在本快速入门中,你将使用 Python 部署基本的 Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB 应用程序。 Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB 是一种无架构的数据存储,允许应用程序使用 MongoDB 库在云中存储非结构化文档。 你将了解如何使用 Python 在 Azure Cosmos DB 资源中创建文档并执行基本任务。
库源代码 | 包 (npm) | Azure Developer CLI
先决条件
- Azure Developer CLI
- Docker Desktop
- Node.js 22 或更高版本
如果你没有 Azure 帐户,请在开始之前创建一个试用帐户。
初始化项目
使用 Azure Developer CLI (azd) 创建 Azure Cosmos DB for Table 帐户并部署容器化示例应用程序。 示例应用程序使用客户端库来管理、创建、读取和查询示例数据。
在空目录中打开终端。
如果尚未经过身份验证,请使用
azd auth login向 Azure Developer CLI 进行身份验证。 按照该工具指定的步骤,使用首选 Azure 凭据向 CLI 进行身份验证。azd auth login使用
azd init来初始化项目。azd init --template cosmos-db-mongodb-nodejs-quickstart在初始化期间,配置唯一的环境名称。
使用
azd up部署 Azure Cosmos DB 帐户。 Bicep 模板还部署示例 Web 应用程序。azd up在预配过程中,选择订阅、所需位置和目标资源组。 等待预配过程完成。 此过程可能需要大约 5 分钟。
预配 Azure 资源后,输出中将包含指向正在运行的 Web 应用程序的 URL。
Deploying services (azd deploy) (✓) Done: Deploying service web - Endpoint: <https://[container-app-sub-domain].azurecontainerapps.io> SUCCESS: Your application was provisioned and deployed to Azure in 5 minutes 0 seconds.使用控制台中的 URL 在浏览器中导航到 Web 应用程序。 观察正在运行的应用的输出。
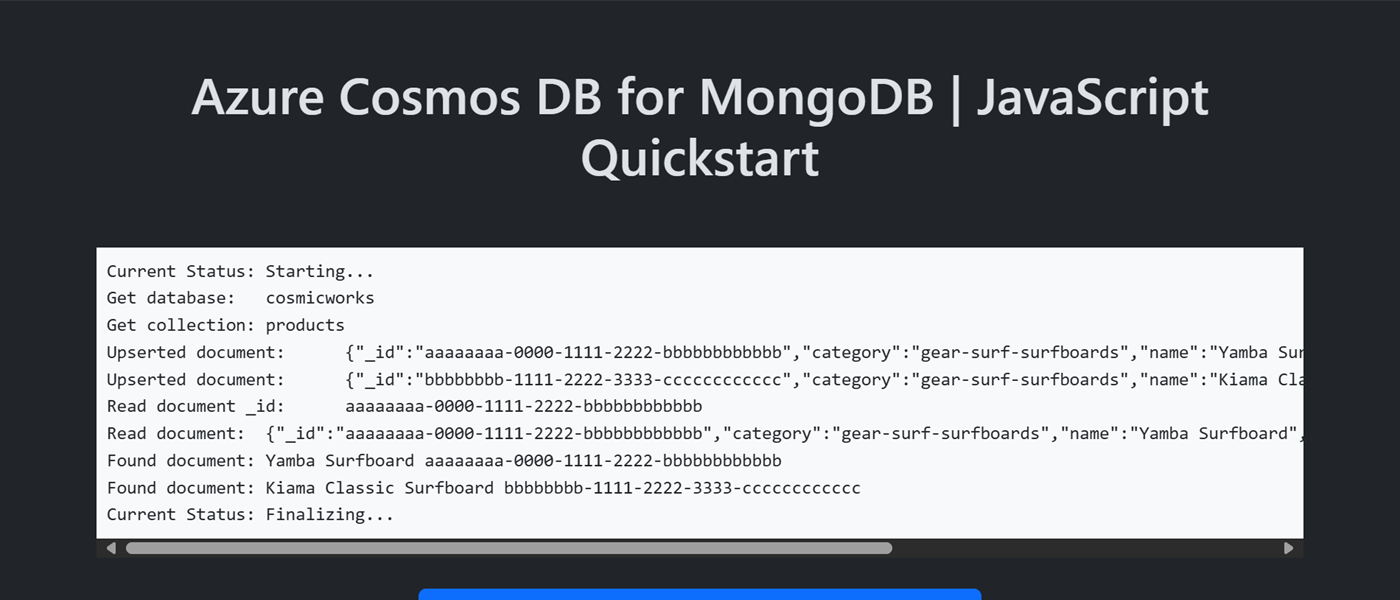
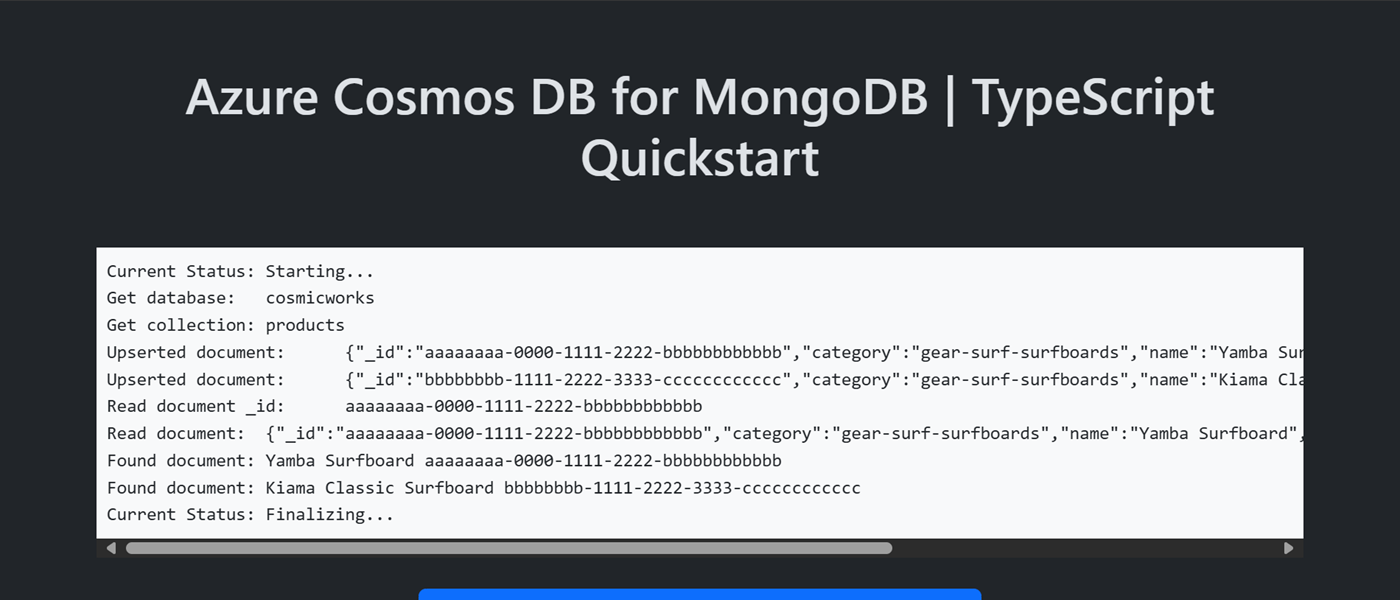
安装客户端库
客户端库可通过 npm 作为 mongodb 包使用。
打开终端并导航到
/src/ts文件夹。cd ./src/ts使用
mongodb安装npm install包(如果尚未安装)。npm install --save mongodb打开并查看 src/ts/package.json 文件以验证
mongodb条目是否存在。
打开终端并导航到
/src/js文件夹。cd ./src/js使用
mongodb安装npm install包(如果尚未安装)。npm install --save mongodb打开并查看 src/js/package.json 文件以验证
mongodb条目是否存在。
导入库文件
将 MongoClient 类型导入应用程序代码。
import { MongoClient } from 'mongodb';
将所有必需的类型导入应用程序代码。
import { Collection, Db, Filter, FindCursor, MongoClient, UpdateFilter, UpdateOptions, UpdateResult, WithId } from 'mongodb';
对象模型
