Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This article reviews the vCore purchasing model for Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Overview
A virtual core (vCore) represents a logical CPU and offers you the option to choose the physical characteristics of the hardware (for example, the number of cores, the memory, and the storage size). The vCore-based purchasing model gives you flexibility, control, transparency of individual resource consumption, and a straightforward way to translate on-premises workload requirements to the cloud. This model optimizes price, and allows you to choose compute, memory, and storage resources based on your workload needs.
In the vCore-based purchasing model, your costs depend on the choice and usage of:
- Service tier
- Hardware configuration
- Compute resources (the number of vCores and the amount of memory)
- Reserved database storage
- Actual backup storage
The virtual core (vCore) purchasing model used by Azure SQL Managed Instance provides the following benefits:
- Control over hardware configuration to better match the compute and memory requirements of the workload.
- Pricing discounts for Azure Hybrid Benefit (AHB).
- Greater transparency in the hardware details that power compute, helping facilitate planning for migrations from on-premises deployments.
- Higher scaling granularity with multiple compute sizes available.
Compute
SQL Managed Instance compute provides a specific amount of compute resources that are continuously provisioned independent of workload activity, and bills for the amount of compute provisioned at a fixed price per hour.
Since three additional replicas are automatically allocated in the Business Critical service tier, the price is approximately 2.7 times higher than it is in the General Purpose service tier. Likewise, the higher storage price per GB in the Business Critical service tier reflects the higher IO limits and lower latency of the local SSD storage.
For instances in the General Purpose service tier, it's possible to save on compute and licensing costs by stopping your instance when you're not using it. Review Stop and start an instance to learn more.
Data and log storage
The following factors affect the amount of storage used for data and log files, and apply to General Purpose and Business Critical tiers.
- In the General Purpose service tier,
tempdbuses local SSD storage, and this storage cost is included in the vCore price. - In the Business Critical service tier,
tempdbshares local SSD storage with data and log files, andtempdbstorage cost is included in the vCore price. - The maximum storage size for a SQL Managed Instance must be specified in multiples of 32 GB.
Important
In both service tiers, you are charged for the maximum storage size configured for a managed instance.
To monitor total consumed instance storage size for SQL Managed Instance, use the storage_space_used_mb metric. To monitor the current allocated and used storage size of individual data and log files in a database using T-SQL, use the sys.database_files view and the FILEPROPERTY(... , 'SpaceUsed') function.
Backup storage
Storage for database backups is allocated to support the capabilities of SQL Managed Instance. This storage is separate from data and log file storage, and is billed separately.
- Point-in-time restore (PITR): The storage consumption depends on the rate of change of the database and the retention period configured for backups. You can configure a separate retention period for each database between 1 to 35 days for SQL Managed Instance. A backup storage amount equal to the configured maximum data size is provided at no extra charge.
- Long-term retention (LTR): You have the option to configure long-term retention of full backups for up to 10 years. The configuration you choose determines how much storage will be used for LTR backups.
Service tiers
The service tier generally defines the storage architecture, space and I/O limits, and business continuity options related to availability and disaster recovery.
Azure SQL Managed Instance has two service tiers:
- General Purpose.
- Business Critical.
For a detailed comparison between service tiers, review resource limits, but use the following table for a brief overview:
| Category | General Purpose | Business Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Most business workloads. Offers budget-oriented, balanced, and scalable compute and storage options. | Offers business applications the highest resilience to failures by using several isolated replicas, and provides the highest I/O performance. |
| Max number of vCores | 80 | 80 |
| Max instance storage size | 16 TB | 16 TB |
| Max databases per instance | 100 | 100 |
| Read-only replicas | 0 | 1 |
| Replicas for availability | Standby nodes for high availability | Three high availability replicas, 1 is also a read-scale replica |
| Pricing/billing | vCore, reserved storage, and backup storage is charged. IOPS is not charged |
vCore, reserved storage, and backup storage is charged. IOPS is not charged. |
Note
For more information on the Service Level Agreement (SLA), see SLA for Azure SQL Managed Instance.
