适用于: 适用于 Python 的 Azure 机器学习 SDK v1
适用于 Python 的 Azure 机器学习 SDK v1
重要
本文提供有关使用 Azure 机器学习 SDK v1 的信息。 SDK v1 自 2025 年 3 月 31 日起弃用。 对它的支持将于 2026 年 6 月 30 日结束。 可以在该日期之前安装和使用 SDK v1。 使用 SDK v1 的现有工作流将在支持结束日期后继续运行。 但是,在产品发生体系结构更改时,可能会面临安全风险或中断性变更。
建议在 2026 年 6 月 30 日之前过渡到 SDK v2。 有关 SDK v2 的详细信息,请参阅 什么是 Azure 机器学习 CLI 和 Python SDK v2? 以及 SDK v2 参考。
本文介绍如何对 Azure 机器学习数据集进行版本控制并跟踪,以便重现。 数据集版本控制可以为数据的特定状态设置书签,方便为将来的试验应用数据集的特定版本。
你可能希望在以下典型场景中对 Azure 机器学习资源进行版本控制:
- 当新数据变得适用于重新训练时
- 应用不同的数据准备或特征工程方法时
先决条件
适用于 Python 的 Azure 机器学习 SDK。 此 SDK 包括 azureml-datasets 包
一个 Azure 机器学习工作区。 创建新工作区,或使用以下代码示例检索现有工作区:
import azureml.core from azureml.core import Workspace ws = Workspace.from_config()
注册和检索数据集版本
可以对注册的数据集进行版本控制、在不同的试验中重复使用它,以及与同事共享它。 可以使用相同的名称注册多个数据集,并按名称和版本号检索特定版本。
注册数据集版本
下面的代码示例将 create_new_version 数据集的参数 titanic_ds 设置为 True注册该数据集的新版本。 如果工作区没有注册现有的 titanic_ds 数据集,则代码会创建一个名为 titanic_ds 的新数据集,并将其版本设置为 1。
titanic_ds = titanic_ds.register(workspace = workspace,
name = 'titanic_ds',
description = 'titanic training data',
create_new_version = True)
按名称检索数据集
默认情况下,Dataset 类的 get_by_name() 方法返回注册到工作区的数据集的最新版本。
以下代码返回 titanic_ds 数据集的版本 1。
from azureml.core import Dataset
