Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server on Azure VM
In this quickstart tutorial, you use the Azure portal to create a Linux virtual machine with SQL Server 2017 installed. You learn the following:
- Create a Linux VM running SQL Server from the gallery
- Connect to the new VM with ssh
- Change the SA password
- Configure for remote connections
Prerequisites
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a Trial Subscription before you begin.
Create a Linux VM with SQL Server installed
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the left pane, select Create a resource.
In the Create a resource pane, select Compute.
Select See all next to the Featured heading.
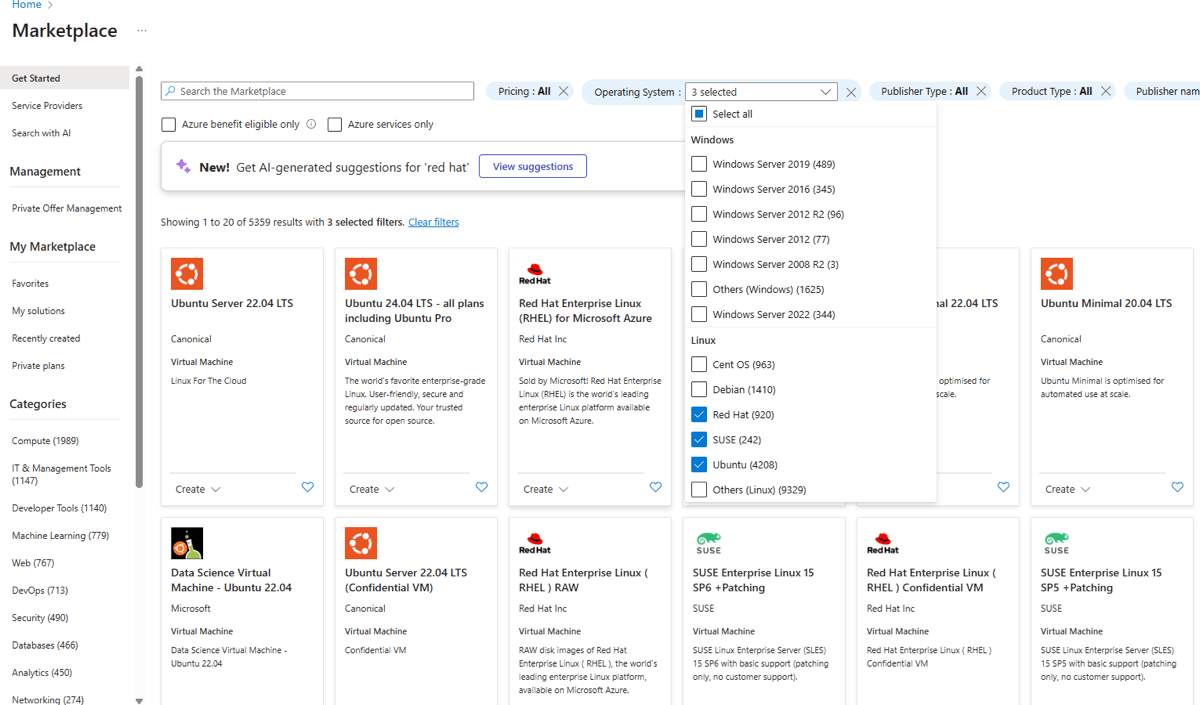
In the Operating System filter, select Red Hat or SUSE or Ubuntu as shown above based on your requirement. In the example here, we have shown all three, but you can select one distribution that you prefer.
Select specific image that suits your needs.
Select Create.
Set up your Linux VM
In the Basics tab, select your Subscription and Resource Group.
