Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Cosmos DB lets you configure standard (manual) or autoscale throughput for databases and containers. Autoscale adjusts throughput (RU/s) to match your workload, ensuring high performance and cost efficiency.
Use cases
Autoscale provisioned throughput is ideal for mission-critical workloads with variable or unpredictable traffic patterns, and that require service level agreements (SLAs) for high performance and scale. Autoscale by default scales workloads based on the most active region and partition. For nonuniform workloads that have different workload patterns across regions and partitions, this scaling can cause unnecessary scale-ups. Dynamic scaling or dynamic autoscale is an enhancement to autoscale provisioned throughout that helps scaling of such nonuniform workloads independently based on usage, at per region and per partition level. Dynamic scaling helps save costs if you often experience hot partitions or have multiple regions.
Benefits of autoscale
Azure Cosmos DB databases and containers that are configured with autoscale provisioned throughput have the following benefits:
Simple: Autoscale simplifies managing RU/s by eliminating the need for custom scripting or manual scaling.
Scalable: Databases and containers automatically scale the provisioned throughput as needed. There's no disruption to client connections, applications, or to Azure Cosmos DB SLAs.
Cost-effective: Autoscale optimizes RU/s and costs by scaling down when not in use. You pay only for the resources your workloads need on a per-hour basis. If you use the full
Tmaxfor 66% or fewer hours in a month, autoscale can save costs. Dynamic scaling also makes adding a secondary region for high availability more cost-efficient, as each region and partition scales independently based on usage. Learn more in the how to choose between standard (manual) and autoscale provisioned throughput article.Highly available: Databases and containers with autoscale use the multiple-regionally distributed, fault-tolerant Azure Cosmos DB backend to ensure data durability and availability.
Use cases of autoscale
Use cases for autoscale include:
Variable or unpredictable workloads: When your workloads have variable or unpredictable spikes in usage, autoscale helps by automatically scaling up and down based on usage. Examples include retail websites with seasonal traffic patterns, IoT workloads with daily usage spikes, and line-of-business applications with occasional peak usage. Autoscale eliminates the need to manually allocate throughput for peak or average capacity.
New applications: If you're developing a new application and unsure about the throughput (RU/s) needed, autoscale simplifies getting started. You can start with the autoscale entry point of 100 - 1000 RU/s, monitor your usage, and determine the right RU/s over time.
Infrequently used applications: If you have an application used only for a few hours several times a day, week, or month—such as a low-volume app, website, or blog. Autoscale adjusts the capacity to handle peak usage and scales down when it's over.
Development and test workloads: If you or your team use Azure Cosmos DB databases and containers during work hours, but don't need them on nights or weekends, autoscale helps save cost by scaling down to a minimum when not in use.
Scheduled production workloads/queries: If you have a series of scheduled requests, operations, or queries that you want to run during idle periods, you can do that easily with autoscale. When the workload runs, throughput automatically scales to the required value and scales down afterward.
Building a custom solution to these problems requires significant time and adds complexity to your application's configuration or code. Autoscale enables the above scenarios out of the box and removes the need for custom or manual scaling of capacity.
Use cases of dynamic scaling
The use cases of dynamic scaling include:
- Database workloads with a highly trafficked primary region and a secondary passive region for disaster recovery.
- With dynamic scaling, achieving high availability with multiple regions is more cost effective. The secondary region independently and automatically scales down while idle. The secondary region also automatically scales up as it becomes active and while handling write replication traffic from the primary region.
- Multi-region database workloads
- These workloads often experience uneven distribution of requests across regions because of natural traffic growth and dips throughout the day. For example, a database is active during business hours across multiple-regionally distributed time zones.
How autoscale throughput works
When configuring containers and databases with autoscale, you specify the maximum throughput Tmax required. Azure Cosmos DB scales the throughput T so that 0.1*Tmax <= T <= Tmax. For example, if you set the maximum throughput to 20,000 RU/s, the throughput scales between 2000 to 20,000 RU/s. Scaling is automatic and instantaneous, so you can consume up to the provisioned Tmax at any time without delay.
You're billed for each hour for the highest throughput T the system scales to during that hour. When dynamic scaling is enabled, scaling is based on the RU/s usage at each physical partition and region. As each partition and region scale independently, this billing can lead to cost savings for nonuniform workloads, as unnecessary scale-ups are avoided.
The entry point for autoscale maximum throughput Tmax is 1000 RU/s, scaling between 100 and 1000 RU/s. You can set Tmax in increments of 1000 RU/s and change the value at any time.
