ASP.NET Core 是一个开源跨平台框架。 此框架用于生成基于云的 Internet 联网应用程序,例如 Web 应用、IoT 应用和移动后端。
本文详细说明了如何通过使用 NuGet 包的 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore. 集在 Service Fabric Reliable Services 中托管 ASP.NET Core 服务。
有关如何在 Service Fabric 中 ASP.NET Core 的介绍性教程以及如何设置开发环境的说明,请参阅教程:使用 ASP.NET Core Web API 前端服务和有状态后端服务创建和部署应用程序。
本文的剩余内容假设你熟悉 ASP.NET Core。 如果不熟悉,请通读 ASP.NET Core 基础知识。
Service Fabric 环境中的 ASP.NET Core
ASP.NET Core 和 Service Fabric 应用都可以在 .NET Core 或完整的 .NET Framework 上运行。 可在 Service Fabric 中以两种不同方式使用 ASP.NET Core:
- 作为来宾可执行文件托管。 此方法主要用于在 Service Fabric 上运行现有 ASP.NET Core 应用程序,无需更改代码。
- 在 Reliable Service 内部运行。 此方法可改善与 Service Fabric 运行时的集成,实现有状态的 ASP.NET Core 服务。
本文的剩余内容说明如何通过 Service Fabric SDK 随附的 ASP.NET Core 集成组件在 Reliable Service 内部使用 ASP.NET Core。
Service Fabric 服务托管
在 Service Fabric 中,服务的一个或多个实例和/或副本在“服务主机进程”中运行:运行服务代码的可执行文件。 服务作者拥有服务主机进程,Service Fabric 为服务作者激活并监视此进程。
传统的 ASP.NET(最高为 MVC 5)通过 System.Web.dll 与 IIS 紧密耦合。 ASP.NET Core 在 Web 服务器和 Web 应用程序之间提供分隔。 这种隔离使 Web 应用程序能够在不同的 Web 服务器之间移植。 此外,还允许 Web 服务器自我托管。 这意味着,你可以在自己的进程(而不是由 IIS 等专用 Web 服务器软件拥有的进程)中启动 Web 服务器。
若要合并 Service Fabric 服务和 ASP.NET,无论是作为来宾可执行文件还是在 Reliable Service 中合并,都必须能够在服务主机进程内启动 ASP.NET。 可借助 ASP.NET Core 的自托管功能执行此操作。
在 Reliable Service 中托管 ASP.NET Core
通常情况下,自托管 ASP.NET Core 应用程序会在应用程序的入口点创建 WebHost,如 static void Main() 中的 Program.cs 方法。 在这种情况下,WebHost 的生命周期绑定到进程的生命周期。

但是,应用程序入口点并不是在 Reliable Service 中创建 WebHost 的正确位置。 这是因为应用程序入口点仅用于向 Service Fabric 运行时注册服务类型,以便它能创建该服务类型的实例。 应在 Reliable Service 中创建 WebHost。 在服务主机进程中,服务实例和/或副本可以完成多个生命周期。
Reliable Service 实例由派生自 StatelessService 或 StatefulService 的服务类表示。 服务的通信堆栈包含在服务类中的 ICommunicationListener 实现内。
Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.* NuGet 包内附 ICommunicationListener 的实现,这些实现可启动和管理 Reliable Service 中 Kestrel 或 HTTP.sys 的 ASP.NET Core WebHost。
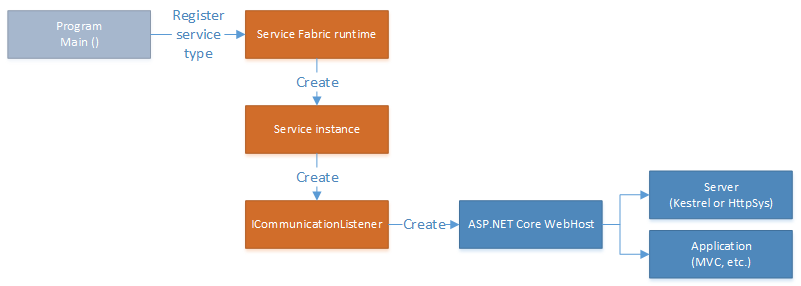
ASP.NET Core ICommunicationListeners
ICommunicationListener NuGet 包中 Kestrel 和 HTTP.sys 的 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.* 实现具有类似的使用模式。 但它们针对每个 Web 服务器所执行的操作略有不同。
这两种通信侦听器都能提供采用以下参数的构造函数:
-
ServiceContext serviceContext:这是包含有关运行中服务的信息的ServiceContext对象。 -
