Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you'll use Azure App Configuration to externalize storage and management of your app settings for an Aspire project. You will use Azure App Configuration Aspire integration libraries to provision an App Configuration resource and use App Configuration in each distributed app.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription.
- Set up the development environment for Aspire.
- Create a new Aspire solution using the Aspire Starter template.
- An OCI compliant container runtime, such as Docker Desktop.
Test the app locally
The Aspire Starter template includes a frontend web app that communicates with a Minimal API project. The API project is used to provide fake weather data to the frontend. The frontend app is configured to use service discovery to connect to the API project. There is also an AppHost project which orchestrates all distributed applications in the Aspire solution.
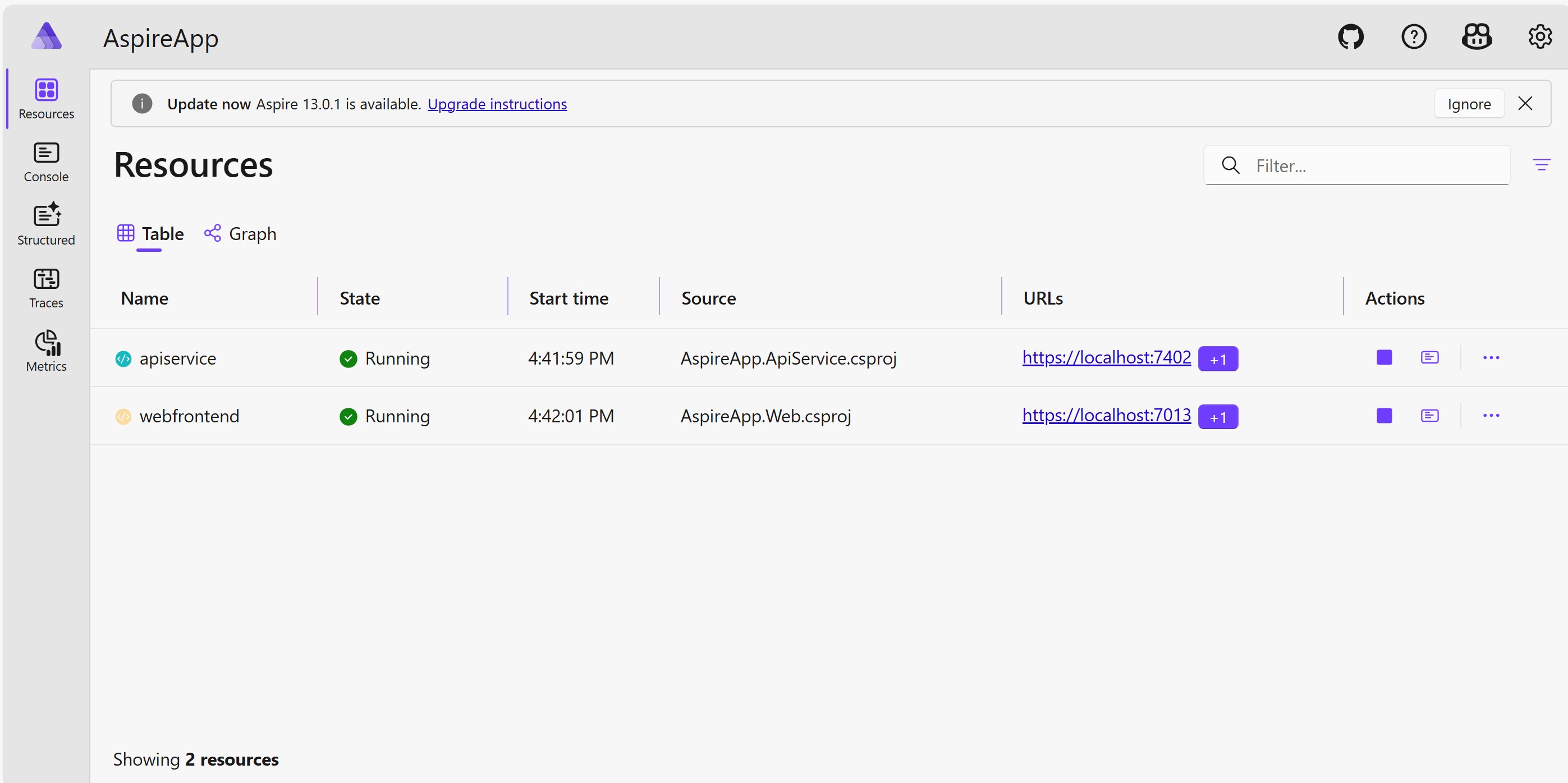
Run the
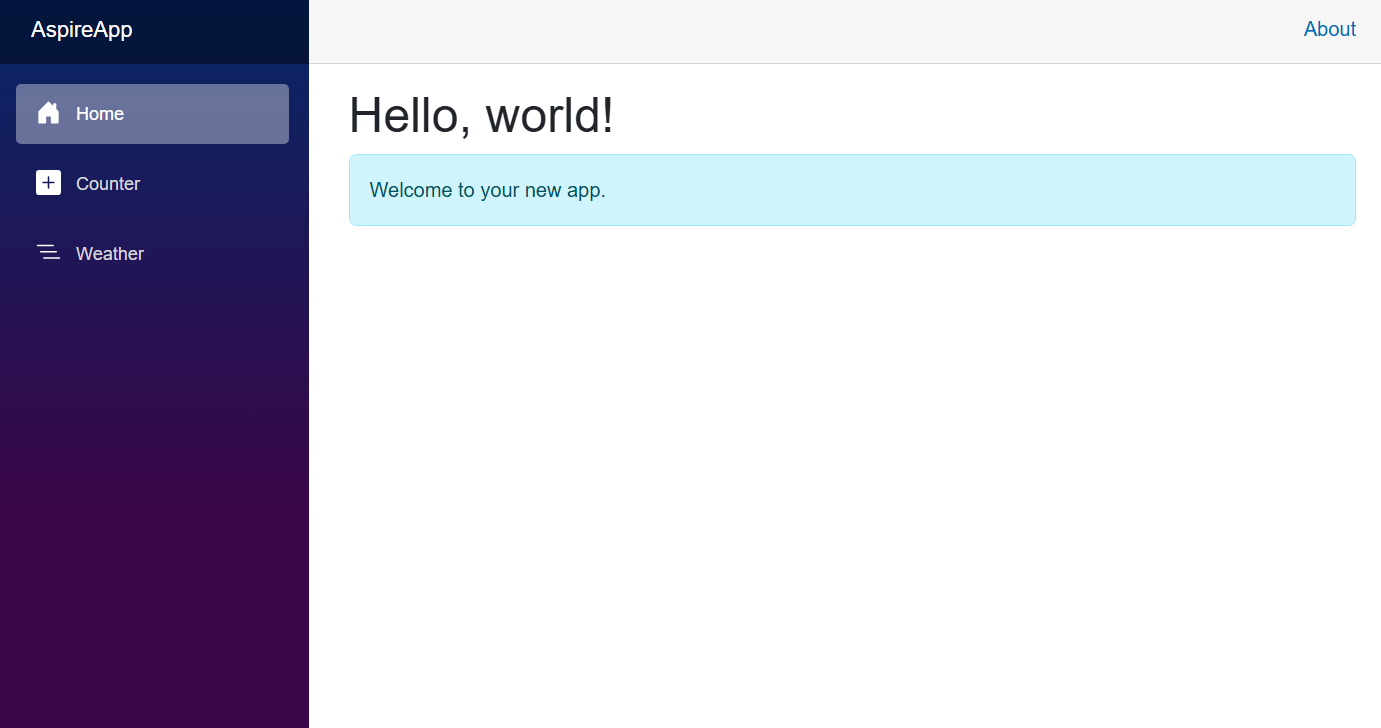
AppHostproject. You see the Aspire dashboard in your browser.Click the URL of the web frontend. You see a page with a welcome message.