| 名称 | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
MongoClient |
用于连接到 MongoDB 的类型。 |
Database |
表示帐户中的数据库。 |
Collection |
表示帐户中数据库内的集合。 |
代码示例
模板中的示例代码使用名为 cosmicworks 的数据库和名为 products 的集合。
products 集合包含每个产品的名称、类别、数量和唯一标识符等详细信息。 该集合使用 /category 属性作为分片键。
验证客户端
此示例创建 MongoClient 类型的新实例。
const connectionString = "<azure-cosmos-db-for-mongodb-connection-string>";
const client = new MongoClient(connectionString);
const connectionString = "<azure-cosmos-db-for-mongodb-connection-string>";
const client = new MongoClient(connectionString);
获取数据库
此示例使用 Db 类型的 db 函数创建 MongoClient 类型的实例。
const database: Db = client.db("<database-name>");
const database = client.db("<database-name>");
获取集合
此示例使用 Collection 类型的 collection 函数创建 Db 类型的实例。
此函数具有一个泛型参数,该参数使用接口中定义的 Product 类型。
const collection: Collection<Product> = database.collection<Product>("<collection-name>");
export interface Product {
_id: string;
category: string;
name: string;
quantity: number;
price: number;
clearance: boolean;
}
const collection = database.collection("<collection-name>");
创建文档
使用 collection.updateOne 在集合中创建文档。 如果该项已经存在,此方法会“更新插入”该项,从而有效地替换该项。
var document: Product = {
_id: 'aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb',
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards',
name: 'Yamba Surfboard',
quantity: 12,
price: 850.00,
clearance: false
};
var query: Filter<Product> = {
_id: 'aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb',
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards'
};
var payload: UpdateFilter<Product> = {
$set: document
};
var options: UpdateOptions = {
upsert: true
};
var response: UpdateResult<Product> = await collection.updateOne(query, payload, options);
var document = {