string endpointName:这是 ServiceManifest.xml 中Endpoint配置的名称。 它是两个通信侦听器的主要不同之处。 HTTP.sys 需要 配置,而 Kestrel 不需要Endpoint。 -
Func<string, AspNetCoreCommunicationListener, IWebHost> build:这是实现的 lambda,在其中创建和返回IWebHost。 它允许按常规方式在在 ASP.NET Core 应用程序中配置IWebHost。 lambda 提供为你生成的 URL,具体取决于使用的 Service Fabric 集成选项和你提供的Endpoint配置。 然后,可以修改 URL 或使用它来启动 Web 服务器。
Service Fabric 集成中间件
Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore NuGet 包包含添加 Service Fabric 可识别的中间件的 UseServiceFabricIntegration 上的 IWebHostBuilder 扩展方法。 此中间件将 Kestrel 或 HTTP.sys ICommunicationListener 配置为向 Service Fabric 命名服务注册唯一的服务 URL。 然后,它验证客户端请求,以确保客户端连接到适当的服务。
为了防止客户端错误地连接到错误的服务,必须执行此步骤。 这是因为,在 Service Fabric 等共享主机环境中,多个 Web 应用程序可在同一物理机或虚拟机上运行,但不使用唯一的主机名。 后续部分将对此方案进行详细说明。
错误标识示例
服务副本(无论哪种协议)侦听唯一的 IP:port 组合。 服务副本开始侦听 IP:port 终结点后,它向 Service Fabric 命名服务报告该终结点地址。 该命名服务中的客户端或其他服务可以发现该地址。 如果服务使用动态分配的应用程序端口,服务副本可能恰巧使用同一物理计算机或虚拟机上其他服务此前使用的相同 IP:port 终结点。 这可能会导致客户端错误地连接到错误的服务。 如果发生以下事件序列,可能会出现此情况:
- 服务 A 通过 HTTP 侦听 10.0.0.1:30000。
- 客户端解析服务 A 并获取地址 10.0.0.1:30000。
- 服务 A 移动到其他节点。
- 服务 B 放置在 10.0.0.1 并恰巧使用了同一端口 30000。
- 客户端尝试使用缓存地址 10.0.0.1:30000 连接到服务 A。
- 客户端现已成功连接到服务 B,但未意识到已连接到错误的服务。
这可能导致在随机时间出现 bug,并且很难诊断。
使用唯一的服务 URL
若要防止这些 bug,服务可向具有唯一标识符的命名服务发布终结点,并在客户端请求期间验证该唯一标识符。 这是非恶意租户受信任环境中的服务之间的协作操作。 这不会在恶意租户环境中提供安全的服务身份验证。
在受信任的环境中,由 UseServiceFabricIntegration 方法自动添加的中间件可对已发布到命名服务的地址追加唯一标识符。 它会在每次请求时验证该标识符。 如果标识符不匹配,该中间件会立即返回 HTTP 410 Gone 响应。
使用动态分配的端口的服务应使用此中间件。
使用固定唯一端口的服务在协作环境中不存在此问题。 固定唯一端口通常用于面向外部的服务,此类服务需要可供客户端应用程序连接到的已知端口。 例如,大多数面向 Internet 的 Web 应用程序将使用端口 80 或 443 进行 Web 浏览器连接。 在此情况下,不应启用唯一标识符。
下图显示了启用中间件时的请求流:
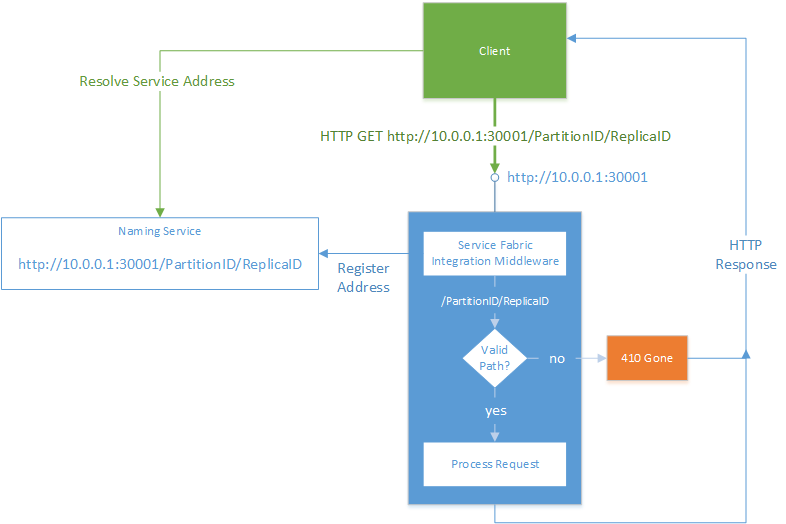
Kestrel 和 HTTP.sys ICommunicationListener 实现以完全相同的方式使用此机制。 尽管 HTTP.sys 可使用底层 HTTP.sys 端口共享功能基于唯一 URL 路径内部区分请求,但 HTTP.sys 实现不使用此功能ICommunicationListener。 这是因为,它会导致上述方案中出现 HTTP 503 和 HTTP 404 错误状态代码。 这进而使客户端难以确定错误原因,因为 HTTP 503 和 HTTP 404 通常用于指示其他错误。
因此,Kestrel 和 HTTP.sys ICommunicationListener 实现会在 UseServiceFabricIntegration 扩展方法提供的中间件上执行标准化。 因而客户端只需对 HTTP 410 响应执行服务终结点重新解析操作。
Reliable Services 中的 HTTP.sys
可以通过导入 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.HttpSys NuGet 包来使用 Reliable Services 中的 HTTP.sys。 此包包含 HttpSysCommunicationListener(ICommunicationListener 的实现)。