# Get a dataset by name and version number
titanic_ds = Dataset.get_by_name(workspace = workspace,
name = 'titanic_ds',
version = 1)
版本控制最佳做法
创建数据集版本时,请勿使用工作区创建额外的数据副本。 由于数据集是对存储服务中数据的引用,因此,你有单个由存储服务管理的事实来源。
重要
如果覆盖或删除数据集引用的数据,则对特定版本的数据集的调用不会还原更改。
从数据集加载数据时,始终会加载数据集引用的当前数据内容。 为了确保每个数据集版本的可重现性,建议避免修改数据集版本引用的数据内容。 当新数据进入时,将新数据文件保存到单独的数据文件夹中,然后创建新的数据集版本以包含该新文件夹中的数据。
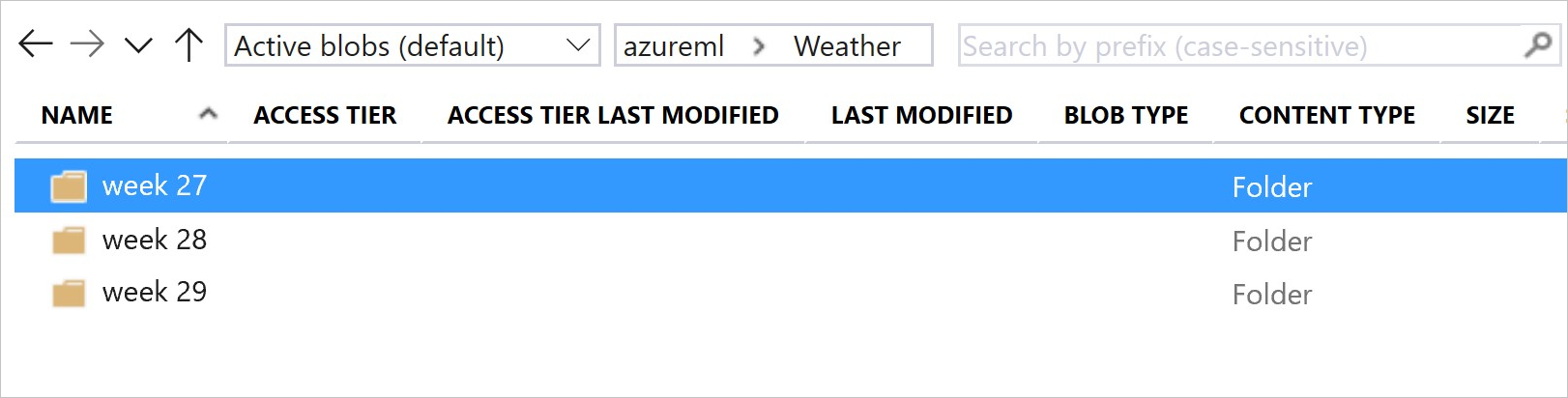
下图和示例代码展示了对数据文件夹进行构造的建议方式,以及创建引用那些文件夹的数据集版本的建议方式:
from azureml.core import Dataset
# get the default datastore of the workspace
datastore = workspace.get_default_datastore()
# create & register weather_ds version 1 pointing to all files in the folder of week 27
datastore_path1 = [(datastore, 'Weather/week 27')]
dataset1 = Dataset.File.from_files(path=datastore_path1)
dataset1.register(workspace = workspace,
name = 'weather_ds',
description = 'weather data in week 27',
create_new_version = True)
# create & register weather_ds version 2 pointing to all files in the folder of week 27 and 28
datastore_path2 = [(datastore, 'Weather/week 27'), (datastore, 'Weather/week 28')]
dataset2 = Dataset.File.from_files(path = datastore_path2)
dataset2.register(workspace = workspace,
name = 'weather_ds',
description = 'weather data in week 27, 28',
