Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server on Azure VM
This article provides VM size guidance and best practices to optimize performance for your SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs).
There's typically a trade-off between optimizing for costs and optimizing for performance. This performance best practices series focuses on getting the best performance for SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines. If your workload is less demanding, you might not need every recommended optimization. Consider your performance needs, costs, and workload patterns as you evaluate these recommendations.
For comprehensive details, see the other articles in this series: Checklist, Storage, Security, HADR configuration, Collect baseline.
Warning
Placing tempdb on the local temp disk for Azure VM images with uninitialized ephemeral disks, such as the FXmdsv2, isn't supported. This issue only affects Azure Virtual Machines with the new NVMe interface that also has local ephemeral storage. These deployments through the Azure portal might fail, and SQL Server can fail to start. Either use a different VM series, or place tempdb on non-ephemeral storage both when you deploy the SQL Server image through the Azure portal, and when you install SQL Server manually. To learn more more about the issue and also see a list of impacted VMs, review VM deployment and SQL Server failures.
Checklist
Review the following checklist for a brief overview of the VM size best practices that the rest of the article covers in greater detail:
- Before choosing a VM size, configure your storage. Collect a baseline from your source environment under the highest stress conditions and then configure your storage based on the IOPS and throughput needs of your workload with a 20% buffer for future growth.
- Identify workload performance characteristics (OLTP vs OLAP, workload size) to determine the appropriate VM size for your business.
- If you're migrating to Azure, assess migration readiness to find the right VM size for your existing SQL Server workload, and then migrate with Azure Database Migration Service.
- Use Azure Marketplace images to deploy your SQL Server VMs as the SQL Server settings and storage options are configured for optimal performance.
- Use VM sizes with 4 or more vCores.
- Use memory optimized virtual machine sizes for the best performance of SQL Server workloads.
- The Mbdsv3-series offers the best overall performance for mission critical OLTP and data warehouse workloads.
- The Ebdsv5-series provides the best price-performance for most production SQL Server workloads.
- The M-series family offers the highest memory configurations in Azure for the largest workloads.
- Start development environments with the lower-tier D-Series, or B-Series, and grow your environment over time.
- Check VM supportability to avoid unsupported configurations.
To compare the VM size checklist with the others, see the comprehensive Performance best practices checklist.
Overview
High performing SQL Server workloads often need larger amounts of memory, IOPS, and throughput without the higher vCore counts.
Most OLTP workloads are application databases driven by large numbers of smaller transactions. With OLTP workloads, you read or modify only a small amount of the data, but the volumes of transactions driven by user counts are much higher. It's important to have the SQL Server memory available to cache plans, store recently accessed data for performance, and ensure physical reads can be read into memory quickly.
These OLTP environments need higher amounts of memory, fast storage, and the I/O bandwidth necessary to perform optimally.
Before choosing a VM size for your SQL Server VM, first get your storage configuration correct. Resizing your VM is simple, but modifying your storage configuration if it doesn't meet your IOPS or throughput needs often requires redeployment.
First, collect a baseline from your source environment under the highest stress conditions and then configure your storage based on the IOPS and throughput needs of your workload. Before settling on a storage configuration, plan for growth - typically 20% in most environments.
If you're using Ultra Disk storage, you can adjust the IOPS and throughput down, but you can't exceed the capability of the deployed storage solution.
Note
- The Azure VM size documentation has the most up-to-date information on available VM sizes in Azure. If any discrepancies exist between this article and the Azure VM size documentation, the Azure VM size documentation takes precedence.
- vCore and vCPU are used interchangeably in this and the Azure VM documentation.
When selecting a VM size for SQL Server on Azure VMs, consider the following performance best practices and guidelines.
Migrating existing environments
When you're creating a SQL Server on Azure VM, carefully consider the type of workload necessary.
If you're migrating an existing environment, collect a performance baseline to determine your SQL Server on Azure VM requirements.
Use the vCore and memory configuration from your source system as a baseline for migrating a current on-premises SQL Server database to SQL Server on Azure VMs.
If you have Software Assurance, take advantage of the Azure Hybrid Benefit which grants you the ability to allocate your SQL Server licenses to SQL Server on Azure VMs.
Creating new VMs
If you're creating a new VM, create your new SQL Server VM based on your application requirements.
If you're creating a new SQL Server VM for a new application built for the cloud, you can easily scale your SQL Server VM as your data and usage requirements evolve.