HttpSysCommunicationListener 允许使用 HTTP.sys 作为 Web 服务器在 Reliable Service 内部创建 ASP.NET Core WebHost。
在 Windows HTTP Server API 上构建 HTTP.sys。 此 API 使用 HTTP.sys 内核驱动程序处理 HTTP 请求,并将其路由到运行 Web 应用程序的进程。 这可允许同一物理计算机或虚拟机上的多个进程在同一端口上托管 Web 应用程序,通过唯一 URL 路径或主机名来消除歧义。 Service Fabric 在同一群集中托管多个网站时,这些功能非常有用。
注意
HTTP.sys 实现仅适用于 Windows 平台。
下图说明了 HTTP.sys 如何在 Windows 上使用“HTTP.sys”内核驱动程序进行端口共享:
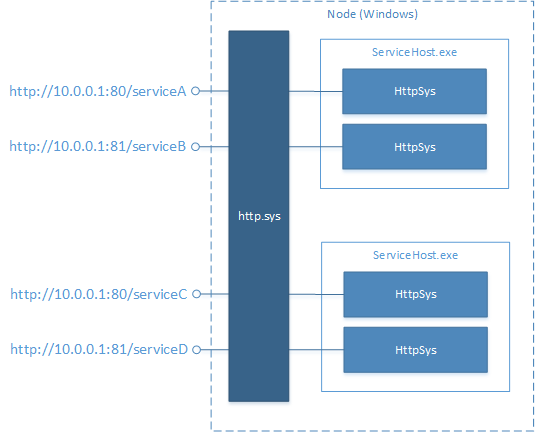
无状态服务中的 HTTP.sys
若要在无状态服务中使用 HttpSys,需替代 CreateServiceInstanceListeners 方法并返回 HttpSysCommunicationListener 实例:
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceInstanceListener> CreateServiceInstanceListeners()
{
return new ServiceInstanceListener[]
{
new ServiceInstanceListener(serviceContext =>
new HttpSysCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
new WebHostBuilder()
.UseHttpSys()
.ConfigureServices(
services => services
.AddSingleton<StatelessServiceContext>(serviceContext))
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseUrls(url)
.Build()))
};
}
有状态服务中的 HTTP.sys
由于底层 HttpSysCommunicationListener 端口共享功能所具有的复杂性,当前不能在有状态服务中使用 。 有关详细信息,请参阅以下关于 HTTP.sys 动态端口分配的部分。 对于有状态服务,Kestrel 是建议的 Web 服务器。
终结点配置
对于使用 Windows HTTP Server API 的 Web 服务器(包括 HTTP.sys),需要配置 Endpoint。 使用 Windows HTTP Server API 的 Web 服务器首先必须保留带有 HTTP.sys 的 URL(通常可使用 netsh 工具实现)。
此操作需要提升的权限,默认情况下服务不具备此权限。 用于 ServiceManifest.xml 中 Protocol 配置的 Endpoint 属性的“http”或“https”选项,可专门用于指示 Service Fabric 运行时代表你注册带有 HTTP.sys 的 URL。 它使用强通配符 URL 前缀来提供此指示。
例如,若要保留服务的 http://+:80,请在 ServiceManifest.xml 中使用以下配置:
<ServiceManifest ... >
...
<Resources>
<Endpoints>
<Endpoint Name="ServiceEndpoint" Protocol="http" Port="80" />
</Endpoints>
</Resources>
</ServiceManifest>
并且必须将终结点名称传递到 HttpSysCommunicationListener 构造函数:
new HttpSysCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
{
return new WebHostBuilder()
.UseHttpSys()
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None)
.UseUrls(url)
.Build();
})
将 HTTP.sys 和静态端口配合使用
要将 HTTP.sys 与静态端口配合使用,请在 Endpoint 配置中提供端口号:
<Resources>
<Endpoints>
<Endpoint Protocol="http" Name="ServiceEndpoint" Port="80" />