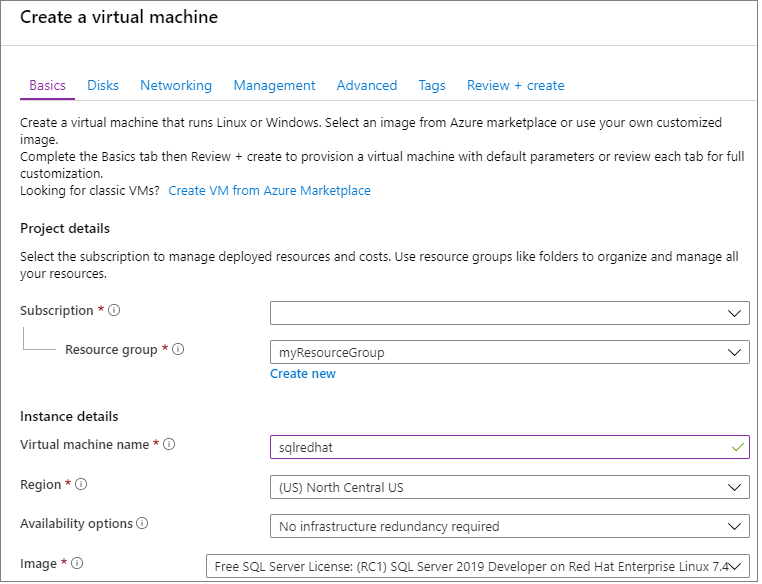
In Virtual machine name, enter a name for your new Linux VM.
Then, type or select the following values:
Region: Select the Azure region that's right for you.
Availability options: Choose the availability and redundancy option that's best for your apps and data.
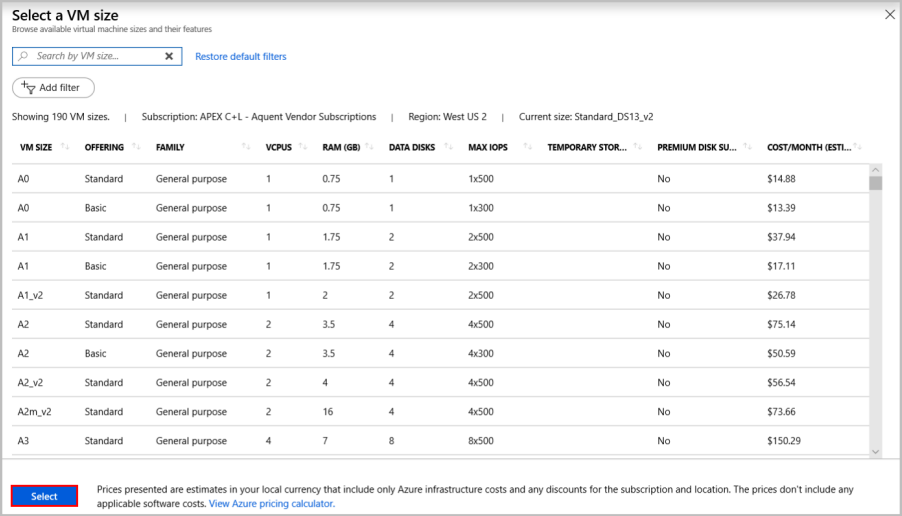
Change size: Select this option to pick a machine size and when done, choose Select. For more information about VM machine sizes, see VM sizes.
Tip
For development and functional testing, use a VM size of DS2 or higher. For performance testing, use DS13 or higher.
Authentication type: Select SSH public key.
Note
You have the choice of using an SSH public key or a Password for authentication. SSH is more secure. For instructions on how to generate an SSH key, see Create SSH keys on Linux and Mac for Linux VMs in Azure.
Username: Enter the Administrator name for the VM.
SSH public key: Enter your RSA public key.
Public inbound ports: Choose Allow selected ports and pick the SSH (22) port in the Select public inbound ports list. In this quickstart, this step is necessary to connect and complete the SQL Server configuration. If you want to remotely connect to SQL Server, you need to manually allow traffic to the default port (1433) used by Microsoft SQL Server for connections over the Internet after the virtual machine is created.