For example, if a collection has 1000 RU/s and 2 partitions, each partition can scale up to 500 RU/s. For one hour of activity, the utilization would look like this:
| Region | Partition | Throughput | Utilization | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Write | P1 | <= 500 RU/s | 100% | 500 RU/s consisting of 50 RU/s used for write operations and 450 RU/s for read operations. |
| Write | P2 | <= 200 RU/s | 40% | 200 RU/s consisting of all read operations. |
| Read | P1 | <= 150 RU/s | 30% | 150 RU/s consisting of 50 RU/s used for writes replicated from the write region. 100 RU/s are used for read operations in this region. |
| Read | P2 | <= 50 RU/s | 10% |
Without dynamic scaling, the system scales all partitions uniformly based on the hottest partition. In this example, because the hottest partition had 100% utilization, all partitions in both the write and read regions are scaled to 1000 RU/s, making the total RU/s scaled to 2000 RU/s.
With dynamic scaling, each partition and region's throughput scales independently, resulting in a total of 900 RU/s, which better reflects the actual traffic pattern and reduces costs.
Enabling autoscale on existing resources
Use the Azure portal, CLI, or PowerShell to enable autoscale on an existing database or container. Switch between autoscale and standard (manual) provisioned throughput at any time. For more information, see this documentation.
Throughput and storage limits for autoscale
For any value of Tmax, the database or container stores a total of 0.1 * Tmax GB. After you reach this storage amount, the maximum RU/s automatically increases based on the new storage value without impacting your application.
For example, if you start with a maximum RU/s of 50,000 RU/s (scales between 5000 and 50,000 RU/s), you can store up to 5,000 GB of data. If storage exceeds 5,000 GB, such as reaching 6,000 GB, the new maximum RU/s becomes 60,000 RU/s (scales between 6000 and 60,000 RU/s).
When you use database level throughput with autoscale, you can have the first 25 containers share an autoscale maximum RU/s of 1000 (scales between 100 - 1000 RU/s), as long as you don't exceed 100 GB of storage. For more information, see this documentation.
Enabling dynamic scaling
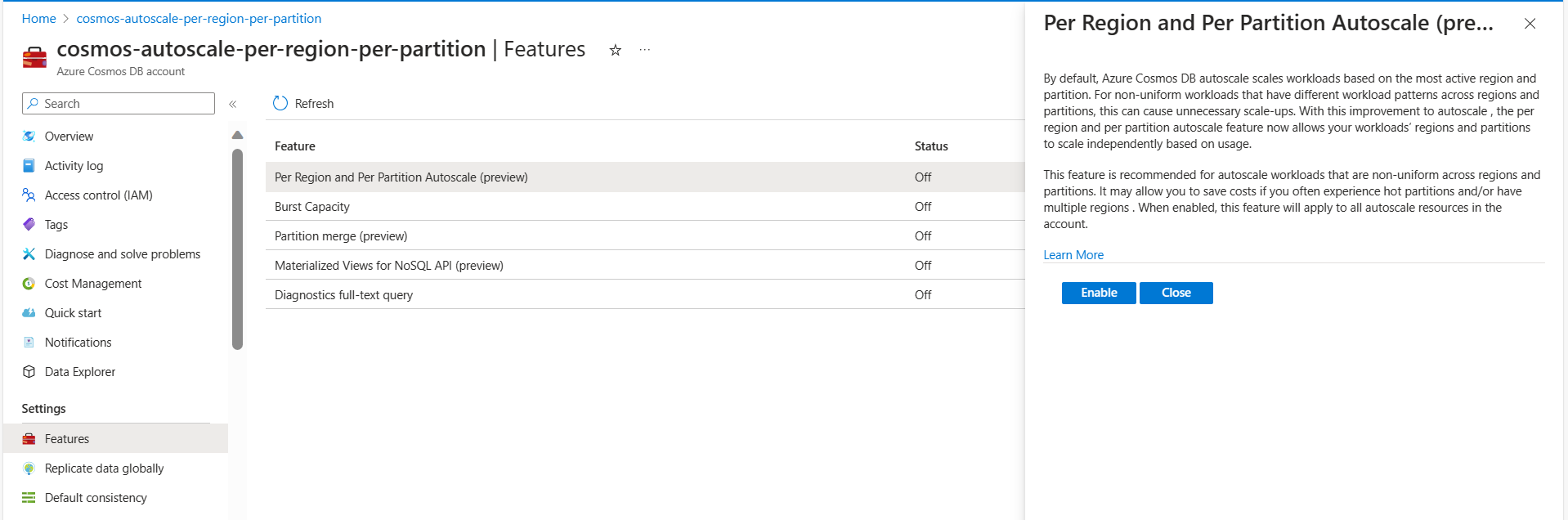
Dynamic scaling is enabled by default for all Azure Cosmos DB accounts created after September 25, 2024. Customers who want to enable this feature for their older accounts can do so programmatically through Azure PowerShell, CLI, REST API, or from the features pane of the Azure portal as shown:
Go to your Azure Cosmos DB account in the Azure portal.