</Endpoints>
</Resources>
将 HTTP.sys 和动态端口配合使用
要将 HTTP.sys 与动态分配端口配合使用,请在 Port 配置中省略 Endpoint 属性:
<Resources>
<Endpoints>
<Endpoint Protocol="http" Name="ServiceEndpoint" />
</Endpoints>
</Resources>
Endpoint 配置分配的动态端口仅为每个主机进程提供一个端口。 当前的 Service Fabric 托管模型允许在同一进程中托管多个服务实例和/或副本。 这意味着,通过 Endpoint 配置分配时,每个实例/副本共享相同的端口。 多个 HTTP.sys 实例可以使用底层 HTTP.sys 端口共享功能共享一个端口。 但 HttpSysCommunicationListener 不支持此做法,因为这会增大客户端请求的复杂性。 对于使用动态端口,Kestrel 是建议的 Web 服务器。
Reliable Services 中的 Kestrel
可以通过导入 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.Kestrel NuGet 包来使用 Reliable Services 中的 Kestrel。 此包包含 KestrelCommunicationListener(ICommunicationListener 的实现)。
KestrelCommunicationListener 允许使用 Kestrel 作为 Web 服务器在 Reliable Service 内部创建 ASP.NET Core WebHost。
Kestrel 是一个用于 ASP.NET Core 的跨平台 Web 服务器。 与 HTTP.sys 不同,Kestrel 不使用集中式终结点管理器。 与 HTTP.sys 的另一个区别在于,Kestrel 不支持在多个进程之间共享端口。 Kestrel 的每个实例必须使用唯一端口。 有关 Kestrel 的详细信息,请参阅实现详细信息。
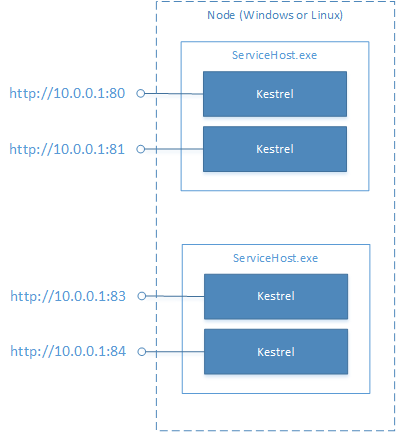
无状态服务中的 Kestrel
若要在无状态服务中使用 Kestrel,需替代 CreateServiceInstanceListeners 方法并返回 KestrelCommunicationListener 实例:
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceInstanceListener> CreateServiceInstanceListeners()
{
return new ServiceInstanceListener[]
{
new ServiceInstanceListener(serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.ConfigureServices(
services => services
.AddSingleton<StatelessServiceContext>(serviceContext))
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.UseUniqueServiceUrl)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseUrls(url)
.Build();
))
};
}
有状态服务中的 Kestrel
若要在有状态服务中使用 Kestrel,需替代 CreateServiceReplicaListeners 方法并返回 KestrelCommunicationListener 实例:
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceReplicaListener> CreateServiceReplicaListeners()
{
return new ServiceReplicaListener[]
{
new ServiceReplicaListener(serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, (url, listener) =>
new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.ConfigureServices(
services => services
.AddSingleton<StatefulServiceContext>(serviceContext)
.AddSingleton<IReliableStateManager>(this.StateManager))