General Purpose
The architectural model for the General Purpose service tier is based on a separation of compute and storage. This architectural model relies on the high availability and reliability of Azure Blob storage that transparently replicates database files and guarantees no data loss if underlying infrastructure failure happens.
The following figure shows four nodes in standard architectural model with the separated compute and storage layers.
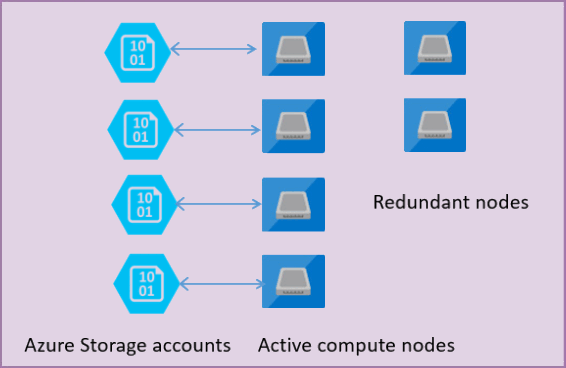
In the architectural model for the General Purpose service tier, there are two layers:
- A stateless compute layer that is running the
sqlservr.exeprocess and contains only transient and cached data (for example - plan cache, buffer pool, columnstore pool). This stateless node is operated by Azure Service Fabric that initializes process, controls health of the node, and performs failover to another place if necessary. - A stateful data layer with database files (.mdf/.ldf) that are stored in Azure Blob storage. Azure Blob storage guarantees that there will be no data loss of any record that is placed in any database file. Azure Storage has built-in data availability/redundancy that ensures that every record in log file or page in data file will be preserved even if the process crashes.
Whenever the database engine or operating system is upgraded, some part of underlying infrastructure fails, or if some critical issue is detected in the sqlservr.exe process, Azure Service Fabric will move the stateless process to another stateless compute node. There is a set of spare nodes that is waiting to run new compute service if a failover of the primary node happens in order to minimize failover time. Data in Azure storage layer is not affected, and data/log files are attached to newly initialized process. This process guarantees 99.99% availability by default. There can be performance impacts to heavy workloads that are in-flight due to transition time and the fact the new node starts with cold cache.
When to choose this service tier
The General Purpose service tier is the default service tier in Azure SQL Managed Instance designed for most of generic workloads. If you need a fully managed database engine with a default SLA and storage latency between 5 and 10 ms, the General Purpose tier is the option for you.
Business Critical
The Business Critical service tier model is based on a cluster of database engine processes. This architectural model relies on a quorum of always available database engine nodes to minimize performance impacts to your workload, even during maintenance activities. Azure upgrades and patches the underlying operating system, drivers, and SQL Server database engine transparently, with minimal down-time for end users.
In the Business Critical model, compute and storage is integrated on each node. Replication of data between database engine processes on each node of a four-node cluster achieves high availability, with each node using locally attached SSD as data storage.