Start development environments with the lower-tier D-Series or B-Series and grow your environment over time.
Consider the following VM series based on your SQL Server workloads:
Highest memory allocation for mission critical workloads: The Mbdsv3-series VMs offer the highest memory allocation in Azure, with the best storage performance.
High I/O throughput-to-vCore ratio: Throughput matters more than IOPS for SQL Server when the workload is dominated by large, sustained, sequential data movement such as analytics, ETL, index maintenance, and backups - where IOPS are plentiful but the storage pipe (MB/s) becomes the bottleneck. The Mbdsv3-series VMs offer some of the highest throughput-to-vCore ratio of any VM series in any cloud with 78.125 Throughput / vCPU (MB/s per vCore). The Ebdsv5-series VMs also offer high throughput-to-vCore with 89.286 Throughput / vCPU (MB/s per vCore).
If you don't know the storage requirements for your SQL Server workload, the Ebdsv5-series is the one most likely to meet your needs. See the storage article to learn more.
Memory-to-vCore ratio scaling
For smaller SQL Server environment that don't require large amounts of memory, a 4:1 memory-to-vCore ratio such as the D-Series is a good starting point in Azure.
For mission critical OLTP, and the best starting point for SQL Server workloads, use an 8:1 memory-to-vCore ratio with the Ebdsv5 as the recommended option.
SQL Server data warehouse and mission critical environments often need to scale beyond the 8:1 memory-to-vCore ratio.
For larger data warehouse environments, choose a 16:1 memory-to-vCore ratio or larger.
Using marketplace images
Use the SQL Server VM marketplace images with the storage configuration in the portal. This approach makes it easier to properly create the storage pools necessary to get the size, IOPS, and throughput necessary for your workloads.
Choose SQL Server VMs that support premium storage performance.
See the storage article to learn more.
Supportability
Consider the following limitations when installing SQL Server to Azure VMs:
- SQL Server on Azure VMs don't support Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets. The Automatic guest patching feature available with Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets replaces the OS disk when a new image version is released. If you use the Automatic guest patching feature with your SQL Server on Azure VM, you're likely to disrupt SQL Server functionality, leading to potential corruption, data loss, and availability problems.
- SQL Server isn't supported on systems with more than 64 vCores per NUMA node. Disable SMT or hyperthreading to use SQL Server on Azure VMs that exceed 64 vCores per NUMA node.
- SQL Server currently supports disks with a standard native sector sizes of 512 bytes and 4 KB. Installing SQL Server to disks with 8-KB sector sizes isn't supported and can lead to installation failures, as well as performance degradation from misaligned I/O.
- SQL Server on Azure VM images fail to deploy with VM sizes that have uninitialized ephemeral disks. To learn more, review Some SQL Server on Azure VM images fail to deploy.
Filtering by VM size
When you deploy an Azure VM, use the naming convention guidance to determine the VM size name to filter by in the portal.
The VM size name combines the family, subfamily, number of CPUs, and any additive features.
Example:
When you filter for an Ebdsv5 series VM, enter the VM size name such as E64bds or the version such as v5, which the portal refers to as Generation.
The following screenshot demonstrates filtering the VM size list by the v5 version in the Azure portal:
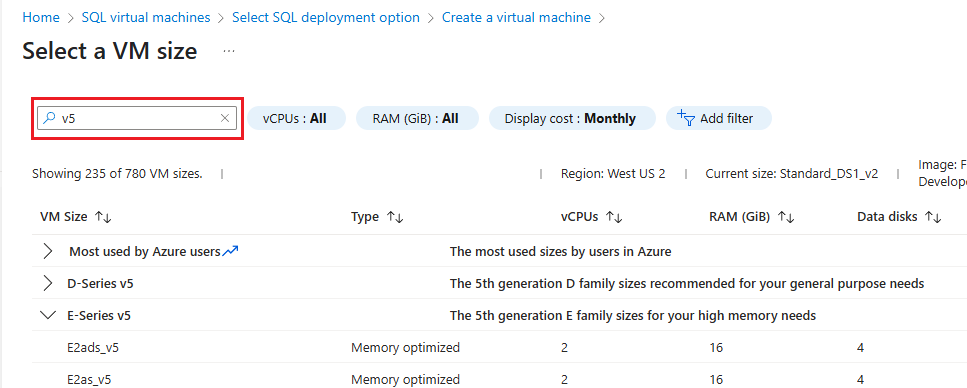
Consider the following points:
- You can apply additional filters by using 'Add filter' to narrow your VM size list based on factors like the VM size, type (family) such as memory-optimized or general purpose, and disk controller type.