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.UseUniqueServiceUrl)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseUrls(url)
.Build();
))
};
}
此示例中为 WebHost 依赖关系注入容器提供 IReliableStateManager 的单一实例。 这不是必需的,但通过此操作,可在 MVC 控制器操作方法中使用 IReliableStateManager 和 Reliable Collections。
有状态服务中不会为 Endpoint 提供 配置名称KestrelCommunicationListener。 后续部分会对此进行详细说明。
将 Kestrel 配置为使用 HTTPS
如要在服务中为 Kestrel 启用 HTTPS,需要设置多个侦听选项。 将 ServiceInstanceListener 更新为使用“EndpointHttps”终结点和侦听特定端口(例如端口 443)。 配置使用 Kestrel Web 服务器的 Web 主机时,须将 Kestrel 配置为针对所有网络接口上的 IPv6 地址进行侦听:
new ServiceInstanceListener(
serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(
serviceContext,
"EndpointHttps",
(url, listener) =>
{
ServiceEventSource.Current.ServiceMessage(serviceContext, $"Starting Kestrel on {url}");
return new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel(opt =>
{
int port = serviceContext.CodePackageActivationContext.GetEndpoint("EndpointHttps").Port;
opt.Listen(IPAddress.IPv6Any, port, listenOptions =>
{
listenOptions.UseHttps(GetCertificateFromStore());
listenOptions.NoDelay = true;
});
})
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((builderContext, config) =>
{
config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true);
})
.ConfigureServices(
services => services
.AddSingleton<HttpClient>(new HttpClient())
.AddSingleton<FabricClient>(new FabricClient())
.AddSingleton<StatelessServiceContext>(serviceContext))
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None)
.UseUrls(url)
.Build();
}))
如需查看教程中的完整示例,请参阅配置 Kestrel 以使用 HTTPS。
终结点配置
使用 Kestrel 时不需要 Endpoint 配置。
Kestrel 是简单的独立 Web 服务器。 与 HTTP.sys(或 HttpListener)不同,Kestrel 不需要 ServiceManifest.xml 中的 Endpoint 配置,因为它在启动之前无需 URL 注册。
将 Kestrel 和静态端口配合使用
可在 ServiceManifest.xml 的 Endpoint 配置中配置静态端口,以将其与 Kestrel 配合使用。 虽然这不是必需的,但这样做有两个潜在好处:
- 如果此端口不在应用程序端口范围内,则会由 Service Fabric 通过 OS 防火墙将其打开。
- 通过
KestrelCommunicationListener提供的 URL 将使用此端口。
<Resources>
<Endpoints>
<Endpoint Protocol="http" Name="ServiceEndpoint" Port="80" />
</Endpoints>
</Resources>
如果已配置 Endpoint,则其名称必须传递到 KestrelCommunicationListener 构造函数:
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) => ...
