Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
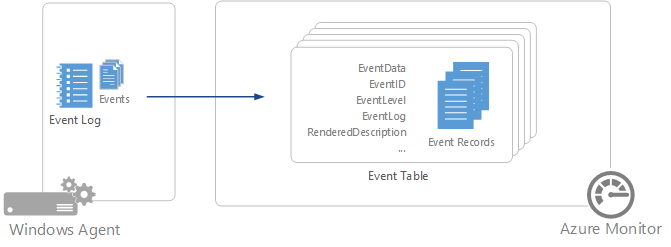
Windows event logs are one of the most common data sources for Log Analytics agents on Windows virtual machines because many applications write to the Windows event log. You can collect events from standard logs, such as System and Application, and any custom logs created by applications you need to monitor.
Important
The legacy Log Analytics agent is deprecated as of August 31, 2024. Microsoft will no longer provide any support for the Log Analytics agent. If you use the Log Analytics agent to ingest data to Azure Monitor, migrate now to Azure Monitor agent.
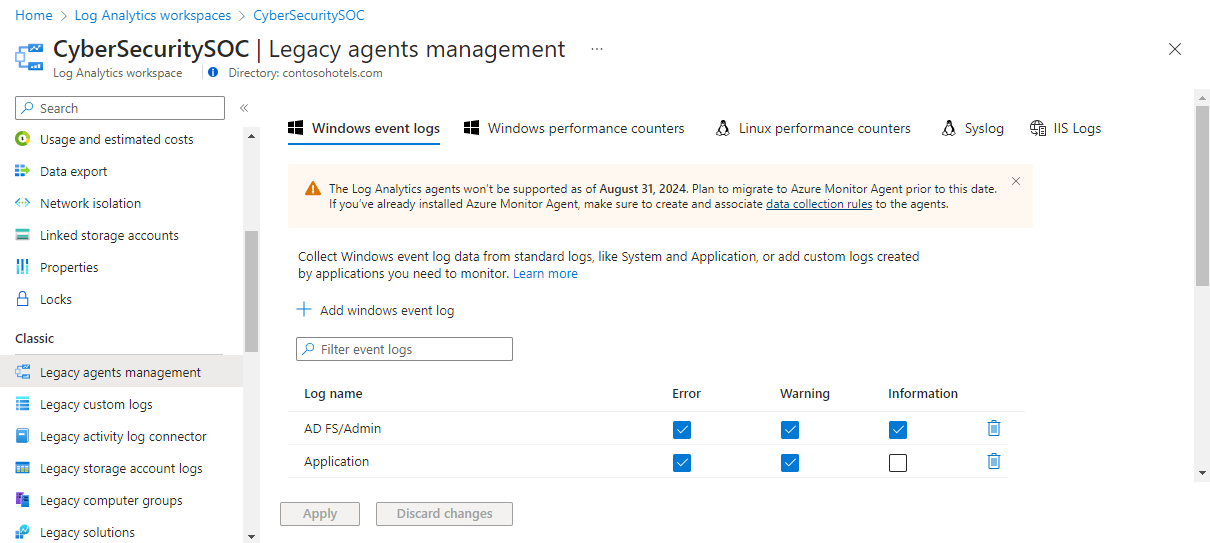
Configure Windows event logs from the Legacy agents management menu for the Log Analytics workspace.
Azure Monitor only collects events from Windows event logs that are specified in the settings. You can add an event log by entering the name of the log and selecting +. For each log, only the events with the selected severities are collected. Check the severities for the particular log that you want to collect. You can't provide any other criteria to filter events.
As you enter the name of an event log, Azure Monitor provides suggestions of common event log names. If the log you want to add doesn't appear in the list, you can still add it by entering the full name of the log. You can find the full name of the log by using event viewer. In event viewer, open the Properties page for the log and copy the string from the Full Name field.
Important
You can't configure collection of security events from the workspace by using the Log Analytics agent. You must use Microsoft Defender for Cloud or Microsoft Sentinel to collect security events. The Azure Monitor agent can also be used to collect security events.
Critical events from the Windows event log will have a severity of "Error" in Azure Monitor Logs.
Azure Monitor collects each event that matches a selected severity from a monitored event log as the event is created. The agent records its place in each event log that it collects from. If the agent goes offline for a while, it collects events from where it last left off, even if those events were created while the agent was offline. There's a potential for these events to not be collected if the event log wraps with uncollected events being overwritten while the agent is offline.
Note
Azure Monitor doesn't collect audit events created by SQL Server from source MSSQLSERVER with event ID 18453 that contains keywords Classic or Audit Success and keyword 0xa0000000000000.
Windows event records have a type of event and have the properties in the following table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Computer | Name of the computer that the event was collected from. |
| EventCategory | Category of the event. |
| EventData | All event data in raw format. |
| EventID | Number of the event. |
| EventLevel | Severity of the event in numeric form. |
| EventLevelName | Severity of the event in text form. |
| EventLog | Name of the event log that the event was collected from. |
| ParameterXml | Event parameter values in XML format. |
| ManagementGroupName | Name of the management group for System Center Operations Manager agents. For other agents, this value is AOI-<workspace ID>. |
| RenderedDescription | Event description with parameter values. |
| Source | Source of the event. |
| SourceSystem | Type of agent the event was collected from. OpsManager - Windows agent, either direct connect or Operations Manager managed. Linux - All Linux agents. AzureStorage - Azure Diagnostics. |
| TimeGenerated | Date and time the event was created in Windows. |
| UserName | User name of the account that logged the event. |
The following table provides different examples of log queries that retrieve Windows event records.
| Query | Description |
|---|---|
| Event | All Windows events. |
| Event | where EventLevelName == "Error" | All Windows events with severity of error. |
| Event | summarize count() by Source | Count of Windows events by source. |
| Event | where EventLevelName == "Error" | summarize count() by Source | Count of Windows error events by source. |
- Configure Log Analytics to collect other data sources for analysis.
- Learn about log queries to analyze the data collected from data sources and solutions.
- Configure collection of performance counters from your Windows agents.