Select the Features page.
Find and enable the Dynamic Scaling (Per Region and Per Partition Autoscale) feature.
Important
The feature is enabled at the account level, so all autoscale containers and autoscales shared throughput databases within the account automatically has this capability applied. Enabling this feature doesn't affect resources in the account that are using manual throughput. Manual resources need to be changed to autoscale to take advantage of dynamic scaling. Enabling this feature has zero downtime or performance effect. This feature isn't applicable for serverless accounts. This feature is supported on all clouds.
Monitoring metrics
You can use the following metrics to monitor autoscale and dynamic scaling:
| Metric Name | Definition | Metric Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Provisioned Throughput | Shows the aggregated highest RU/s scaled to across the hour, and represents the total RU/s scaled to for the hour. | You can use the Provisioned Throughput metric to see the RU/s you're billed for in each hour. With autoscale, you're billed based on the most active partition for each hour, and the same applies to all partitions and regions. With dynamic autoscale, you're billed for the aggregated highest RU/s scaled to in each hour at each partition and region level. |
| Normalized RU Consumption | This metric represents the ratio of consumed RU/s to provisioned RU/s at each partition and region level. | Use this metric to determine if the autoscale maximum throughput is under or over-provisioned. If the metric value is consistently 100%, and your application sees rate-limiting (429 error code), you might need more RU/s. In contrast, if this metric value is low and there's no rate-limiting, then there might be room to optimize and scale-down the RU/s. Learn how to interpret and debug code 429 rate limiting errors. The Normalized RU Consumption metric reflects the RU/s consumed in secondary region due to write replication traffic from the primary, in addition to any read traffic on the secondary. |
| Autoscaled RU | Shows the dynamically scaled provisioned throughput at each partition and region level only for dynamic autoscale enabled accounts. | Use this metric to see how partitions in each region scale independently based on their usage. Use Azure Monitor metrics— Autoscaled RU—to analyze how the new autoscaling applies across partitions and regions. Filter to your desired database account and container, then filter or split by the Physical PartitionID metric. This metric shows all partitions across their various regions. |
Important
We recommend using Azure Cosmos DB's native dynamic scaling capability to manage your capacity. However, if needed, the Normalized RU Consumption metric in Azure Monitor can be used to make programmatic scaling decisions. Other approaches, like using the ReadThroughputAsync() call in the Azure Cosmos DB software development kits (SDKs) to get the ProvisionedThroughput value, or using the ProvisionedThroughput metric in Azure Monitor aren't recommended and leads to inaccurate results. These metrics represent billed throughput with a delay and shouldn't be used for scaling decisions.
Comparison – containers configured with manual vs. autoscale throughput
For more information, see this documentation about choosing between standard (manual) and autoscale throughput.
| Containers with standard (manual) throughput | Containers with autoscale throughput | |
|---|---|---|
| Provisioned throughput (RU/s) | Manually provisioned. | Automatically and instantaneously scaled based on the workload usage patterns. |
| Rate-limiting of requests/operations (429) | Might happen if consumption exceeds provisioned capacity. | Doesn't happen if you consume RU/s within the autoscale throughput range that is configured. |
| Capacity planning | You need to plan capacity and set the exact throughput you need. | The system automatically handles capacity planning and management. |
| Pricing | You pay for the manually provisioned RU/s per hour, using the standard (manual) RU/s per hour rate. | You pay per hour for the highest RU/s the system scaled up to within the hour. For single write region accounts, you pay for the RU/s used on an hourly basis, using the autoscale RU/s per hour rate. For accounts with multiple write regions, there's no extra charge for autoscale. You pay for the throughput used on hourly basis using the same multi-region write RU/s per hour rate. |
| Best suited for workload types | Predictable, stable workloads | Unpredictable, variable workloads |
Migrate standard provisioned throughput to autoscale
Users who want to migrate many resources from standard provisioned throughput to autoscale can use an Azure CLI script to migrate all throughput resources in an Azure subscription to autoscale.
Related content
- Review the autoscale FAQ.
- Learn how to choose between manual and autoscale throughput.
- Learn how to allocate autoscale throughput on an Azure Cosmos DB database or container.
- Learn more about partitioning in Azure Cosmos DB.