Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can use diagnostic settings in Azure Monitor to collect resource logs and to send platform metrics and the activity log to various destinations. Create a separate diagnostic setting for each resource that you want to collect data from. Each setting defines the data from the resource to collect and the destinations to send that data to. This article describes the details of diagnostic settings, including how to create them and the destinations available for sending data.
Warning
Delete any diagnostic settings for a resource if you delete or rename that resource, or if you migrate it across resource groups or subscriptions. If the diagnostic setting isn't removed and this resource is re-created, any diagnostic settings for the deleted resource could be applied to the new one. For some resource types, this situation would resume the collection of resource logs as defined in the diagnostic setting.
Sources
Diagnostic settings can collect data from the sources in the following table. For details on the data that each source collects and its format in each destination, see the linked article.
| Data source | Description |
|---|---|
| Platform metrics | Automatically collected without configuration. Use a diagnostic setting to send platform metrics to other destinations. |
| Activity log | Automatically collected without configuration. Use a diagnostic setting to send activity log entries to other destinations. |
| Resource logs | Aren't collected by default. Create a diagnostic setting to collect resource logs. |
Destinations
Diagnostic settings send data to the destinations in the following table. To help ensure the security of data in transit, all destination endpoints are configured to support TLS 1.2.
A single diagnostic setting can define no more than one of each destination. If you want to send data to more than one of a particular destination type (for example, two Log Analytics workspaces), create multiple settings. Each resource can have up to five diagnostic settings.
Any destinations that a diagnostic setting uses must exist before you can create the setting. The destination doesn't have to be in the same subscription as the resource that's sending logs if the user who configures the setting has appropriate Azure role-based access control (RBAC) access to both subscriptions. Use Azure Lighthouse to include destinations in another Microsoft Entra tenant.
| Destination | Description | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Log Analytics workspace | Retrieve data by using log queries and workbooks. Use log alerts to proactively alert on data. For the tables that various Azure resources use, see the Azure Monitor resource log reference. | Any tables in a Log Analytics workspace are created automatically when the first data is sent to the workspace, so only the workspace itself must exist. |
| Azure Storage account | Store for audit, static analysis, or backup. Storage might be less expensive than other options and can be kept indefinitely. Send data to immutable storage to prevent its modification. Set the immutable policy for the storage account as described in Configure immutability policies for blob versions. | Storage accounts must be in the same region as the resource that you're monitoring if the resource is regional. Diagnostic settings can't access storage accounts when virtual networks are enabled. You must enable Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall setting in storage accounts so that the Azure Monitor diagnostic settings service is granted access to your storage account. Azure DNS zone endpoints (preview) and any Premium storage accounts aren't supported as destinations. Any Standard storage accounts are supported. |
| Azure Event Hubs | Stream data to external systems such as non-Microsoft security information and event management (SIEM) solutions and other Log Analytics solutions. | Event hubs must be in the same region as the resource that you're monitoring if the resource is regional. You can't use a compacted event hub because it requires the message to have a partition key, which Azure Monitor doesn't include. Diagnostic settings can't access event hubs when virtual networks are enabled. You must enable Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall setting in event hubs so that the Azure Monitor diagnostic settings service is granted access to your event hub resources. The shared access policy for an Event Hubs namespace defines the permissions that the streaming mechanism has. Streaming to event hubs requires Manage, Send, and Listen permissions. To update the diagnostic setting to include streaming, you must have the ListKey permission on that Event Hubs authorization rule. |
Methods for creating a diagnostic setting
You can create a diagnostic setting by using any of the following methods.
To create a diagnostic setting for the activity log by using the Azure portal, see Export activity log. To create a diagnostic setting for a management group, see Management Group Diagnostic Settings.
Use the following steps to create a new diagnostic setting or to edit an existing one in the Azure portal:
On a resource's menu, in the Monitoring section, select Diagnostic settings. Or, on the Azure Monitor menu, select Settings > Diagnostic settings. Then select the resource.
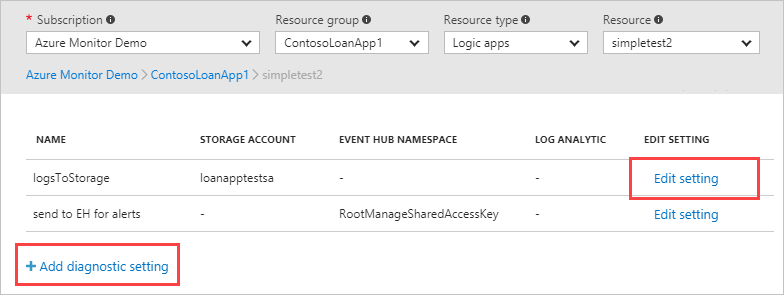
Select Add diagnostic setting to add a new setting, or select Edit setting to edit an existing one.
You might need multiple diagnostic settings for a resource if you want to send to multiple destinations of the same type. The following example shows the settings for a key vault resource, but the screen is similar for other resources.
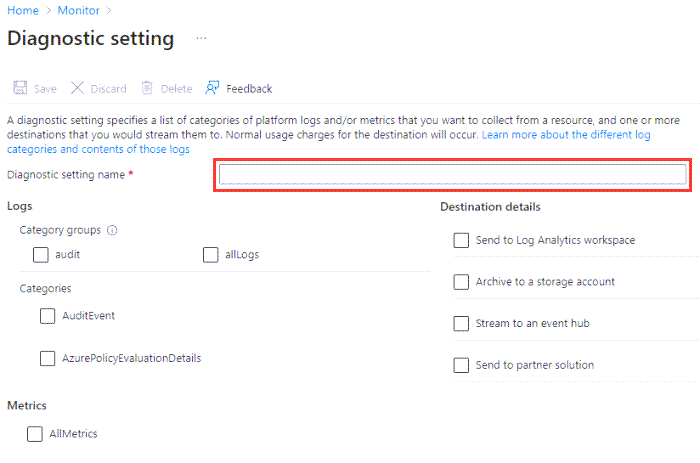
Give your setting a descriptive name if it doesn't already have one.