Add Azure App Configuration to the Aspire solution
Navigate into to the
AppHostproject's directory. Run the following command to add theAspire.Hosting.Azure.AppConfigurationNuget package.dotnet add package Aspire.Hosting.Azure.AppConfigurationOpen the AppHost.csproj file to verify packages. You should see a package named
Aspire.Hosting.AppHostbeing referenced. Ensure that theAspire.Hosting.AppHostpackage version is at least as high as the version ofAspire.Hosting.Azure.AppConfigurationthat was installed.Open the AppHost.cs file and add the following code.
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add an Azure App Configuration resource var appConfiguration = builder.AddAzureAppConfiguration("appconfiguration");Important
When you call
AddAzureAppConfiguration, you instruct the app to generate Azure resources dynamically during app startup. The app must configure the appropriate subscription and location. For more information, see Local Azure provisioning. If you are using the latest Aspire SDK, you can configure the subscription information through the Aspire dashboard.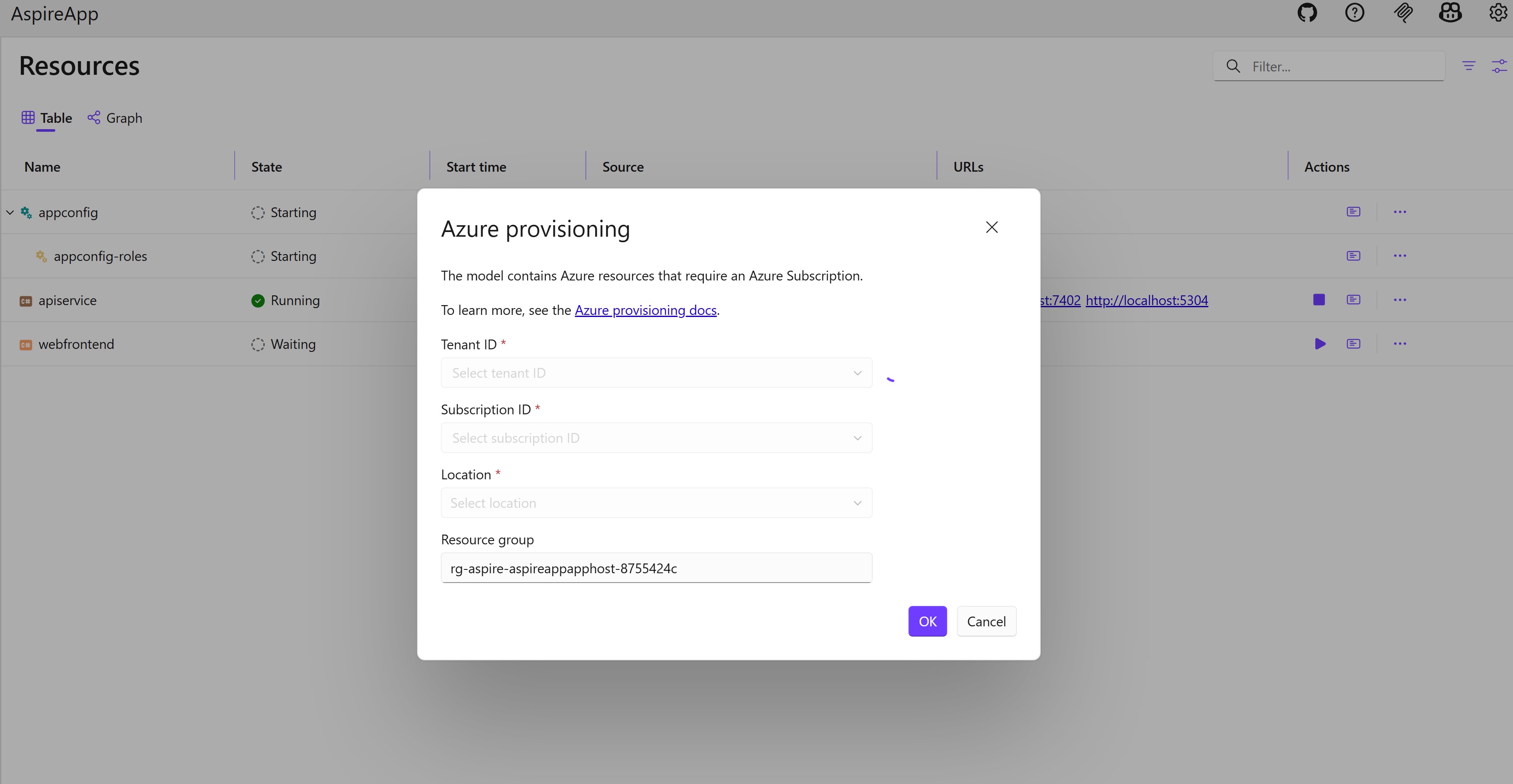
Note
You must have either the Owner or User Access Administrator role assigned on the Azure subscription. These roles are required to create role assignments as part of the provisioning process.