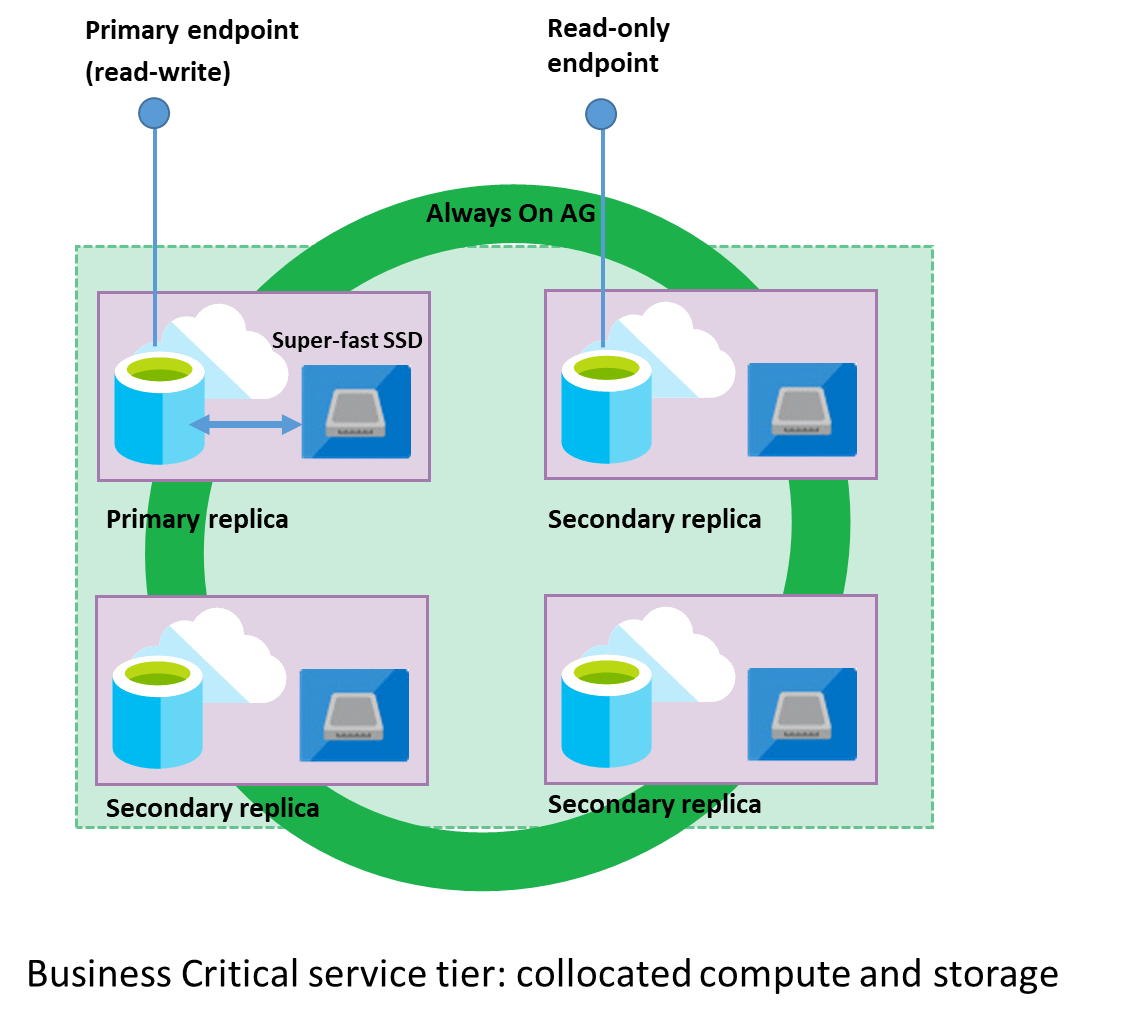
Both the SQL Server database engine process and underlying .mdf/.ldf files are placed on the same node with locally attached SSD storage providing low latency to your workload. High availability is implemented using technology similar to SQL Server Always On availability groups.
Every instance is a cluster of database engine nodes that contain copies of all the databases on an instance, with a primary database accessible for customer workloads, and three secondary databases containing copies of the data, ready for failover. The primary node constantly pushes changes to the secondary nodes in order to ensure the data is available on secondary replicas if the primary node fails for any reason.
Failover is handled by the SQL Server database engine - one secondary replica becomes the primary node and a new secondary replica is created to ensure there are enough nodes in the cluster. The workload is automatically redirected to the new primary node.
In addition, the Business Critical cluster has a built-in Read Scale-Out capability that provides a free-of charge read-only replica used to run read-only queries (such as reports) that won't affect the performance of the workload on your primary replica.
When to choose this service tier
The Business Critical service tier is designed for applications that require low-latency responses from the underlying SSD storage (1-2 ms in average), faster recovery if the underlying infrastructure fails, or need to off-load reports, analytics, and read-only queries to the free-of-charge readable secondary replica of the primary database.