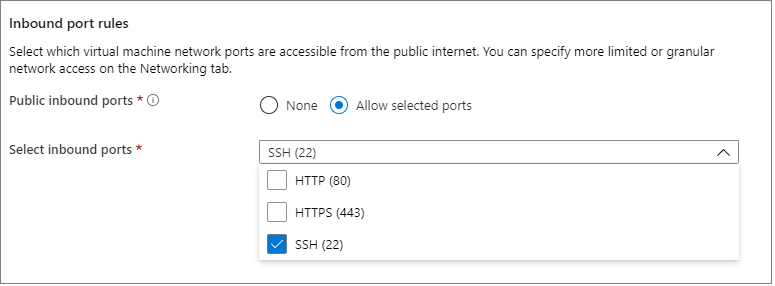
Make any changes you want to the settings in the following additional tabs or keep the default settings.
- Disks
- Networking
- Management
- Guest config
- Tags
Select Review + create.
In the Review + create pane, select Create.
Connect to the Linux VM
If you already use a BASH shell, connect to the Azure VM using the ssh command. In the following command, replace the VM user name and IP address to connect to your Linux VM.
ssh azureadmin@40.55.55.555
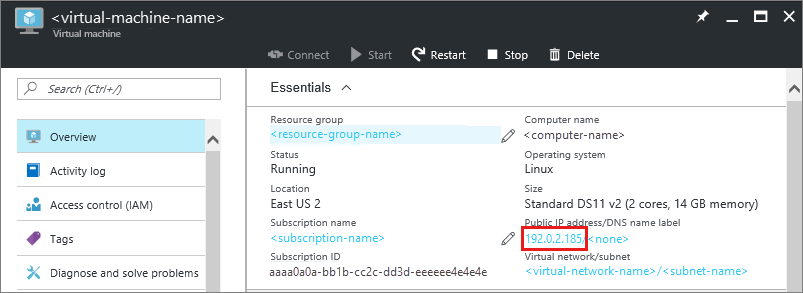
You can find the IP address of your VM in the Azure portal.
If you're running on Windows and don't have a BASH shell, install an SSH client, such as PuTTY.
Run PuTTY.
On the PuTTY configuration screen, enter your VM's public IP address.
Select Open and enter your username and password at the prompts.
For more information about connecting to Linux VMs, see Create a Linux VM on Azure using the Azure portal.
Note
If you see a PuTTY security alert about the server's host key not being cached in the registry, choose from the following options. If you trust this host, select Yes to add the key to PuTTy's cache and continue connecting. If you want to carry on connecting just once, without adding the key to the cache, select No. If you don't trust this host, select Cancel to abandon the connection.
Change the SA password
The new virtual machine installs SQL Server with a random SA password. Reset this password before you connect to SQL Server with the SA login.
After connecting to your Linux VM, open a new command terminal.
Change the SA password with the following commands:
sudo systemctl stop mssql-server sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set-sa-passwordEnter a new SA password and password confirmation when prompted.
Restart the SQL Server service.
sudo systemctl start mssql-server
Add the tools to your path (optional)
Several SQL Server packages are installed by default, including the SQL Server command-line Tools package. The tools package contains the sqlcmd and bcp tools. For convenience, you can optionally add the tools path, /opt/mssql-tools/bin/, to your PATH environment variable.
Run the following commands to modify the PATH for both login sessions and interactive/non-login sessions:
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/opt/mssql-tools/bin"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/opt/mssql-tools/bin"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
Configure for remote connections
If you need to remotely connect to SQL Server on the Azure VM, you must configure an inbound rule on the network security group. The rule allows traffic on the port on which SQL Server listens (default of 1433). The following steps show how to use the Azure portal for this step.
Tip
If you selected the inbound port MS SQL (1433) in the settings during provisioning, these changes have been made for you. You can go to the next section on how to configure the firewall.
In the portal, select Virtual machines, and then select your SQL Server VM.