Tip
You can reference existing App Configuration resources by chaining a call
RunAsExisting()onbuilder.AddAzureAppConfiguration("appconfig"). For more information, go to Use existing Azure resources.Add the reference of App Configuration resource and configure the
webfrontendproject to wait for it.builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireApp_Web>("webfrontend") .WithExternalHttpEndpoints() .WithHttpHealthCheck("/health") .WithReference(apiService) .WaitFor(apiService) .WithReference(appConfiguration) // reference the App Configuration resource .WaitFor(appConfiguration); // wait for the App Configuration resource to enter the Running state before starting the resourceRun the
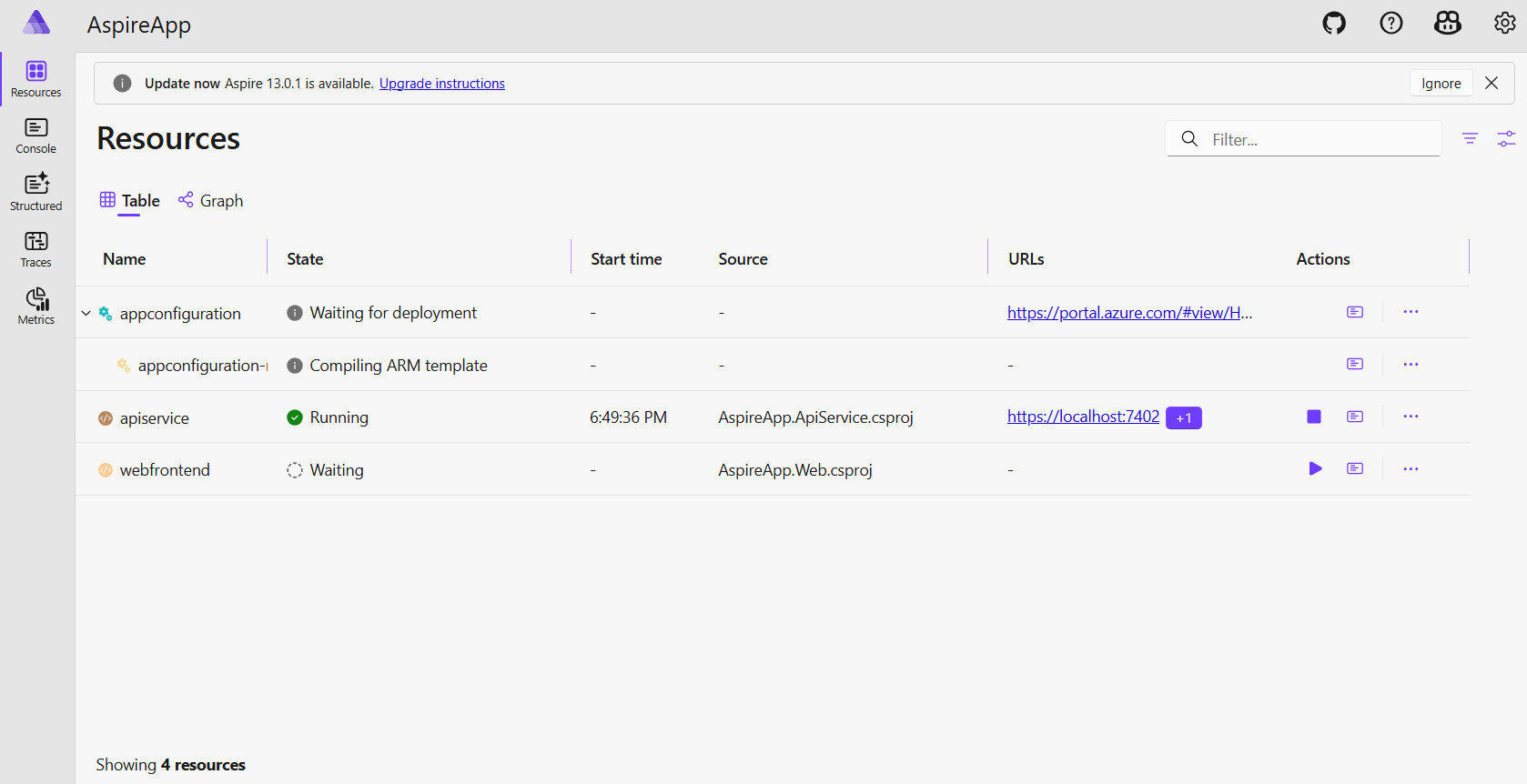
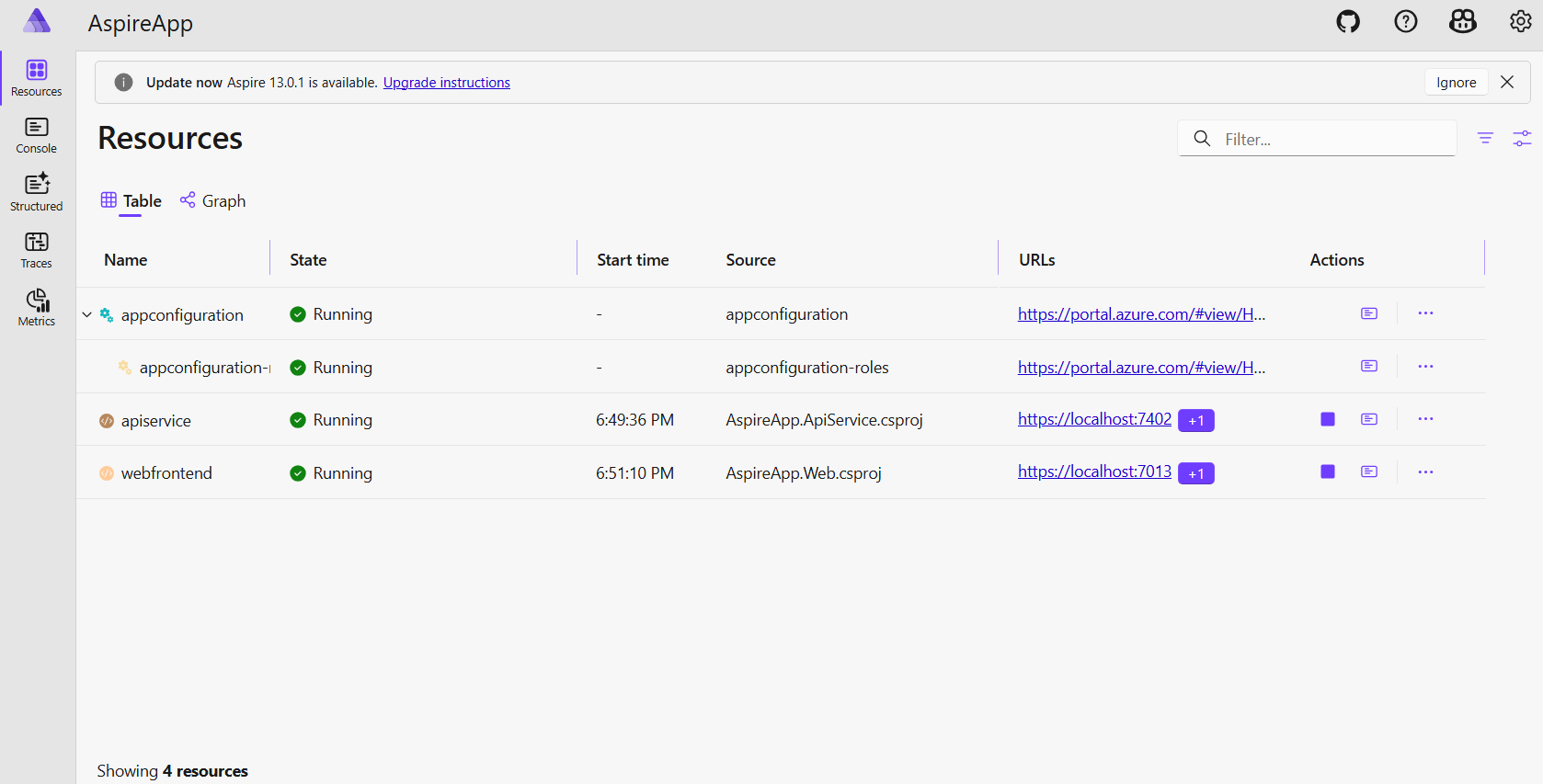
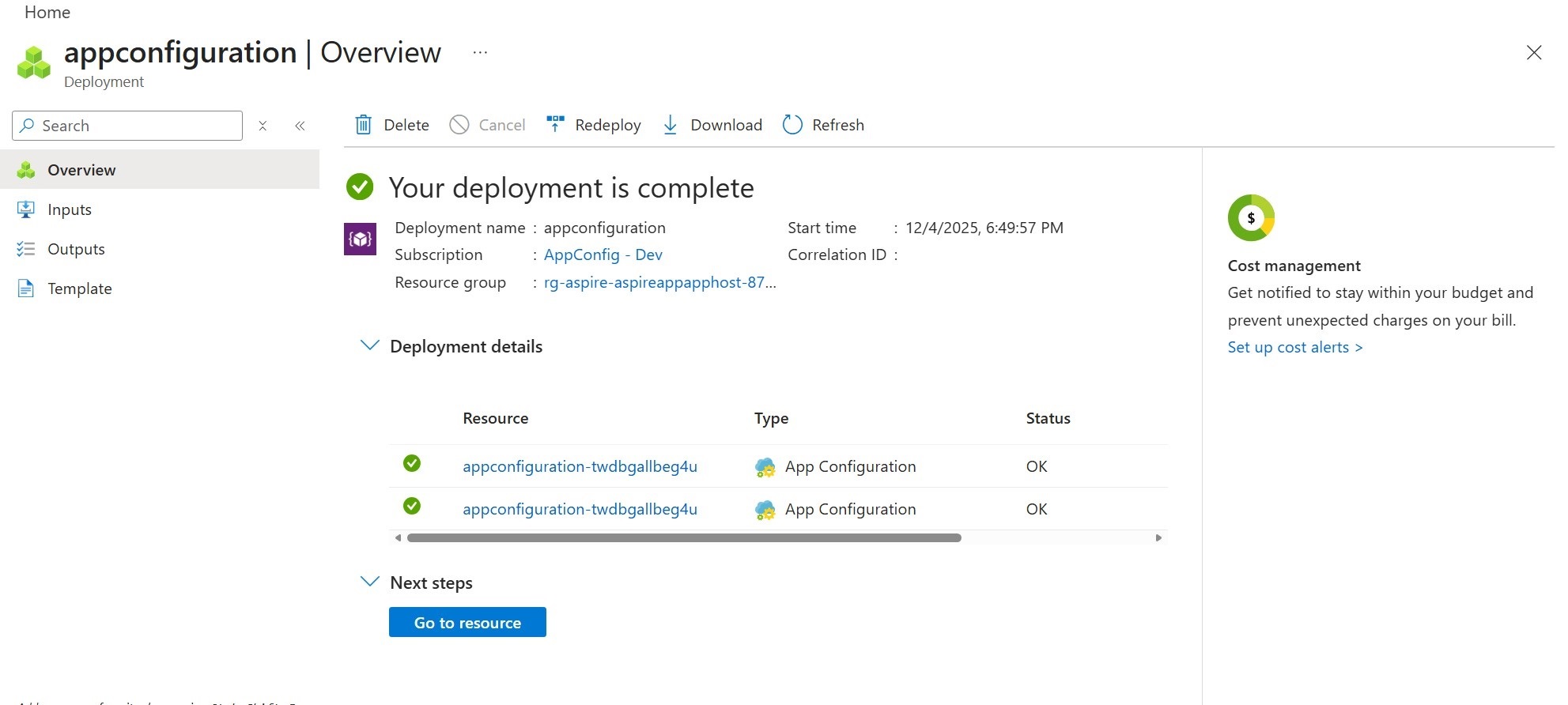
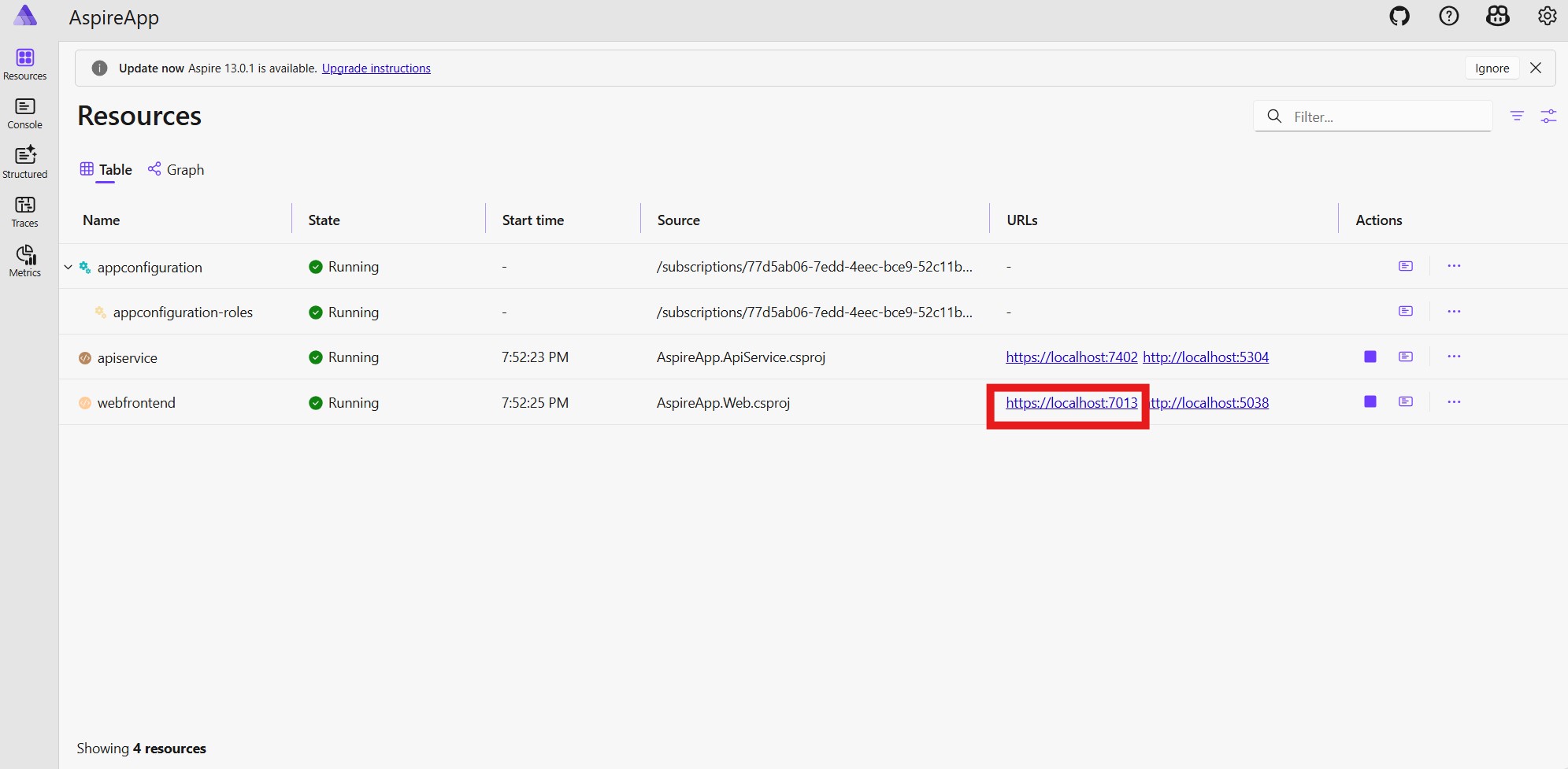
AppHostproject. You see the Azure App Configuration resource is provisioning.Wait for a few minutes and you see the Azure App Configuration resource is provisioned and is running.