create_new_version = True)
对 ML 管道输出数据集进行版本控制
可以使用数据集作为每个 ML 管道步骤的输入和输出。 重新运行管道时,每个管道步骤的输出将注册为一个新的数据集版本。
机器学习管道每次重新运行时都会将每个步骤的输出填充到一个新文件夹中。 已进行版本控制的输出数据集然后就变得可重现。 有关详细信息,请访问管道中的数据集。
from azureml.core import Dataset
from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep
from azureml.pipeline.core import Pipeline, PipelineData
from azureml.core. runconfig import CondaDependencies, RunConfiguration
# get input dataset
input_ds = Dataset.get_by_name(workspace, 'weather_ds')
# register pipeline output as dataset
output_ds = PipelineData('prepared_weather_ds', datastore=datastore).as_dataset()
output_ds = output_ds.register(name='prepared_weather_ds', create_new_version=True)
conda = CondaDependencies.create(
pip_packages=['azureml-defaults', 'azureml-dataprep[fuse,pandas]'],
pin_sdk_version=False)
run_config = RunConfiguration()
run_config.environment.docker.enabled = True
run_config.environment.python.conda_dependencies = conda
# configure pipeline step to use dataset as the input and output
prep_step = PythonScriptStep(script_name="prepare.py",
inputs=[input_ds.as_named_input('weather_ds')],
outputs=[output_ds],
runconfig=run_config,
compute_target=compute_target,
source_directory=project_folder)