The key reasons why you should choose Business Critical service tier instead of General Purpose tier are:
- Low I/O latency requirements - workloads that need a fast response from the storage layer (1-2 milliseconds in average) should use Business Critical tier.
- Workload with reporting and analytic queries that can be redirected to the free-of-charge secondary read-only replica.
- Higher resiliency and faster recovery from failures. In case there is system failure, the databases on the primary instance are taken offline, and one of the secondary replicas will immediately become the new read-write primary instance, ready to process queries. There is no need for the database engine to analyze and redo transactions from the log file or load data into memory buffers.
- Advanced data corruption protection. Since the Business Critical tier uses databases replicas behind the scenes, the service leverages automatic page repair available with mirroring and availability groups to help mitigate data corruption. If a replica can't read a page due to a data integrity issue, a fresh copy of the page is retrieved from another replica, replacing the unreadable page without data loss or customer downtime. This functionality is available in the General Purpose tier if the managed instance has geo-secondary replica.
- Higher availability - The Business Critical tier in a multi-availability zone configuration provides resiliency to zonal failures and a higher availability SLA.
- Fast geo-recovery - If a failover group is configured, the Business Critical tier has a guaranteed Recovery Point Objective (RPO) of 5 seconds and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) of 30 seconds for 100% of deployed hours.
When specifying service tier in templates or scripts, tier is provided by using its name. The following table applies:
| Hardware | Name |
|---|---|
| General Purpose | GeneralPurpose |
| Business Critical | BusinessCritical |
High availability
By default, Azure SQL Managed Instance achieves availability through local redundancy, making your instance available during maintenance operations, issues with data center outages, and other problems with the SQL database engine. However, to minimize a potential outage to an entire zone impacting your data, you can achieve high availability by enabling zone redundancy. Without zone redundancy, failovers happen locally within the same data center, which might result in your instance being unavailable until the outage is resolved - the only way to recover is through a disaster recovery solution, such as through a failover group, or a geo-restore of a geo-redundant backup.
Hardware configurations
Hardware configuration options in the vCore model include standard-series (Gen5), premium-series, and memory optimized premium-series. Hardware configuration generally defines the compute and memory limits and other characteristics that impact workload performance.
For more information on the hardware configuration specifics and limitations, see Hardware configuration characteristics.
In the sys.dm_user_db_resource_governance dynamic management view, hardware generation for instances using Intel® SP-8160 (Skylake) processors appears as Gen6, while hardware generation for instances using Intel® 8272CL (Cascade Lake) appears as Gen7. The Intel® 8370C (Ice Lake) CPUs used by premium-series and memory optimized premium-series hardware generations appear as Gen8. Resource limits for all standard-series (Gen5) instances are the same regardless of processor type (Broadwell, Skylake, or Cascade Lake).
Select a hardware configuration
You can select hardware configuration at the time of instance creation, or you can change hardware of an existing instance.
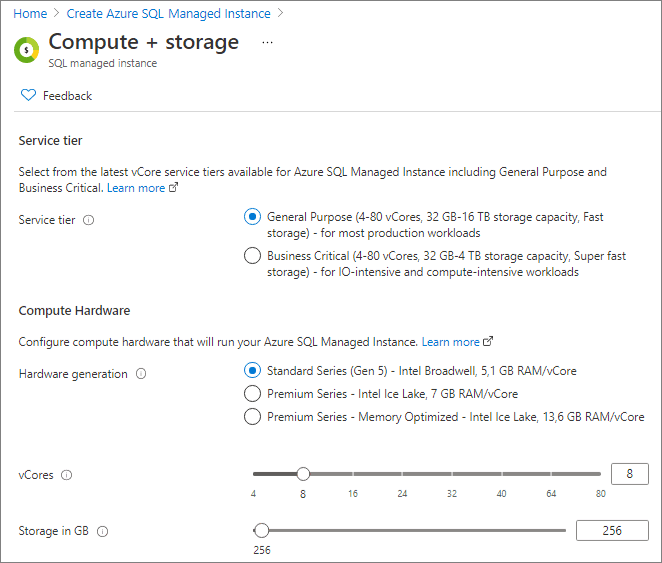
To select hardware configuration when creating a SQL Managed Instance
For detailed information, see Create a SQL Managed Instance.