Go to the Azure portal by clicking the deployment URL on the Aspire dashboard. You see the deployment is complete and you can go to your Azure App Configuration resource.
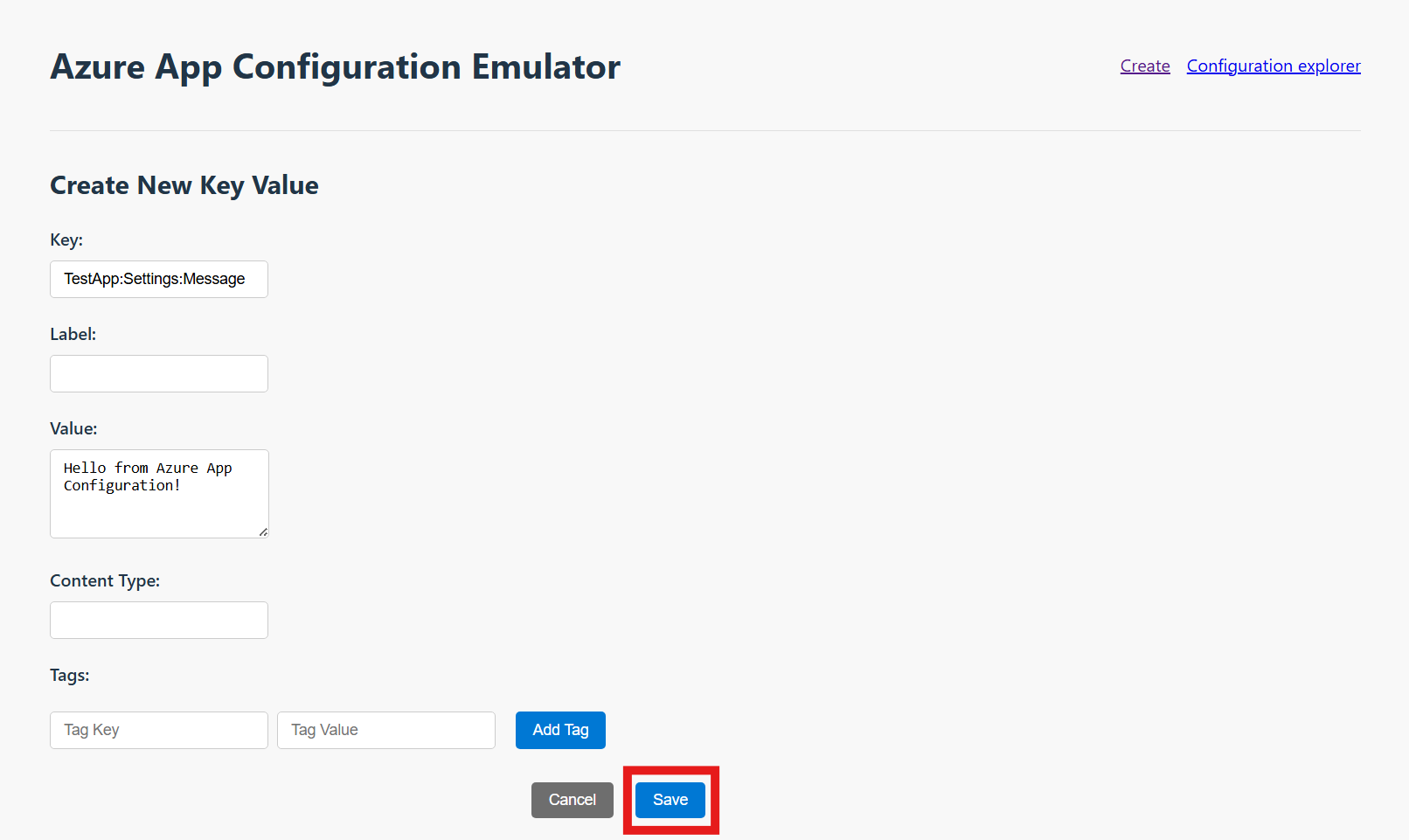
Add a key-value
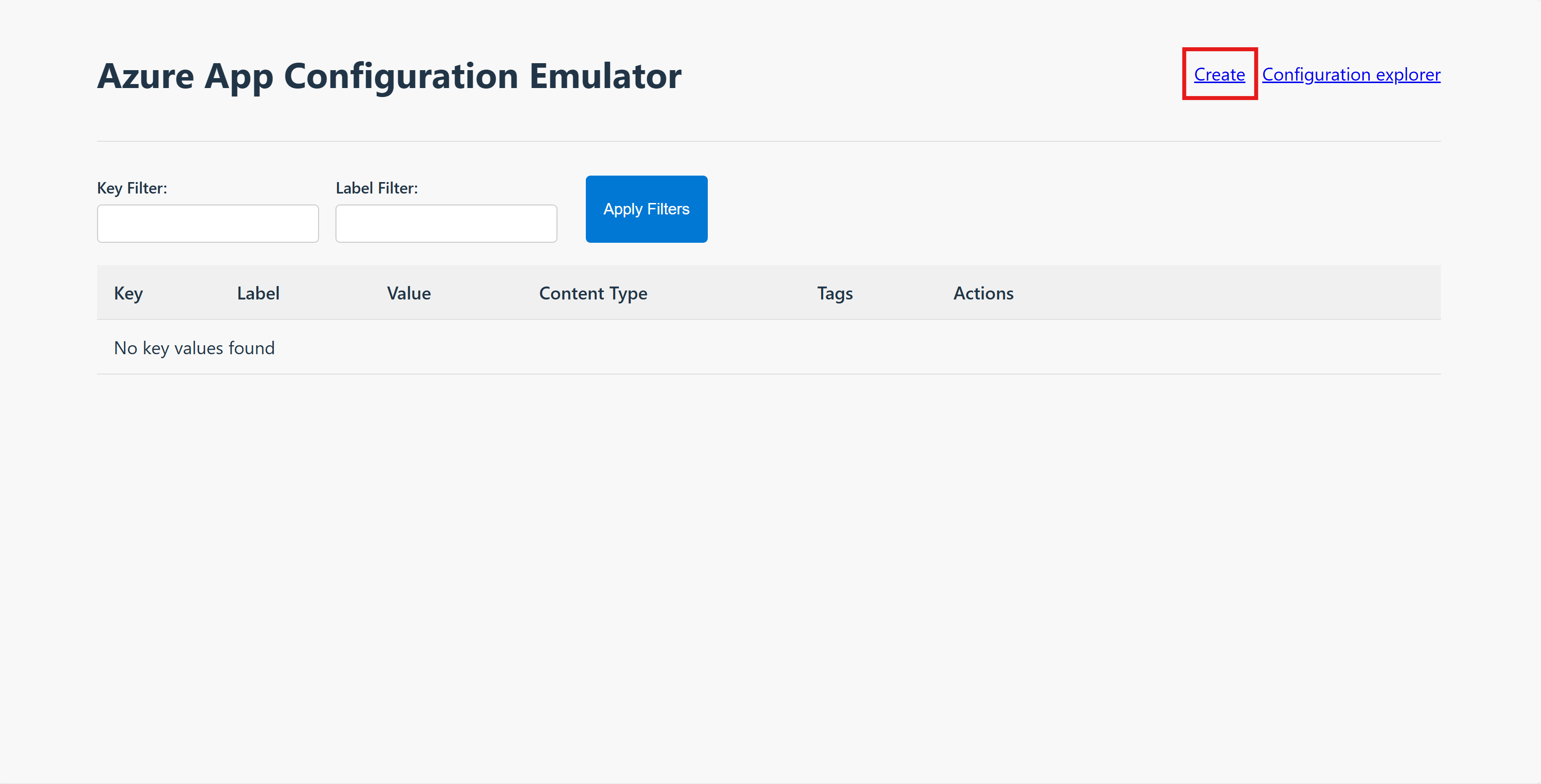
Add the following key-value to your App Configuration store and leave Label and Content Type with their default values. For more information about how to add key-values to a store using the Azure portal or the CLI, go to Create a key-value.
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| TestApp:Settings:Message | Hello from Azure App Configuration! |
Add Azure App Configuration to the Aspire solution
Navigate into to the
AppHostproject's directory. Run the following command to add theAspire.Hosting.Azure.AppConfigurationNuget package.dotnet add package Aspire.Hosting.Azure.AppConfigurationOpen the AppHost.csproj. Make sure that the
Aspire.Hosting.AppHostpackage version is not earlier than the version you installed. Otherwise, you need to upgrade theAspire.Hosting.AppHostpackage.Open the AppHost.cs file and add the following code.