跟踪试验中的数据
Azure 机器学习在整个试验过程中跟踪数据作为输入和输出数据集。 在以下场景中,数据作为输入数据集进行跟踪:
提交试验作业时,通过
DatasetConsumptionConfig对象的inputs或arguments参数传递ScriptRunConfig对象当脚本调用某些方法(例如
get_by_name()或get_by_id())时。 将数据集注册到工作区时分配给该数据集的名称就是显示的名称
在以下场景中,数据作为输出数据集进行跟踪:
提交试验作业时,通过
OutputFileDatasetConfig或outputs参数传递arguments对象。OutputFileDatasetConfig对象也可在管道步骤之间保留数据。 有关详细信息,请访问在 ML 管道步骤之间移动数据在脚本中注册数据集。 您在将数据集注册到工作区时为其分配的名称即为显示名称。 在以下代码示例中,
training_ds是显示的名称:training_ds = unregistered_ds.register(workspace = workspace, name = 'training_ds', description = 'training data' )在脚本中使用未注册的数据集提交子作业。 该提交会生成一个匿名保存数据集
在试验作业中跟踪数据集
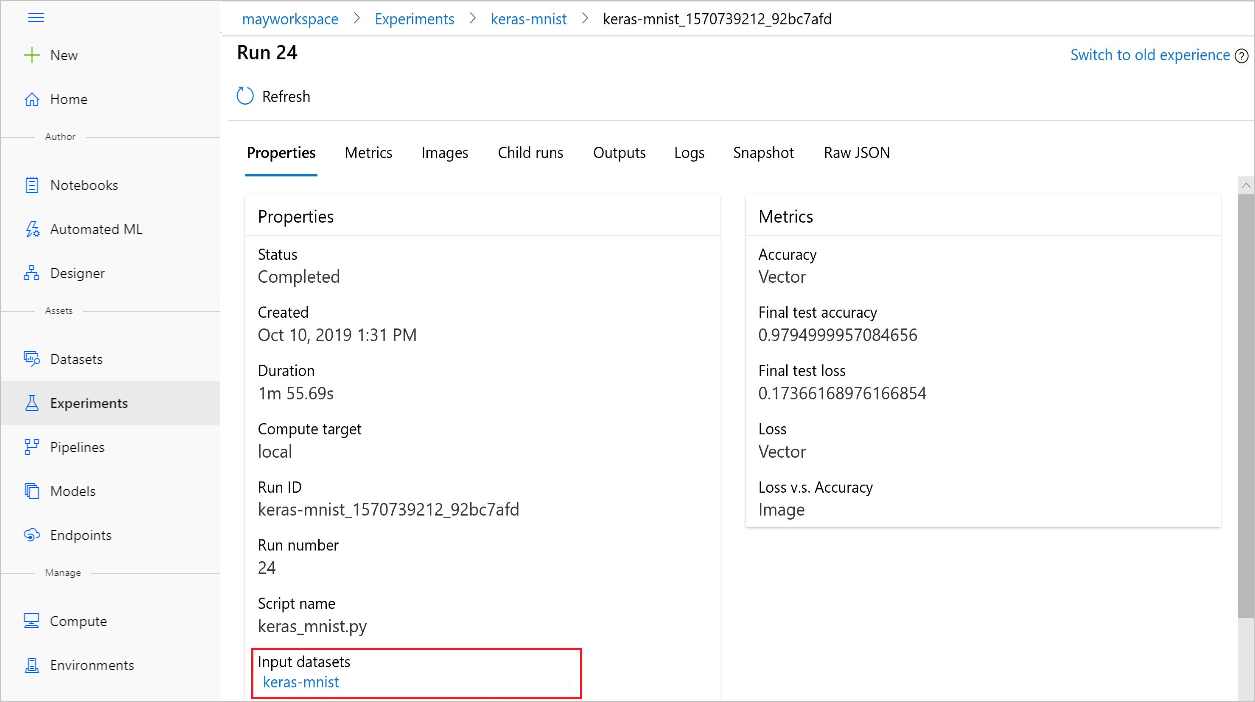
对于每个机器学习试验,可以跟踪试验 Job 对象的输入数据集。 以下代码示例使用 get_details() 方法跟踪与试验运行配合使用的输入数据集:
# get input datasets
inputs = run.get_details()['inputDatasets']
input_dataset = inputs[0]['dataset']
# list the files referenced by input_dataset
input_dataset.to_path()
以下屏幕截图展示了在 Azure 机器学习工作室中从何处查找试验的输入数据集。 对于此示例,请从试验窗格开始,然后为试验的特定运行打开属性选项卡。
以下代码向数据集注册模型:
model = run.register_model(model_name='keras-mlp-mnist',
model_path=model_path,
datasets =[('training data',train_dataset)])
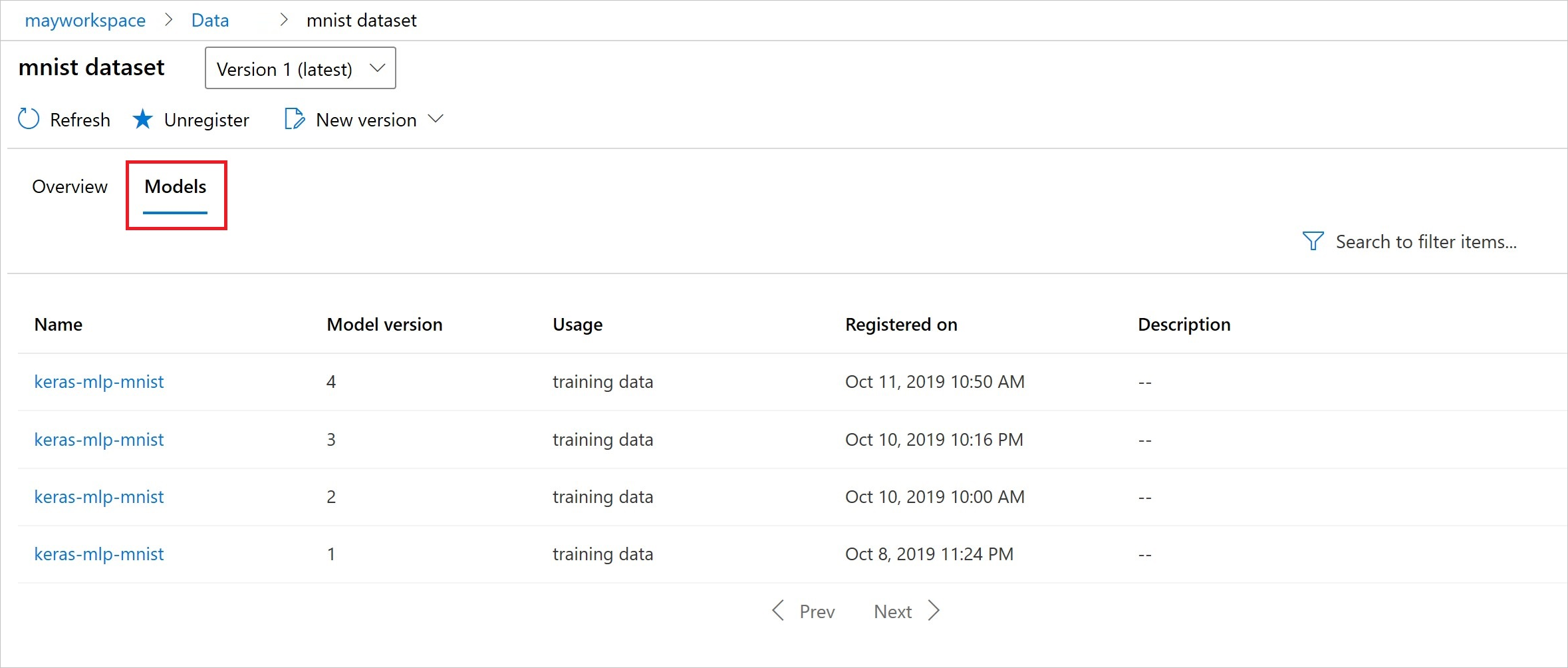
注册后,可以使用 Python 或工作室查看已注册到数据集的模型的列表。
以下屏幕截图来自“资产”下的“数据集”窗格。 选择数据集,然后选择“模型”选项卡以获取向数据集注册的模型的列表。