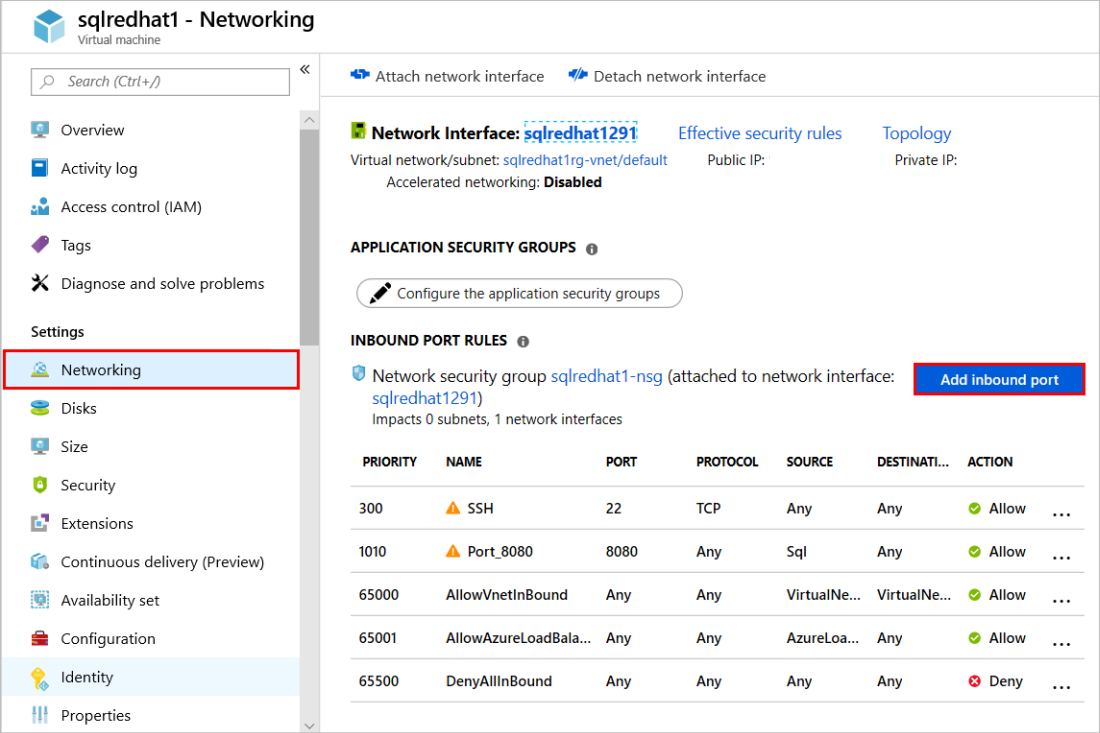
In the left navigation pane, under Settings, select Networking.
In the Networking window, select Add inbound port under Inbound Port Rules.
In the Service list, select MS SQL.
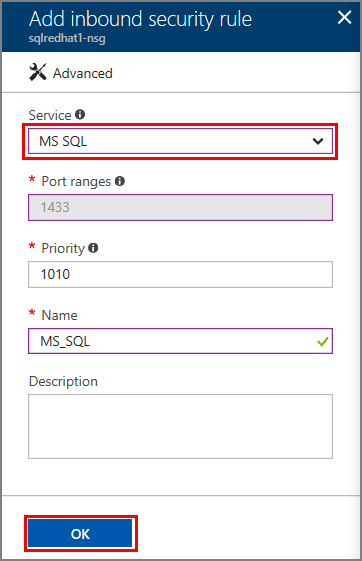
Select OK to save the rule for your VM.
Open the firewall on RHEL
This tutorial directed you to create a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) VM. If you want to connect remotely to RHEL VMs, you also have to open up port 1433 on the Linux firewall.
Connect to your RHEL VM.
In the BASH shell, run the following commands:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=1433/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload