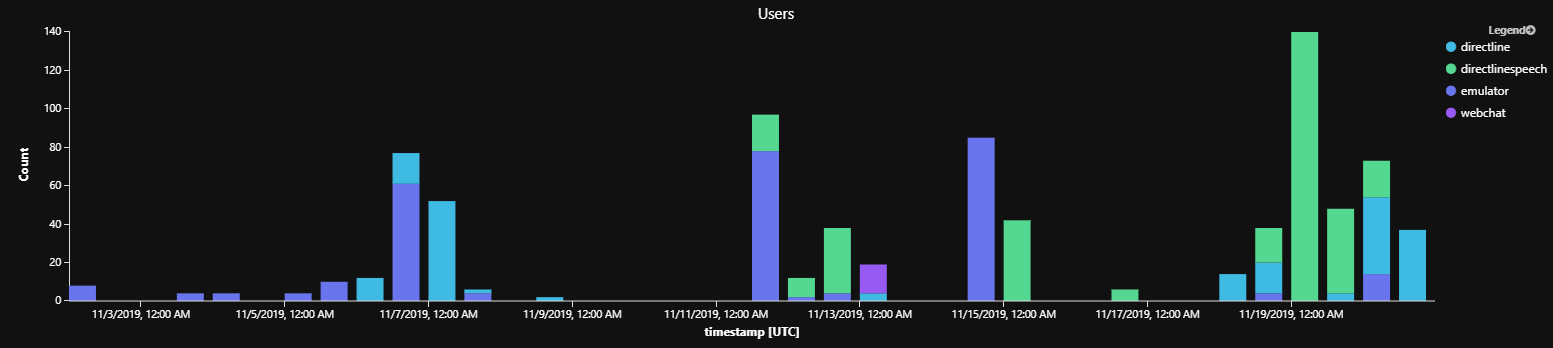
解释:仿真器测试曾经是最受欢迎的通道,但我们将 DirectLineSpeech 投入使用后,后者就成为了最受欢迎的通道。
按受欢迎程度分类的总意向数
此示例适用于启用 LUIS 的机器人。 它按流行程度对所有意向进行了总结,并给出了相应的意向检测确定性分数。
注意
语言理解 (LUIS) 将于 2025 年 10 月 1 日停用。 从 2023 年 4 月 1 日开始,将无法创建新的 LUIS 资源。 语言理解的较新版本现已作为 Azure AI 语言的一部分提供。
对话语言理解(CLU)是 Azure AI 语言的一项功能,是 LUIS 的更新版本。 有关 Bot Framework SDK 中的语言理解支持的更多信息,请参阅 自然语言理解。
- 在实践中,应为每个指标分隔视图。
- 常见意向路径应针对用户体验进行优化。
- 较低的平均分数表示识别能力差,可能缺少实际用户意向。
// show total intents
let queryStartDate = ago(14d);
let queryEndDate = now();
customEvents
| where timestamp > queryStartDate
| where timestamp < queryEndDate
| where name startswith "LuisResult"
| extend intentName = tostring(customDimensions['intent'])
| extend intentScore = todouble(customDimensions['intentScore'])
| summarize ic=count(), ac=avg(intentScore)*100 by intentName
| project intentName, ic, ac
| order by ic desc nulls last
| render barchart with (kind=unstacked, xcolumn=intentName, ycolumns=ic,ac, title="Intents Popularity")
按受欢迎程度进行分类的意向数的查询结果示例
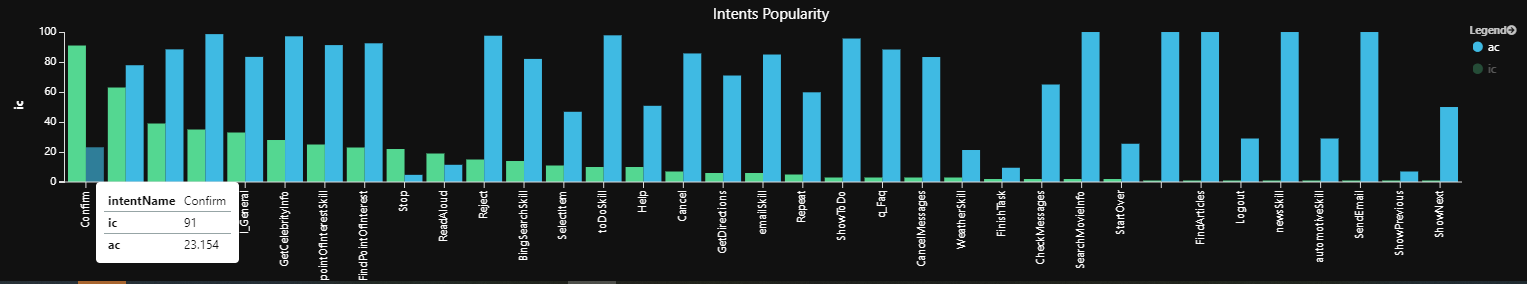
解释:例如,在最常见的意向中,检测到确认平均只有 23% 的置信度。
提示
条形图是 Kusto 查询提供的数十个选项中的一个。 其他一些选项包括:异常图、分区图、柱状图、折线图和散点图。 有关详细信息,请参阅 render 运算符主题。
机器人分析检测的架构
下表显示了机器人将向其记录遥测数据的最常见字段。
常规包络线
Application Insights 检测中的常见日志分析字段。
| 字段 | 描述 | 示例值 |
|---|---|---|
| name | 消息类型 | BotMessageSend、BotMessageReceived、LuisResult、WaterfallStep、WaterfallStart、SkillWebSocketProcessRequestLatency、SkillWebSocketOpenCloseLatency、WaterfallComplete、QnaMessage、WaterfallCancel、SkillWebSocketTurnLatency、AuthPromptValidatorAsyncFailure |
| customDimensions | SDK 机器人分析 | activityId=<id>、activityType=message、channelId=emulator、fromId=<id>、fromName=User、locale=zh-cn、recipientId=<id>、recipientName=Bot、text=查找咖啡店 |
| timestamp | 事件时间 | 2019-09-05T18:32:45.287082Z |
| instance_Id | 对话 ID | f7b2c416-a680-4b2c-b4cc-79c0f03d8711 |
| operation_Id | 轮次 ID | 084b2856947e3844a5a18a8476d99aaa |
| user_Id | 唯一通道用户 ID | emulator7c259c8e-2f47… |
| client_IP | 客户端 IP 地址 | 127.0.0.1(由于隐私限制可能不存在) |
| client_City | 客户城市 | Redmond(如果检测到,可能不存在) |
注意
Azure QnA Maker 将于 2025 年 3 月 31 日停用。 从 2022 年 10 月 1 日开始,你将无法创建新的 QnA Maker 资源或知识库。 问答功能的较新版本现已作为 Azure AI 语言的一部分提供。