- If you don't see a result for the VM you're searching for, it's likely due to a filter you applied to the VM size list. Clear the filter and try again.
- The disk controller filter helps you identify if the storage is iSCSI or NVMe.
Memory optimized M-series VMs
The memory-optimized M-series offers vCore counts and memory for some of the largest SQL Server workloads.
The following list describes the capabilities of M-series VMs:
- Support premium storage, premium storage caching, ultra disks, write acceleration, and accelerated networking.
- Are suitable for SQL Server workloads that require high computing capabilities with large memory footprints and less emphasis on storage performance.
Mbdsv3 series
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel® Xeon® Scalable 4th Gen (Sapphire Rapids) |
| Memory-to-vCore ratio | 8:1 to 22:1 (varies by size) |
| Max vCores | 176 |
| Memory | Up to 3,892 GiB (~3.8 TiB) |
| Max IOPS | 650,000 |
| Max throughput | 10,000 MBps (Ultra Disk) |
| Premium storage | Yes |
| Premium storage caching | Yes |
| Intended workload | Mission critical OLAP, data warehouse, tempdb optimization, reporting |
Ephemeral storage for tempdb |
Yes (capacity varies by size) |
The Mbdsv3-series is a memory-optimized VM series designed for large in-memory databases and workloads that need a high memory-to-vCore ratio. The VMs in this series use 4th generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable (Sapphire Rapids) processors and come in different memory sizes and vCore counts to fit your SQL Server workloads. Use Mbdsv3 VMs for mission critical and data warehouse workloads.
Mbdsv3 VMs work well for large in-memory databases and workloads that need a high memory-to-vCore ratio. They're great for relational database servers, data warehousing, heavy reporting, large caches, and in-memory analytics.
Mbdsv3 VMs provide up to 176 vCores with extensive memory capacity and exceptional storage performance. This VM series delivers more than a 50% improvement in IOPS and throughput compared to the top-performing Ebdsv5 VMs. Mbdsv3 VMs are one of the highest-performing VM options available in any cloud. Mbdsv3 VMs have similar performance characteristics to Mbsv3 VMs but include strong local and ephemeral storage. This storage makes them perfect for tempdb performance optimization, reporting, mission critical OLAP, and data warehousing workloads.
Memory-optimized E-series VMs
The memory-optimized E-series VMs are designed for memory-intensive workloads, such as large databases, big data analytics, and enterprise applications that require significant amounts of RAM to maintain high performance.
Ebdsv5 series
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8370C (Ice Lake) |
| Memory-to-vCore ratio | 8:1 |
| Max vCores | 112 |
| Memory | Up to 672 GiB |
| Max IOPS | 400,000 (Ultra Disk) |
| Max throughput | 10,000 MBps (NVMe sizes) |
| Premium storage | Yes |
| Premium storage caching | Yes |
| Intended workload | Production SQL Server (most workloads), OLTP, data warehouse |
Ephemeral storage for tempdb |
Yes (75-3,800 GiB capacity) |
The Ebdsv5-series is the recommended starting point for SQL Server workloads as it covers scenarios that benefit from local temp storage. This VM series is a balanced, memory-optimized, and tuned option for SQL Server on Azure virtual machines. With an 8:1 memory-to-vCore ratio, predictable remote storage performance, and support for Premium SSD, and Ultra Disk, this series aligns well with the core requirements of most production SQL Server OLTP workloads. These VMs run on the Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8370C (Ice Lake) processors.
Ebdsv5 VMs provide sufficient memory per core, strong and consistent storage throughput, and scalable I/O characteristics without requiring you to overprovision CPU simply to reach acceptable memory or storage levels. This balance makes it well‑suited for transactional workloads, mixed OLTP scenarios, and general-purpose production databases where stability, efficiency, and cost control matter as much as peak scale.
The Ebdsv5 series offers performance that works for the majority of production deployments, while still allowing you to scale up or move to more specialized VM families as workload characteristics evolve.
General Purpose
The General Purpose virtual machine sizes provide balanced memory-to-vCore ratios for smaller entry level workloads such as development and test, web servers, and smaller database servers.