如果 ServiceManifest.xml 不使用 Endpoint 配置,请在 KestrelCommunicationListener 构造函数中省略此名称。 在此情况下,将使用动态端口。 有关详细信息,请参阅下一部分。
将 Kestrel 和动态端口配合使用
Kestrel 无法使用 ServiceManifest.xml 的 Endpoint 配置中的自动端口分配。 这是因为,Endpoint 配置中的自动端口分配将为每个主机进程分配唯一端口,并且单个主机进程可以包含多个 Kestrel 实例。 此方案不可行,因为 Kestrel 不支持端口共享。 因此,必须在唯一端口上打开每个 Kestrel 实例。
要将 Kestrel 和动态端口分配配合使用,请全省略 ServiceManifest.xml 中的 Endpoint 配置,并且不要将终结点名称传递到 KestrelCommunicationListener 构造函数,如下所示:
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, (url, listener) => ...
在此配置中,KestrelCommunicationListener 会自动从应用程序端口范围中选择未使用的端口。
对于 HTTPS,它应为终结点配置 HTTPS 协议,而无需在 ServiceManifest.xml 中指定端口,并将终结点名称传递给 KestrelCommunicationListener 构造函数。
IHost 和最小托管集成
除了 IWebHost/IWebHostBuilder,KestrelCommunicationListener 和 HttpSysCommunicationListener 还支持使用 IHost/IHostBuilder 生成 ASP.NET Core 服务。
从 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.Kestrel 和 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.HttpSys 包的 v5.2.1363 开始提供此功能。
// Stateless Service
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceInstanceListener> CreateServiceInstanceListeners()
{
return new ServiceInstanceListener[]
{
new ServiceInstanceListener(serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
{
return Host.CreateDefaultBuilder()
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseKestrel()
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None)
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseUrls(url);
})
.ConfigureServices(services => services.AddSingleton<StatelessServiceContext>(serviceContext))
.Build();
}))
};
}
// Stateful Service
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceReplicaListener> CreateServiceReplicaListeners()
{
return new ServiceReplicaListener[]
{
new ServiceReplicaListener(serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
{
return Host.CreateDefaultBuilder()
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseKestrel()
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.UseUniqueServiceUrl)
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseUrls(url);
})
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
services.AddSingleton<StatefulServiceContext>(serviceContext);
services.AddSingleton<IReliableStateManager>(this.StateManager);
})
.Build();
}))
};
}
注意
由于 KestrelCommunicationListener 和 HttpSysCommunicationListener 用于 Web 服务,因此需要在 IHost 上注册/配置 Web 服务器(使用 ConfigureWebHostDefaults 或 ConfigureWebHost 方法)
ASP.NET 6 引入了最小托管模型,这是一种创建 Web 应用的更简化和流畅的方式。 最小托管模型也可以与 KestrelCommunicationListener 和 HttpSysCommunicationListener 一起使用。
// Stateless Service
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceInstanceListener> CreateServiceInstanceListeners()
{
return new ServiceInstanceListener[]
{
new ServiceInstanceListener(serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder();
builder.Services.AddSingleton<StatelessServiceContext>(serviceContext);
builder.WebHost
.UseKestrel()
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None)
.UseUrls(url);
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews();
var app = builder.Build();
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
return app;
}))
};
}
// Stateful Service
protected override IEnumerable<ServiceReplicaListener> CreateServiceReplicaListeners()
{
return new ServiceReplicaListener[]
{
new ServiceReplicaListener(serviceContext =>
new KestrelCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder();
builder.Services
.AddSingleton<StatefulServiceContext>(serviceContext)
.AddSingleton<IReliableStateManager>(this.StateManager);
builder.WebHost
.UseKestrel()
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseServiceFabricIntegration(listener, ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.UseUniqueServiceUrl)
.UseUrls(url);
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews();
var app = builder.Build();
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
return app;
}))
};
}
Service Fabric 配置提供程序
ASP.NET Core 中的应用程序配置基于配置提供程序建议的键值对。 请阅读 ASP.NET Core 中的配置,详细了解一般的 ASP.NET Core 配置支持。
本部分介绍如何通过导入 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.Configuration NuGet 包,将 Service Fabric 配置提供程序与 ASP.NET Core 配置相集成。
AddServiceFabricConfiguration 启动扩展
导入 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.Configuration NuGet 包后,需要将 Service Fabric 配置源注册到 ASP.NET Core 配置 API。 为此,可以针对 检查 Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.Configuration 命名空间中的 IConfigurationBuilder 扩展。
using Microsoft.ServiceFabric.AspNetCore.Configuration;
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env)
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true)
.AddServiceFabricConfiguration() // Add Service Fabric configuration settings.