_id: 'aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb',
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards',
name: 'Yamba Surfboard',
quantity: 12,
price: 850.00,
clearance: false
};
const query = {
_id: 'aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb',
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards'
};
const payload = {
$set: document
};
const options = {
upsert: true,
new: true
};
var response = await collection.updateOne(query, payload, options);
阅读文档
同时使用唯一标识符 (id) 和分片键字段来执行点读取操作。 使用 collection.findOne 以有效检索特定项。
var query: Filter<Product> = {
_id: 'aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb',
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards'
};
var response: WithId<Product> | null = await collection.findOne(query);
var query = {
_id: 'aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb',
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards'
};
var response = await collection.findOne(query);
查询文档
使用 collection.find 对容器中的多个项执行查询。 此查询查找指定类别(分片键)中的所有项。
var query: Filter<Product> = {
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards'
};
var response: FindCursor<WithId<Product>> = await collection.find(query);
for await (const item of response) {
// Do something with each item
}
var query = {
category: 'gear-surf-surfboards'
};
var response = await collection.find(query);
for await (const item of response) {
// Do something with each item
}
探索您的数据
使用适用于 Azure Cosmos DB 的 Visual Studio Code 扩展来浏览 MongoDB 数据。 可以执行核心数据库操作,这些操作包括但不限于:
- 使用剪贴簿或查询编辑器执行查询
- 修改、更新、创建和删除文档
- 从其他源导入批量数据
- 管理数据库和集合
有关详细信息,请参阅如何使用 Visual Studio Code 扩展来浏览 Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB 数据。
清理资源
不再需要示例应用程序或资源时,请删除相应的部署和所有资源。
azd down --force --purge