自定义问答是 Azure 语言认知服务的一项功能,是 QnA Maker 服务的更新版本。 有关 Bot Framework SDK 中的问答支持的详细信息,请参阅自然语言理解。
注意
语言理解 (LUIS) 将于 2025 年 10 月 1 日停用。 从 2023 年 4 月 1 日开始,将无法创建新的 LUIS 资源。 语言理解的较新版本现已作为 Azure AI 语言的一部分提供。
对话语言理解(CLU)是 Azure AI 语言的一项功能,是 LUIS 的更新版本。 有关 Bot Framework SDK 中的语言理解支持的更多信息,请参阅 自然语言理解。
自定义维度
大多数机器人特定活动数据都存储在“customDimensions”字段中。
| 字段 | 描述 | 示例值 |
|---|---|---|
| activityId | 消息 ID | <id>:8da6d750-d00b-11e9-80e0-c14234b3bc2a |
| activityType | 消息类型 | 消息、聊天更新、事件、调用 |
| channelId | 渠道标识符 | 模拟器、directline、msteams、webchat |
| fromId | 起始标识符 | <id> |
| fromName | 来自客户端的用户名 | John Bonham、Keith Moon、Steve Smith、Steve Gadd |
| 区域设置 | 客户端源区域设置 | en-us、zh-cn、en-GB、de-de、zh-CN |
| recipientId | 收件人标识符 | <id> |
| recipientName | 收件人姓名 | John Bonham、Keith Moon、Steve Smith、Steve Gadd |
| text | 消息中的文本 | 寻找咖啡店 |
自定义维度:LUIS
注意
语言理解 (LUIS) 将于 2025 年 10 月 1 日停用。 从 2023 年 4 月 1 日开始,将无法创建新的 LUIS 资源。 语言理解的较新版本现已作为 Azure AI 语言的一部分提供。
对话语言理解(CLU)是 Azure AI 语言的一项功能,是 LUIS 的更新版本。 有关 Bot Framework SDK 中的语言理解支持的更多信息,请参阅 自然语言理解。
LUIS 检测用于将其数据存储在以下自定义维度字段中。
| 字段 | 描述 | 示例值 |
|---|---|---|
| 意向 | LUIS 检测到的意向 | pointOfInterestSkill |
| intentScore | LUIS 识别分数 | 0.98 |
| 实体 | LUIS 检测到的实体 | FoodOfGrocery = [["coffee"]], KEYWORD= ["coffee shop"] |
| 问题 | LUIS 检测到的问题 | 寻找咖啡店 |
| sentimentLabel | LUIS 检测到的情绪 | 积极 |
自定义维度:QnAMaker
注意
Azure QnA Maker 将于 2025 年 3 月 31 日停用。 从 2022 年 10 月 1 日开始,你将无法创建新的 QnA Maker 资源或知识库。 问答功能的较新版本现已作为 Azure AI 语言的一部分提供。
自定义问答是 Azure 语言认知服务的一项功能,是 QnA Maker 服务的更新版本。 有关 Bot Framework SDK 中的问答支持的详细信息,请参阅 自然语言理解。
QnAMaker 检测用于将其数据存储在以下自定义维度字段中。
提示
若要启用个人信息(如问题和答案)的日志记录,应在 QnA Maker 类的构造函数中将 log personal information 参数设置为 true。
| 字段 | 描述 | 示例值 |
|---|---|---|
| 问题 | QnA 检测到的问题 | 你可以做什么? |
| answer | QnA 解答 | 你提出问题,我来解答。 |
| articleFound | QnA | true |
| questionId | QnA 问题 ID | 488 |
| knowledgeBaseId | QnA KB ID | 2a4936f3-b2c8-44ff-b21f-67bc413b9727 |
| matchedQuestion | 匹配问题数组 | [“你可以向我说明你的角色是什么吗?”、“你能介绍一下你自己吗”、“你能告诉我你的情况吗?”、“你能帮助我吗”、“那么你能做什么?”、“你如何帮助我”、“你如何帮助我?”、“你能帮什么忙?”、“我如何才能在我的项目中使用?”、“告诉我你的功能?”、“你能做什么?”…] |
另请参阅
- 有关编写日志查询的教程,请参阅 Azure Monitor 中的日志查询入门
- 直观显示 Azure Monitor 中的数据
- 了解如何将遥测功能添加到机器人
- 了解 Azure Monitor 日志查询的详细信息
- Bot Framework Application Insights 事件的完整列表
- 创建和共享 Log Analytics 数据的仪表板