Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Azure Cache for Redis announced its retirement timeline for all SKUs. We recommend moving your existing Azure Cache for Redis instances to Azure Managed Redis as soon as you can.
For more details about the retirement:
Managing access to your Azure Redis cache instance is critical to ensuring that the right users have access to the right set of data and commands. Redis version 6 introduced the Access Control List (ACL), which lists the keys that specific users can access and the commands that they can execute. For example, you can prohibit specific users from using the DEL command to delete keys in the cache.
Azure Cache for Redis integrates this ACL functionality with Microsoft Entra to allow you to configure and assign data access policies for your application's users, service principal, and managed identity. Azure Cache for Redis offers three built-in access policies that you can assign via role-based access control (RBAC): Data Owner, Data Contributor, and Data Reader.
If the built-in access policies don't satisfy your data protection and isolation requirements, you can create and use your own custom data access policies. This article describes configuring a custom data access policy for Azure Cache for Redis and enabling RBAC via Microsoft Entra authentication.
Scope of availability
| Tier | Basic, Standard, Premium |
|---|---|
| Availability | Yes |
Limitations
- Redis ACL and data access policies aren't supported on Azure Redis instances that run Redis version 4.
- Microsoft Entra authentication and authorization are supported only for Secure Socket Layer (SSL) connections.
- Some Redis commands are blocked in Azure Cache for Redis. For more information, see Redis commands not supported in Azure Cache for Redis.
Redis ACL permissions
Redis ACL in Redis version 6.0 allows configuring access permissions for three areas: command categories, commands, and keys.
Command categories
Redis created command categories, such as administrative commands and dangerous commands, to make setting permissions on a group of commands easier. In a permissions string, use +@<category> to allow a command category or -@<category> to disallow a command category.
Redis supports the following useful command categories. For more information and a full list, see the Command Categories heading in the Redis ACL documentation.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
admin |
Administrative commands, such as MONITOR and SHUTDOWN. Normal applications never need to use these commands. |
dangerous |
Potentially dangerous commands, including FLUSHALL, RESTORE, SORT, KEYS, CLIENT, DEBUG, INFO, and CONFIG. Consider each with care, for various reasons. |
keyspace |
Includes DEL, RESTORE, DUMP, RENAME, EXISTS, DBSIZE, KEYS, EXPIRE, TTL, and FLUSHALL. Writing or reading from keys, databases, or their metadata in a type agnostic way. Commands that only read the keyspace, key, or metadata have the read category. Commands that can modify the keyspace, key, or metadata also have the write category. |
pubsub |
PubSub-related commands. |
read |
Reading from keys, values or metadata. Commands that don't interact with keys don't have either read or write. |
set |
Data type: sets related. |
sortedset |
Data type: sorted sets related. |
stream |
Data type: streams related. |
string |
Data type: strings related. |
write |
Writing values or metadata to keys. |
Note
Commands that are blocked for Azure Redis remain blocked within the categories.
Commands
Commands allow you to control which specific commands a particular Redis user can run. In a permissions string, use +<command> to allow a command or -<command> to disallow a command.
Keys
Keys allow you to control access to specific keys or groups of keys stored in the cache. Use ~<pattern> in a permission string to provide a pattern for keys. Use either ~* or allkeys to indicate that the permissions apply to all keys in the cache.
Configure a custom data access policy for your application
To configure a custom data access policy, you create a permissions string to use as your custom access policy, and enable Microsoft Entra authentication for your cache.
Specify permissions
Configure permission strings according to your requirements. The following examples show permission strings for various scenarios:
| Permissions string | Description |
|---|---|
+@all allkeys |
Allow application to execute all commands on all keys. |
+@read ~* |
Allow application to execute only read command category. |
+@read +set ~Az* |
Allow application to execute read command category and set command on keys with prefix Az. |
Create the custom data access policy
In the Azure portal, select the Azure Redis cache where you want to create the data access policy.
Select Data Access Configuration under Settings in the left navigation menu.
On the Data Access Configuration page, select Add > New Access Policy.
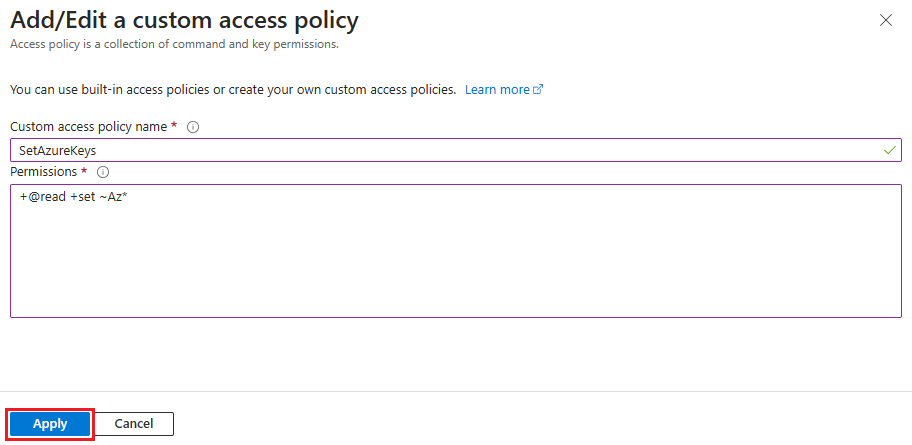
On the Add/Edit a custom access policy screen, provide a name for your access policy.
Under Permissions, add your custom permissions string, and then select Apply.
The custom policy now appears on the Access Policies tab of the Data Access Configuration page, along with the three built-in Azure Redis policies.
Enable Microsoft Entra authentication
To assign a user to an access policy by using Microsoft Entra, you must have Microsoft Entra rather than Access Keys authentication enabled on your cache. To check your authentication method, select Authentication under Settings in the left navigation menu for your cache.
On the Authentication screen, if Disable Access Keys Authentication is selected and no access keys appear on the screen, your cache already uses Microsoft Entra authentication. Otherwise, select the checkbox next to Disable Access Keys Authentication and then select Save.

Respond Yes to the popup dialog box asking if you want to disable access keys authentication.
Important
Once the Microsoft Entra enable operation is complete, the nodes in your cache instance reboot to load the new configuration. The operation can take up to 30 minutes. It's best to perform this operation during your maintenance window or outside peak business hours.
Configure your Redis client to use Microsoft Entra ID
Most Azure Cache for Redis clients assume that a password and access key are used for authentication. You might need to update your client workflow to support authentication and authorization using a specific Microsoft Entra user name and password. To learn how to configure your client application to connect to your cache instance as a specific Redis user, see Configure your Redis client to use Microsoft Entra ID.