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add an Azure App Configuration resource var appConfiguration = builder.AddAzureAppConfiguration("appconfiguration") .RunAsEmulator(emulator => { // use the App Configuration emulator emulator.WithDataBindMount(); });Important
When you call
RunAsEmulator, it pulls the App Configuration emulator image and runs a container as the App Configuration resource. Make sure that you have an OCI compliant container runtime on your machine. For more information, go to Aspire Container Runtime.Tip
You can call
WithDataBindMountorWithDataVolumeto configure the emulator resource for persistent container storage so that you don't need to recreate key values each time.Add the reference of App Configuration resource and configure the
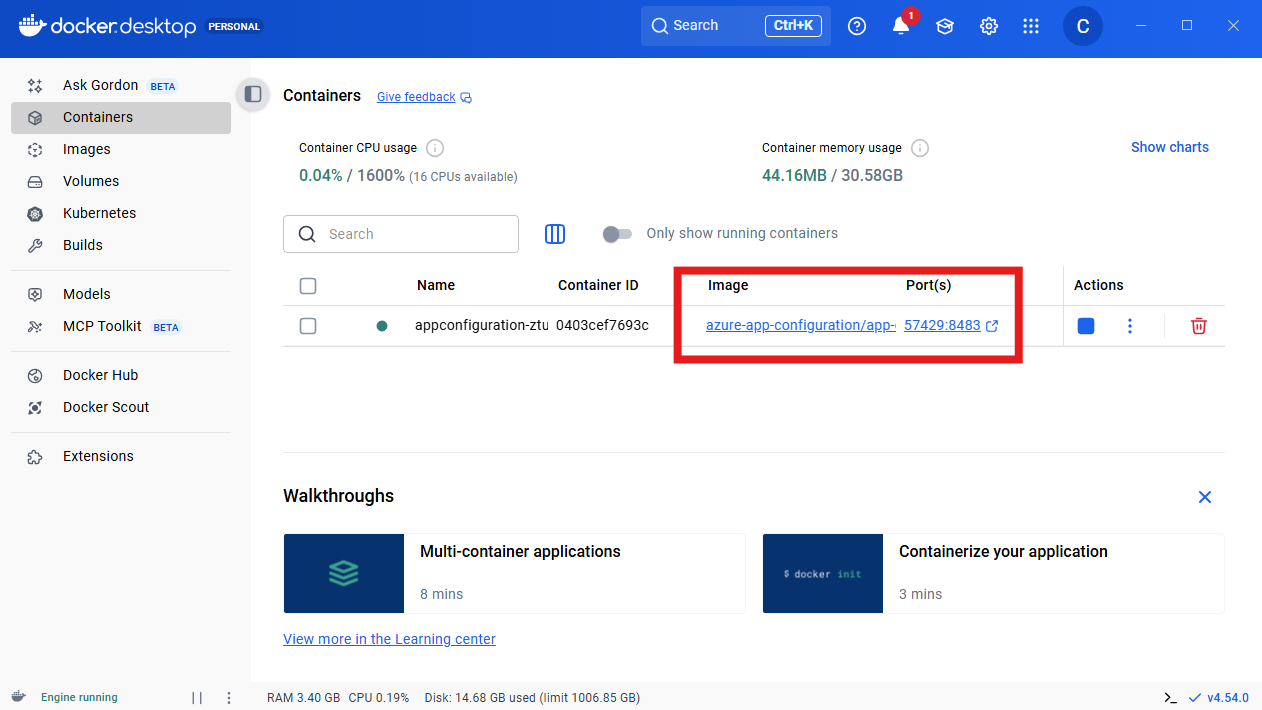
webfrontendproject to wait for it.builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireApp_Web>("webfrontend") .WithExternalHttpEndpoints() .WithHttpHealthCheck("/health") .WithReference(apiService) .WaitFor(apiService) .WithReference(appConfiguration) // reference the App Configuration resource .WaitFor(appConfiguration); // wait for the App Configuration resource to enter the Running state before starting the resourceStart your container runtime. In this tutorial, we use Docker Desktop.
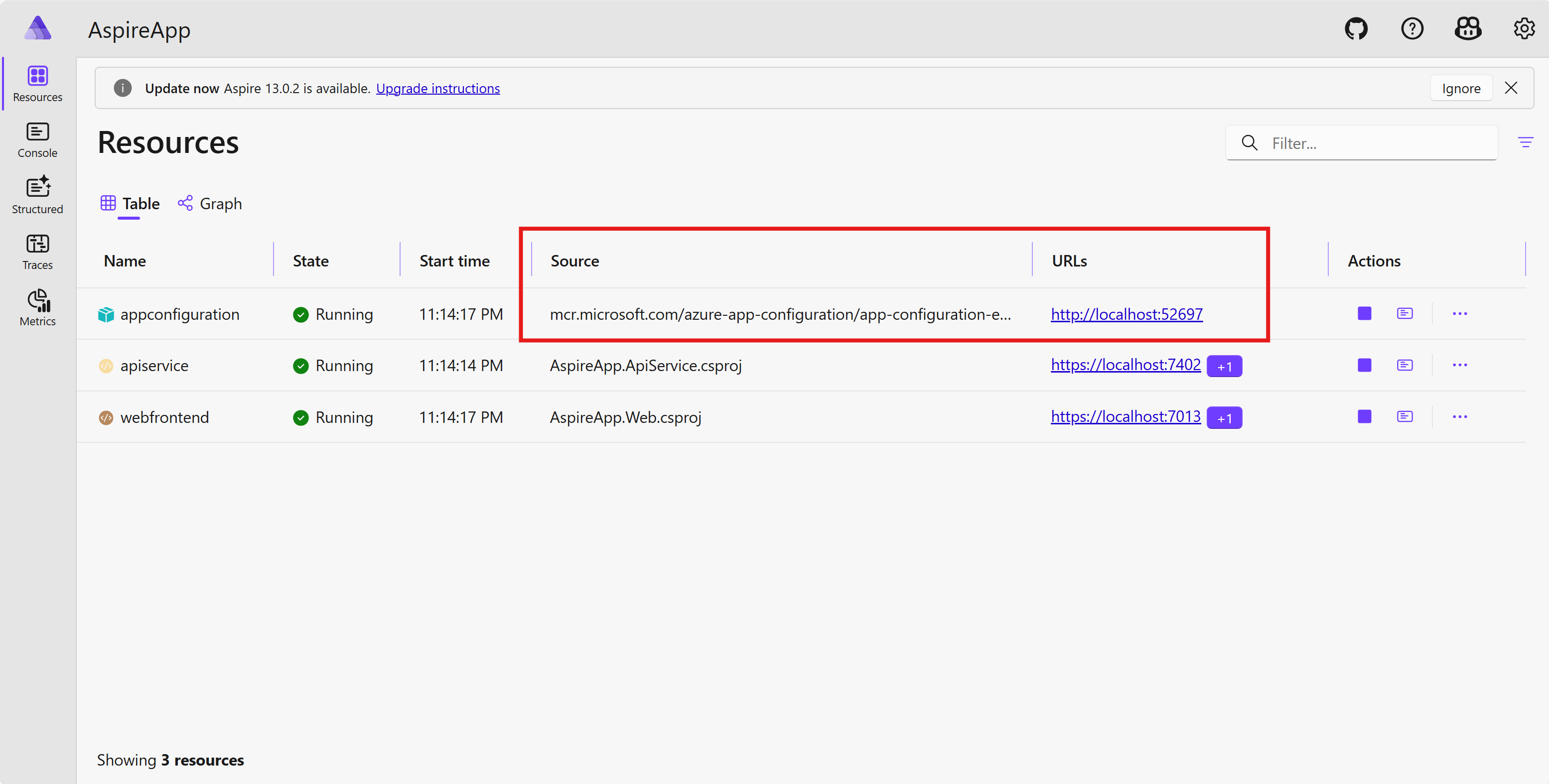
Run the
AppHostproject. Go to the Aspire dashboard. You see the App Configuration emulator resource is running.A container is started to run the App Configuration emulator.