Because of the smaller memory-to-vCore ratios with the General Purpose virtual machines, it's important to carefully monitor memory-based performance counters to ensure SQL Server gets the buffer cache memory it needs. For more information, see memory performance baseline. General Purpose VMs may not be suitable for larger production SQL Server workloads as their minimum recommended memory-to-vCore ratio is below the recommended starting point of 8:1 for production SQL Server workloads.
Ddsv5 series
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8370C (Ice Lake) |
| Memory-to-vCore ratio | 4:1 below the 8:1 recommended for production SQL Server; suitable for small apps and dev/test only |
| Max vCores | 96 |
| Memory | Up to 384 GiB |
| Max IOPS | 80,000 |
| Max throughput | 2,600 MBps |
| Premium storage | Yes |
| Premium storage caching | Yes |
| Intended workload | Dev/test, small apps, side-by-side SQL and app deployments |
Ephemeral storage for tempdb |
Yes (75-3,600 GiB capacity) |
The Ddsv5-series offers a fair combination of vCores, memory, and temporary disk but with smaller memory-to-vCore support.
The Ddsv5 VMs include lower latency and higher-speed local storage.
These machines are ideal for side-by-side SQL and app deployments that require fast access to temp storage and departmental relational databases. There's a standard memory-to-vCore ratio of 4 across all of the virtual machines in this series.
For this reason, use the Standard_D8ds_v5 as the minimum recommended VM size in this series. The largest VM size is the Standard_D96ds_v5, which has 96 vCores.
B-series
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel® Xeon® (varies by size) |
| Memory-to-vCore ratio | 0.5:1 to 4:1 (varies by size) Below the 8:1 recommended for production SQL Server |
| Max vCores | 32 (Bsv2-series) |
| Memory | Up to 128 GiB |
| Max IOPS | Up to 80,000 (remote storage) |
| Max throughput | Up to 960 MBps |
| Premium storage | Yes |
| Premium storage caching | No |
| Intended workload | Proof of concept, dev/test, intermittent workloads |
Ephemeral storage for tempdb |
Yes (4-160 GiB capacity) |
The burstable B-series VM sizes are ideal for workloads that don't need consistent performance, such as proof of concept and very small application and development servers. This series is unique as the apps have the ability to burst during business hours with burstable credits varying based on VM size. When credits are exhausted, the VM returns to the baseline VM performance.
Most of the burstable B-series VM sizes have a memory-to-vCore ratio of 4 or less. If you must pick a B-series VM for SQL Server, choose the Bsv2 series, targeting machines with higher memory. The Standard_B32s_v2 has 32 vCores with high storage performance.
The benefit of the B-series is the compute savings you achieve compared to the other VM sizes in other series, especially if you need the processing power sparingly throughout the day.
Note
The burstable B-series doesn't have the memory-to-vCore ratio of 8:1 that is recommended for SQL Server workloads. As such, consider using these virtual machines for smaller applications, web servers, and development workloads only.
Constrained vCPUs
To maintain an acceptable level of performance without incurring higher SQL Server licensing costs, Azure offers VM sizes with reduced vCore counts through a feature called constrained vCPUs.
This feature helps you control licensing costs by reducing the available vCores while maintaining the same memory, storage, and I/O bandwidth of the parent virtual machine.
You can constrain the vCore count to one-half to one-quarter of the original VM size. By reducing the vCore available to the virtual machine, you get higher memory-to-vCore ratios, but the compute and OS cost stays the same.
These new VM sizes have a suffix that specifies the number of active vCores to make them easier to identify.
For example, the M64-32ms requires licensing only 32 SQL Server vCores with the memory, I/O, and throughput of the M64ms. The M64-16ms requires licensing only 16 vCores. While the M64-16ms has a quarter of the SQL Server licensing cost of the M64ms, the compute and OS cost of the virtual machines is the same.
Consider the following points:
- Constrained vCPUs are most beneficial when higher computing resources are unnecessary, especially for larger VM sizes, but the memory and storage are a priority to improve memory-to-vCore ratios.
- Constrained vCPU options are one-fourth to one-half of the parent Azure VM size.
- You pay the SQL Server licensing costs of the resulting constrained vCPUs, which significantly reduces the cost of the deployment.
- The compute cost, which includes operating system licensing, stays the same as the parent virtual machine.
- Not all VM series support constrained vCPUs. Review the constrained vCPU documentation for the latest supported VM sizes.
Related content
To learn more, see the other articles in this best practices series:
For other SQL Server Virtual Machine articles, see SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines Overview. If you have questions about SQL Server virtual machines, see the Frequently Asked Questions.