.AddEnvironmentVariables();
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; }
现在,ASP.NET Core 服务可以访问 Service Fabric 配置设置,如同访问任何其他应用程序设置一样。 例如,可以使用选项模式将设置加载到强类型化对象中。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<MyOptions>(Configuration); // Strongly typed configuration object.
services.AddMvc();
}
默认键映射
默认情况下,Service Fabric 配置提供程序包含包名称、节名称和属性名称。 它们共同构成了 ASP.NET Core 配置键,按如下所示:
$"{this.PackageName}{ConfigurationPath.KeyDelimiter}{section.Name}{ConfigurationPath.KeyDelimiter}{property.Name}"
例如,如果名为 MyConfigPackage 的配置包包含以下内容,则可以通过 IConfiguration 在 ASP.NET Core 上使用配置值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<Settings xmlns:xsd="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/2011/01/fabric">
<Section Name="MyConfigSection">
<Parameter Name="MyParameter" Value="Value1" />
</Section>
</Settings>
Service Fabric 配置选项
Service Fabric 配置提供程序还支持使用 ServiceFabricConfigurationOptions 来更改键映射的默认行为。
加密的设置
与 Service Fabric 配置提供程序一样,Service Fabric 也支持加密的设置。 默认情况下,加密的设置不会解密到 ASP.NET Core IConfiguration, 而是存储在其中。 但是,若要解密该值并将其存储在 ASP.NET Core IConfiguration 中,可以在 扩展中将 AddServiceFabricConfiguration 标志设置为 false,如下所示:
public Startup()
{
ICodePackageActivationContext activationContext = FabricRuntime.GetActivationContext();
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddServiceFabricConfiguration(activationContext, (options) => options.DecryptValue = false); // set flag to decrypt the value
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
多个配置包
Service Fabric 支持多个配置包。 默认情况下,包名称将包含在配置键中。 但是,可将 IncludePackageName 标志设置为 false,如下所示:
public Startup()
{
ICodePackageActivationContext activationContext = FabricRuntime.GetActivationContext();
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
// exclude package name from key.
.AddServiceFabricConfiguration(activationContext, (options) => options.IncludePackageName = false);
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
自定义键映射、值提取和数据填充
Service Fabric 配置提供程序还支持使用更高级的方案来通过 ExtractKeyFunc 自定义键映射,以及通过 ExtractValueFunc 按自定义方式提取值。 甚至可以使用 ConfigAction,来更改将 Service Fabric 配置中的数据填充到 ASP.NET Core 配置的整个过程。
以下示例演示如何使用 ConfigAction 来自定义数据填充:
public Startup()
{
ICodePackageActivationContext activationContext = FabricRuntime.GetActivationContext();
this.valueCount = 0;
this.sectionCount = 0;
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder();
builder.AddServiceFabricConfiguration(activationContext, (options) =>
{
options.ConfigAction = (package, configData) =>
{
ILogger logger = new ConsoleLogger("Test", null, false);
logger.LogInformation($"Config Update for package {package.Path} started");
foreach (var section in package.Settings.Sections)
{
this.sectionCount++;
foreach (var param in section.Parameters)
{
configData[options.ExtractKeyFunc(section, param)] = options.ExtractValueFunc(section, param);
this.valueCount++;
}
}
logger.LogInformation($"Config Update for package {package.Path} finished");
};
});
Configuration = builder.Build();
}
配置更新
Service Fabric 配置提供程序还支持配置更新。 可以使用 ASP.NET Core IOptionsMonitor 接收更改通知,然后使用 IOptionsSnapshot 重新加载配置数据。 有关详细信息,请参阅 ASP.NET Core 选项。
默认支持这些选项。 无需进一步编写代码即可启用配置更新。
方案和配置
本部分提供 Web 服务器、端口配置、Service Fabric 集成选项的组合,以及建议用来排查以下问题的其他设置:
- 外部公开的 ASP.NET Core 无状态服务
- 仅限内部的 ASP.NET Core 无状态服务
- 仅限内部的 ASP.NET Core 有状态服务
外部公开的服务公开可从群集外部调用的终结点(通常通过负载均衡器)。
仅限内部的服务的终结点只能从群集内部调用。
注意
通常不应将有状态服务终结点公开到 Internet。 位于无法识别 Service Fabric 服务解析的负载均衡器(如 Azure 负载均衡器)后的群集将无法公开有状态服务。 这是因为,负载均衡器无法找到流量并将其路由到相应的有状态服务副本。
外部公开的 ASP.NET Core 无状态服务
对于公开面向 Internet 的外部 HTTP 终结点的前端服务,Kestrel 是建议的 Web 服务器。 在 Windows 上,HTTP.sys 可提供端口共享功能,允许使用同一端口在同一组节点上托管多个 Web 服务。 在此情况下,Web 服务按主机名或路径进行区分,而不依赖前端代理或网关来提供 HTTP 路由。
向 Internet 公开时,无状态服务应使用可通过负载均衡器到达的已知稳定终结点。 需将此 URL 提供给应用程序的用户。 建议使用以下配置:
| 类型 | 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Web 服务器 | 茶隼 | Windows 和 Linux 都支持 Kestrel,因此它是首选的 Web 服务器。 |
| 端口配置 | 静态 | 应在 ServiceManifest.xml 的 Endpoints 配置中配置已知静态端口,例如为 HTTP 配置 80 或为 HTTPS 配置 443。 |
| ServiceFabric集成选项 | 无 | 配置 Service Fabric 集成中间件时应使用 ServiceFabricIntegrationOptions.None 选项,以使服务不会验证传入请求是否具有唯一标识符。 应用程序的外部用户不会知道中间件使用的唯一标识信息。 |
| 实例计数 | -1 | 在典型用例中,应将实例计数设置设置为 -1。 这样,便可以在从负载均衡器接收流量的所有节点上使用某个实例。 |
如果多个外部公开的服务共享同一组节点,可通过唯一且稳定的 URL 路径使用 HTTP.sys。 可以通过修改配置 IWebHost 时提供的 URL 来实现此目的。 请注意,这仅适用于 HTTP.sys。
new HttpSysCommunicationListener(serviceContext, "ServiceEndpoint", (url, listener) =>
{
url += "/MyUniqueServicePath";
return new WebHostBuilder()
.UseHttpSys()
...
.UseUrls(url)
.Build();
})
仅限内部的无状态 ASP.NET Core 服务
仅从群集内部调用的无状态服务应使用唯一的 URL 和动态分配的端口,以确保多个服务之间的协作正常进行。 建议使用以下配置:
| 类型 | 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Web 服务器 | 茶隼 | 尽管 HTTP.sys 可用于内部无状态服务,但 Kestrel 是最佳的服务器,它允许多个服务实例共享一台主机。 |
| 端口配置 | 动态分配 | 有状态服务的多个副本可能会共享主机进程或主机操作系统,因此需要唯一端口。 |
| ServiceFabric集成选项 | 使用唯一服务网址 | 通过动态端口分配,此设置可以防止前面所述的错误标识问题。 |
| 实例数量 | 任意 | 可根据操作服务的需要将实例计数设置设置为任何值。 |
仅限内部的有状态 ASP.NET Core 服务
仅从群集内部调用的有状态服务应使用动态分配的端口,以确保多个服务之间的协作正常进行。 建议使用以下配置:
| 类型 | 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Web 服务器 | 茶隼 |
HttpSysCommunicationListener 不能用于副本在其中共享主机进程的有状态服务。 |
| 端口配置 | 动态分配 | 有状态服务的多个副本可能会共享主机进程或主机操作系统,因此需要唯一端口。 |
| ServiceFabric集成选项 | 使用唯一服务网址 | 通过动态端口分配,此设置可以防止前面所述的错误标识问题。 |