On the Basics tab, select the Configure database link in the Compute + storage section, and then select desired hardware:
To change hardware of an existing SQL Managed Instance
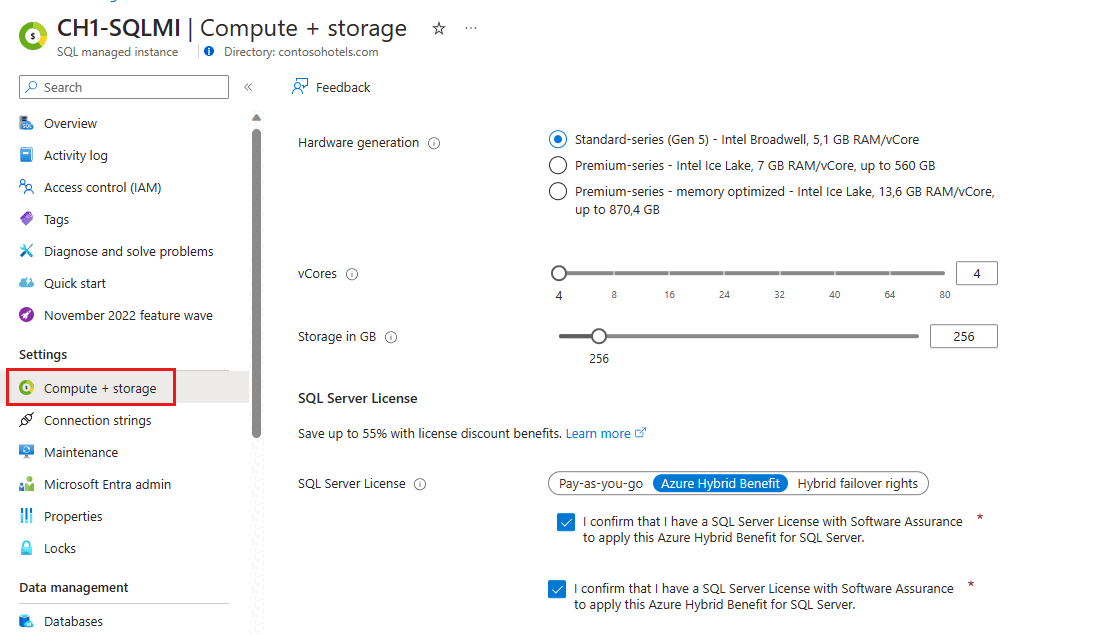
From the SQL Managed Instance page, select Compute + storage under Settings:
On the Compute + Storage page, you can change your hardware under Hardware generation by using the sliders for vCores and Storage.
When specifying hardware parameter in templates or scripts, hardware is provided by using its name. The following table applies:
| Hardware | Name |
|---|---|
| Standard-series (Gen5) | Gen5 |
| Premium-series | G8IM |
| Memory optimized premium-series | G8IH |
SKU names
Note
When specifying hardware and service tier in templates or scripts, you can specify them independently, or you can provide a SKU name. When specifying the SKU name, the following table applies:
| SKU | Service Tier | Hardware |
|---|---|---|
| GP_Gen5 | General Purpose | Standard-series |
| GP_G8IM | General Purpose | Premium-series |
| GP_G8IH | General Purpose | Premium-series memory-optimized |
| BC_Gen5 | Business Critical | Standard-series |
| BC_G8IM | Business Critical | Premium-series |
| BC_G8IH | Business Critical | Premium-series memory-optimized |
Hardware availability
Standard-series (Gen5) and premium-series
Standard-series (Gen5) and premium-series hardware is available in all regions.
Memory optimized premium-series hardware is in preview, and has limited regional availability. For more information, see Azure SQL Managed Instance resource limits.