This screenshot shows an example key vault. Other types of resources have different sets of categories.
For Logs, either choose a category group or select the individual checkboxes for each category of data that you want to send to the destinations. The list of categories varies for each Azure service.
For Metrics, select AllMetrics if you want to collect platform metrics.
For Destination details, select the checkbox for each destination that you want to include in the diagnostic settings. Then provide the details for each destination.
If you select a Log Analytics workspace as a destination, you might need to specify the collection mode. For details, see Collection mode.
Warning
When you create or update diagnostic settings for a storage account or an Event Hubs namespace, you can't select that account or namespace a destination for the resource logs or metrics data. This limitation is by design. Sending resource logs or metrics from a resource to the same resource would generate an infinite loop of generating and writing data.
This design applies only to the Azure portal UX layer. If there's truly a need to write data to the same resource and you're willing to accept the associated risks, you can create the diagnostic setting by using Azure PowerShell, the Azure CLI, the REST API, a Resource Manager template, or a supported Microsoft SDK.
Category groups
You can use category groups to collect resource logs based on predefined groupings instead of selecting individual log categories. Microsoft defines the groupings to help monitor common use cases. If the categories in the group are updated, your log collection is modified automatically.
Not all Azure services use category groups. If category groups aren't available for a particular resource, the option won't be available when you create the diagnostic setting.
If you do use category groups in a diagnostic setting, you can't select individual category types. Currently, there are two category groups:
allLogs: All categories for the resource.audit: All resource logs that record customer interactions with data or the settings of the service. You don't need to select this category group if you select theallLogscategory group.
Note
Enabling the audit category in the diagnostic settings for Azure SQL Database does not activate auditing for the database. To enable database auditing, you have to enable it from the auditing pane for Azure SQL Database.
Metrics limitations
Not all metrics can be sent to a Log Analytics workspace with diagnostic settings. See the Exportable column in the list of supported metrics.
Diagnostic settings don't currently support multidimensional metrics. Metrics with dimensions are exported as flattened single-dimensional metrics and aggregated across dimension values. For example, the IOReadBytes metric on a blockchain can be explored and charted on a per-node level. When the metric is exported with diagnostic settings, it shows all read bytes for all nodes.
To work around the limitations for specific metrics, you can manually extract them by using the Metrics REST API. You can then import them into a Log Analytics workspace by using the Logs Ingestion API.
Controlling costs
There might be a cost for data that diagnostic settings collect. The cost depends on the destination that you choose and the volume of collected data. For more information, see Azure Monitor pricing.
Collect only the categories that you need for each service. You might also not want to collect platform metrics from Azure resources, because this data is already being collected in Metrics. Configure your diagnostic data to collect metrics only if you need metric data in the workspace for more complex analysis with log queries.
Diagnostic settings don't allow granular filtering within a selected category. You can filter data for supported tables in a Log Analytics workspace by using transformations. For details, see Transformations in Azure Monitor.
Time before data gets to destinations
After you create a diagnostic setting, data should start flowing to your selected destinations within 90 minutes. When you're sending data to a Log Analytics workspace, the table is created automatically if it doesn't already exist. The table is created only when the destinations receive the first log records.
If you get no information within 24 hours, you might be experiencing one of the following problems:
- No logs are being generated.
- Something is wrong in the underlying routing mechanism.
Try disabling the configuration and then reenabling it. If the problem continues, contact Azure support through the Azure portal.
Application Insights
Consider the following information for diagnostic settings for Application Insights applications:
- The destination can't be the same Log Analytics workspace that your Application Insights resource is based on.
- The Application Insights user can't have access to both workspaces. Set the Log Analytics access control mode to Requires workspace permissions. Through Azure RBAC, ensure that the user has access to only the Log Analytics workspace that the Application Insights resource is based on.
These steps are necessary because Application Insights accesses data across resources to provide complete end-to-end transaction operations and accurate application maps. These resources include Log Analytics workspaces. Because diagnostic logs use the same table names, duplicate data can appear if the user has access to multiple resources that contain the same data.
Troubleshooting
Metric category isn't supported
You might receive an error message similar to "Metric category 'xxxx' is not supported" when you're using a Resource Manager template, the REST API, the Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell. Metric categories other than AllMetrics aren't supported, except for a limited number of Azure services. Remove any metric category names other than AllMetrics and repeat your deployment.
Setting disappears due to non-ASCII characters in a resource ID
Diagnostic settings don't support resource IDs with non-ASCII characters (for example, Preproduccón). Because you can't rename resources in Azure, you must create a new resource without the non-ASCII characters. If the characters are in a resource group, you can move the resources to a new group.
Resource is inactive
When a resource is inactive and exporting zero-value metrics, the diagnostic settings' export mechanism backs off incrementally to avoid unnecessary costs of exporting and storing zero values. This back-off might lead to a delay in the export of the next nonzero value. This behavior applies only to exported metrics and doesn't affect metrics-based alerts or autoscale.
When a resource is inactive for one hour, the export mechanism backs off to 15 minutes. This situation means that there's a potential latency of up to 15 minutes for the next nonzero value to be exported. The resource reaches maximum backoff time of two hours after seven days of inactivity. After the resource starts exporting nonzero values, the export mechanism reverts to the original export latency of three minutes.