Add a key-value
Use App Configuration in the web application
Navigate into to the
Webproject's directory. Run the following command to add theAspire.Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.AzureAppConfigurationNuget package.dotnet add package Aspire.Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.AzureAppConfigurationOpen the Program.cs file and add the following code.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Use Azure App Configuration builder.AddAzureAppConfiguration("appconfiguration"); // use the resource name defined in the AppHost projectOpen the Components/Pages/Home.razor file and update it with the following code.
@page "/" @inject IConfiguration Configuration <PageTitle>Home</PageTitle> <h1>Hello, world!</h1> @if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(message)) { <div class="alert alert-info">@message</div> } else { <div class="alert alert-info">Welcome to your new app.</div> } @code { private string? message; protected override void OnInitialized() { string msg = Configuration["TestApp:Settings:Message"]; message = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(msg) ? null : msg; } }Restart the
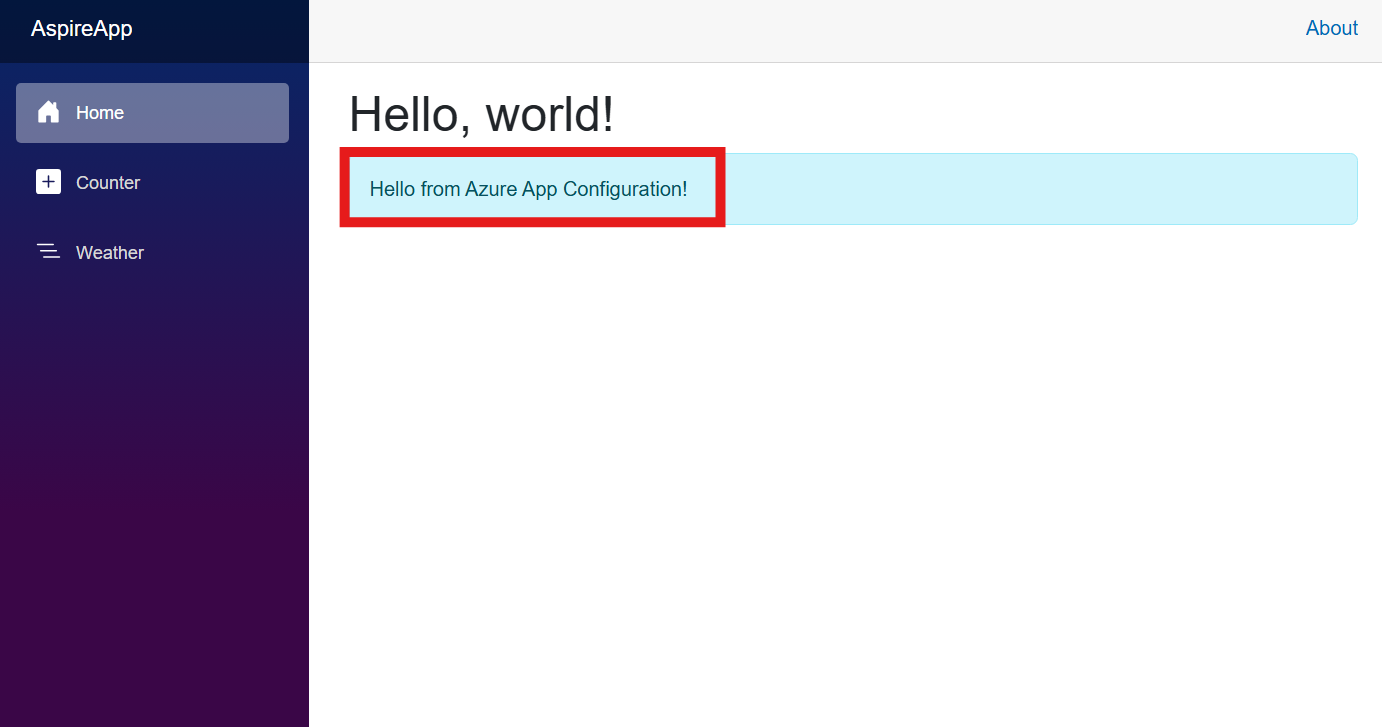
AppHostproject. Go to the Aspire dashboard and click the URL of the web frontend.You see a page with a welcome message from Azure App Configuration.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you:
- Added an Azure App Configuration resource in an Aspire solution.
- Read your key-values from Azure App Configuration with the App Configuration Aspire integration library.
- Displayed a web page using the settings you configured in your App Configuration.
To learn how to configure your Aspire app to dynamically refresh configuration settings, continue to the next tutorial.
To learn how to use feature flags in your Aspire app, continue to the next tutorial.
To learn more about the Azure App Configuration emulator, continue to the following document.